38 refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be
Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing output ... Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: asked Aug ... A monopolist may choose a price lower than the profit maximizing price because? asked Apr 29, 2019 in Economics by ... 50 items by Ethann189. Business - Accounting And Taxation, Quiz Level 2. 35 items by achristensen11. Criminal Justice - Core ... Profit Maximization | MR equals MC | Derivation and Example Profit maximization rule (also called optimal output rule) specifies that a firm can maximize its economic profit by producing at an output level at which its marginal revenue is equal to its marginal cost. Marginal revenue is the change in revenue that results from a change in a change in output. For example, if a firm sells 99 units for $198 ...
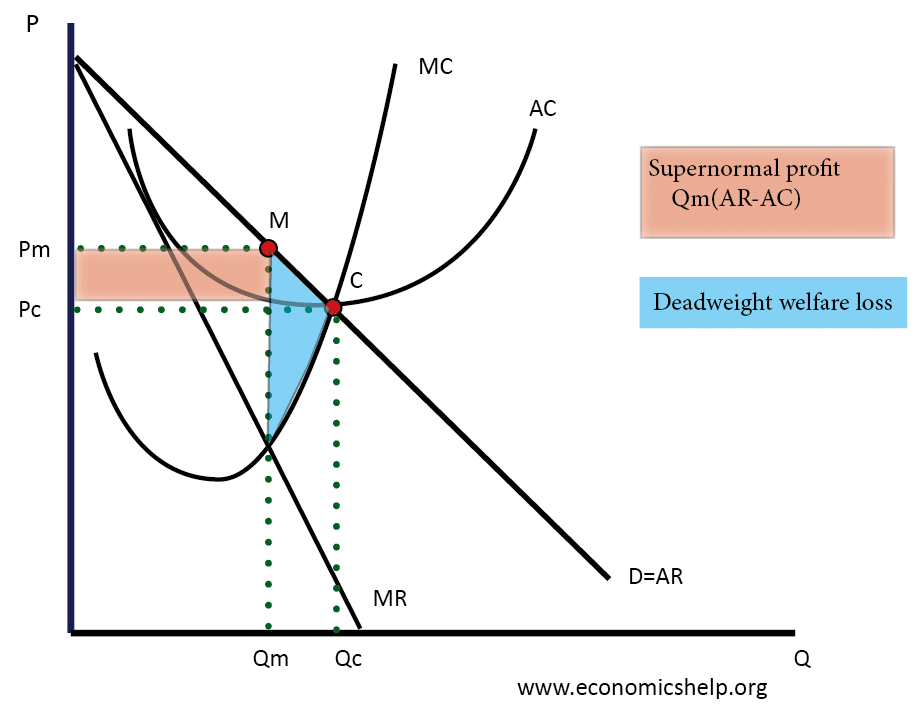
9.2 How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and ... Profits will be highest at the quantity of output where total revenue is most above total cost. Of the choices in Table 2, the highest profits happen at an output of 4. The profit-maximizing level of output is not the same as the revenue-maximizing level of output, which should make sense, because profits take costs into account and revenues do ...
Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be
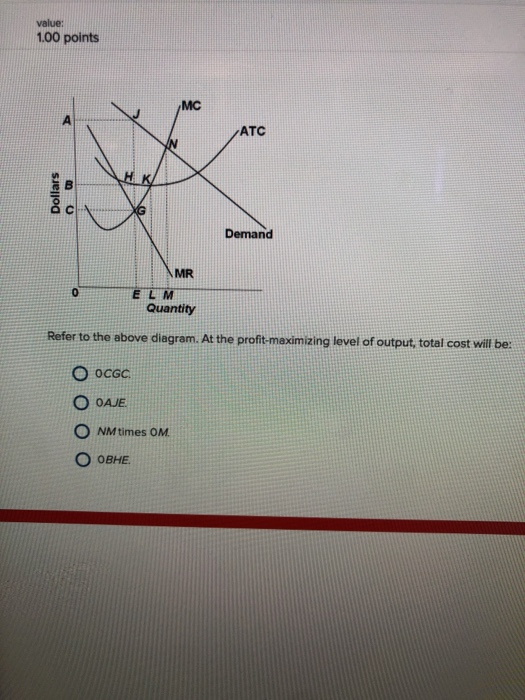
DOC Chapter 9: Four Market Models 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be: 1. NM times 0M. 2. 0AJE. 3. 0CGC. 4. 0BHE. 10. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: 1. an economic profit of ABHJ. 2. an economic profit of ACGJ. 3. a loss of GH per unit. 4. PDF MPP 801 Monopoly Kevin Wainwright 1) A) total revenue is rising, although marginal revenue is falling. B) total revenue is at a maximum. C) marginal revenue is always positive. D) total profits are at a maximum. E) total revenue is falling. 9) 10) A profit-maximizing monopolist sets price where the price elasticity of demand is A) inelastic. B) elastic. econ exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by $30; $20.50 Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist.
Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be. 7 Refer to the above diagram At the profit maximizing ... Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be: A) NM times 0 M B) 0 AJE C) 0 CGC D) 0 BHE Answer: D - 0BHE . . . . 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ B) an economic profit of ACGJ C) a loss of GH per unit. Question: Consider The Following Diagram Where A Perfectly ... Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitivefirm faces a price of $40. 1.) Refer to Figure 8.1. The profit-maximizing output is 2.) At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenueis 3.) At the profit-maximizing level of output, totalrevenue is Show transcribed image text Solved Refer to the figure. At the profit-maximizing level ... The change in total cost from producing the eightieth unit of output is seventh unit of output is and the change in total revenue from; Question: Refer to the figure. At the profit-maximizing level of output in this diagram, the firm's average cost is Price $20 18 -МС 16 14 MR 12 AC 10 8 6 4 2 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Quantity ... Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of ... For a pure monopolist, the relationship between total revenue and marginal revenue is such that; Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize; Refer to the diagram. at output level q2: Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, total variable cost is equal to:
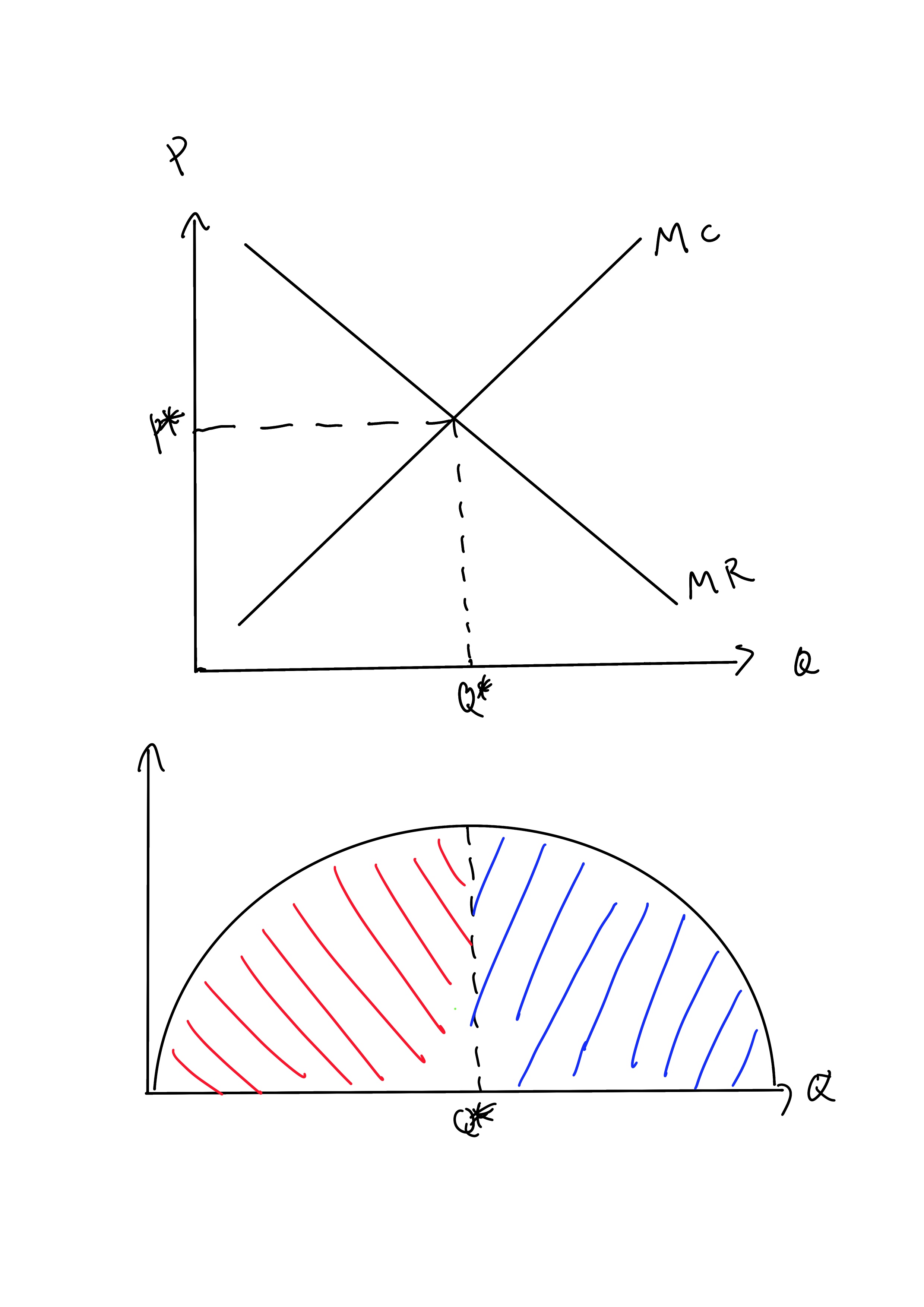
(Get Answer) - The accompanying diagram shows the demand ... The accompanying diagram shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost of a monopolist. a. Determine the profit-maximizing output and price. b. What price and output would prevail if this firm's product were sold by price-taking firms in a perfectly competitive market? c. Calculate the deadweight loss of this monopoly. pure competition questions numbered Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total variable cost is equal to: A. 0AHE. B. 0CFE. C. 0BGE. D. ABGH. 30. Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A. a loss equal to BCFG. B. a loss equal to ACFH. C. an economic profit of ACFH. D. an economic profit of ABGH. Refer to the diagram. at output level q2: Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be; Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: Refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing output, total variable cost is equal to: Refer to the diagram in which qf ... PDF AP Unit 6 37. Marginal revenue is the addition to total revenue resulting from the sale of one more unit of output. True False 38. Refer to the above diagram. This firm will maximize profits by producing output D. True False 39. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output total revenue will be 0GLD. True False 40. Refer to the above diagram.
PDF Chapter 10 Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony To find the profit-maximizing price, substitute this quantity into the demand equation: P = 27 −(1.5)(5.67)= $18.5. Total revenue is price times quantity: TR =(18.5)(5.67) =$104 .83. The profit of the firm is total revenue minus total cost, and total cost is equal to average cost times the level of output produced. Profit Maximisation Theory (With Diagram) In Figure 2, the profit maximising level of output is OQ and the profit maximisation price is OP (=QA). If more than OQ output is produced, MC will be higher than MR, and the level of profit will fall. If cost and demand conditions remain the same, the firm has no incentive to change its price and output. The firm is said to be in equilibrium. Economics Micros - Subjecto.com 8. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: A. 0AHE. B. 0BGE. C. 0CFE. D. ABGE. A. 0AHE. 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize: A. a loss equal to BCFG. B. a loss equal to ACFH. C. an economic profit of ACFH. D. an economic profit of ABGH. D. an economic ... ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: OAJE. Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be: OBHE. Refer to the diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: An economic profit of ABHJ.
ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 3. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram.
Practice Quiz Chp 8 - ProProfs Questions and Answers. 1. If managers do not choose to maximize profit, but pursue some other goal such as revenue maximization or growth, A. They are more likely to become takeover targets of profit-maximizing firms. B.
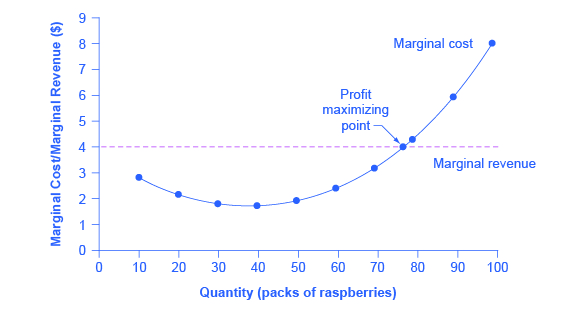
How do you calculate profit maximizing output? The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost: that is, MR = MC. If the monopoly produces a lower quantity, then MR > MC at those levels of output, and the firm can make higher profits by expanding output. Beside above, what is the maximum profit?
Answered: To maximize its profit, a monopolist… | bartleby Solution for To maximize its profit, a monopolist will a. raise output as long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. Use diagram to explain this…
Refer to the above diagram At the profit maximizing output ... 91. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total profit is: A. efbc . B. fgab C. egac D. 0 fbn . . . AACSB: Reflective Thinking Skills Bloom's: Analysis Learning Objective: 9-3 Topic: Profit maximizing in the short run 92. Refer to the above diagram.
Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics The profit-maximizing level of output is not the same as the revenue-maximizing level of output, which should make sense, because profits take costs into account and revenues do not. Total costs for a monopolist follow the same rules as for perfectly competitive firms.
Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level ... At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: A) NM times 0M B) 0AJE C) 0EGC D) 0EH. Get the detailed answer: Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: A) NM times 0M B) 0AJE C) 0EGC D) 0EH ...
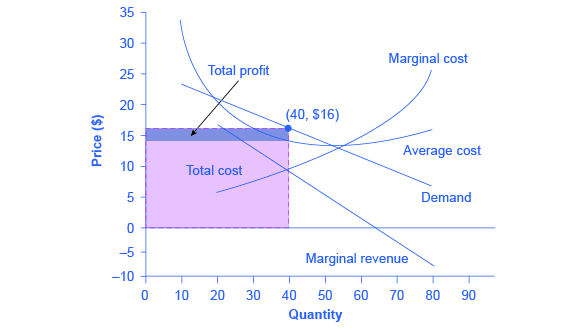
Profit Maximization under Monopolistic Competition ... The profit margin is $16.00 - $14.50 = $1.50 for each unit that the firm sells. Total profit is the profit margin times the quantity or $1.50 x 40 = $60. Alternatively, we can compute profit as total revenue minus total cost. Total revenue is price times quantity or $16.00 x 40 = $640.
DOC Chapter 7 Review Questions 8. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be: A) NM times 0M. B) 0AJE. C) 0CGC. D) 0BHE. 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ. B) an economic profit of ACGJ. C) a loss of GH per unit. D) a loss of JH per unit. 10.
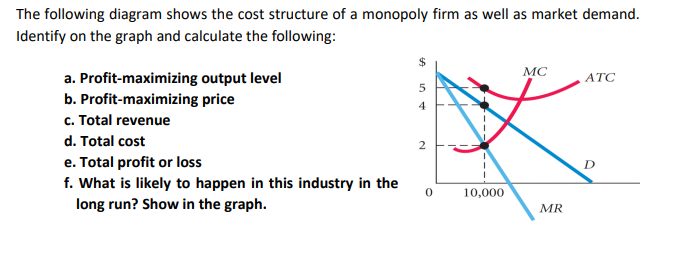
Calculating profit-maximizing output and price level Please refer attached file for diagram. The follwing diagram shows the cost structure of a mononpoly firm as well as market demand. Identify on the graph and calculate the following: a. Profit-maximizing output level b. Profit-maximizing price c. Total Revenue d. Total Cost e. Total profit or loss. State the correct formula and show calculations.
econ exam #2 Flashcards - Quizlet At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's price will exceed its marginal cost by ____ and its average total cost by $30; $20.50 Refer to the above data for a nondiscriminating monopolist.
PDF MPP 801 Monopoly Kevin Wainwright 1) A) total revenue is rising, although marginal revenue is falling. B) total revenue is at a maximum. C) marginal revenue is always positive. D) total profits are at a maximum. E) total revenue is falling. 9) 10) A profit-maximizing monopolist sets price where the price elasticity of demand is A) inelastic. B) elastic.
DOC Chapter 9: Four Market Models 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total cost will be: 1. NM times 0M. 2. 0AJE. 3. 0CGC. 4. 0BHE. 10. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: 1. an economic profit of ABHJ. 2. an economic profit of ACGJ. 3. a loss of GH per unit. 4.














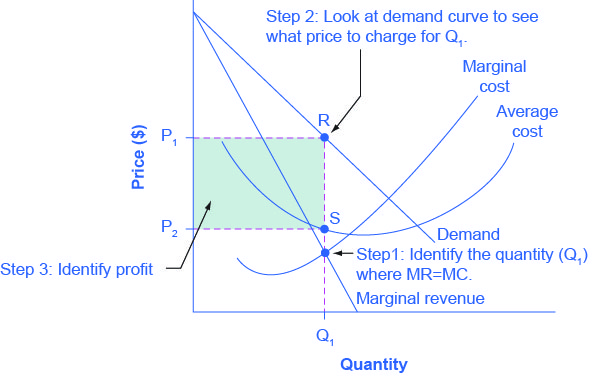

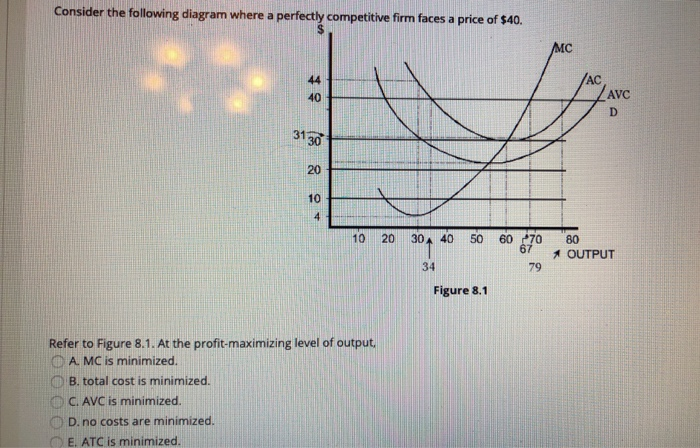

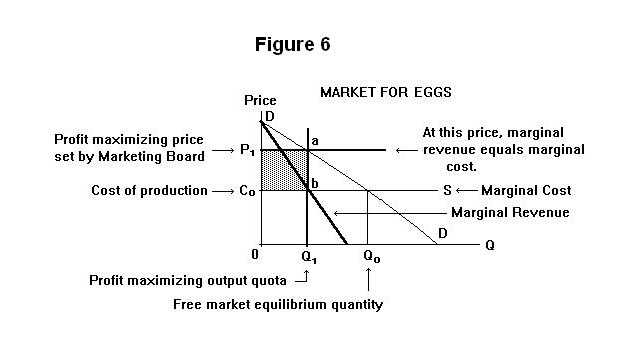

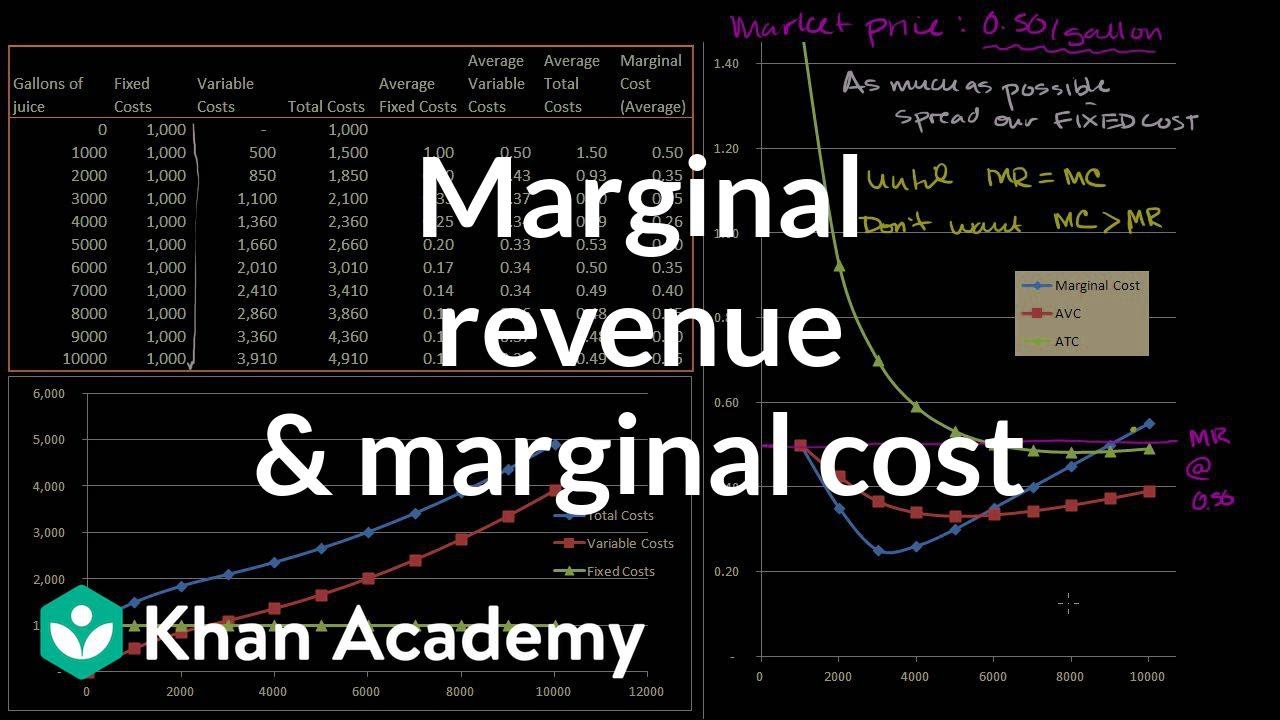

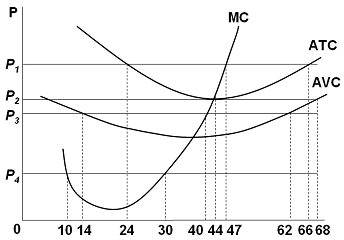
0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram. at the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be"
Post a Comment