42 free body diagram pendulum
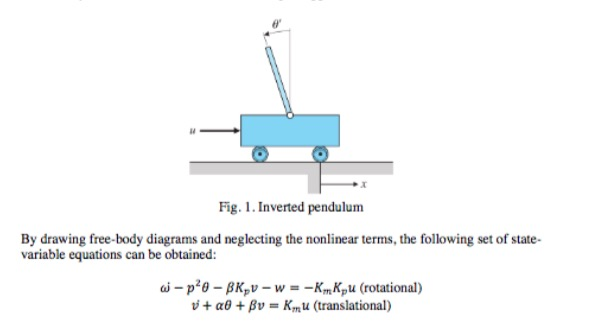
Pendulum Free Body Diagram. free body diagram of pendulum 1 the problem statement all variables and given known data i am asked to draw a free body diagram of a pendulum and a bob with it s maximum amplitude of planar pendulum free body diagram lecture 26 feedback example the inverted pendulum 1200px Double Pendulumg Free Body Diagram of an Inverted Pendulum in TikZ. April 20, 2021 April 15, 2021 by admin. In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inverted pendulum in LaTeX using TikZ package. We will draw a cart and place a moving rod on top of it, then place the arrows to represent forces and label our elements.
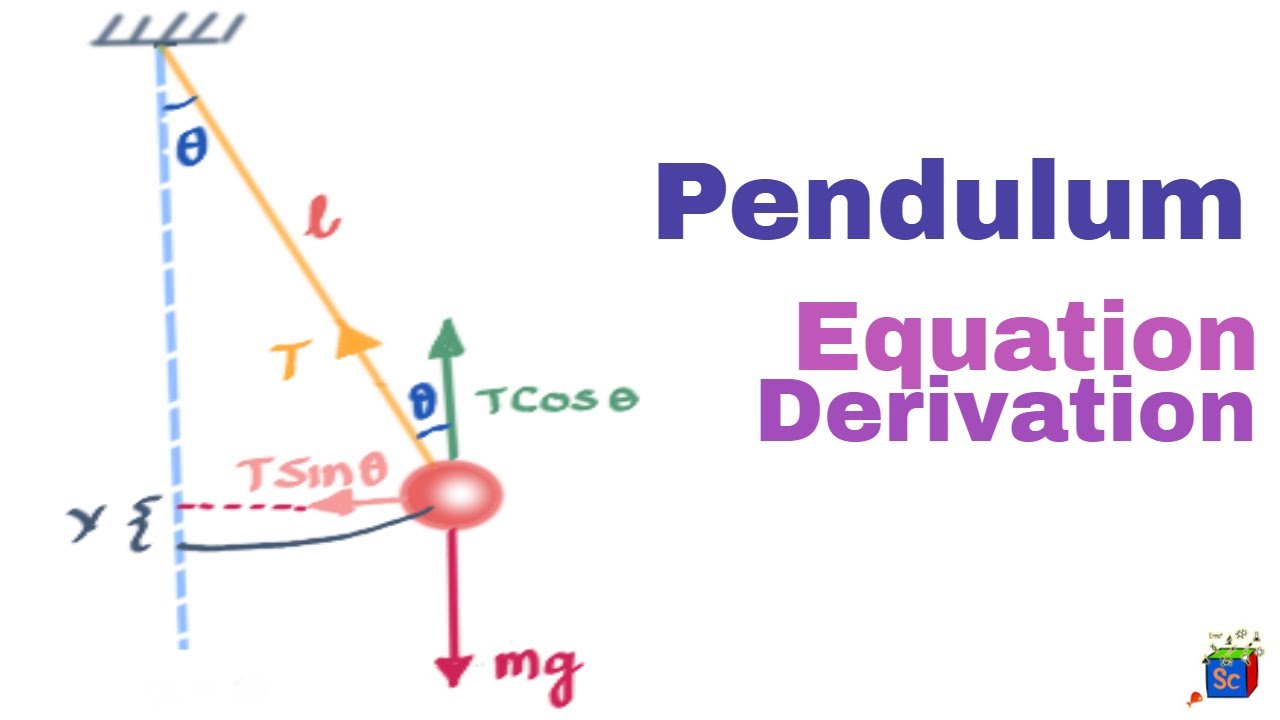
Let us consider the pendulum to be in simple harmonic motion, in this case, the restoring force, −mgsinθ − m g sin θ acting on the bob of the pendulum is ...
