40 reaction energy diagram labeled
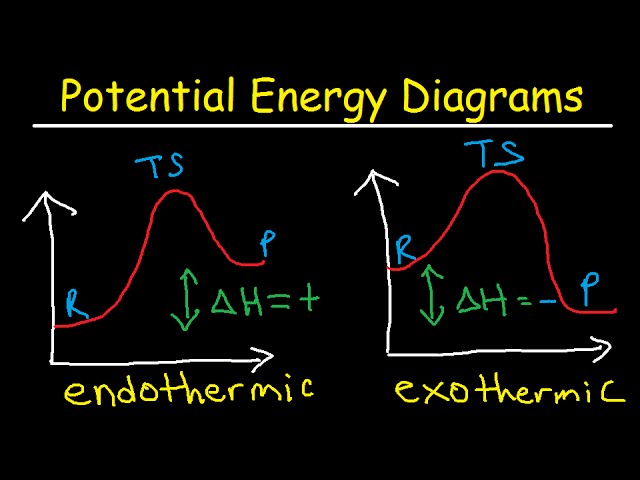
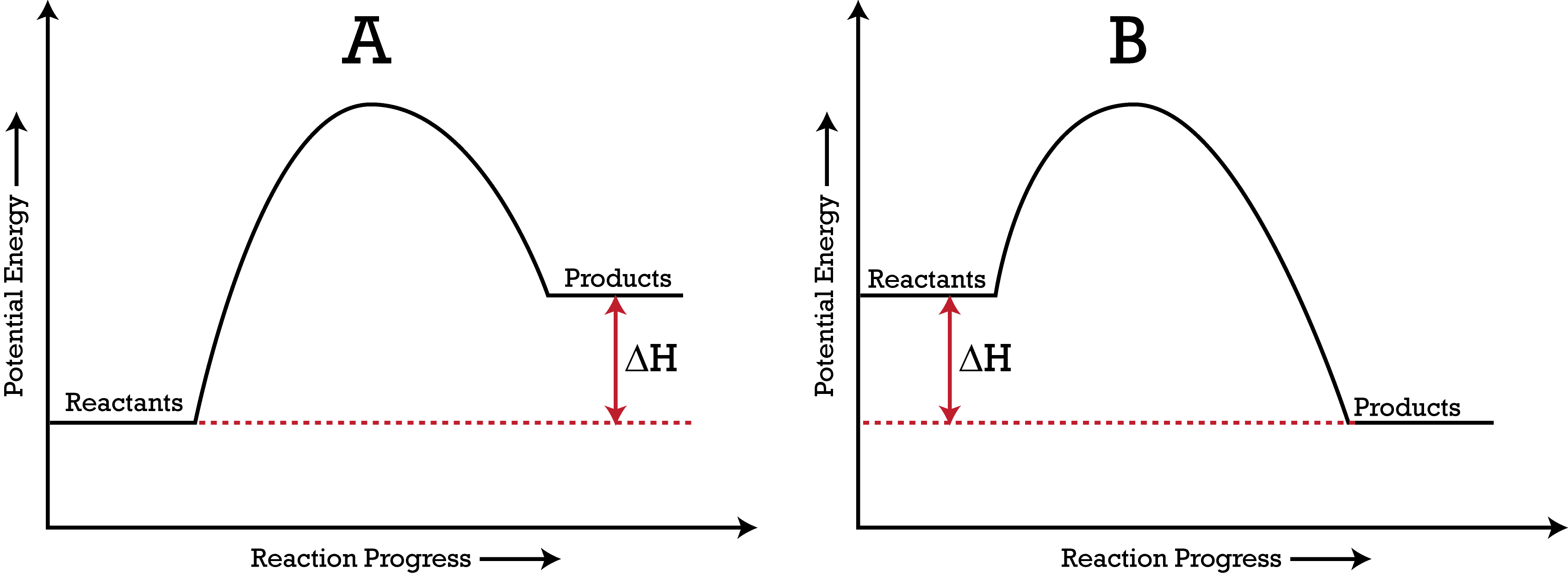
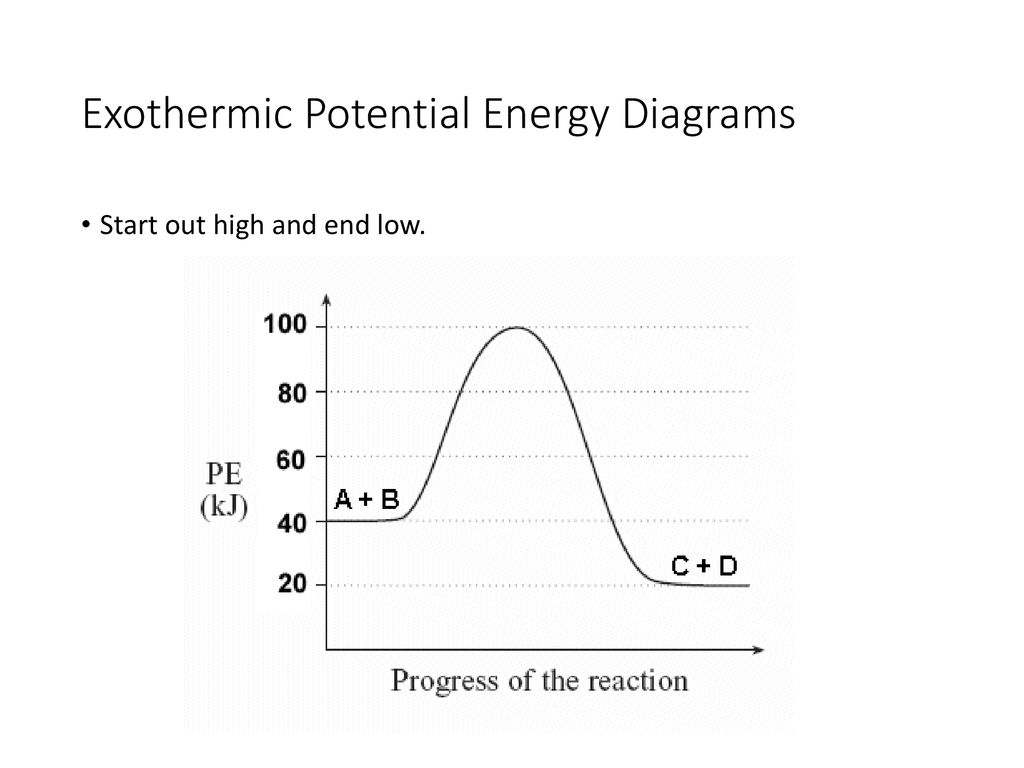
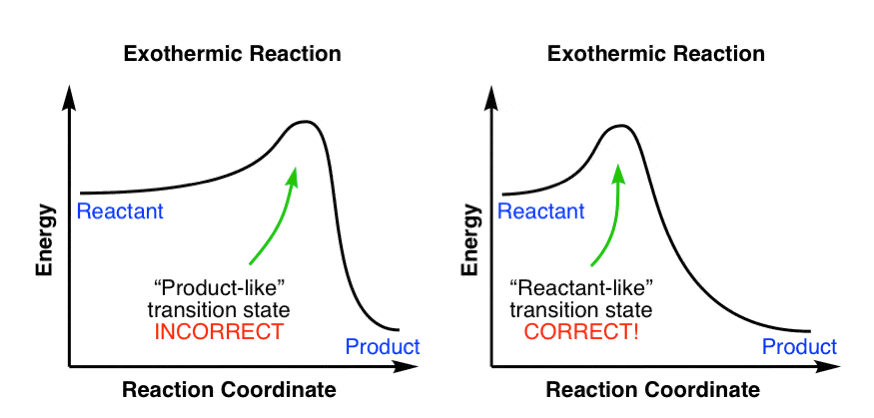
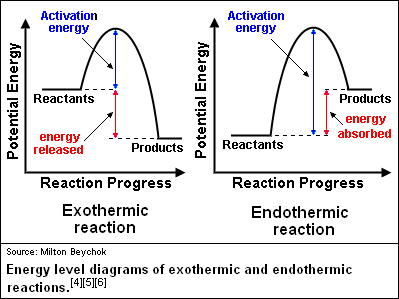
The overall change in energy in a reaction is the difference between the energy of the reactants and products. Exothermic reactions The diagram shows a reaction profile for an exothermic reaction. The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction. Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction.
1. Draw and label a pair of axes. Label the vertical axis "Potential Energy" and the horizontal axis "Reaction Coordinate". 2. Draw and label two short horizontal lines to mark the energies of the reactants and products. 3. Draw the energy level diagram. There must be a hump in the curve to represent the energy level of the activated complex. 4.

Reaction energy diagram labeled
In this reaction, the total energy of the reactants is 80 kJ mol-1, the total energy of the products is -90 kJmol-1 and the activation energy for the forward reaction is 120 kJ mol-1. a) Draw a diagram of the energy profile for this reaction. Label the diagram. b) State whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic. Label ΔH as positive or negative. Figure shows the energy level diagram for the reaction between methane and oxygen. Based on Figure, the following information can be obtained. (a) The reaction between methane and oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water is an exothermic reaction. (b) During the reaction, the temperature of the mixture increases. The reaction is exothermic. The reaction is slow at 25°C; however, a catalyst will cause the reaction to proceed faster. (e) Using the axes provided below, draw the complete potential-energy diagram for both the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. Clearly label the curve that represents the catalyzed reaction.
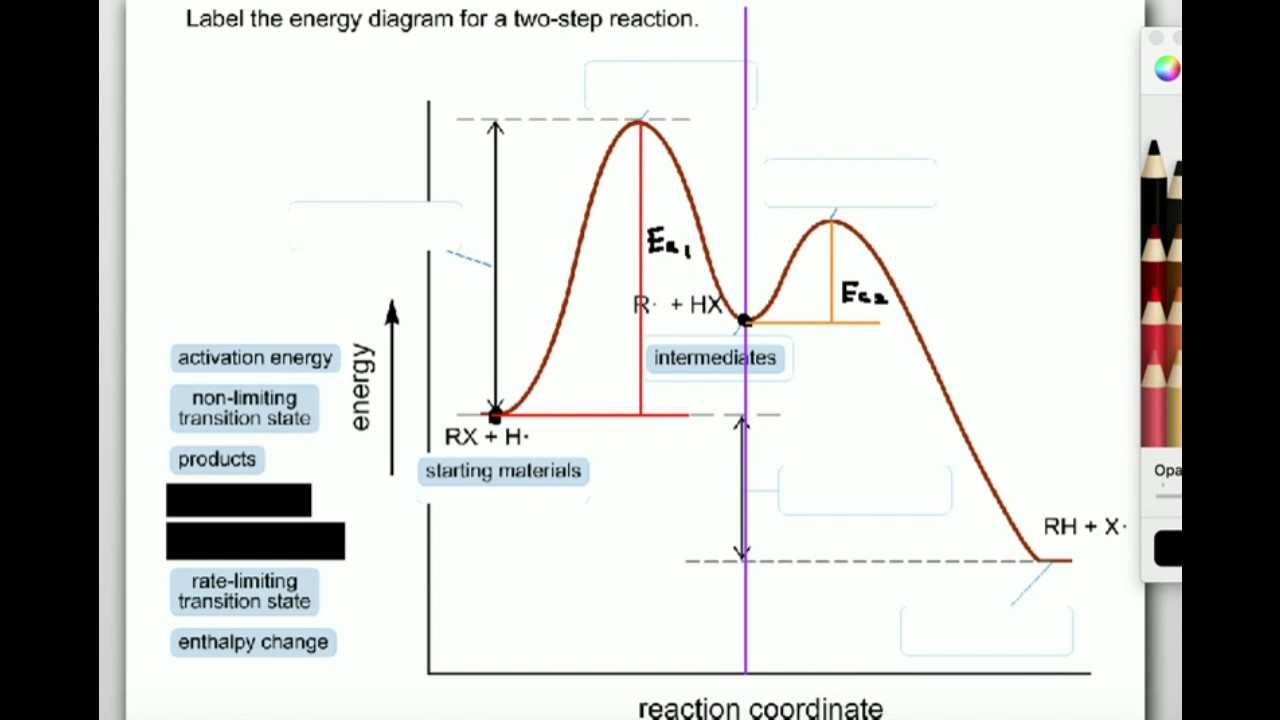
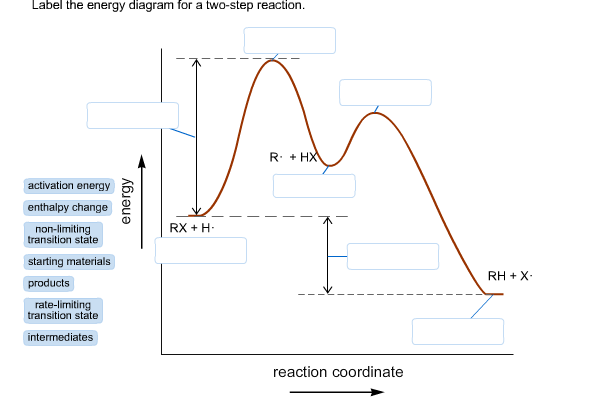
Reaction energy diagram labeled. A potential energy diagram plots the change in potential energy that occurs during a chemical reaction. This first video takes you through all the basic parts of the PE diagram. Sometimes a teacher finds it necessary to ask questions about PE diagrams that involve actual Potential Energy values. Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. Q. A reaction coordinate diagram is shown below for the reaction of A to form E. Answer the following questions.i) Identify the transition state (s)?ii) W... Q. Which reaction coordinate diagram represents a reaction in which the activation energy, Ea, is 50 kj.mol-1 and the ΔHrxn is -15 kj. mol-1? This video looks at the features of a reaction energy diagram and how you can use it to interpret and understand the mechanism of a reaction. In the energy diagram shown below, the ΔH of the reaction is labeled by D. Answer: FALSE. ... The ΔH for the reaction depicted by the energy diagram below is _____. Answer: -25 kJ. 36. Most reactions are carried out in liquid solution or in the gaseous phase because in such situations.
An enthalpy diagram allows us to easily see details of a chemical reaction. By knowing how to draw and label an enthalpy diagram we can see what the starting energy level is, how much energy is ... Reaction coordinate diagrams for exergonic and endergonic reactions. In the exergonic reaction, the reactants are at a higher free energy level than the products (reaction goes energetically downhill). In the endergonic reaction reaction, the reactants are at a lower free energy level than the products (reaction goes energetically uphill). An energy profile is a diagram representing the energy changes that take place during a chemical reaction. Enthalpy change , ΔH, is the amount of energy absorbed or released by a chemical reaction. On an energy profile, the enthalpy change for the reaction is measured from the energy of the reactants to the energy of the products. Jun 22, 2015 · Energy diagrams for these processes will often plot the enthalpy (H) instead of Free Energy for simplicity. The standard Gibbs Free Energy change for a reaction can be related to the reaction's equilibrium constant (K eq) by a simple equation: Δ G˚ = -RT ln K eq. where: K eq = [product] / [reactant] at equilibrium.
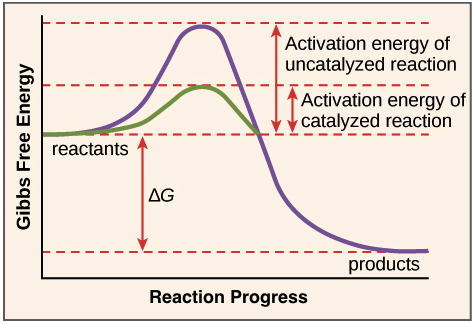
Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ... The activation energy for each step is labeled e a1 and e a2. Label the energy diagram for a two step reaction. Endothermic because energy is needed to break the a b bond. Each elementary step has its own activated complex labeled ac 1 and ac 2. Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction Entropy (ΔSo): a measure of freedom of motion ΔGo = ΔHo - TΔSo ΔG,ΔH,ΔS, ΔE are state ... Solved Label the components of an energy diagram for a | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Label the components of an energy diagram for a spontaneous reaction. Answer Bank reactants activation energy products uncatalyzed reaction catalyzed reaction Reaction progress-. Question: Label the components of an energy ...
Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Our mission is to help you succeed in your Chemistry class. "Clutch really helped me by reinforcing the things I learned in class and making exam reviews a breeze.
1. Identify the general shape of the energy diagram Energy should conserve for any chemical reaction. The reaction in question is exothermic (releases heat) hence its products shall have chemical potential energies lower than that of its reactants- some of the potential energies have been converted to thermal energy during the reaction process.
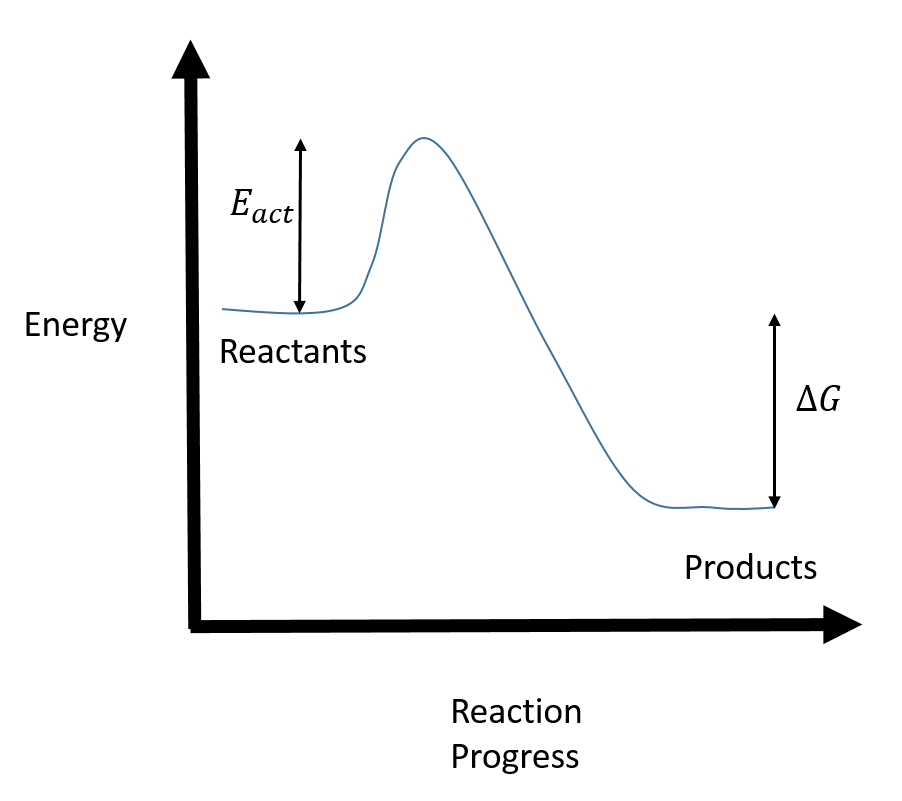
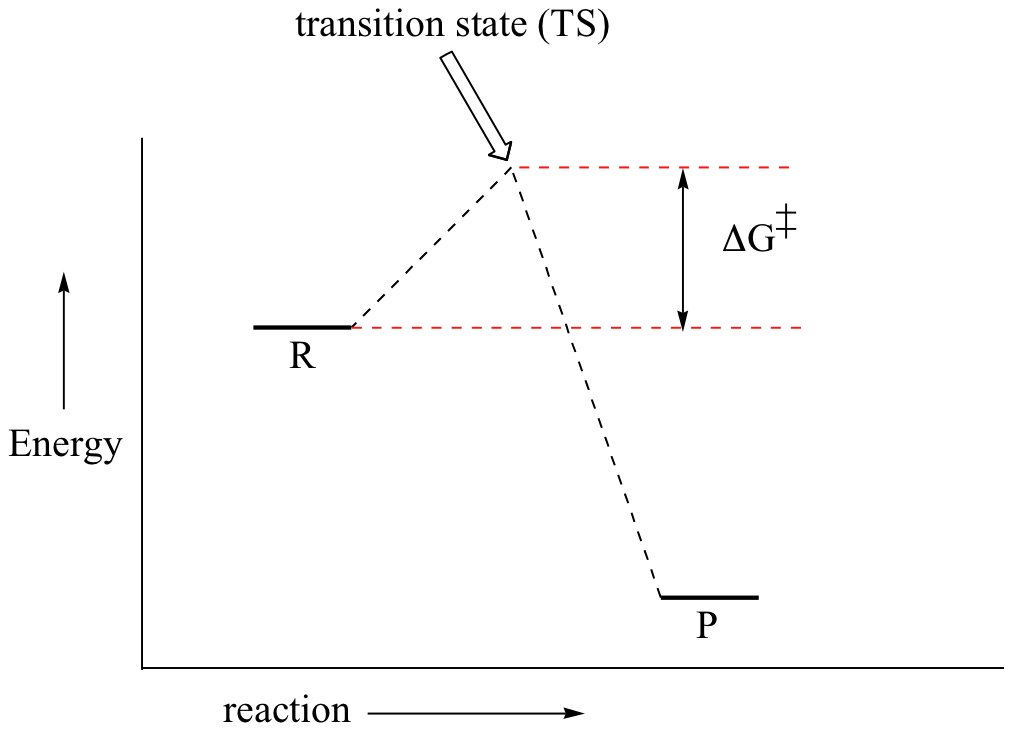
use a Reaction Energy Diagram to discuss transition states, Ea, intermediates & rate determining step. draw the transition state of a reaction. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ‘ reaction coordinate ’, tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to ...
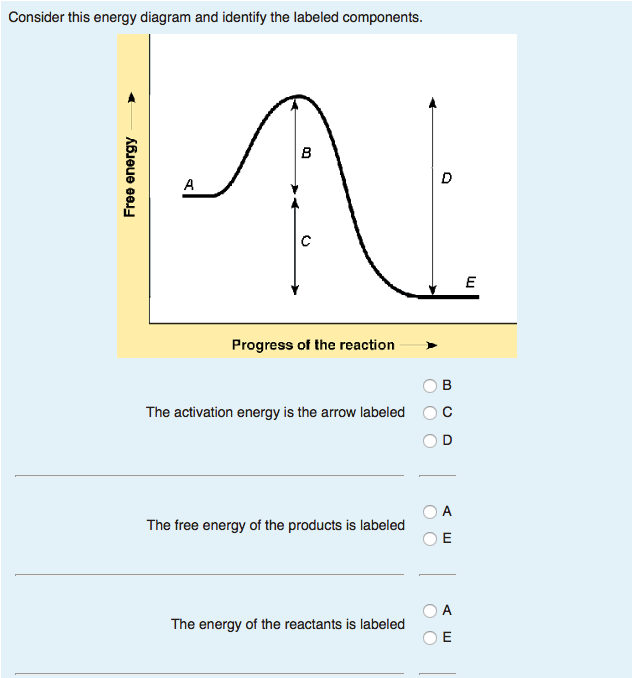
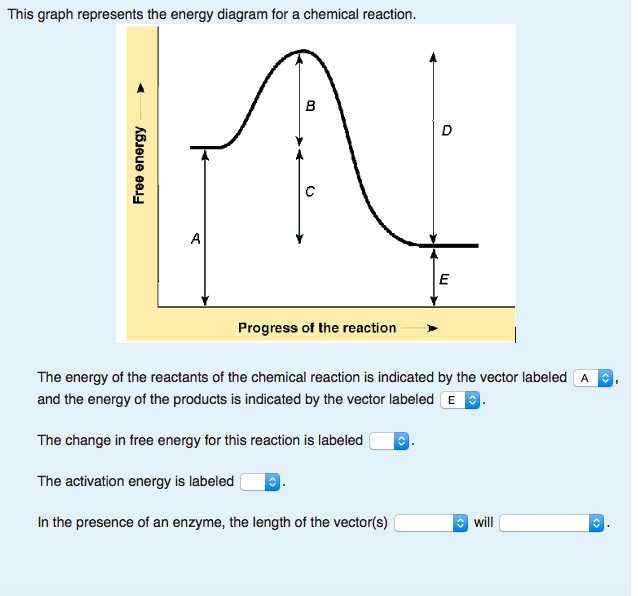
Transcribed image text: This is the energy diagram for a chemical reaction. The energy of the reactants of the reaction are indicated by the vector labeled E and the change in free energy of the reaction is labeled _____. In the presence of an enzyme, the activation energy of the reaction is affected. The activation energy is indicated by the ...
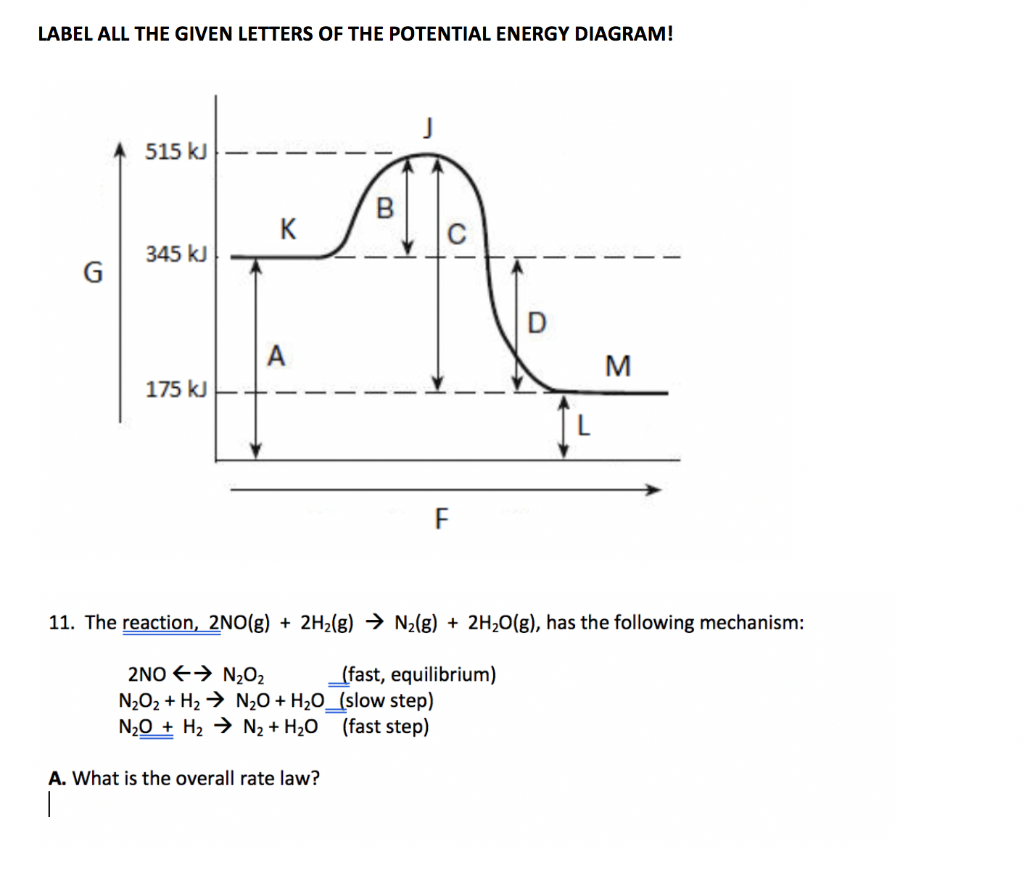
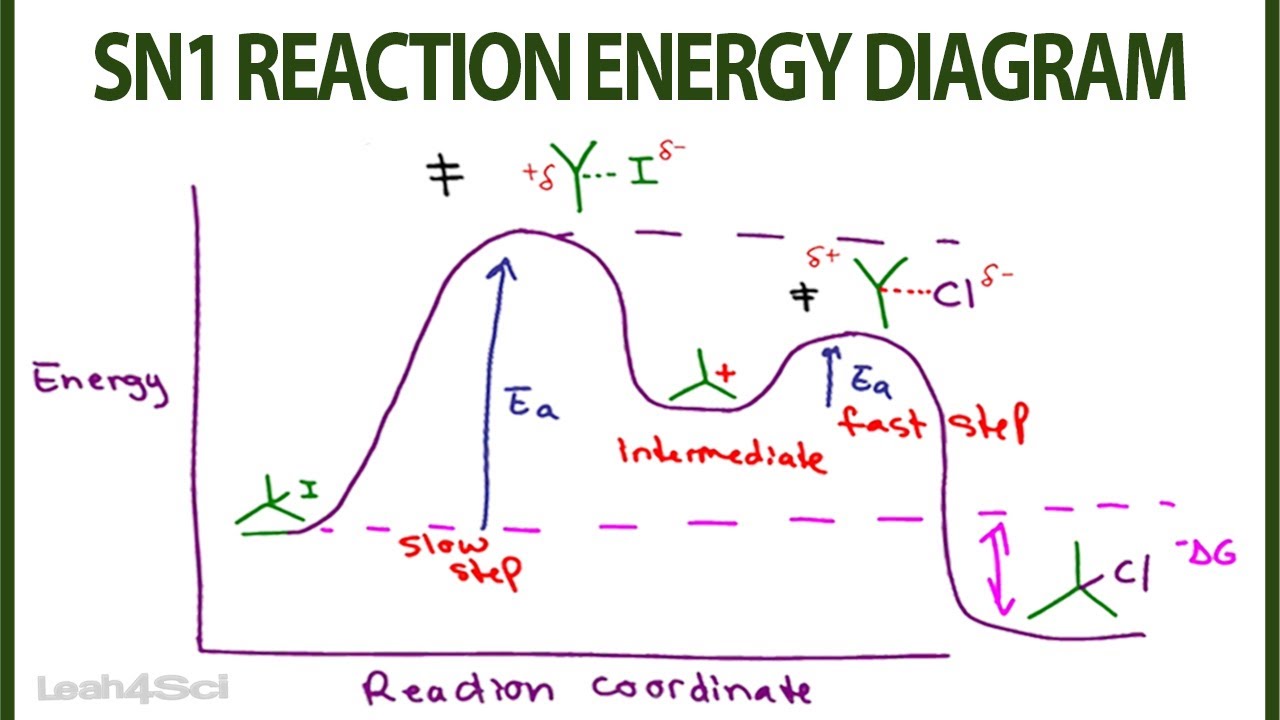
The reaction whose potential energy diagram is shown in the figure is a two-step reaction. The activation energy for each step is labeled \(E_{a1}\) and \(E_{a2}\). Each elementary step has its own activated complex, labeled \(AC_1\) and \(AC_2\). Note that the overall enthalpy change of the reaction \(\left( \Delta H \right)\) is unaffected by ...
Energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions. Energy changes accompany chemical reactions. Energy diagrams are quite useful in illustrating these changes on a continuous basis as the reaction proceeds. Terms such as "activation energy" (E a ), "transition state" (*), and "enthalpy change" are easy to define by referring to a graph such as ...
Thermochemistry and Energy Diagrams. The activation energy ( Ea) of this reaction is. - 80 kJ. 240 kJ. 40 kJ. 160 kJ. 80 kJ.
Potential Energy of Products for FORWARD reaction and Potential Energy of Reactants for REVERSE reaction ... Start studying Labeling an Energy Diagram. Learn ...
Draw and label potential energy diagram for the reaction including a molecular structure that could represent an activated complex. The activated complex would show an unstable association of one CH 4(g) molecule and O 2(g) molecule with partial bonds. Check Your Solution The potential energy diagram should match the given information.
This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f...
6. Draw an energy diagram for a reaction. Label the axis, PE of reactants = 350 KJ/mol, Ea = 100 KJ/mol, PE of products = 250 KJ/mol. 7. Is the reaction in # 6 exothermic or endothermic? Explain. Exothermic. The ΔH is -100 KJ/mol which means heat is released. 8. How could you lower the activation energy for the reaction in #6? Add a catalyst.
Question: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Transition State Transition State Transition intermediate Reaction Intermediate Transition State Transition Uncatalyzed Transition State Reactants Products Catalyzed Ea (fwd) no catalyst Uncatalyzed AHxn < 0 Potential energy Ea (rev) no catalyst Ea ...
energy diagram . These diagrams can be useful in describing motion for all types of objects. Once you have the potential energy diagram for a situation, you can describe the motion of an object. The usual method of using potential energy diagrams is to: • start with the physical situation • use the physics to draw the potential energy diagram
The reaction is exothermic. The reaction is slow at 25°C; however, a catalyst will cause the reaction to proceed faster. (e) Using the axes provided below, draw the complete potential-energy diagram for both the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. Clearly label the curve that represents the catalyzed reaction.
Label ΔH as positive or negative. Figure shows the energy level diagram for the reaction between methane and oxygen. Based on Figure, the following information can be obtained. (a) The reaction between methane and oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water is an exothermic reaction. (b) During the reaction, the temperature of the mixture increases.
In this reaction, the total energy of the reactants is 80 kJ mol-1, the total energy of the products is -90 kJmol-1 and the activation energy for the forward reaction is 120 kJ mol-1. a) Draw a diagram of the energy profile for this reaction. Label the diagram. b) State whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.
















0 Response to "40 reaction energy diagram labeled"
Post a Comment