40 crystal field energy level diagram
Crystal_Field_Splitting_Energy_Diagram_from_Octahedral_to_Square_Planar.png (620 × 182 pixels, file size: 7 KB, MIME type: image/png). English: CFSE diagram going from octahedral to square planar. In general, the energy level diagram of the ion consists of a low-lying group, with an overall spacing of probably less than typically 1 cm-1, and a large gap to the next set of levels. 4. Crystal field 4.1 Overview 4.2 Series expansion of the crystal field 4.3 Mathematica program 4.4 Summary.
Crystal field d orbital splitting diagrams for common geometries. FIGURE 2.8 . Simplified MO energy level diagram for the formation of a sigma-bonded octahedral ML 6 complex in which there are no π-bonding interactions between metal and ligand.
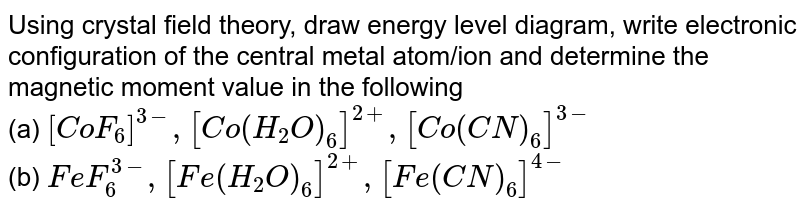
Crystal field energy level diagram
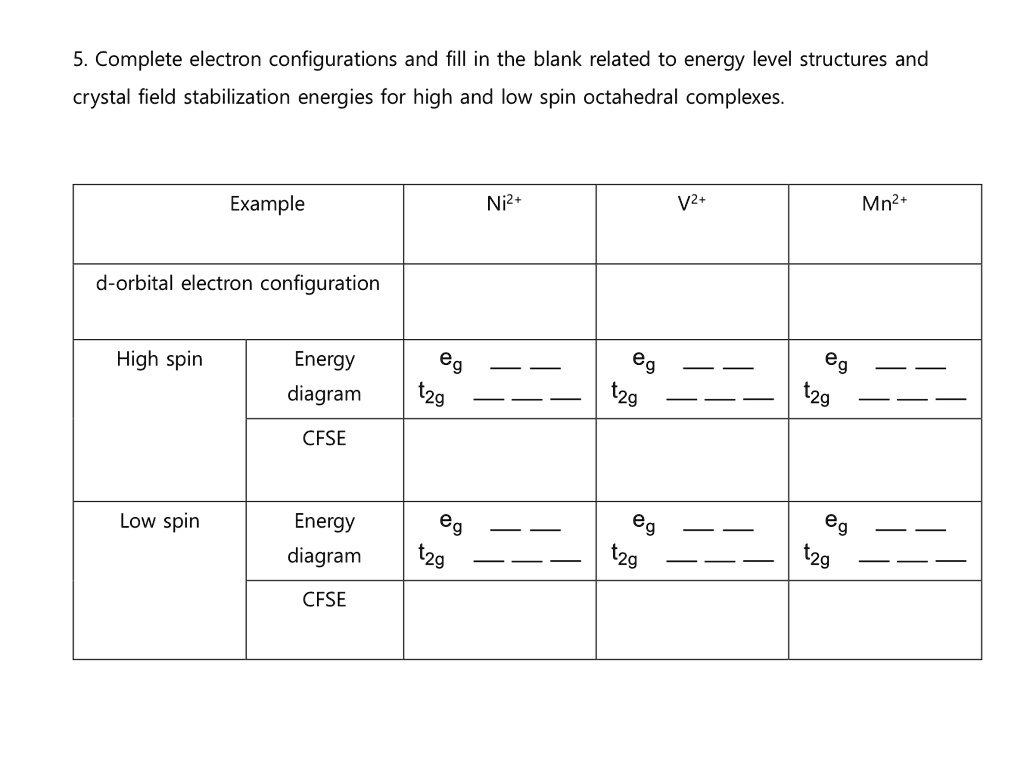
2.1 Introduction Crystal field theory describes the origins and consequences of interactions of the surroundings on the orbital energy levels of a transition metal analogous energy separation between t2g and eg orbital groups exists in the. schematic molecular orbital energy level diagram shown in fig. Crystal field splitting energy or crystal field stabilisation energy is the difference in energy between the two sets of d- orbitals (CFSE). It is denoted by the letter Δ O , which stands for the octahedral complex. The e g orbitals have an energy level of +0.6 Δ 0 or 3/5 Δ 0 above the average... To understand how crystal field theory explains the electronic structures and colors of metal We begin by considering how the energies of the d orbitals of a transition-metal ion are affected by an We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure 23.10 "An Octahedral Arrangement of Six...
Crystal field energy level diagram. This is called the crystal field stabilization energy, CFSE. For the general configuration t2g x eg y the CFSE The energy diagram shown below illustrates the behavior of a π donor ligand on Δo. Such low energy transitions require closely spaced energy levels, some of which contain electrons and... Crystal field theory (CFT) describes the breaking of orbital degeneracy in transition metal complexes due to the presence of ligands. Once the ligands' electrons interact with the electrons of the d-orbitals, the electrostatic interactions cause the energy levels of the d-orbital to fluctuate depending... Upon spin-polarization, the total energy lowers by about 0.43 eV, which is paralleled by a strengthening of the Fe—Fe bonds by roughly 5 per cent. The shifts in the majority (red) and minority (blue) spin sublattices have removed the antibonding states at the Fermi level, thereby maximizing the Fe—Fe bonding as far as possible. I am asked to draw an energy level diagram that shows the relationship between the energy quantities involved in the problem. What I did was I calculated the standard enthalpy change of the reaction first (-43.16 kJ/mol-rxn) and then drew the diagram below. Did I draw the diagram correctly? [Energy Diagram I drew](https://preview.redd.it/yl8e8l4byg081.jpg?width=1280&format=pjpg&auto=webp&s=2f24a33862f2e8c7dace0351ce643c3a2666e2ac) [The Question](https://preview.redd.it/fry8myexxg0...
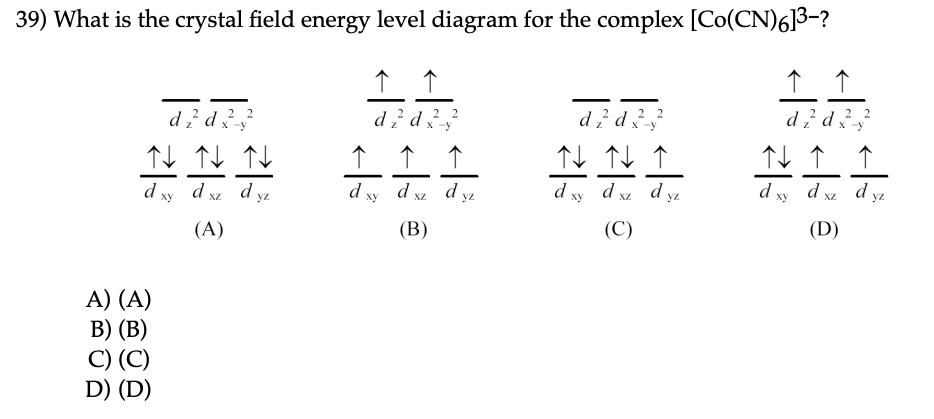
No unpaired electron so diamagnetic. Since CN- is strong field ligand all the electrons get paired. It's almost that time! FIRST has released the password protected versions of the 2022 game manual and other resources. Just a couple of reminders: * Don't try to crack the password * Don't rehost the official FIRST manual on another website to avoid confusion if FIRST releases updates. [2022 Game Manual](https://firstfrc.blob.core.windows.net/frc2022/Manual/2022FRCGameManual.pdf) [Rapid React Specific Field Drawings](https://firstfrc.blob.core.windows.net/frc2022/FieldAssets/2022FieldDrawings... Crystal field for octahedral complexes. In an octahedral complex, there are six ligands attached to the central transition metal. The two upper energy levels are named dx2−y2 ,dz2 (collectively referred to as eg ). The reason they split is because of the electrostatic interactions between the electrons of the... Energy level diagram. In order to do temperature averaging it is important to understand the number of excited states that are important. plots were one shows the eigen-state energy as a function of some parameter (crystal- -- field strength) are called energy level diagrams or Sugano - Tanabe...
The crystal field of the six O2- ions in MnO therefore splits the degeneracy of the five 3d orbitals. Three of these orbitals are now lower in energy than Octahedral transition-metal ions with d1, d2, or d3 configurations can therefore be described by the following diagrams. When we try to add a fourth... The crystal behaves as an insulator if the allowed energy bands are all either filled or empty, for then no electrons can move in an electric field. The possibility of a band gap is the most important new property that emerges. Figure 11.7 Energy level diagrams for a metal, a semiconductor, and an... Say you have an octahedral metal ion. Any textbook will tell you that the d-orbitals will split as [this image shows](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crystal_field_theory#/media/File:Octahedral_crystal-field_splitting.png). Every textbook I've read stops short of saying how this is calculated. Usually the explanation is "just look at it, lol" In simple geometries such as tetrahedral or octahedral, this method works fine. However in more complex geometries "just look at it" becomes a very unhelpful... 3 _ ... _ Octahedral crystal field d orbital energy levels metal ion in octahedral complex Octahedral crystal field d orbital energy levels dz2 dx2- y2 _ ... _ E dxy dxz dyz isolated metal ion _ _ _ _ _ Metal ion and the nature of the ligand determines d-orbitals.
