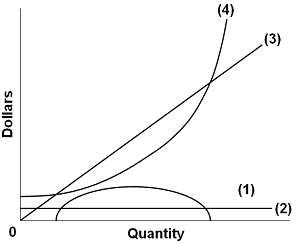
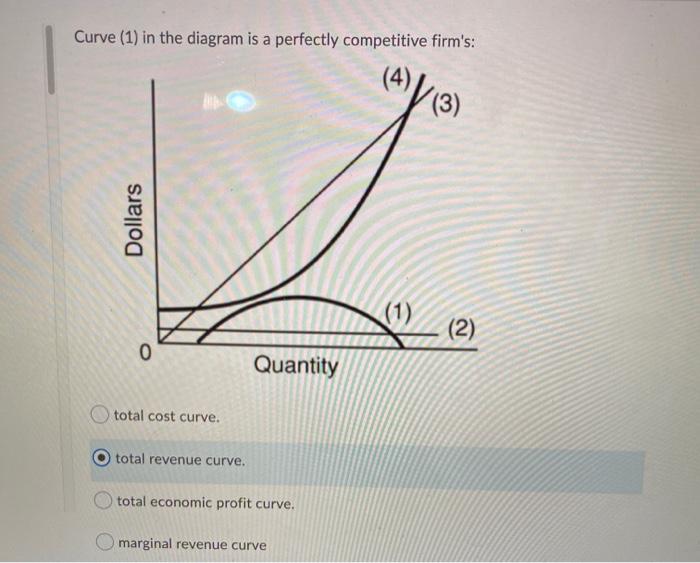
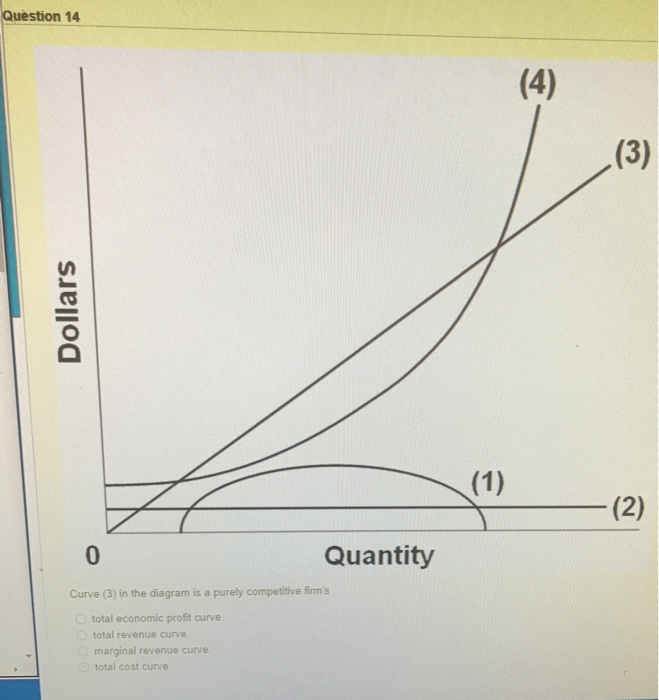
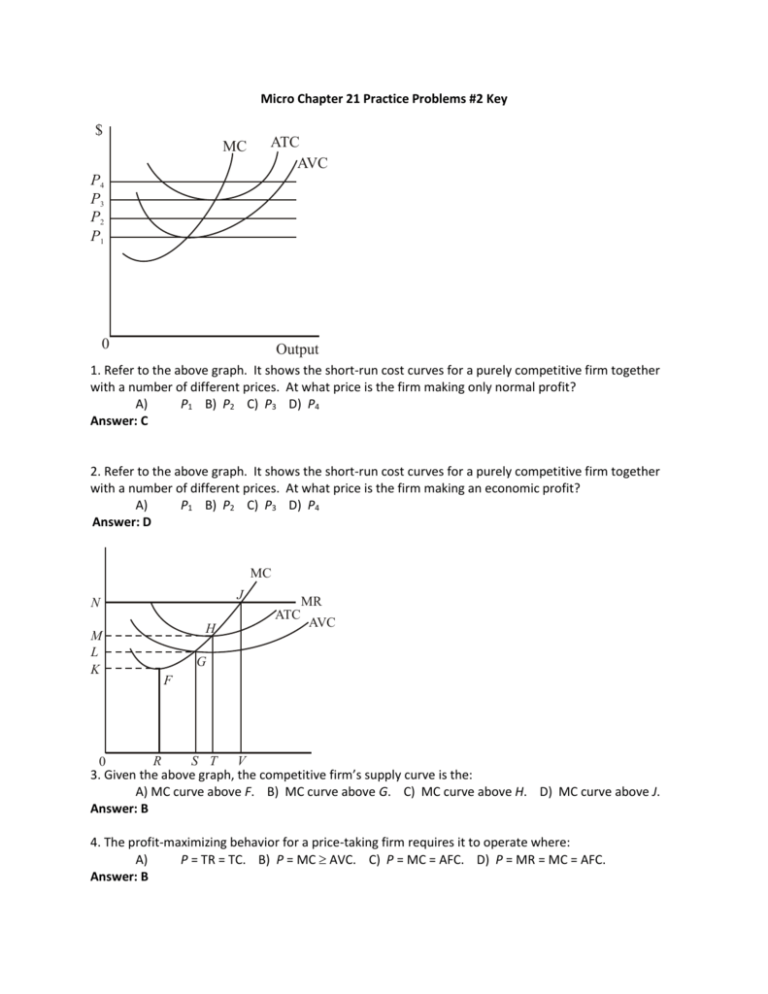
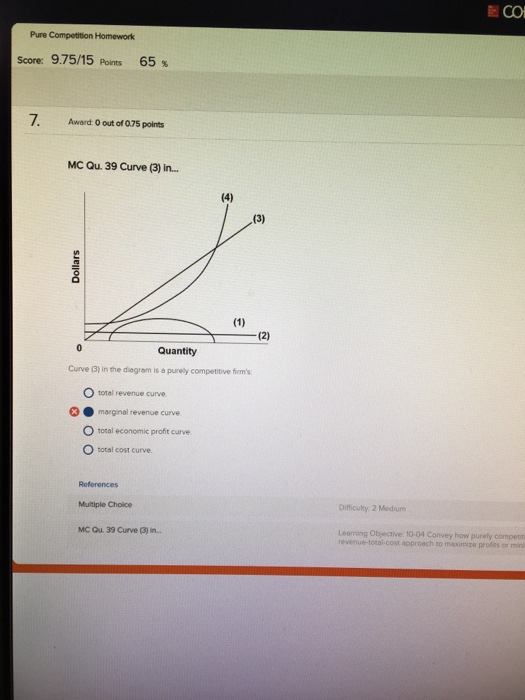
41 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - 46151 - Facebook It is the same as the market demand curve. The following table applies to a purely competitive industry composed of 100 identical firms. 29. Refer to the above table. If each of the 100 firms in the industry is maximizing its profit, each must have a marginal cost of: A. $5. B. $4. C. $3. D. $2. Prof Keep Econ Pr-Test Chap 21 ed 17 Page 9 of 9 30. ECON202 CH10 Heath Flashcards - Quizlet total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's marginal revenue curve Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), and an upward shift in curve (1). Output Marginal Revenue Marginal Cost 0 -- --
Chapter 8 Microeconomic DD2013 Flashcards | Chegg.com The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. ... 69. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: D. total economic profit curve. 70. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: C. marginal revenue curve. 71. Curve ...

Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve c. marginal revenue curve d. total profit curve. Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... The firm represented by the above diagram would maximize its profit where: A. curves (2) and (1) intersect. B. curve (1) touches the horizontal axis for the second time. C.the vertical distance between curves (3) and (4) is the greatest. D. curves (3) and (4) intersect. Marginal Revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand This is so because the demand for the firm’s product is completely elastic. The following one is a perfectly elastic demand curve. This is often used to depict the price and output behaviour of a firm under pure competition. Here dP/dQ = 0. Therefore, the graphing of P in terms of Q in Figure 10.7, has a slope of zero. In other words, the demand curve is completely (perfectly) elastic ...
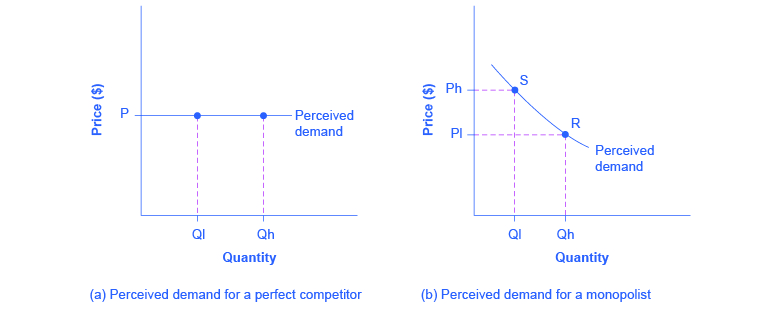
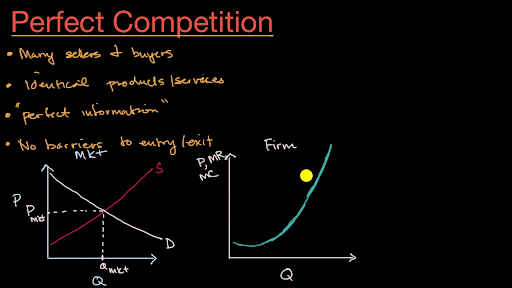
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. revmncmp - harpercollege.edu less elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a purely competitive seller. B. less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a purely competitive seller. ... This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. ... production for the firm shown in the diagram above is: A. Chapter 10 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: marginal revenue curve. A purely competitive seller should produce (rather than shut down) in the short run: The Psychological Contract - BusinessBalls.com Here is a Venn diagram representing quite a complex view of the Psychological Contract, significantly including external influences, which are often overlooked in attempting to appreciate and apply Psychological Contracts theory. Venn diagrams (devised c.1880 by British logician and philosopher John Venn, 1834-1923) are useful in representing all sorts of situations where two … Perfect Competition | Boundless Economics - Lumen Learning In a perfectly competitive market individual firms are price takers. The price is determined by the intersection of the market supply and demand curves. The demand curve for an individual firm is different from a market demand curve. The market demand curve slopes downward, while the firm's demand curve is a horizontal line.
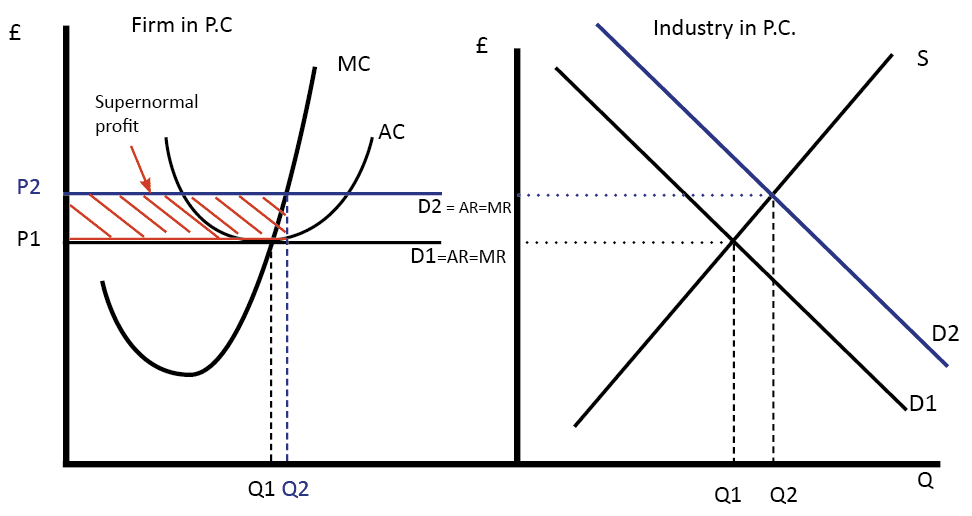
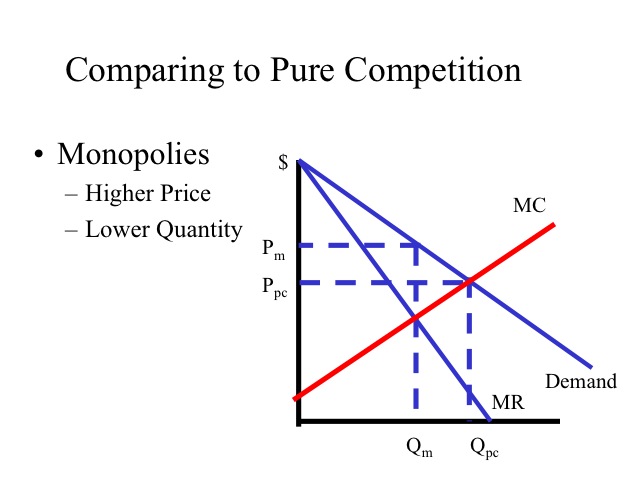
Oligopoly Questions and Answers - Study.com In an oligopoly, each firm's share of the total market is typically determined by: a. Scarcity and competition. b. Kinked-demand curves and payoff matrices. c. … revmonop - harpercollege.edu The pure monopolist's demand curve is: A. identical with the industry demand curve. B. ... Comparing a pure monopoly and a purely competitive firm with identical costs, we would find in long-run equilibrium that the pure monopolist's: ... Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's; Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual, purely competitive firm is; The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual purely competitive firm is ... econ exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: the bcd segment and above on the MC curve. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce . E units at price A. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 0AHE. Refer to the above …