Free body diagram pendulum
-Rigid Body Kinematics x y z = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 X Y Z i j k = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 I J K . Derivation of Equations of Motion -Rigid Body Kinematics Free Body Diagram After substitutions and evaluation: Derivation of Equations of Motion-Lagrange Equations ... Spring Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation ... Answer to 1. Draw a free body diagram of a pendulum while in. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading The free body diagram depicting the torques on the body is shown below. The forces on the pendulum are the tension in the rod t and gravity. The diagram at the right shows the pendulum bob at a position to the right of its equilibrium position and midway to the point of maximum displacement. Solved 1 2 3 Draw The Free Body Diagrams For Pendulum.
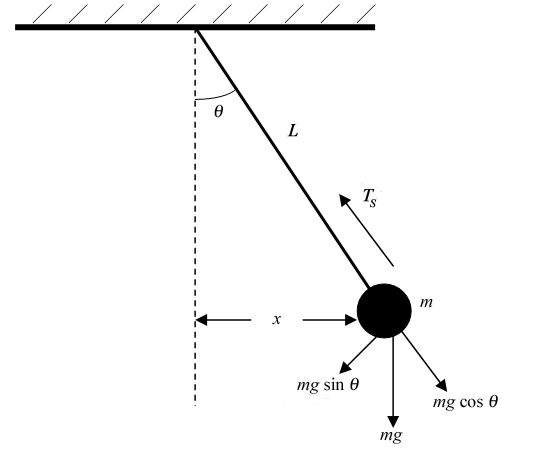
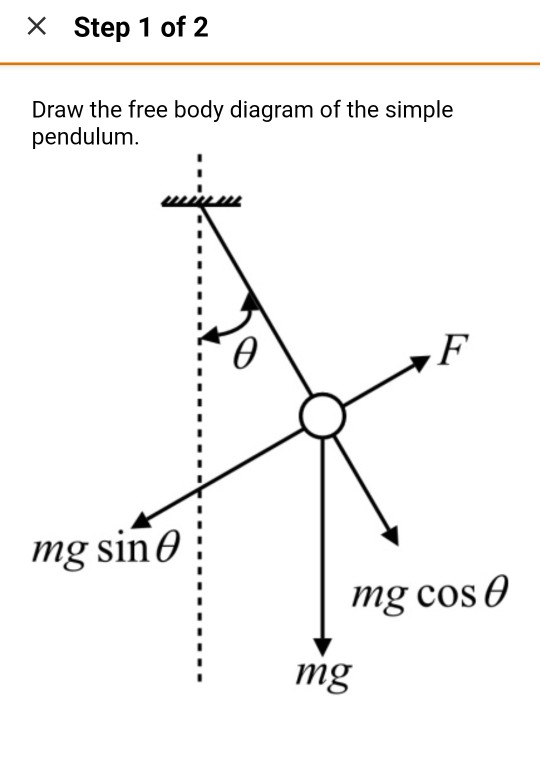
Free body diagram pendulum. So in the case of a pendulum, it is the gravity force which gets resolved since the tension force is already directed perpendicular to the motion. The diagram ... Begin by drawing the free body diagram for the upper mass and writing an expression for the net force acting on it. Define these variables: T = tension in the rod; m = mass of pendulum; g = gravitational constant; The forces on the upper pendulum mass are the tension in the upper rod T 1, the tension in the lower rod T 2, and gravity −m 1 g ... The force of the gravity can be decomposed into two components; one is parallel to the pendulum or the tension, and one perpendicular [3], as shown in Fig. 1. A worked example finding all force vectors acting on a pendulum moving in a horizontal circle. ... Free-body diagrams for objects in uniform circular motion.