The energy band gap, E g, is located between the two bands. The distance between the conduction band edge, E c, and the energy of a free electron outside the crystal (called the vacuum level labeled E vacuum) is quantified by the electron affinity, c multiplied with the electronic charge q.
Crystal field. Different ligands have different ability to split the d levels - depends mainly on the degree of covalent interaction. Correlation diagrams (d orbitals, octahedra, weak crystal field). Crystal field. 56. Correlation diagram d2 - octahedral symmetry.
Dec 03, 2018 · With their well-defined surface structures, optical and electric field properties, and the ability to be modelled at the atomic level, single …
I only know how to fill the right side? I should pair the arrows up to dxy since it's 3d8 but how do I fill the one the left? https://i.redd.it/j0e2ey02mdp61.gif
Zero-point energy (ZPE) is the lowest possible energy that a quantum mechanical system may have. Unlike in classical mechanics, quantum systems constantly fluctuate in their lowest energy state as described by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Therefore, even at absolute zero, atoms and molecules retain some vibrational motion.Apart from atoms and molecules, the …
The energy level diagram of Cr3+ ions calculated using the crystal-field theory is in good agreement with experimental data. Room-temperature stationary induced absorption spectra of crystals exhibit strong absorption in the 400-700-nm region, which was assigned to transitions from the excited...
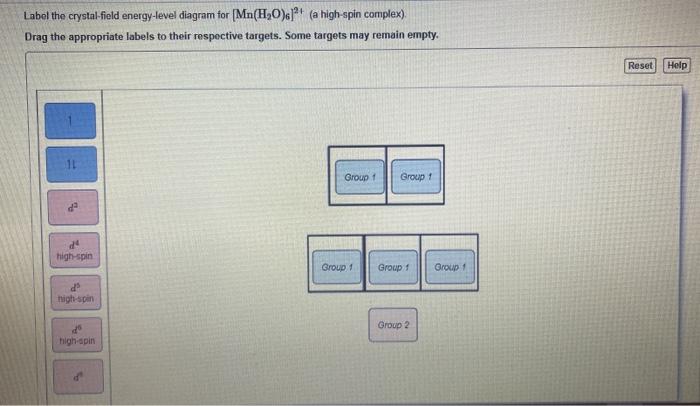
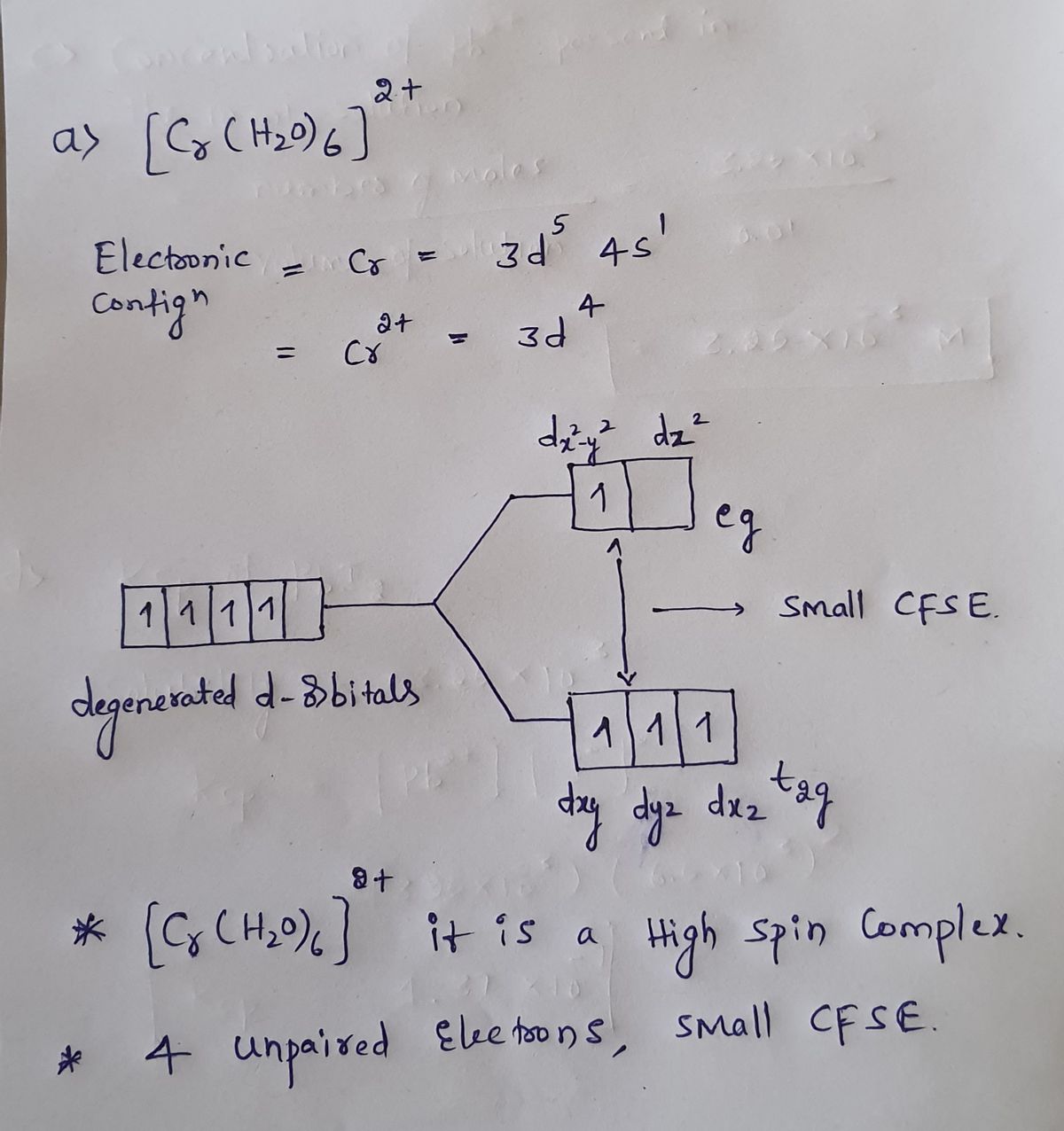
Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagrams and showthe placement of d electrons for each of the following:(a) [Cr(H2O)6]2+ (four unpaired electrons), (b) [Mn(H2O)6]2+(a high-spin complex), (c) [Ru(NH3)5(H2O)]2+ (a low-spincomplex), (d) [IrCl6]2
Coordination compounds (or complexes) are molecules and extended solids that contain bonds between a transition metal ion and one or more ligands. In forming these coordinate covalent bonds, the metal ions act as Lewis acids and the ligands act as Lewis bases.
• Focus: Crystal Field Theory energies of the d orbitals • Assumptions • 1. Ligands: negative point charges • 2. Metal-ligand bonding: entirely ionic • strong-field (low-spin): large splitting of d orbitals • weak-field (high-spin): small splitting of d orbitals d-orbital energy level diagram for tetrahedral dxy...
Figure 2.3: Crystal field splitting diagram for a transition metal in a tetrahedral geometry. The square planar crystal field. hole theory According to hole theory , a d2 system will behave as a d8 system, but with the energy levels inverted. For instance, a d2 system with octahedral symmetry will be like a...
Crystal Field Theory. Focus: energies of the d orbitals Assumptions 1. Ligands: negative point charges 2. Metal-ligand bonding: entirely ionic strong-field (low-spin): large splitting of d orbitals weak-field (high-spin): small splitting of d orbitals. d xy. d xz. d yz. Slideshow 6910513 by...
Crystal field theory splitting diagram: Example of influence of ligand electronic properties on d orbital splitting. This shows the comparison of low-spin versus high-spin electrons. In order for this to make sense, there must be some sort of energy benefit to having paired spins for our cyanide complex.
Table 2. Energy-level diagram for C -3+ in an octahedral crystal field (L—S coupling not included) for the special choices and 30 (lowest doublet-levels only observed... 2. The simplified energy level diagram for Oj, 02, and 02 in their ground state. When a crystal field is present, the n, and nu levels...
The ligands repells them and the 3d are closer to the nucleus so shouldn't they be repelled into the nucleus and so reducing it's energy level rather than increasing it?
Crystal field theory (CFT) describes the breaking of degeneracies of electron orbital states, usually d or f orbitals, due to a static electric field produced by a surrounding charge distribution (anion neighbors).
It seems that I can't wrap my head around the concept of the k-vector and crystal momentum. From my waves course I remember that the wave vector sorta represents where the wave propagates (in an isotropic and homogeneous material). So in solid state that could be thought as the same thing applied to the wave function, right? And here comes the troubles: why and how is it related to the momentum of a particle? I think I get the math behind it but not the concept. Furthermore, given th...
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound—that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy, called energy levels.This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any amount of energy. The term is commonly used for the energy levels of the electrons in atoms, ions, or molecules, which are bound by the electric field of the nucleus, but …
Maybe a good play with rising Ukraine Gas prices: KUB (CAD) / TPNEF (USD) looks even better with Ukraine Gas prices rising to 18,000 MCM (valuta is UAH). 18,000 MCM in September (Cubic Meters, Before VAT/Taxes) according to the table on the website and last quarter was an average of $6.50 MCF (Cubic Feet, After VAT/Taxes) in the MD&A Q2. This was with an average 9,400 MCM (April - June) on the website. Meaning Gas prices will be up with 66% in Q3 (upcoming numbers) compared to Q2. KUB uses...
Step 2: Find the appropriate crystal field splitting diagram for this geometry. Step 3: Figure out how many $d$ electrons there are. $\Delta$ is the energy different between the $e_g$ and $t_{2g}$ sets of orbitals. This Wikipedia page walks through an octahedral complex.
The magnitude of these energy separations, or crystal field splittings, depend on the valence of the transition metal ion and the symmetry, type and distances of ligands surrounding the cation. The statement was made in 2.8 that separations between the 3d orbital energy levels may be evaluated...
The energy level diagram including four lowest multiplets of Er3+ ion (4I15/2, 4I13/2, 4I11/2 and 4I9/2) in the hexagonal GaN can be easily established according to the previously measured data of Makarova and Glukhanyuk et al.
this question gives us six different complexes and asks us to draw the crystal field energy level diagrams and to show the placement of the D electrons. So this first complex I this two plus, we're all complex shows us that this CR has is a two plus because this cold water molecules, uh, don't have...
The energy level diagram and the wave functions for the Ti3+ ions (3d1) in LaTiO3 are calculated using modern crystal-field theory. The relative orbital ordering of these ions in the ground state is obtained. It turns out that the states of the ground triplet are considerably split and therefore the effect...
To understand how crystal field theory explains the electronic structures and colors of metal We begin by considering how the energies of the d orbitals of a transition-metal ion are affected by an We can use the d-orbital energy-level diagram in Figure 23.10 "An Octahedral Arrangement of Six...
Crystal field splitting energy or crystal field stabilisation energy is the difference in energy between the two sets of d- orbitals (CFSE). It is denoted by the letter Δ O , which stands for the octahedral complex. The e g orbitals have an energy level of +0.6 Δ 0 or 3/5 Δ 0 above the average...
2.1 Introduction Crystal field theory describes the origins and consequences of interactions of the surroundings on the orbital energy levels of a transition metal analogous energy separation between t2g and eg orbital groups exists in the. schematic molecular orbital energy level diagram shown in fig.







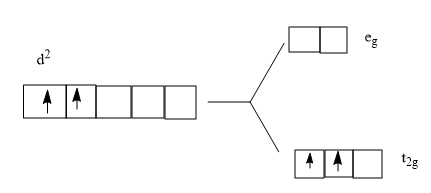

![Consider the complex ion [Co(H2O)6]3+. Dra... | Clutch Prep](https://lightcat-files.s3.amazonaws.com/clutch_answers_images/1566182342248.jpg)





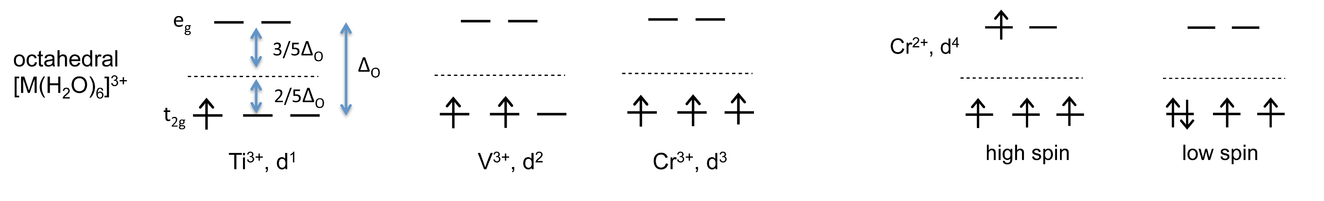













0 Response to "40 crystal field energy level diagram"
Post a Comment