37 d orbital energy diagram
23.2.2016 · The orbital filling diagram of lithium. The electron configuration of lithium is 1s²2s¹. This means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, and one electron in the higher energy 2s orbital. If you want to make a cool picture, you can do it like this: Energy Levels, sublevels and orbital Notes Tamara Lookabaugh Moore High School Chemistry 2017. DAY ONE: October 3 ... orbital available. This is an AUFBAU diagram. Order of Orbitals—Periodic Table For the d block n-1 For the f block n-2. Hotel analogy video s s s s p d d p p f …
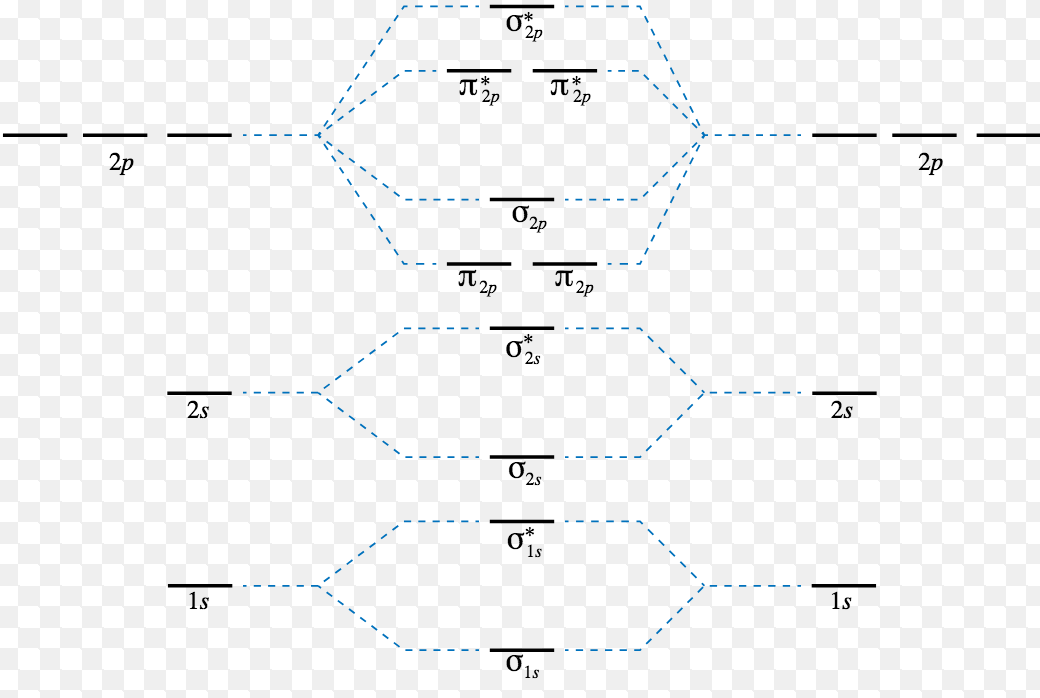
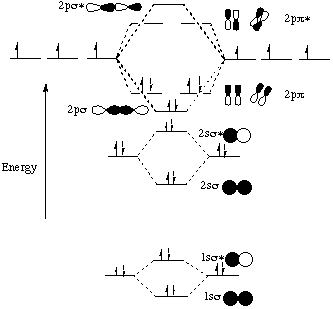
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown:(i) Electronic configuration:(ii) Bond order: Here Nb = 8; Na = 4The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent bonds ...
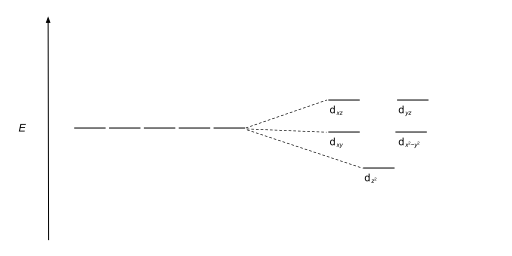
D orbital energy diagram
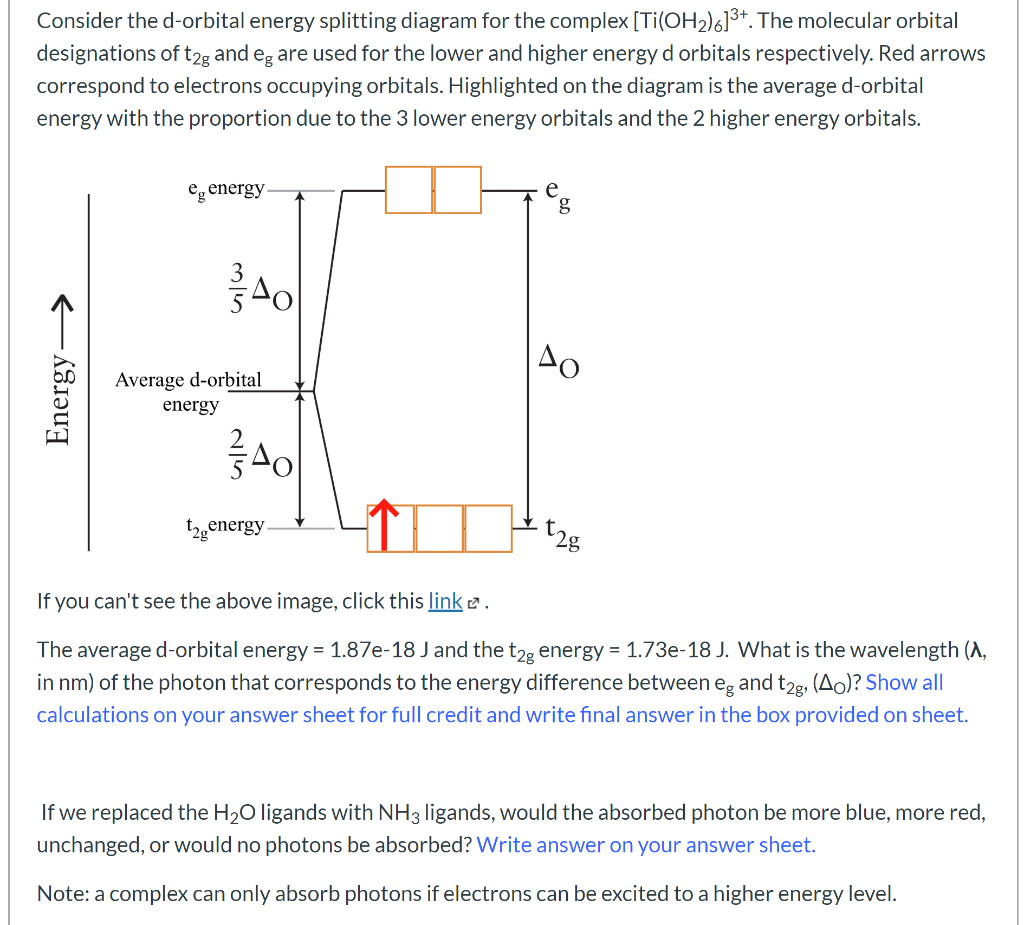
Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability. This is why the hydrogen atom has an electron configuration of 1s 1. 2) Orbitals are combined when bonds form between atoms in a molecule. There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d … Mar 18, 2020 · We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) to predict electronic structures and some of the properties of transition-metal complexes. We start with the Ti 3 + ion, which contains a single d electron, and proceed across the first row of the transition metals by adding a single electron at a time. Orbitals Chemistry (s, p, d, and f Orbital) - Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds, denoted s, p, d, and f, each with a different shape. Of the four, we'll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry. Learn more about atomic orbital at Byjus
D orbital energy diagram. In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be ... with the. d. orbital being one level lower than the energy level it is on. orbital diagram for arsenic see more ideas approximately from diagram electron configuration gallery & create your house design images related to pictures as well help you in locating the solution are seeking about itOrbital diagram for arsenic. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... The third electron goes into the next orbital in the energy diagram, the 2s orbital. Li (Z = 3): 1s 2 2s 1. The fourth electron fills this orbital. Be (Z = 4): 1s 2 2s 2. After the 1s and 2s orbitals have been filled, the next lowest energy orbitals are the three 2p orbitals.
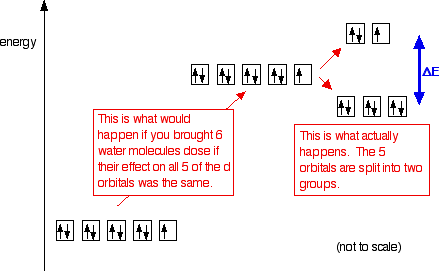
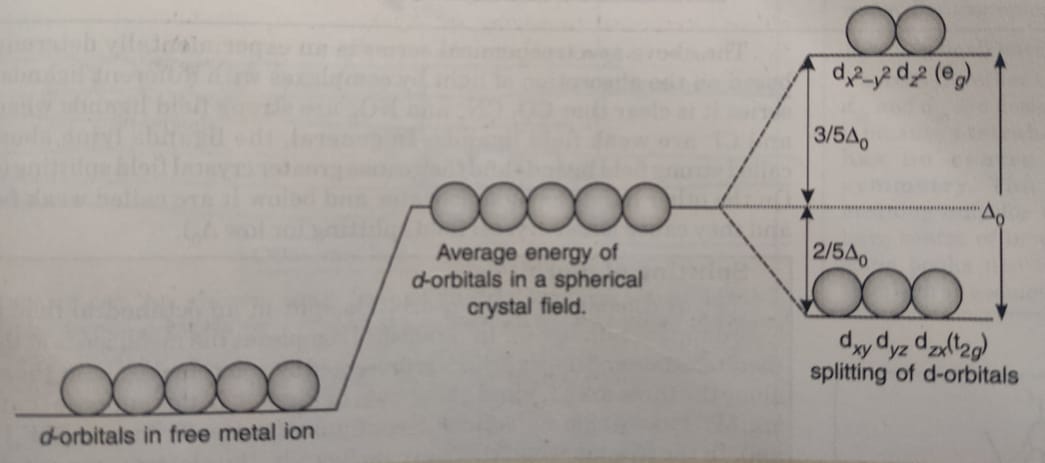
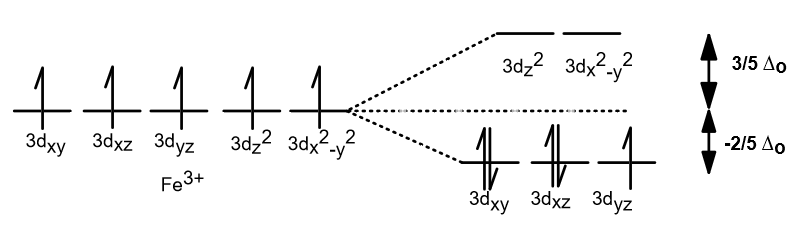
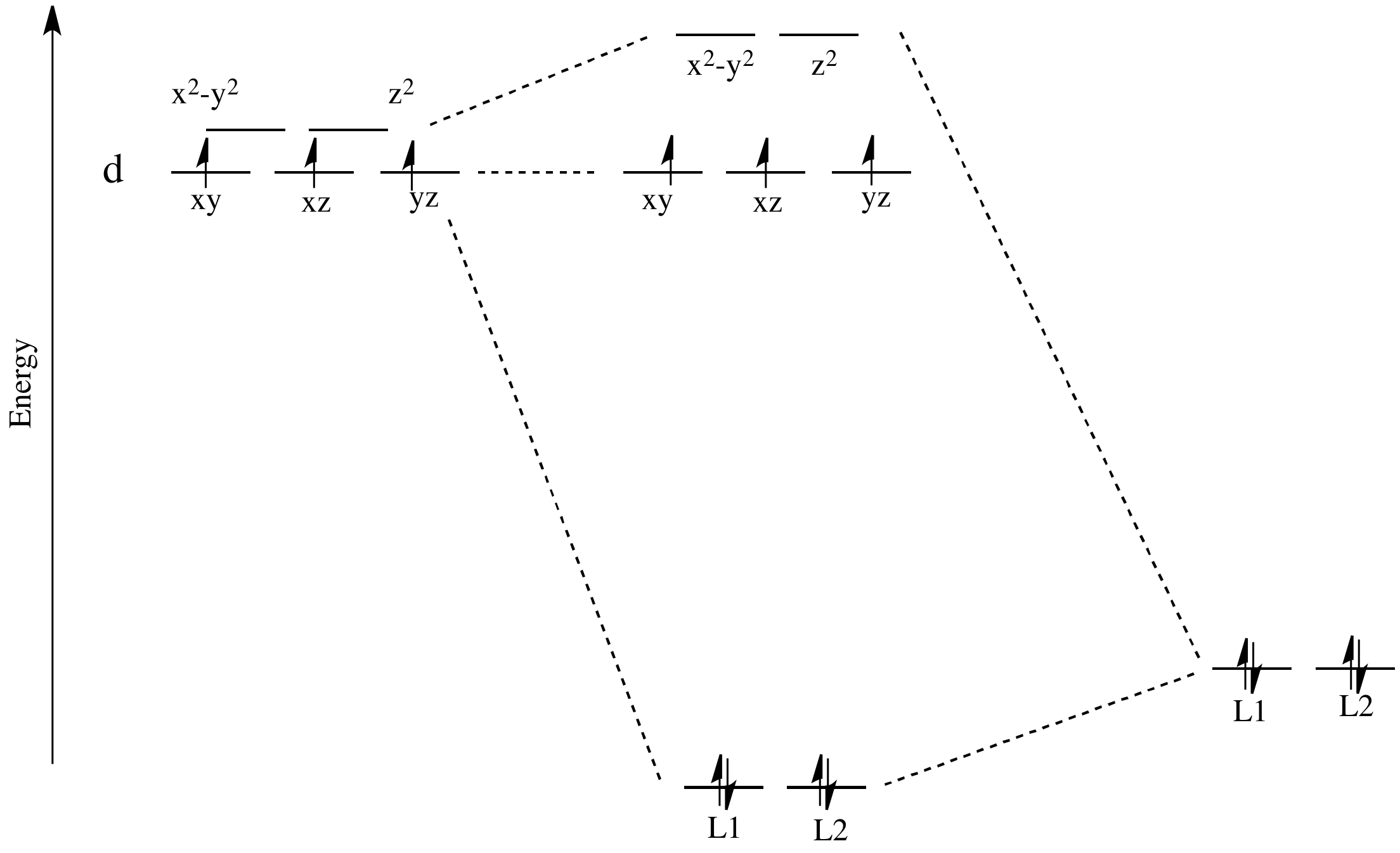
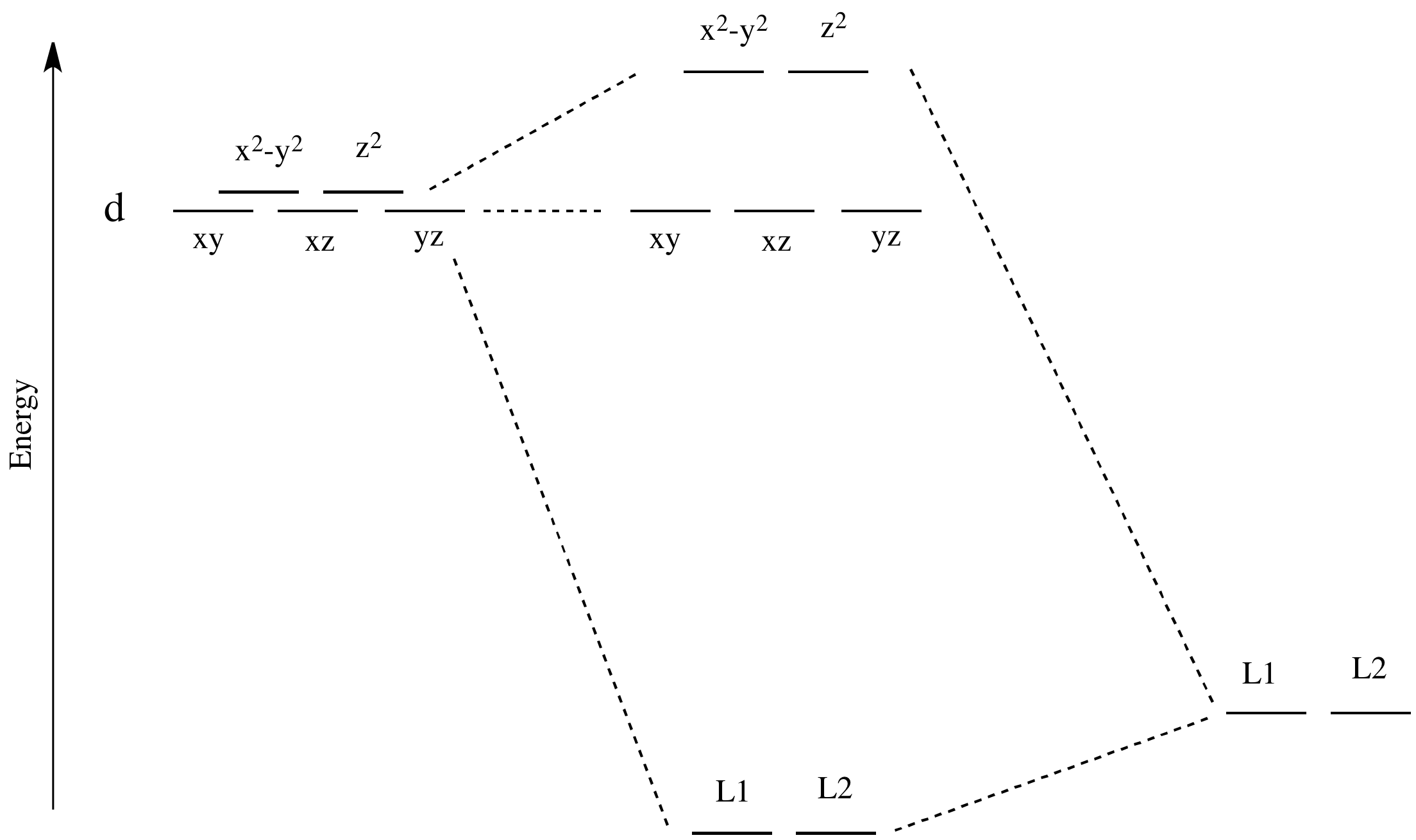
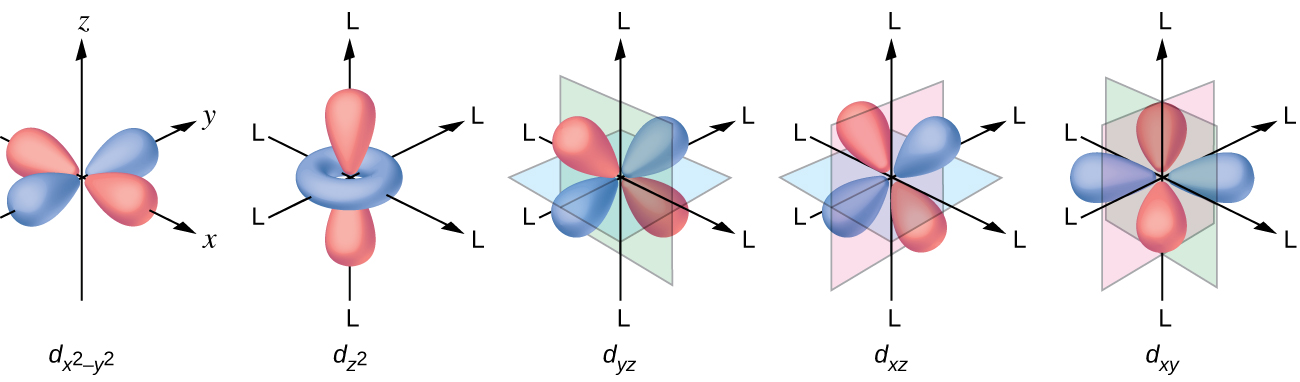
Figure 46. The splitting pattern of d-orbital energy levels of d3-metal complexes in tetragonal distortion. 2. Rhombic distortion: The unequal amount of elongation or compression along two four-fold axes of rotation in octahedral complexes produces rhombic distortions. The common examples of rhombic distortion are high- A 3s orbital is even larger, and it has three nodes. p ORBITALS. Not all electrons inhabit s orbitals. At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital. However, at the second level, there are also orbitals called 2p orbitals in addition to the 2s orbital. But two of the d orbitals have lobes pointing along those axes - the 3d x 2 - y 2 and 3d z 2 orbitals. Those will feel more repulsion than the other three, which have lobes in between the axes. That means that two of the d orbitals will now have a higher energy than the other three - which is exactly what the diagram we have been using shows. LCAO MO Energy Diagram for H2 Energy H-H ∆E1 ∆E2 • ∆E2> ∆E1, so the antibonding orbital is always more anti-bonding than the bonding orbital is bonding H2molecule: two 1s atomic orbitals combine to make one bonding and one antibonding molecular orbital. Ha Hb
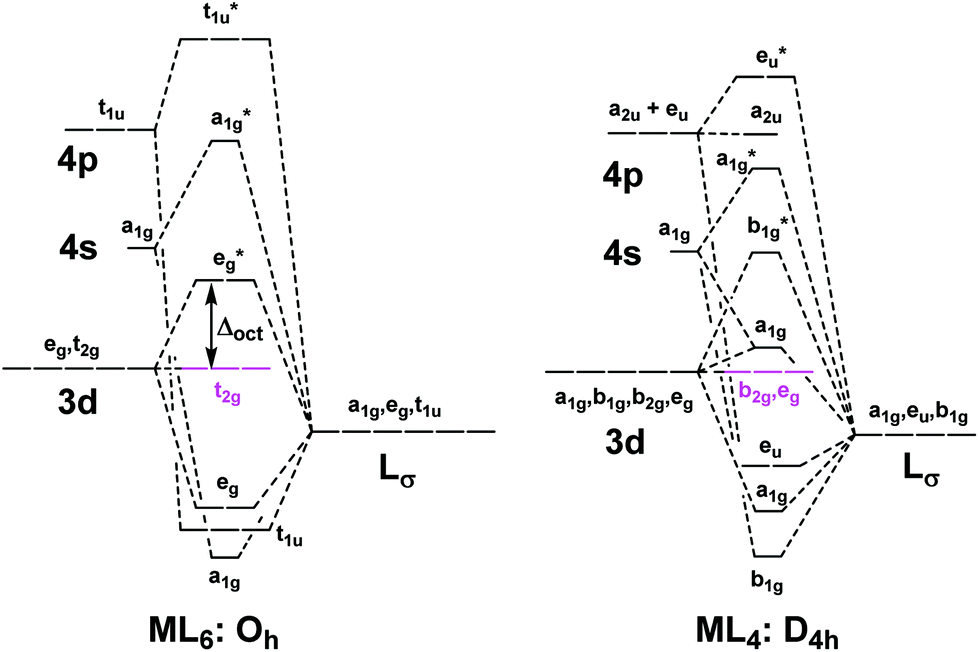
A general d-orbital splitting diagram for square planar (D 4h) transition metal complexes can be derived from the general octahedral (O h) splitting diagram, in which the d z 2 and the d x 2 −y 2 orbitals are degenerate and higher in energy than the degenerate set of d xy, d xz and d yz orbitals. Consequently, the d x2-y 2 remains unoccupied ... Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration. Orbitals Chemistry (s, p, d, and f Orbital) - Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds, denoted s, p, d, and f, each with a different shape. Of the four, we'll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry. Learn more about atomic orbital at Byjus Mar 18, 2020 · We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) to predict electronic structures and some of the properties of transition-metal complexes. We start with the Ti 3 + ion, which contains a single d electron, and proceed across the first row of the transition metals by adding a single electron at a time.
Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability. This is why the hydrogen atom has an electron configuration of 1s 1. 2) Orbitals are combined when bonds form between atoms in a molecule. There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d …






















0 Response to "37 d orbital energy diagram"
Post a Comment