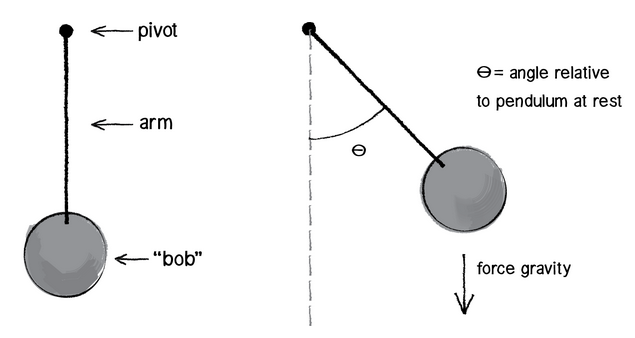
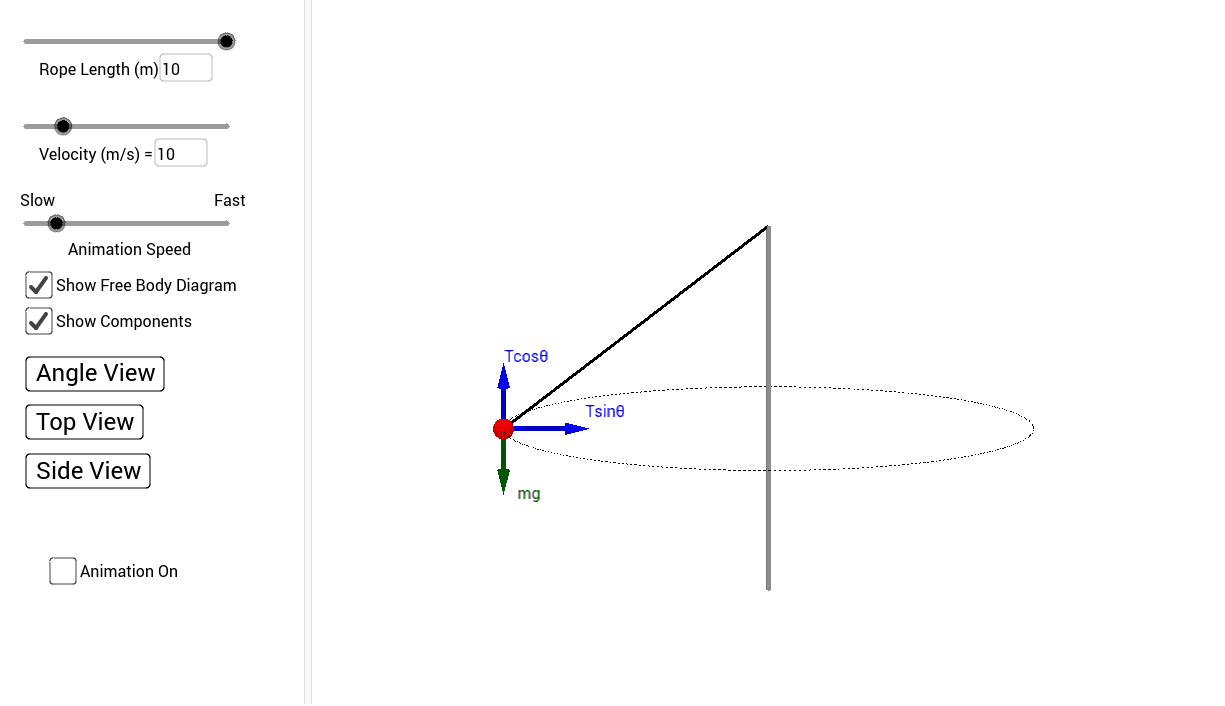
Simulate Simple Pendulum ODEs in MATLAB- Free Body Diagram- Equations of Motion ... We appreciate people who want to support this channel: Paypal: ... Free-body-diagram of the pendulum Figure 2 shows all the forces acting on the pendulum of mass . The tension in the rope attached to the mass prevents it from flying away, and is given by . The gravitational force, , acts vertically downward and affects the motion of the pendulum. The other immediately after it is released. The free-body diagram is drawn in Figure 12.18). There is a downward force of gravity, and a force of tension.2 pages Check here to show the free-body diagram Purple is the true motion; orange is the comparison motion. This is a simulation of a simple pendulum (a ball attached to a massless rod). If the damping is set to zero, the pendulum moves without ... Find the equation of motion of this pendulum by taking the time rate of change of the angular momentum computed with respect to the pivot. ... Be sure to include a free body diagram. Pendulum with Torsional Spring - Solution: The free body diagram depicting the torques on the body is shown below. Note the directions of the unit
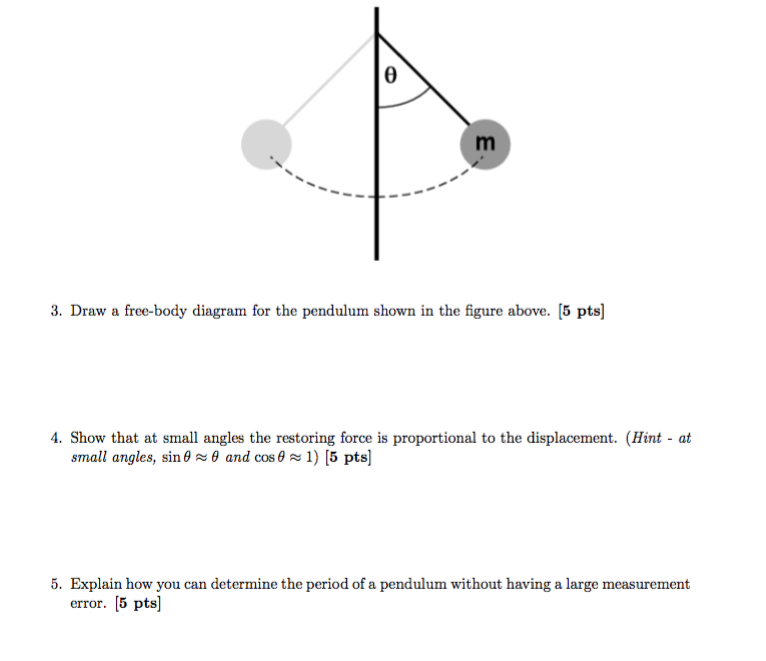
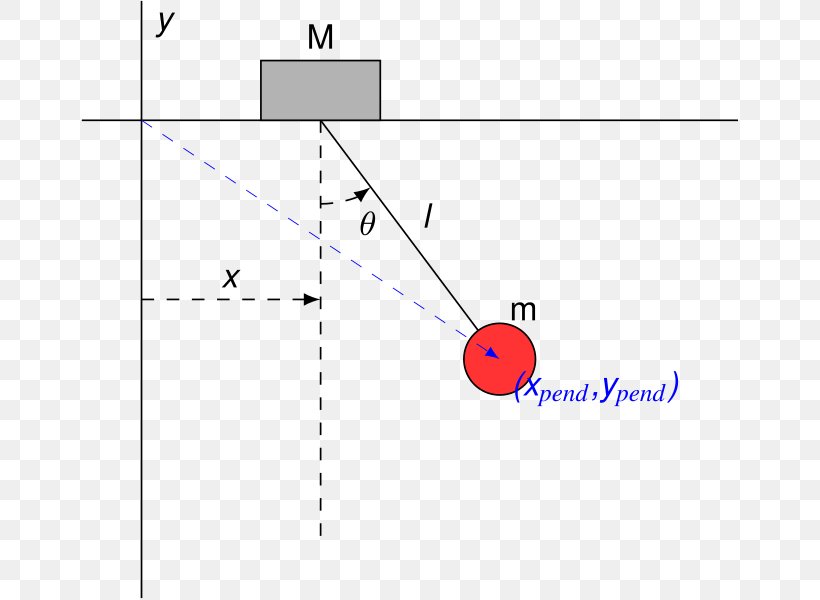
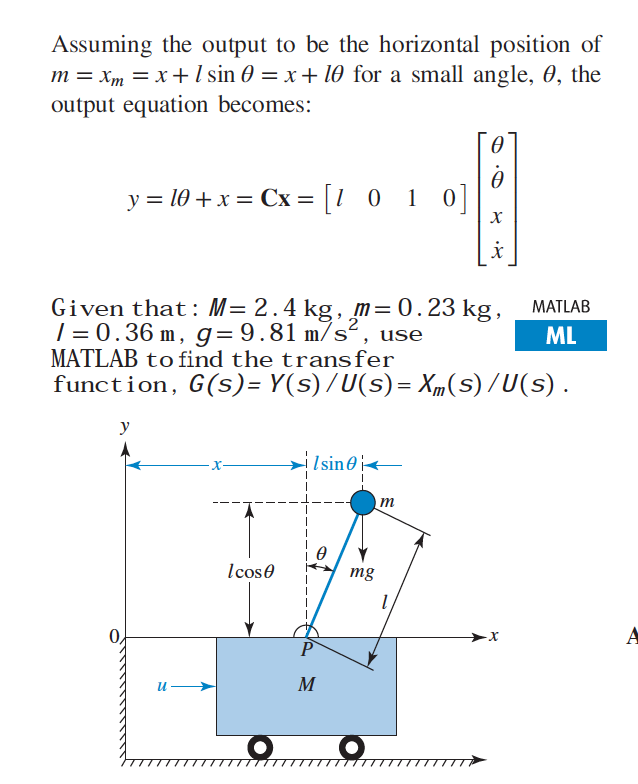
Below are the free-body diagrams of the two elements of the inverted pendulum system. Summing the forces in the free-body diagram of the cart in the horizontal direction, you get the following equation of motion. (1) Note that you can also sum the forces in the vertical direction for the cart, but no useful information would be gained. To begin, we first draw the free-body diagram where the forces acting on the pendulum are its weight and the reaction at the rotational joint. We also include a moment due to the friction in the joint (and the rotary potentiometer). Free body diagram of pendulum Thread starter-EquinoX-Start date Nov 30, 2008; Nov 30, 2008 #1 -EquinoX-564 1. Homework Statement I am asked to draw a free body diagram of a pendulum and a bob with it's maximum amplitude of 30 degrees. Below is my attempt, I just forgot to say that theta is equal to We treat the