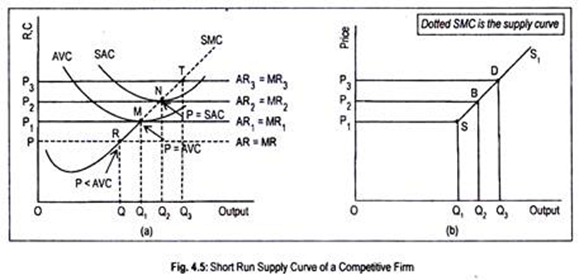
quizlet.com › 577855540 › problems-for-macro-chapterProblems For Macro Chapter 1-10 Flashcards | Quizlet If the growth rate in year 3 had been a positive 2 percent rather than a negative 2 percent, what would have been Econoland's average growth rate over the five years?((3+1+2+4+5)/5)= 3 Suppose that Glitter Gulch, a gold mining firm, increased its sales revenues on newly mined gold from $100 million to $200 million between one year and the next. OneClass: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely ... Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. What does curve c represent? a) total revenue and marginal reve Supply Curve of a Firm and Industry (With Diagram) Short run supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm is that portion of marginal cost curve which is above average variable cost curve. According to C.E. Ferguson, "The short run supply curve of a firm in perfect competition is precisely its Marginal Cost Curve for all rates of output equal to or greater than the rate of output associated with minimum average variable cost." en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Transfer_pricingTransfer pricing - Wikipedia There are two markets each with its own price (Pf and Pt in the next diagram). The aggregate market is constructed from the first two. That is, point C is a horizontal summation of points A and B (and likewise for all other points on the net marginal revenue curve (NMRa)). The total optimum quantity (Q) is the sum of Qf plus Qt.
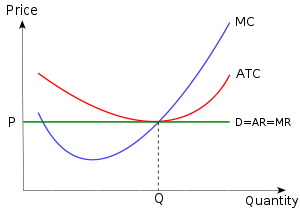
Curve 1 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 43. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. D ) total economic profit curve . McConnell/Brue: Economics, 16/e Page 695. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44.
Econ test 2 Flashcards - Quizlet An industry comprising a very large number of sellers producing a standardized product is known as pure competition An industry comprising a small number of firms, each of which considers the potential reactions of its rivals in making price-output decisions, is called oligopoly
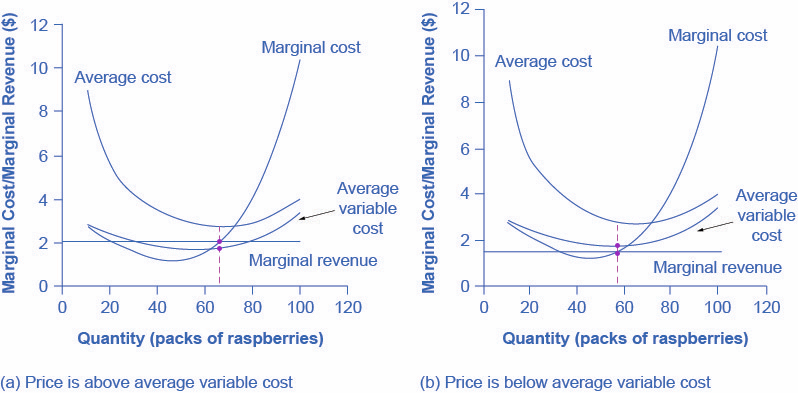
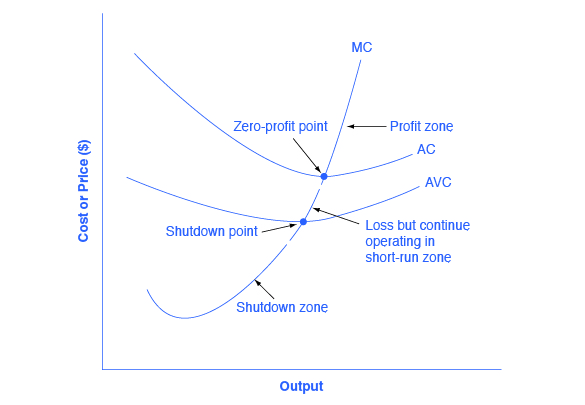
Pure Competition - harpercollege.edu A supply curve which shows the quantity of a product a firm in a purely competitive industry will offer to sell at various prices in the short run; the portion of the firm's short-run marginal cost curve which lies above its average variable cost curve.
