39 square planar molecular orbital diagram
It uses 3-D pictorial presentations of molecular orbitals to elucidate organic reaction . As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4(Td), CH4(D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. Generate the Molecular Orbitals for CH4 (Td), CH4 (D4h) and Cyclopropane using diagram between the bonding MOs of square planar and tetrahedral CH4. The molecular orbital description of bonding in methane does several things for us. Here is an energy level diagram showing how the 4 hydrogen 1s orbitals.Jan 18, · Using LCAO to Construct MOs for ...
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Square planar molecular orbital diagram
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds.As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners. For information on South Africa's response to COVID-19 please visit the COVID-19 Corona Virus South African Resource Portal. the result is called a square planar shape. The bond angles between equatorial positions is 90°. 1). Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CO3 2 ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ ...
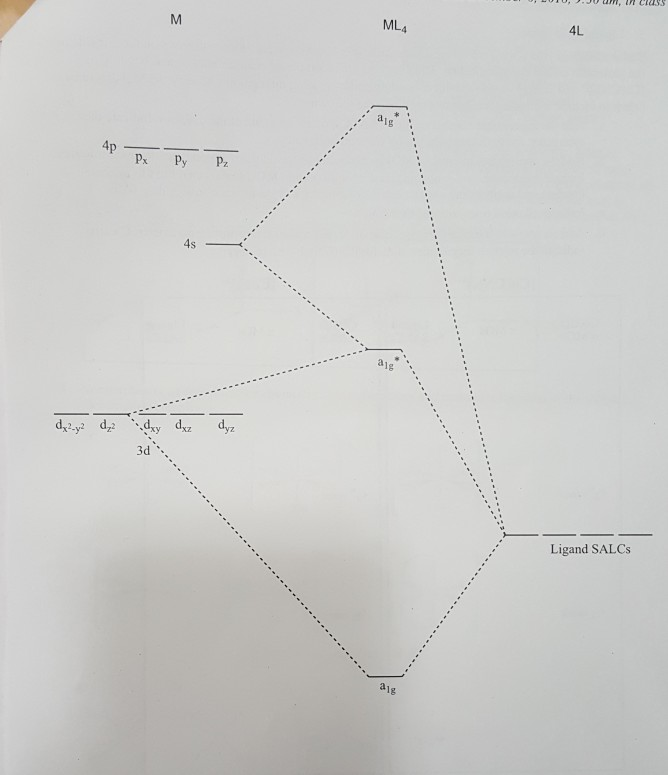
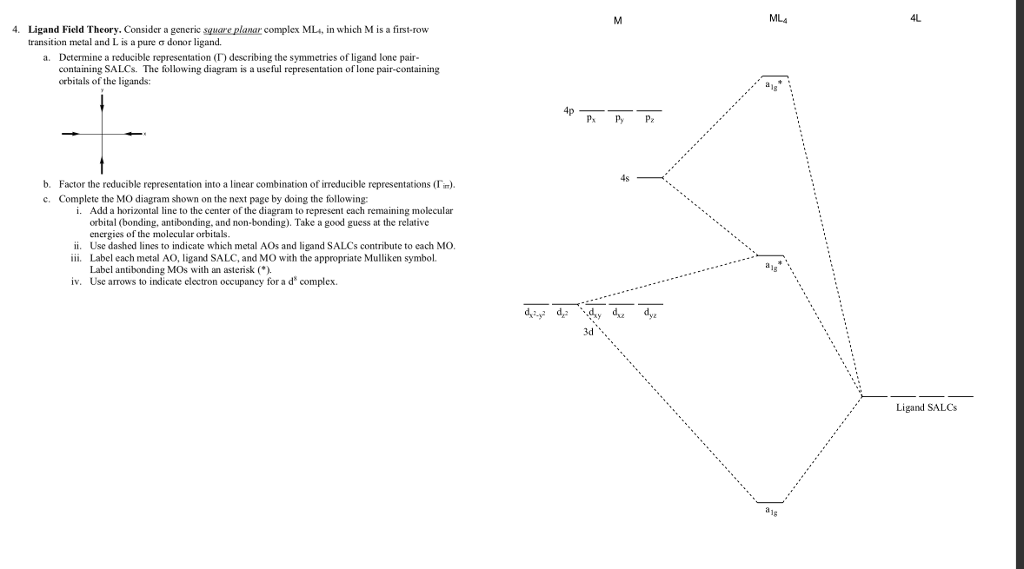
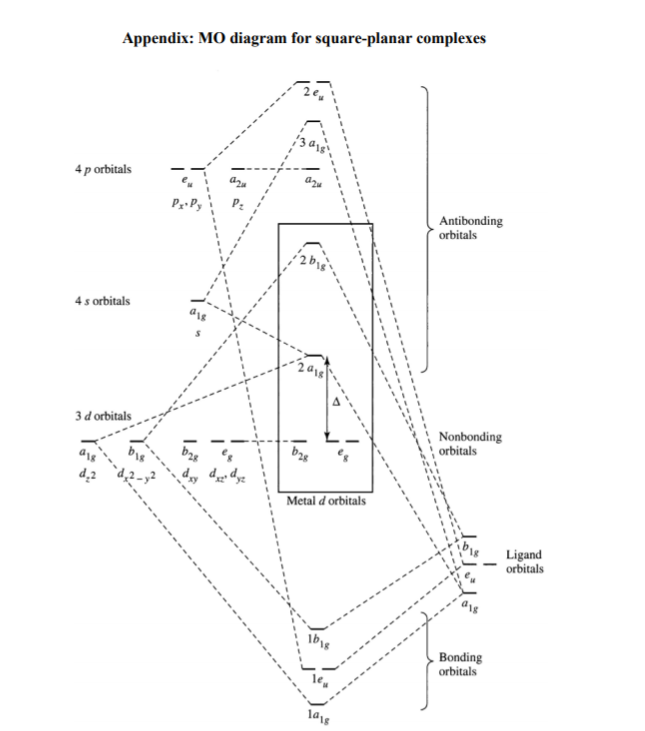
Square planar molecular orbital diagram. CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes are Best ever notes prepared by our awesome team members. We have spend more that 2 years to prepare these Class 11 chemistry notes.After analyzing our notes in deep, we have uploaded our notes on the website. Molecular orbitals for σσσσ bonding in Tdcomplexes • Thesetof nA−Bσ bondsinAB n ... • In each case we may bring the central orbital and the SALC together to give ... MO description of σσσσ only bonding in a square planar D4h transition metal complex Metal valence orbitals Symmetry adapted linear combinations Difficult to use other than octahedral, square planar, tetrahedral. Deal with a variety of possible geometries and with a mixture of ligand. →Angular Overlap Model The strength of interaction between individual ligand orbitals and metal d orbitals based on the overlap between them. Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar Complexes The crystal field theory fails to explain many physical properties of the transition metal complexes because it does not consider the interaction between the metal and ligand orbitals. The molecular orbital theory
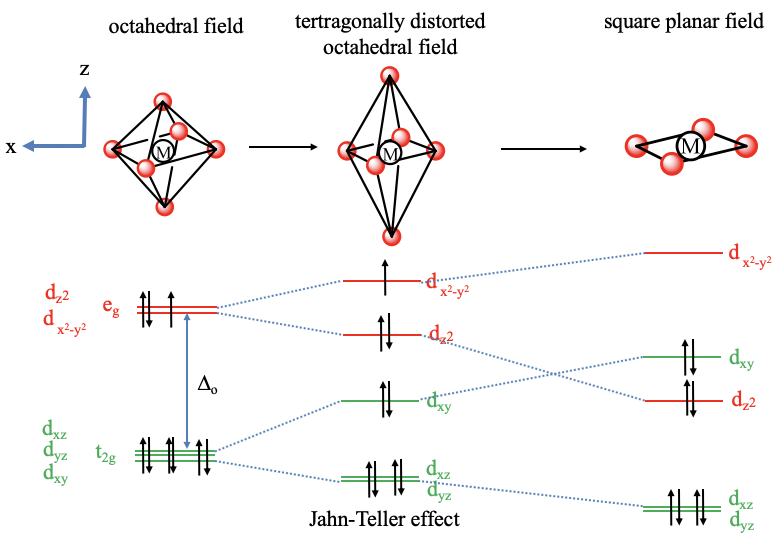
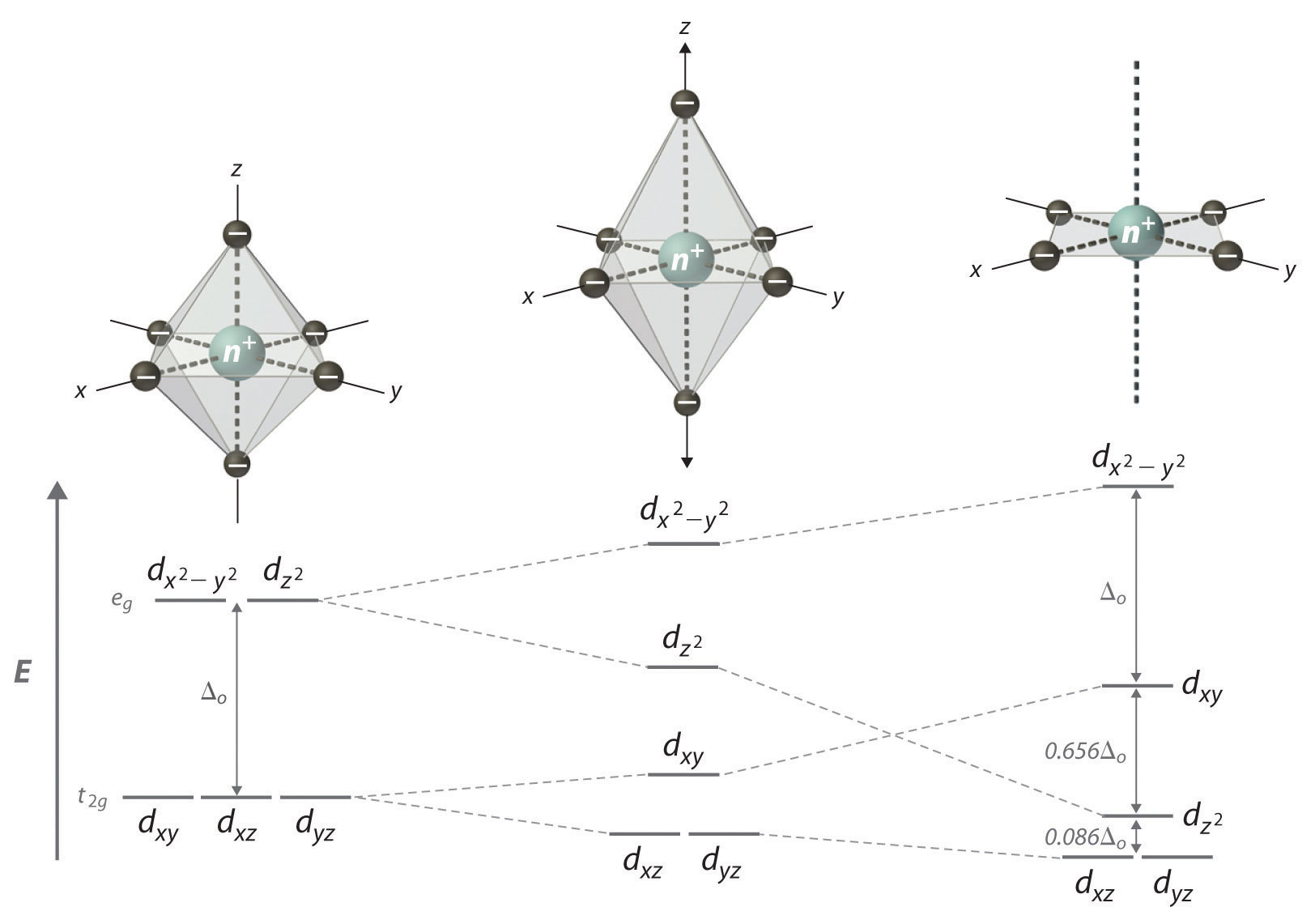