pendulum bob as a point particle. Drawing the free body diagram for the pendulum bob lets us write an expression for the net force acting on it. Define these variables: \( T = \) tension in the rod \( m = \) mass of pendulum \( g = \) gravitational constant \( b = \) damping (friction) constant \( F_d = \) damping force
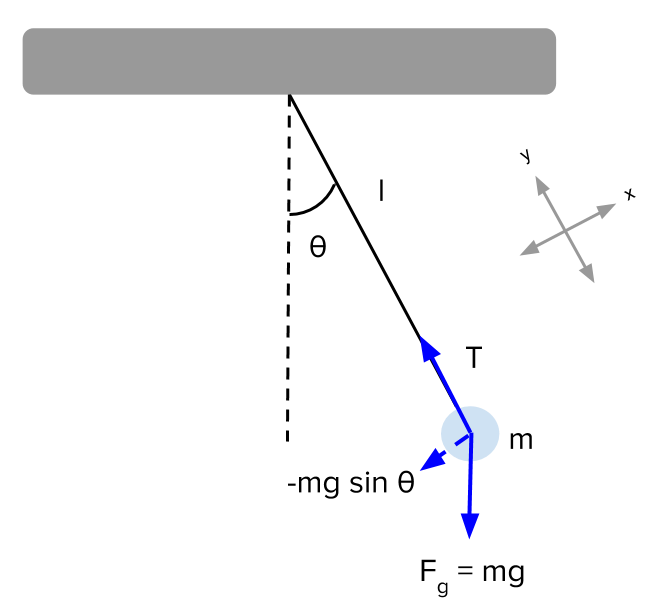
The free-body diagram is drawn in Figure 12.18). There is a downward force of gravity, and a force of tension directed away from the ball along the string.
Draw free-body diagrams that conform to the assumed displacement positions and their resultant reaction forces (i.e., tension or compression). c. Apply to the free body diagrams to obtain the governing equations of motion. The matrix statement of Eqs.(3.123) is The mass matrix is diagonal, and the stiffness matrix is symmetric.
Dr. Massa and the great Orbax discuss the conical pendulum, drawing free body diagrams and centripetal acceleration.
A simpler and more cost efficient experimental procedure is the free-decay pendulum test, which utilises minimal apparatus to infer hydrodynamic parameters. The ...
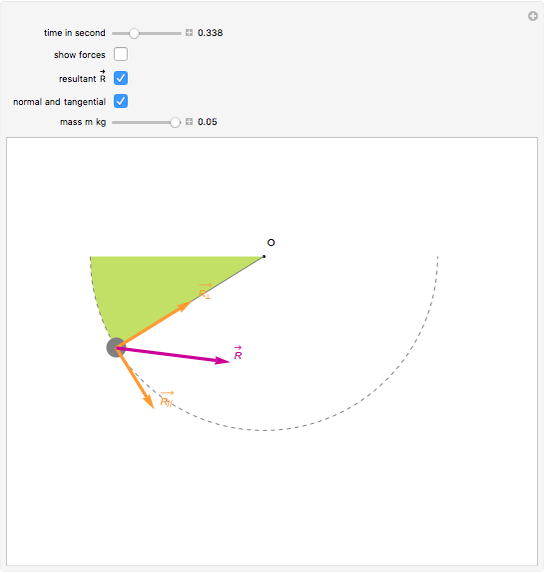
moving projectile. After the capture, the pendulum swings to a maximum opening angle of µ. Using conservation of momentum and energy, the initial velocity v of the projectile can be determine based on the opening angle µ. The center of mass of the pendulum is labeled "cm". Figure 3.2: The free-body diagram for the ballistic pendulum.
Check here to show the free-body diagram Purple is the true motion; orange is the comparison motion. This is a simulation of a simple pendulum (a ball attached to a massless rod). If the damping is set to zero, the pendulum moves without resistance. The larger the damping, the larger the resistive torque.
Good Answers: 3. # 2. Re: Free Body Diagram of Simple Inverted Pendulum. 09/16/2010 1:26 AM. The reason that B is correct and A is not, is because the forces are applied at Point O. There is no force applied at M. To balance the system in the vertical, at the point if origin, by most efficient means, the initial Fx will be negative (to the left ...
Planar pendulum free body diagram. Watch later. Share. Copy link. Info. Shopping. Tap to unmute. If playback doesn't begin shortly, ...
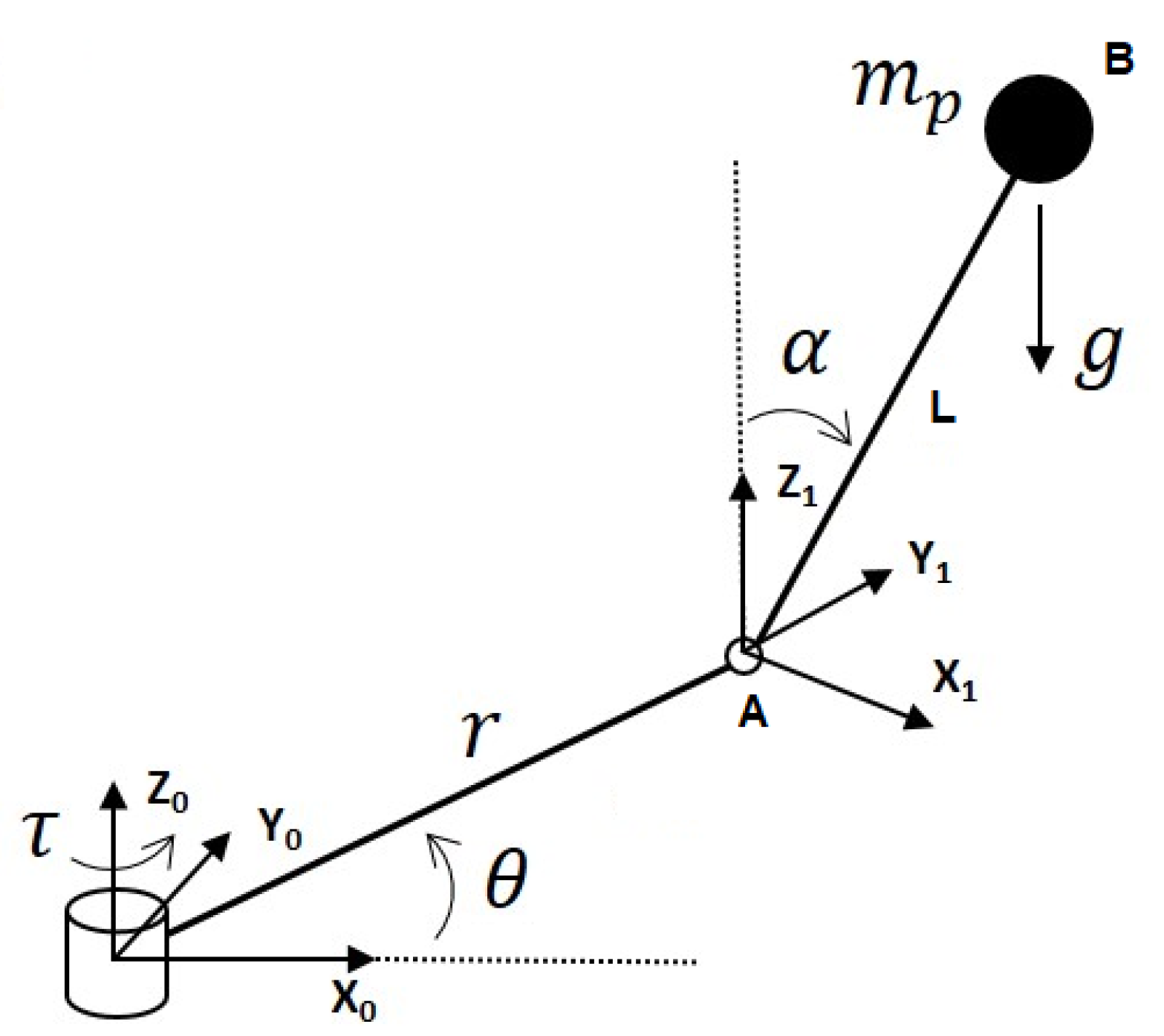
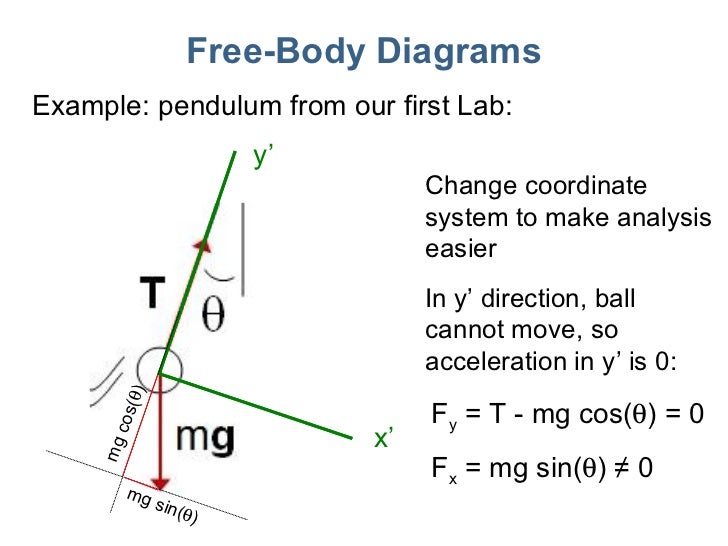
free body diagram in Fig. 6 below. Free Body Diagram Fig. 6 The free body diagram of the pendulum bob shows the gravitational force mg, the tension force T and the centripetal acceleration ac. The components of the gravitational force are also shown. Applying Newton's second law along the direction of tension force on gets T mg θ mgCos(θ)
The free body diagram depicting the torques on the body is shown below. The forces on the pendulum are the tension in the rod t and gravity. The diagram at the right shows the pendulum bob at a position to the right of its equilibrium position and midway to the point of maximum displacement. Solved 1 2 3 Draw The Free Body Diagrams For Pendulum.
Answer to 1. Draw a free body diagram of a pendulum while in. This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading
-Rigid Body Kinematics x y z = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 X Y Z i j k = cosθ sinθ 0 −sinθ cosθ 0 0 0 1 I J K . Derivation of Equations of Motion -Rigid Body Kinematics Free Body Diagram After substitutions and evaluation: Derivation of Equations of Motion-Lagrange Equations ... Spring Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation ...
















0 Response to "42 free body diagram pendulum"
Post a Comment