Type: D... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A) the abcd segment of the MC curve. C) the cd segment of the MC curve. B) the bcd segment of the MC curve. D) not shown. Answer: B. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 74. The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based on ...
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual purely competitive firm is Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve a represents Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's Comments
Microecon Final Exam Practice Test Flashcards - Quizlet Terms in this set (25) Assuming a firm is selling its output in a purely competitive market, its resource demand curve can be determined by multiplying marginal product by product price. A profit-maximizing firm employs resources to the point where MRP = MRC.
PureCompetitionShortRun_GA.docx - Curve (1) in the above ... View PureCompetitionShortRun_GA.docx from ECON 2302 at Birdville High School. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the above
Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be . $16. Answer the question on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm. Demand DataCost Data(1) Price(2) Price(3) QuantityOutputTotal Cost$11.00$10.0066$619.998.8577629.008.0088648.007.0099677.106.101010726.005.001111795.154.15121286 …
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A total cost curve B from ECON 302 at University of Sharjah
International Economics, Theory and Policy, Global Edition ... International Economics, Theory and Policy, Global Edition by Paul R. Krugman, Maurice Obstfeld, Marc J. Melitz
pure competition questions numbered The fact that a purely competitive firm's total revenue curve is linear and upsloping to the right implies that: A. product price increases as output increases. B. product price decreases as output increases. C. product price is constant at all levels of output. D. marginal revenue declines as more output is produced. 9.
PDF UNF PMASON - University of North Florida the demand curve in a purely competitive industry is while the demand curve to a single firm in that indllstry is perfectly inelastic, perfectly elastic downsloping, perfectly elastic c) downslopmg, perfectly inelastic d) peffectly elastic, dowllsloptng usc the following to answer questions 6-7: in answering the next question(s), assume a graph …
› the-economy › bookUnit 9 The labour market: Wages, profits, and unemployment - CORE Figure 9.9 depicts the market’s demand curve and the firm’s isoprofit curves. Based on this information, which of the following statements is correct? The slope of the demand curve is the firm’s marginal rate of substitution. Between points A and C, the firm would prefer point A as the output is higher.
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive School Johnson County Community College Course Title ECON 230 Type Notes Uploaded By kaigefighter08 Pages 45 Ratings 94% (50) This preview shows page 10 - 12 out of 45 pages. View full document See Page 1 44. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's A) total cost curve.
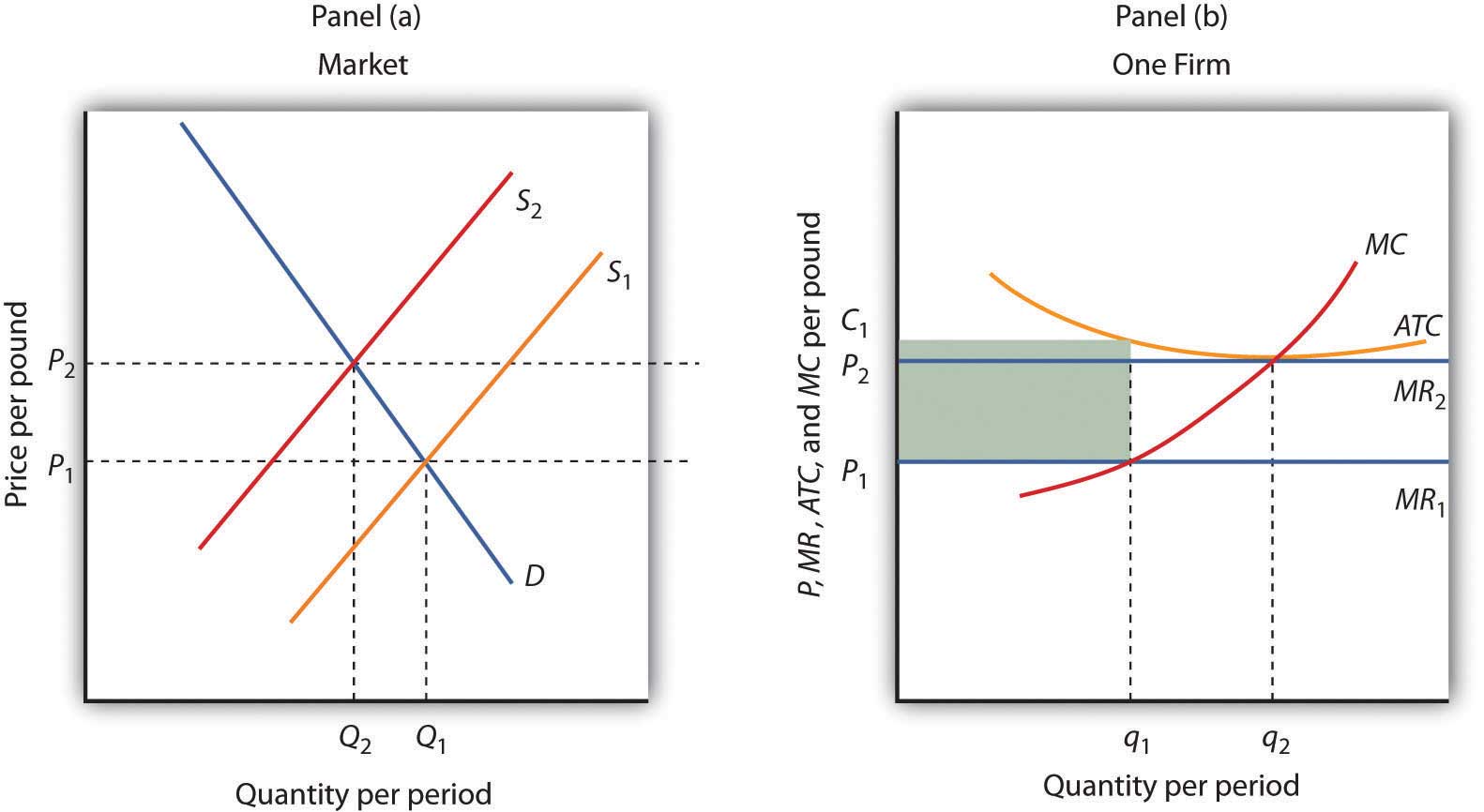
Economies of Scale and International Trade - GitHub Pages Keep in mind that these same effects are occurring for every other firm in the industry, both domestically and in the foreign country. The demand curve shifts from D 1 to D 2 and the marginal revenue from MR 1 to MR 2 as a result of trade. The firm’s cost curves remain the same. Entry or exit of firms causes the final demand curve to be ...