The extreme case of a tetragonal distortion is to form a true square planar complex in which the ligands along the z-axis are completely removed. In this case, the d z 2 orbital drops even lower in energy, and the molecule has the following orbital splitting diagram. A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. Answer (1 of 4): There are 5 d orbitals. dxy, dyz, dzx, dx2-y2 and dz2. They all have double dumbled shape. They are so named on the basis of their orientation with respect to X, Y and Z axis. 3 d orbitals are present between the axis: dxy, dyz, dzx 2 d orbitals are present on the axis: dx2-y2,... The next step is to start drawing an orbital diagram. The five d-orbitals should initially be on one level corresponding to the ionisation energy of nickel(II). The virtual 4s and 4p orbitals somewhat higher. The π-type ligand group orbital should be on a level corresponding to the ionisation energy of ammonia, the σ-type ones slightly below.
Square Planar Complexes Consider a CFT diagram of a tetragonal elongation taken to its extreme: tetragonal elongation removal of z ligands eg t2g b2g dxydxzdyz eg dz2 dx2-y2 dxzdyz dxy dz2 dx2-y2 a1g b1g b2g eg dxzdyz dxy dz2 dx2-y2 a1g b1g ∆1,sp Octahedral Square Planar Δ> Π (tetrahedral vs. square planar) B. Ligand Type π - acceptors π - donors σ - donors many ligands are a combination of donor types, but the "pure" donor diagrams can be considered π - acceptors CO, NO+, CNR, CN-filled empty d-orbitals π* The CFT diagram for tetrahedral complexes has d x 2 −y 2 and d z 2 orbitals equally low in energy because they are between the ligand axis and experience little repulsion. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. In this video, I have explained the detailed molecular orbital diagram for square planar complexes. Formation of sigma lgo and pi lgo have been discussed in ...
Bond Square planar Tetrahedral ... Molecular orbital 'resembles' ... Walsh diagrams summarise changes in MO diagram wrt structure note a combination of first and second order effects. d orbitals Less important in hypervalent main-group molecules such as XeF 2, SF 6
DISCLAIMER: LONG ANSWER! TENDENCIES OF #bb(d^8)# METALS #"Ni"^(2+)#, a #d^8# metal cation, is the metal center here, and #bb(d^8)# metals tend to make four-coordinate complexes like these, which are either tetrahedral or square planar. The difference in energy between these configurations tends to be small. Tetrahedral #d^8# tends to be high spin, while square planar #d^8# tends to be low-spin.
