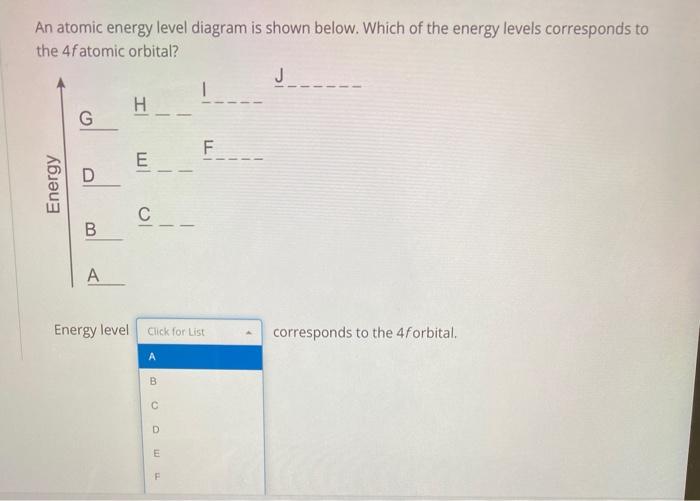
37 atomic energy level diagram
Total energy of an electron in Bohr’s nth stationary orbit is: E n = - \[\frac{2πmK^{2}Z^{2}e^{4}}{n^{2}h^{2}}\] ….(5) Or, E n = - \[\frac{13.6}{n^{2}}\] …(6) Here, TE of an e-in a stationary orbit is negative, which means the electron is tightly bound to the nucleus. Energy Level Diagram [Image will be Uploaded Soon] Energy level diagrams are a means of analyzing the energies electrons can accept and release as they transition from one accepted orbital to another. These energies differences correspond to the wavelengths of light in the discreet spectral lines emitted by an atom as it goes through de-excitation or by the wavelengths absorbed in an absorption ...
The energy levels agree with the earlier Bohr model, and agree with experiment within a small fraction of an electron volt. If you look at the hydrogen energy levels at extremely high resolution, you do find evidence of some other small effects on the energy. The 2p …
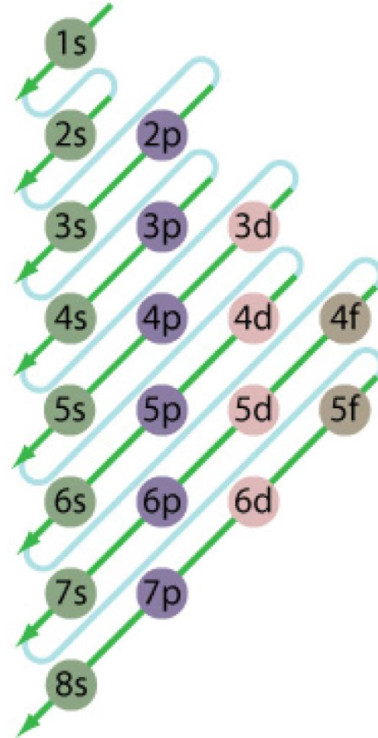
Atomic energy level diagram
How did Rutherford figure out the structure of the atom without being able to see it? Simulate the famous experiment in which he disproved the Plum Pudding model of the atom by observing alpha particles bouncing off atoms and determining that they must have a small core. What is energy level diagram? In chemistry, an electron shell, or energy level, may be imagined as an orbit with electrons around the nucleus of an atom. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the “K shell” followed by the “L shell” then the “M shell” and so on away from the nucleus. The shells can be denoted by alphabets (K, L ... In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be ...
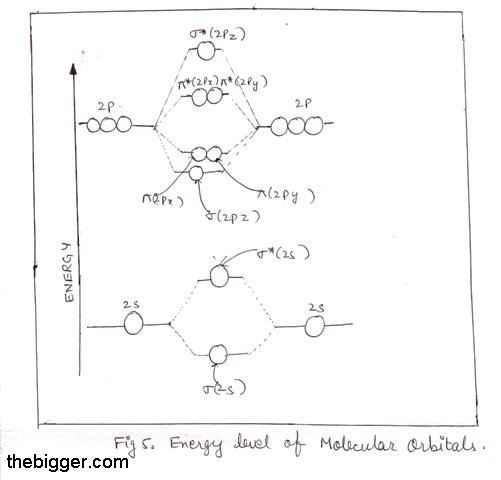
Atomic energy level diagram. Oct 11, 2021 · The energy level of an atom is the amount of energy contained within corresponding orbitals. Explore the definition of energy levels, study the … The energy level diagram is therefore as shown below. Note that the total pi electron energy is more negative (more bonding) than the two electrons of the ethene pi bond, by 0.82b. This is the delocalization energy, i.e., the additional stabilization of these two electrons derived from their delocalization over three atoms, instead of just two. The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. The electronic configuration of N2 is KK (σ(2s)) 2 (σ ∗ (2s)) 2 (π(2p x)) 2 (π(2p y)) 2 (σ(2p z)) 2. N b = 8, Na= 2. Bond Order= 3. Bond order value of 3 means that N 2 contains a triple bond. High value of bond order implies that it should have highest bond dissociation energy. Energy level diagrams are the representation of placements or arrangements of orbitals (also known as subshells) according to their increasing energy levels. Image will be uploaded soon. Above is the blank energy level diagram which can be used to represent the electrons for any atom under study.
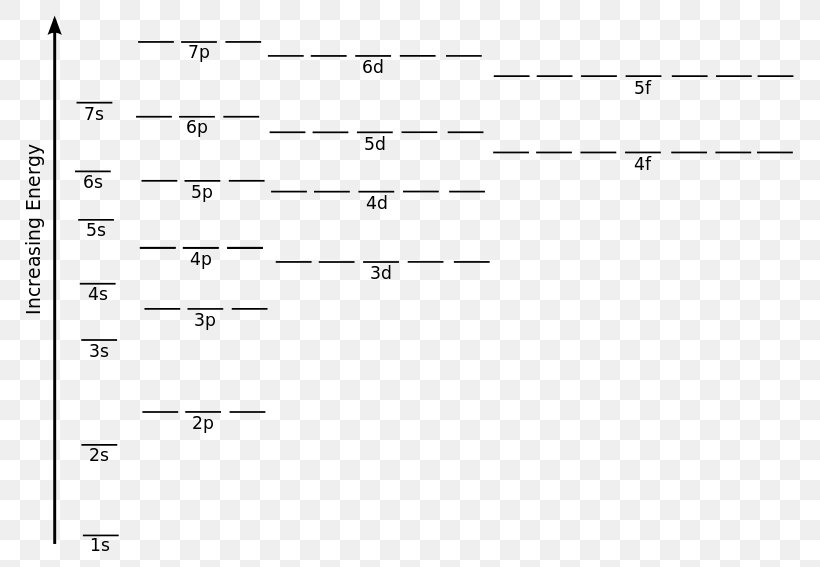
In such cases, the orbital types (determined by the azimuthal quantum number ℓ) as well as their levels within the molecule affect Z eff and therefore also affect the various atomic electron energy levels. The Aufbau principle of filling an atom with electrons for an electron configuration takes these differing energy levels into account. For filling an atom with electrons in the ground ... Energy Level Diagrams Atomic Number Atomic # represents the number of protons (p+) in the nucleus of an atom. For a neutral atom the # protons = # electrons. (total positive charge equals the total negative charge). The atomic number is the top right number on the periodic table for each atom. Example: Carbon has atomic # 6 which means C has We like representing these energy levels with an energy level diagram. The energy level diagram gives us a way to show what energy the electron has without having to draw an atom with a bunch of circles all the time. Let's say our pretend atom has electron energy levels of zero eV, four eV, six eV, and seven eV. Description. Atomic Energy Levels and Grotrian Diagrams, Volume I: Hydrogen I - Phosphorus XV presents diagrams of various elements that show their energy level and electronic transitions. The book covers the first 15 elements according to their atomic number. The text will be of great use to researchers and practitioners of fields such as ...
Band Theory of Solids A useful way to visualize the difference between conductors, insulators and semiconductors is to plot the available energies for electrons in the materials. Instead of having discrete energies as in the case of free atoms, the available energy states form bands.Crucial to the conduction process is whether or not there are electrons in the conduction band. Powered by FlexBook® textbook Platform ® © CK-12 Foundation 2021; Please wait... Please wait... Fig. 6-1. Energy level diagram of some of the excited states of the 12C nucleus. The angular momentum (J), parity (P), and isospin (T) quantum numbers of the states are indicated on the left using the notation J P. P and n respectively at the top of the diagram indicate the separation energies for a proton and a neutron. Atomic Basics Answer Key Part A: Atomic Structure 1. Draw five protons in the nucleus of the atom. Label them with their charge. 2. Draw six neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. 3. Draw two electrons in the first energy level and label them with their charge. 4. Draw three electrons in the second energy level and label them with their charge. 5.
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be ...
What is energy level diagram? In chemistry, an electron shell, or energy level, may be imagined as an orbit with electrons around the nucleus of an atom. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the “K shell” followed by the “L shell” then the “M shell” and so on away from the nucleus. The shells can be denoted by alphabets (K, L ...
How did Rutherford figure out the structure of the atom without being able to see it? Simulate the famous experiment in which he disproved the Plum Pudding model of the atom by observing alpha particles bouncing off atoms and determining that they must have a small core.








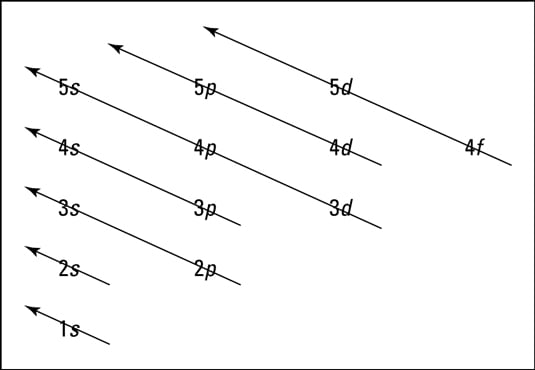
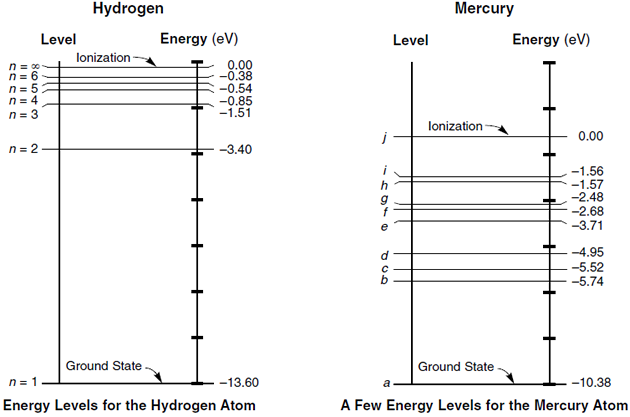

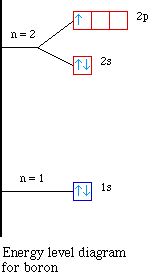













0 Response to "37 atomic energy level diagram"
Post a Comment