Short Run Supply Curve of a Competitive Firm and Industry ... Or MC curve above the shut-down point is the supply curve. Supply drops to zero if price of the commodity falls below AVC. However, there are numerous firms in a competitive industry, each producing that quantity of goods where its MC curve intersects the horizontal AR = MR curve. Now, all firms sell the product at the same price.
Fountain Essays - Your grades could look better! High Speed Rail and Infrastructure Year 2 Engineering. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Other. 9. View this sample Annotated bibliography. Alcohol addiction. Undergrad. (yrs 3-4) Psychology. 6. View this sample Case study. Case Study. Undergrad. (yrs 1-2) Psychology. 2. View this sample Research proposal. Writer's choice based on the given 6 options please/thanks. Undergrad. (yrs 1-2) …
Solved Dollar (1) 0 Quantity 5 Curve (2) in the diagram is ... Question: Dollar (1) 0 Quantity 5 Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's Multiple Choice total cost curve. total economic profit curve. marginal revenue curve. total revenue curve. This problem has been solved! See the answer question 31 Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Marginal revenue curve. MR=P for a …
Solved O pure competition. O oligopoly. Question 16 0 ... O oligopoly. Question 16 0 Quantity Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O marginal revenue curve. O total revenue curve. O total economic profit curve. O total cost curve. Question 17 Previous question Next question