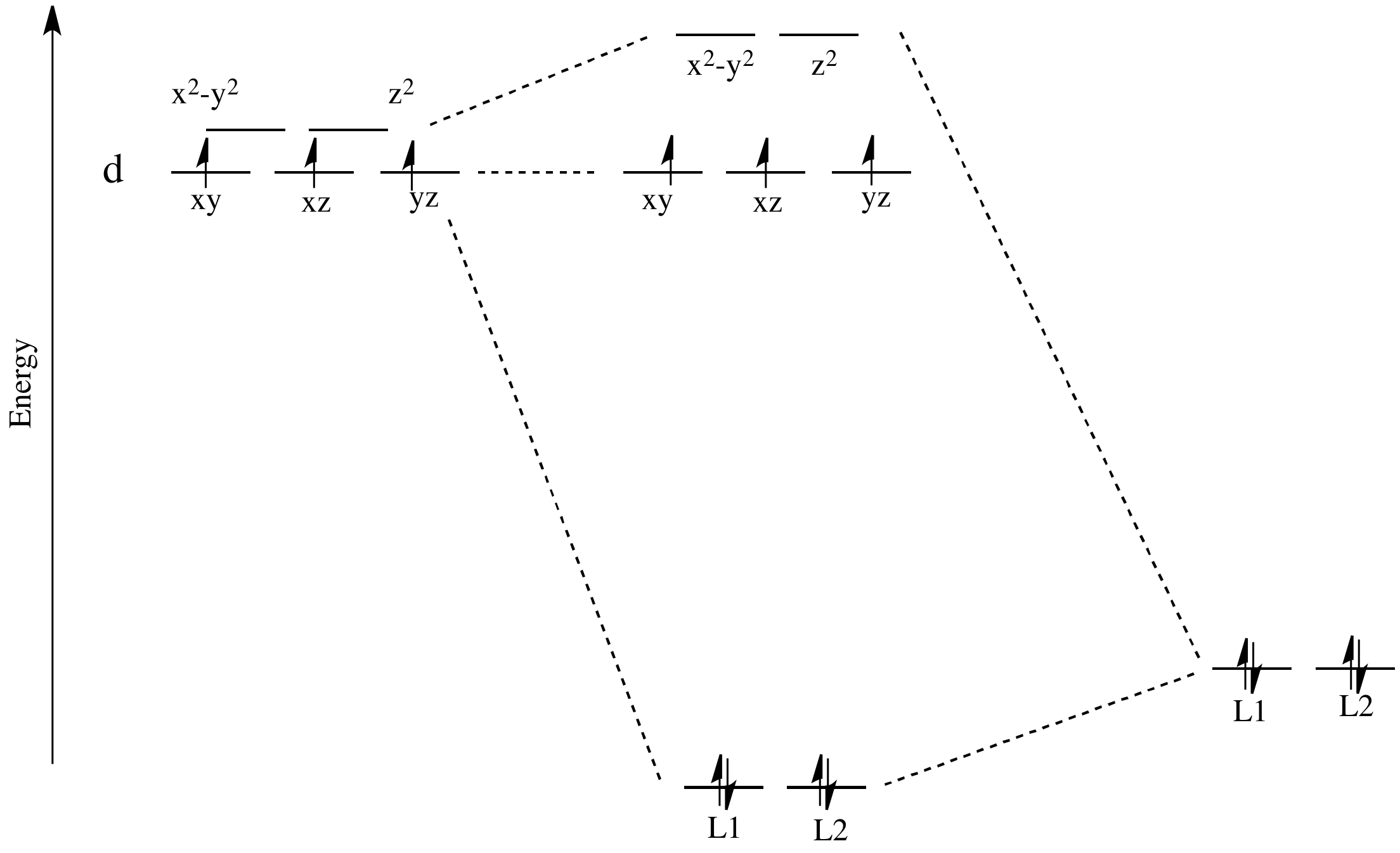
Apr 18, 2014 · Description. This in-class activity walks students through the preparation of a molecular-orbital diagram for methane in a square-planar environment. The students generate ligand-group orbitals (LGOs) for the set of 4 H (1s) orbitals and then interact these with carbon, ultimately finding that such a geometry is strongly disfavored because it does not maximize H/C bonding and leaves a lone pair on C.
The molecule $\ce{[PdCl4]^2-}$ is diamagnetic, which indicates a square planar geometry as all eight d electrons are paired in the lower-energy orbitals. However, $\ce{[NiCl4]^2-}$ is also $\mathrm{d^8}$ but has two unpaired electrons, indicating a tetrahedral geometry. Why is $\ce{[PdCl4]^2-}$ square planar if $\ce{Cl}$ is not a strong-field ...

Scielo Brasil Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. Consequently, the d x2-y 2 remains unoccupied ...
In the square planar structure, 2s and 2p orbitals of the carbon atom does not point in the direction of the 1s orbital of hydrogen. For the square planar structure, the methane molecule should have sp 3 d 2 hybridization. For this, there must be one s-orbital, three p-orbitals, and two d-orbitals.
In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. The square planar geometry is prevalent for transition metal complexes with d 8 configuration. The CFT diagram for square planar complexes can be derived from octahedral complexes yet the dx2-y2 level is ...
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals.
Download "Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar Complexes" ATOICV1-7-2-Molecular-Orbital-Theory-Octahedral-Tetrahedral-or-Square-Planar-Complexes.pdf - Downloaded 87 times - 834 KB. Share this article/info with your classmates/friends and help them to succeed in their exams.
Use the character table of square planar metal complexes, ML4 (point group D4h) to answer the following questions: (total 25 marks) (a) determine the orbitals symmetries of the central metal atom. (b) draw symmetry labelled molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Given that the four (4) sigma-ligand group orbitals (0-LGOs) symmetries are aig, big, and eu.
A rectangle box with a volume of 1088 ft^3 is to be constructed with a square base and top. The cost per square foot for the bottom is 15 cents, for the top is 10 cents, and for the sides is 1.5 ce...
together to produce a sigma molecular orbital [σ = (1sa + 1sb)]. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms, this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This ...
Square Planar D Orbital Splitting Diagram. Crystal Field Theory (CFT) is a model that describes the breaking of degeneracies of electron In a tetrahedral crystal field splitting, the d-orbitals again split into two groups, with an energy difference of Δtet. The lower energy Square planar and other complex geometries can also be described by CFT.
Produce the molecular orbital diagram of the hypothetical square-planar CH4 molecule. Then produce the MO diagram for the tetrahedral CH_4 molecule. Make sure you organize MO energies in the tetrahedral version so that it has four C-H bonds. Why exactly is the planar CH_4 molecule unstable relative to the tetrahedral arrangement?
Solved Q Use Group Theory To Construct A Qualitative Mo Molecular Orbital Diagram For Ah4 Square Planar D4h Orbital Energy S P D A 17 1 Course Hero
3.2 Molecular orbital theory for square planar complexes For square planar complexes, molecular orbitals can be described as resulting from the combination of central metal atom accepting a pair of electrons from each of the four σ donor ligands. Also π bonding can take place between the metal and ligands by either π donor ligands or
Deriving the MO diagram for square planar methane. ... suggesting that the carbon based orbital is the LUMO.5 However, the ionization energy of four hydrogen 1s orbitals in a square plane at approximately 1 Å ... M. Molecular Orbitals of Square-Planar Tetrahydrides.
Lewis dot diagrams for elements are a handy way of picturing valence electrons, and especially, what electrons are available to be shared in covalent bonds. The valence electrons are written as dots surrounding the symbol for the element: one dot is place on each side first, and when all four positions are filled, the remaining dots are paired with one of the first set of dots, with a maximum ...
the result is called a square planar shape. The bond angles between equatorial positions is 90°. 1). Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CO3 2 ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ ...
For information on South Africa's response to COVID-19 please visit the COVID-19 Corona Virus South African Resource Portal.
Solved Generate The Mo Diagram For Ch4 As Square Planar And Ch4 As Tetrahedral Why Does Ch4 Not Exist As A Swaure Planar But It Does As A Tetrahed Course Hero
The square planar molecular geometry in chemistry describes the stereochemistry (spatial arrangement of atoms) that is adopted by certain chemical compounds.As the name suggests, molecules of this geometry have their atoms positioned at the corners.















0 Response to "39 square planar molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment