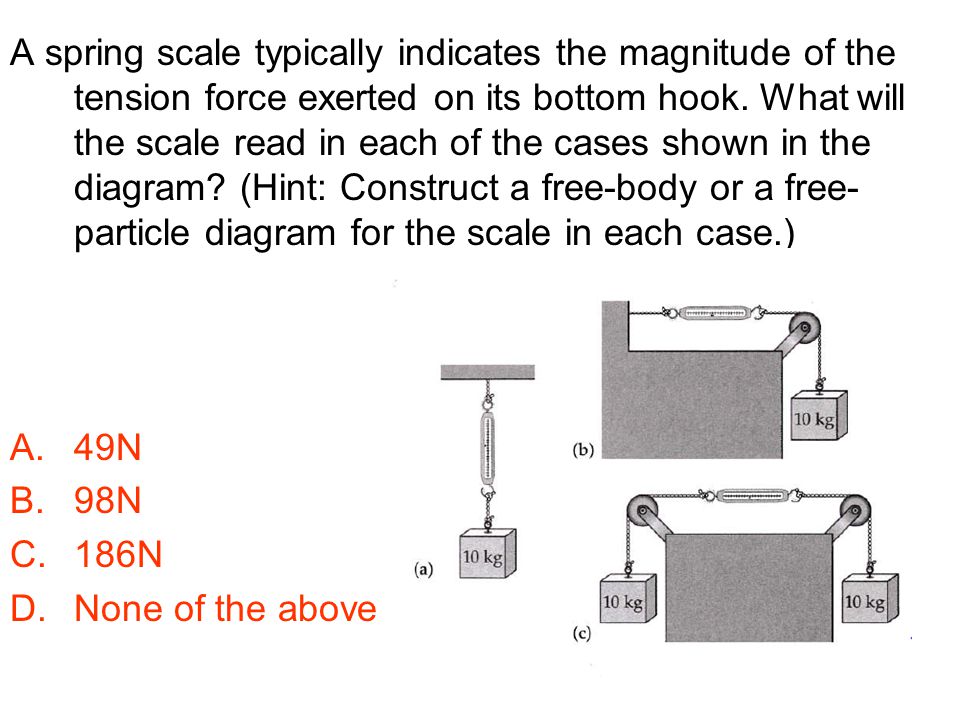
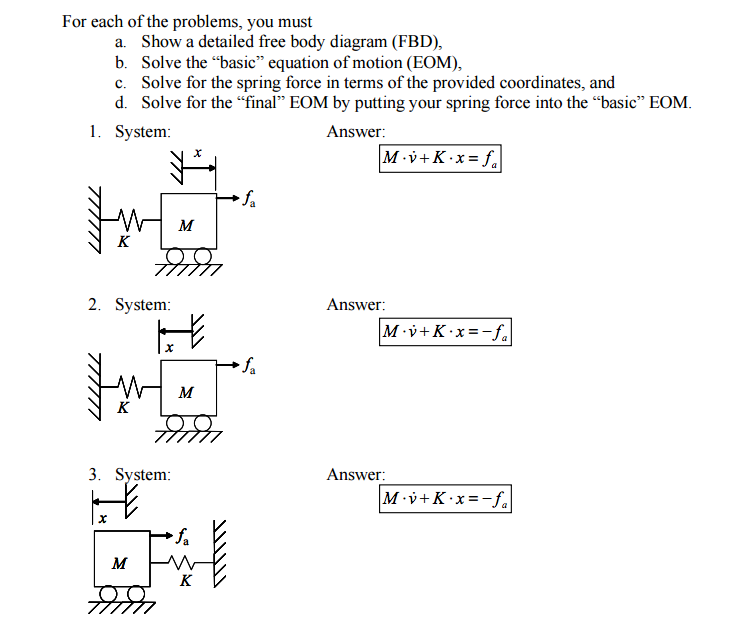
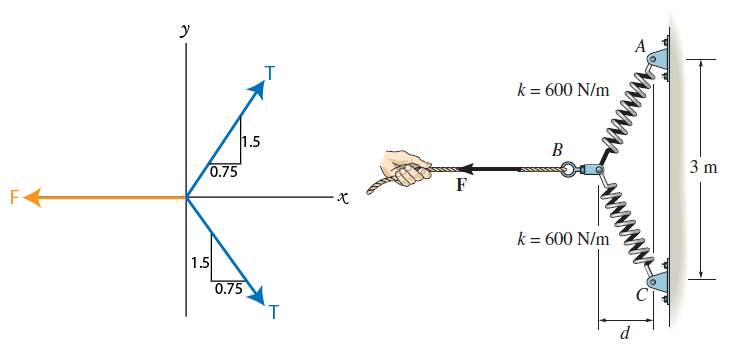
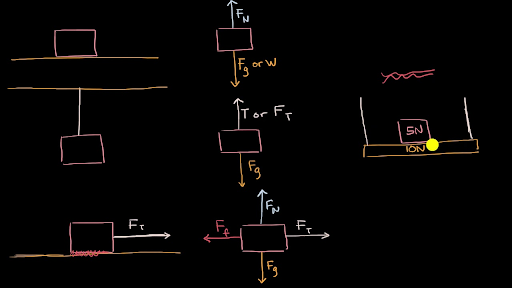
39 spring free body diagram
A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting.
Spring-mass-damper Free-body diagram ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 2 ky t r t dt dy t b dt d y t M chp3 14. Example 2: Mechanical System •Draw a free body diagram, showing all forces and their directions •Write equation of motion and derive transfer function of response x to input u chp3 15.
mass attached to a spring is a good model system for such motion. 2. Theory X m mg F FIG. 1 A. Single spring From the free-body diagram in Fig. 1 F = -mg = - kx (symbols in bold type are vectors), where x is the displacement from the natural equilibrium length of the vertical spring. Because F = mg = kx, k can be determined as the

Spring free body diagram
easy way to draw free body diagram of spring mass system𝐏𝐫𝐨𝐝𝐮𝐜𝐭𝐬 𝐮𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐛𝐲 𝐦𝐞: ═⋗ ...
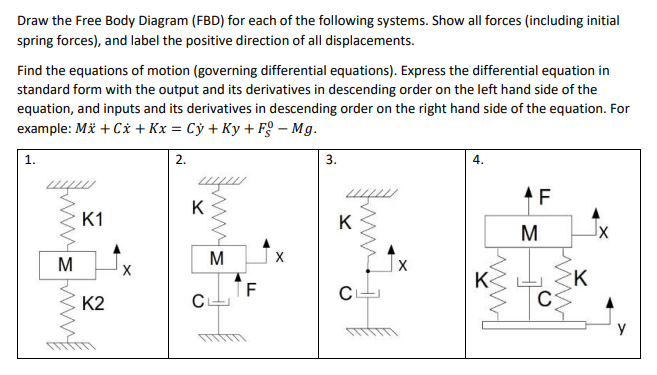
Draw free-body diagrams that conform to the assumed velocity conditions and their resultant damper forces (i.e., tension or compression). c. Apply to the free-body diagrams to obtain the governing equations of motion. The spring and damper forces can be developed sequentially.
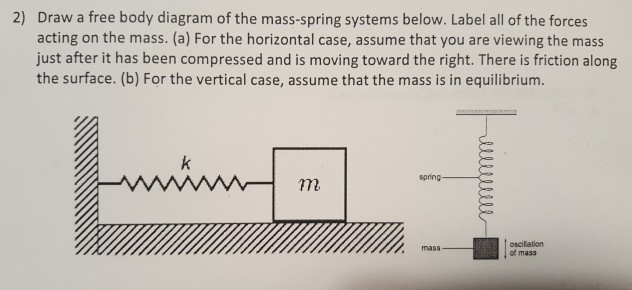
The idea of a free body diagram is to show the forces of acting on a mass. These forces can be forces due to passive elements such as springs and friction ...3 pages
Spring free body diagram.
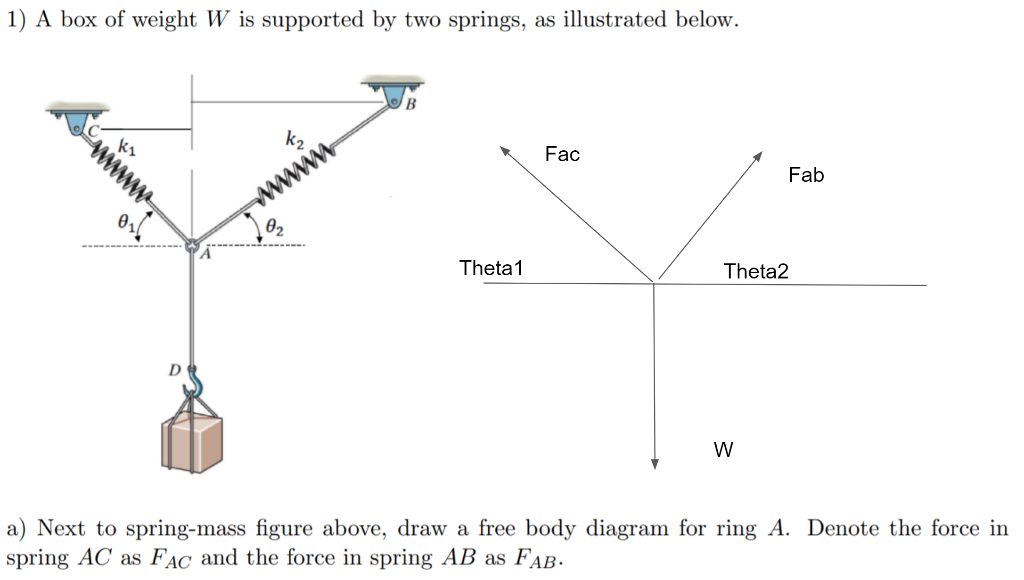
Free-body diagrams are shown in. Figure 12.2, illustrating how the force exerted by the spring on the block depends on the displacement of the end of the spring ...2 pages
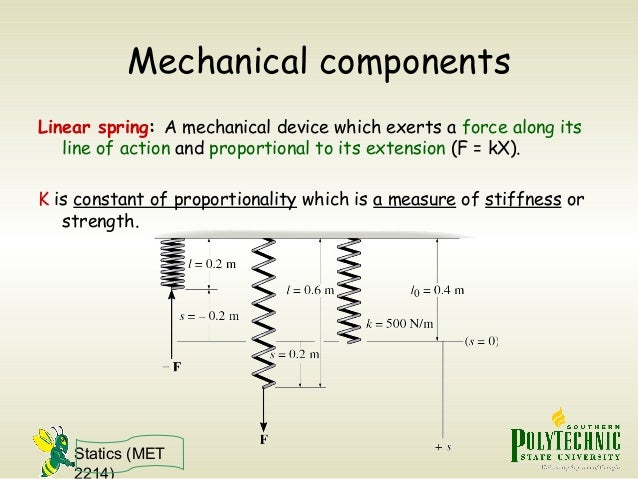
The magnitude of this force is proportional to ∆x, the extension or compression of the spring from its equilibrium position. The force law for springs that.10 pages
Mass – spring – viscous damper system Model Force balance Free body diagram F K0 Mg Free body diagram (no motion) F K0 Mg force due to spring in equilibrium force because spring changes length during motion force due to viscous damping System ODE : 8 m d 2 x < = F K +F v (2 nd order ordinary > dt 2 =) m d 2 x = Kx + Ku f v x˙ + f v u˙ F K
A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newton’s first law or acceleration according to Newton’s second law. Key Equations Conceptual Questions
of action that lies along the spring itself 20 Free Body Diagrams Wednesday, October 3, 2012 Free Body Diagrams ! We also considered the effect of gravity on a system ! Gravity always pulls down (toward the center of the earth) ! If the weight or the mass of a system isn’t given, it can be considered as negligible to the rest of ...
Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting ... friction, tension, and spring force—as well as weight and applied force.Definition of weight, vector form: →w=m→gw...Net external force: →Fnet=∑→F=→F1+→F2+...Newton’s second law, vector form: →Fnet=∑...Newton’s second law, component form: ∑→Fx...
5 Nov 2020 — Include only those forces acting ON the object whose free body diagram you are drawing. Any force exerted BY the object on some other object ...
Fig. 3 shows the mass-spring-damper system and its free-body diagram. The spring force is proportional to the displacement of the mass, x ( ...
Mass-Spring free body diagram Thread starter dondiego; Start date Oct 21, 2010; Oct 21, 2010 #1 dondiego. 5 0. I am trying to get started on a problem. I have two masses M1 = M2 and three springs all with the same constant. The weights and springs are on a frictionless table and the outer springs are attached to walls
The spring is maximally stretched initially so U is the maximum at t=0. This is consistent with the red curve. On the other hand, when U is maximum, K is zero. This is ... Free-body diagrams for a simple pendulum, I. Sketch a free-body diagram for a pendulum when











![10th Grade Physics: Springs] How do I calculate the final ...](https://preview.redd.it/mzrub4xz4ml61.jpg?auto=webp&s=ebc38b5c10638dfc1587baf537b8f22bc1bb203b)


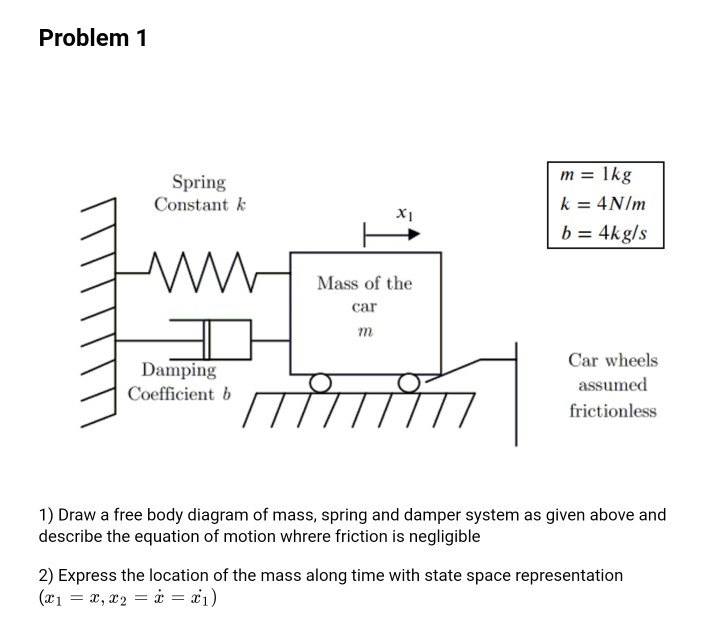


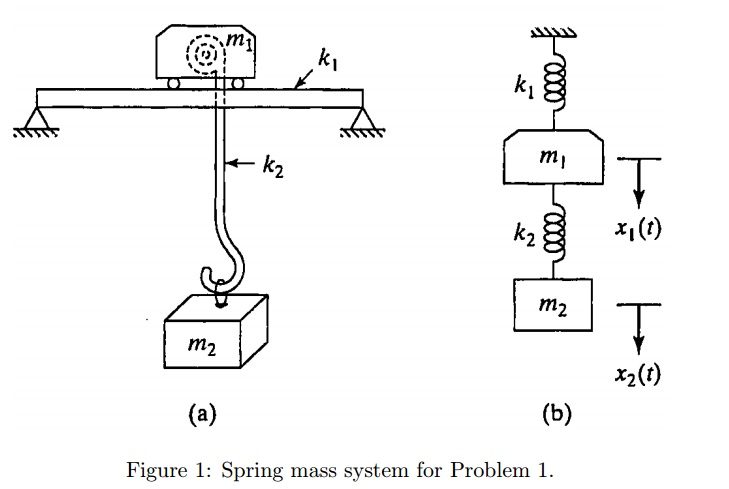

0 Response to "39 spring free body diagram"
Post a Comment