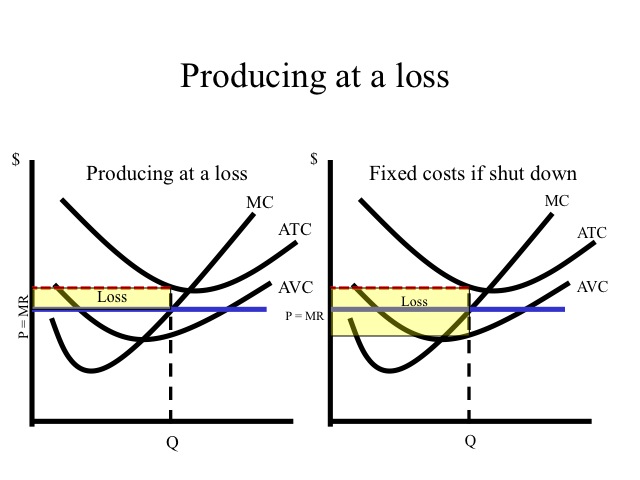
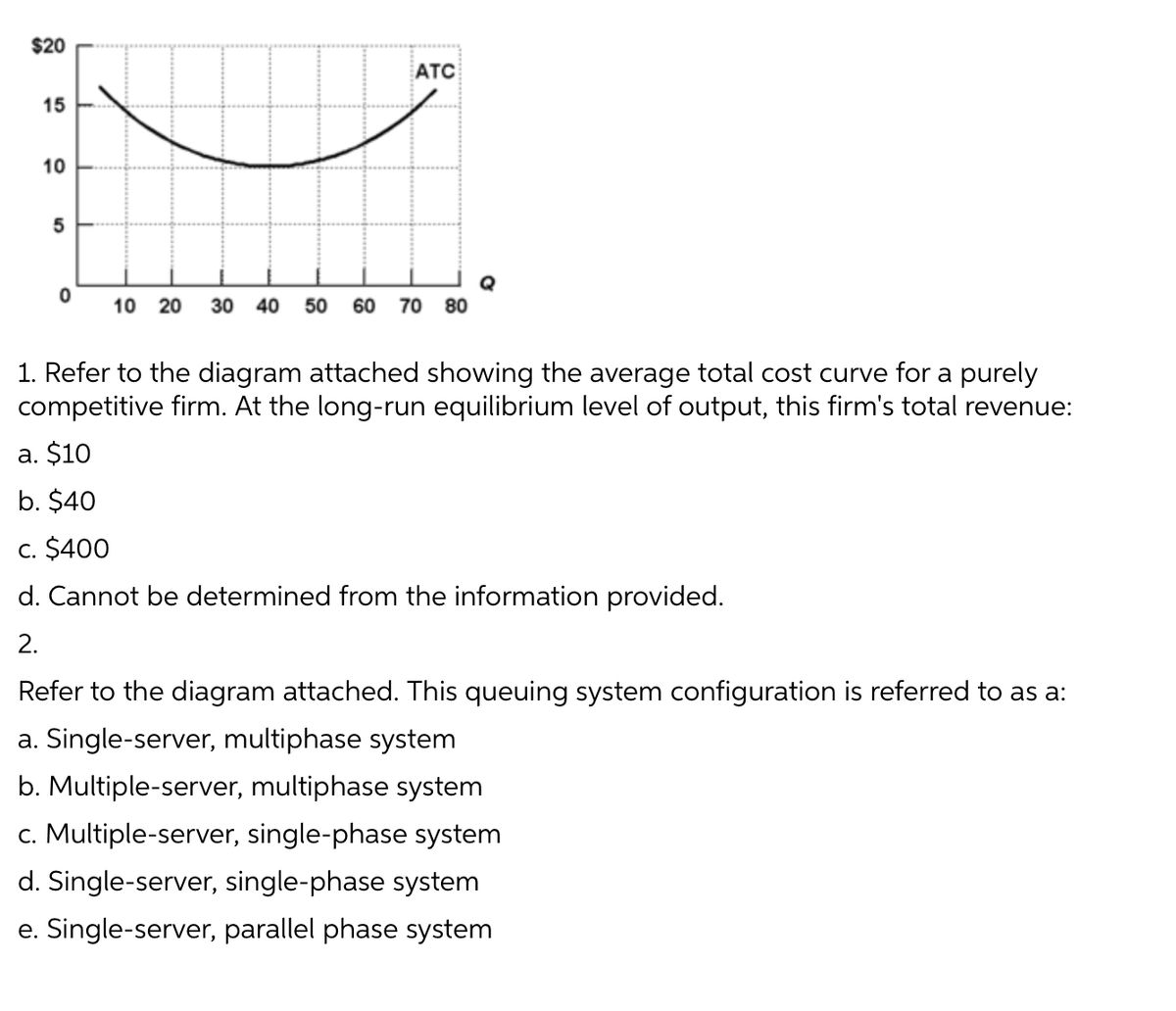
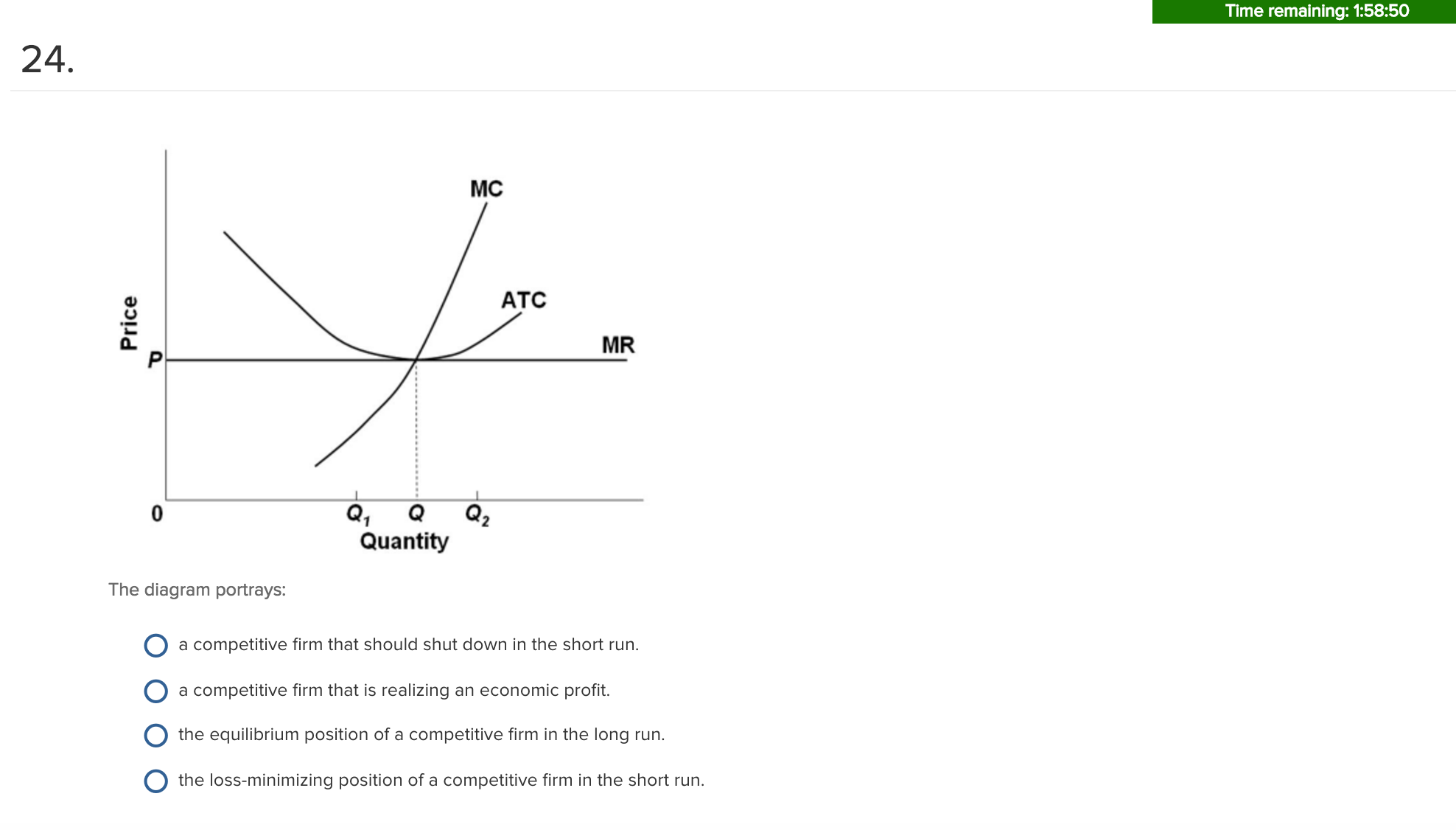
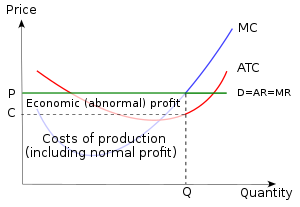
Ch10quiz - paws.wcu.edu Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose this firm is maximizing its total profit and the market price is $15. The firm's per unit profit is:
ECON Pure Competition 1 Short run Flashcards | Quizlet The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
Externality - Wikipedia In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either consumer or producer market transactions. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by …
Marginal Revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand This is so because the demand for the firm’s product is completely elastic. The following one is a perfectly elastic demand curve. This is often used to depict the price and output behaviour of a firm under pure competition. Here dP/dQ = 0. Therefore, the graphing of P in terms of Q in Figure 10.7, has a slope of zero. In other words, the demand curve is completely (perfectly) elastic ...
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... The firm represented by the above diagram would maximize its profit where: A. curves (2) and (1) intersect. B. curve (1) touches the horizontal axis for the second time. C.the vertical distance between curves (3) and (4) is the greatest. D. curves (3) and (4) intersect.
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve c. marginal revenue curve d. total profit curve.
















0 Response to "41 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment