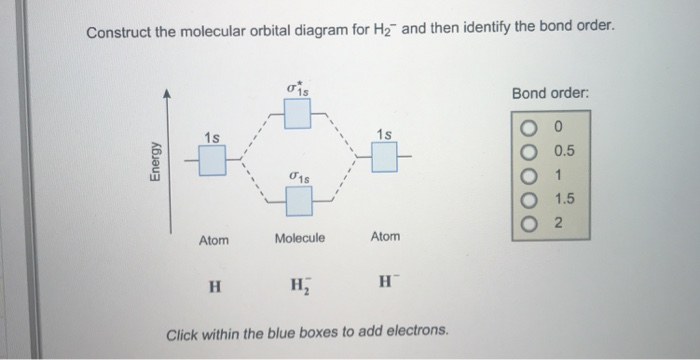
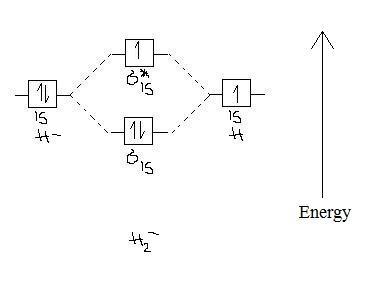
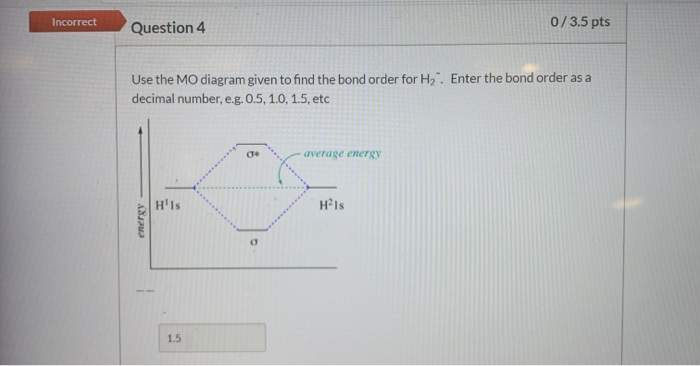
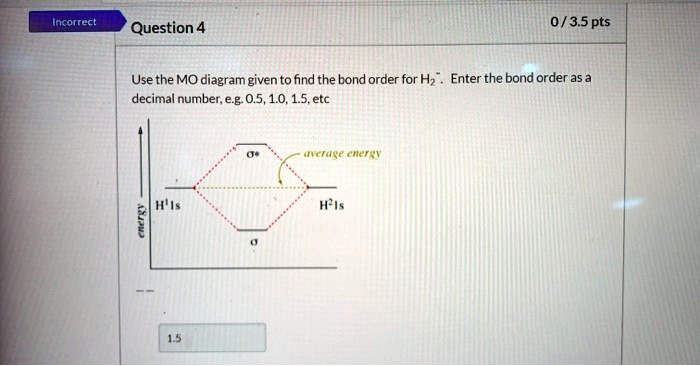
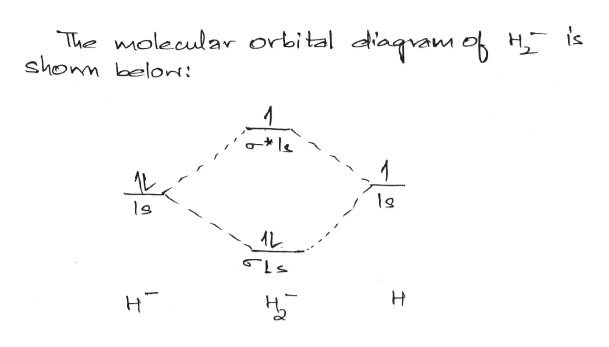
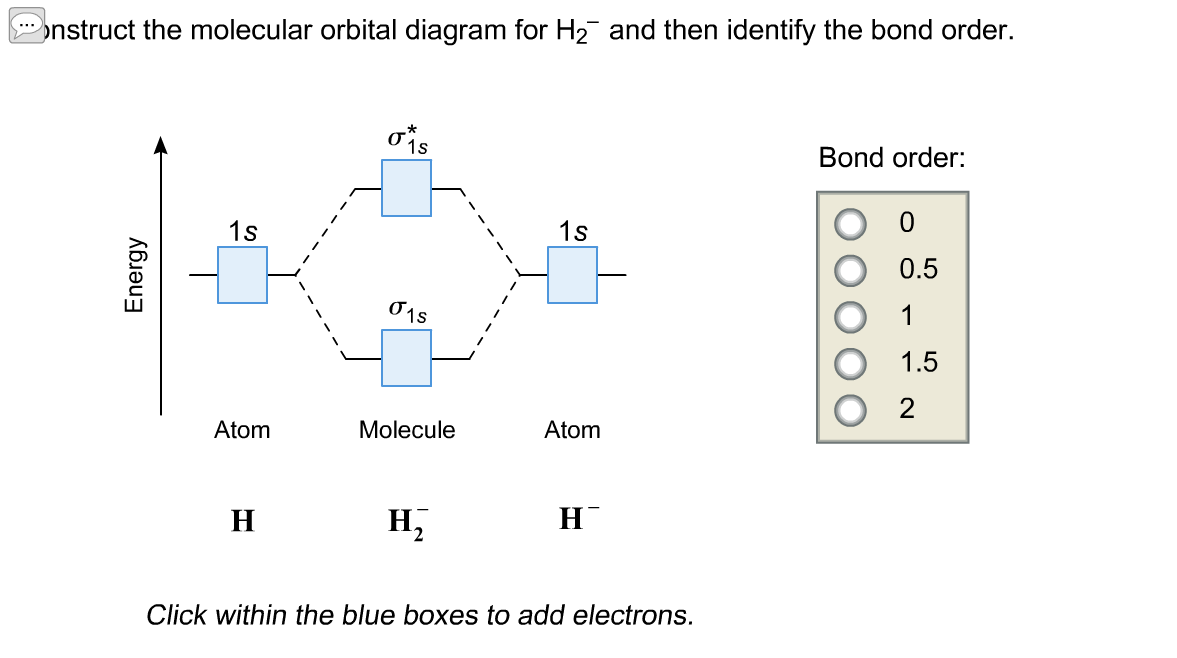
42 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-.
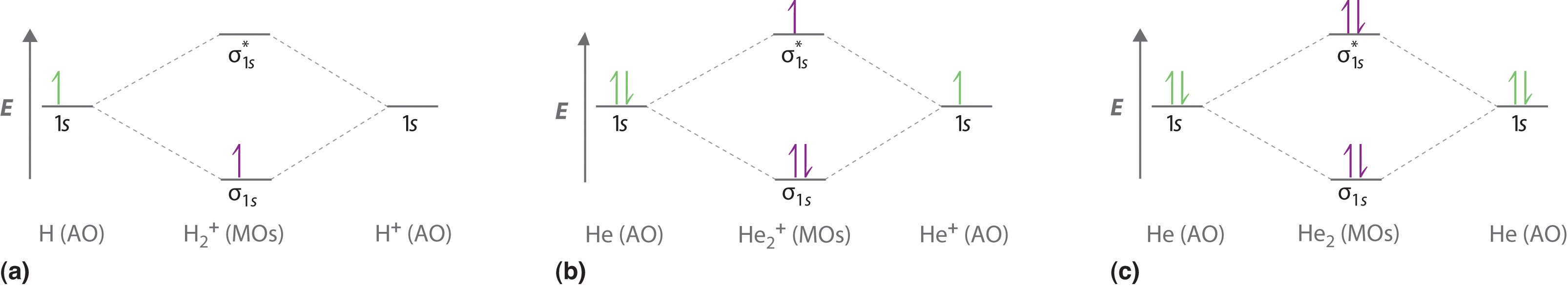
Let's draw the Molecular orbital diagram of Helium gas (He 2 ) and find out the bond order. Number of Bonding electron = 2 Number of antibonding electrons = 2 Bond order = (Nb - Na) / 2 = (2- 2)/ 2 = 0 From the above Molecular orbital diagram of Helium gas, it can be concluded, there are two bonding and anti-bonding electrons in Helium gas.
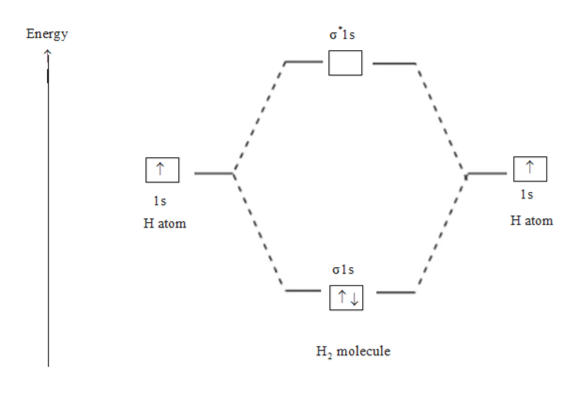
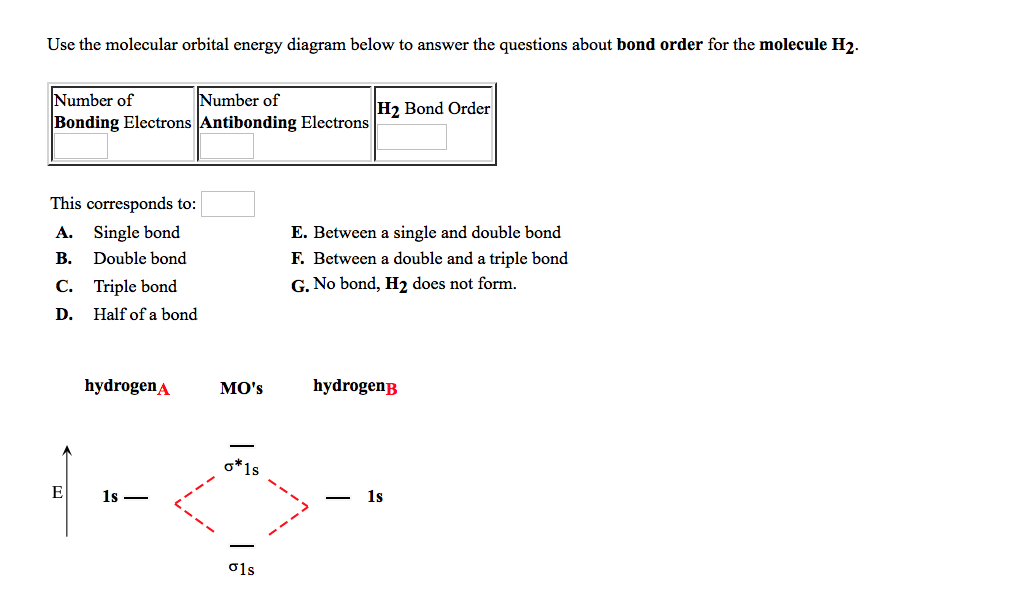
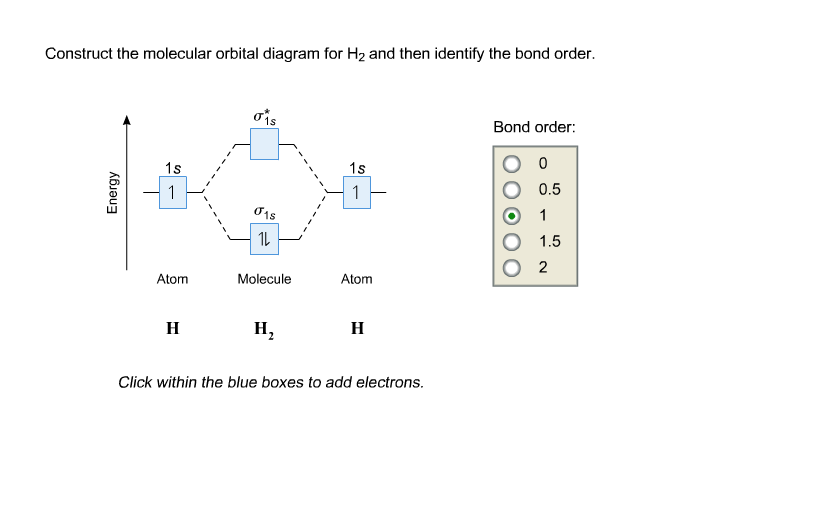
Bond order Bond order = 1/2 (#e- in bonding MO - #e- in antibonding MO) For H 2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H 2 has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H 2 is a stable molecule. Again, in the MO, there is no unpaired electron, so H 2 is diamagnetic. References Chang, Raymond. Physical Chemistry for the Biosciences.
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − Antibonding)

Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-.
the molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the h 2 molecule is shown in figure on either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms a and b, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.the …
Bond Order. The bond order for a molecule can be determined as follows: bond order = ½ (bonding electrons − antibonding electrons). Therefore, the H 2 molecule has a bond order of ½ (2 − 0) = 1. In other words, there is a single bond connecting the two H atoms in the H 2 molecule. In the case of He 2, on the other hand, the bond order is ...
- The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict the stability of a species. - The MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electron in each MO. Molecular orbitals that lie along the internuclear axis are called _____ MOs because they are cylindrically symmetrical.
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-..
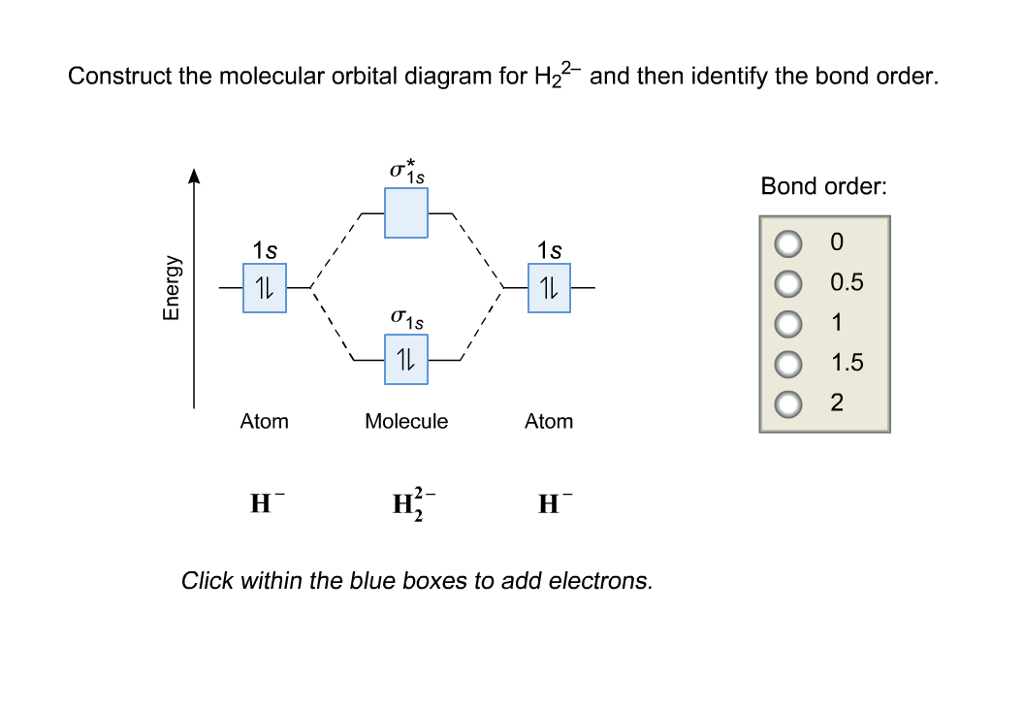
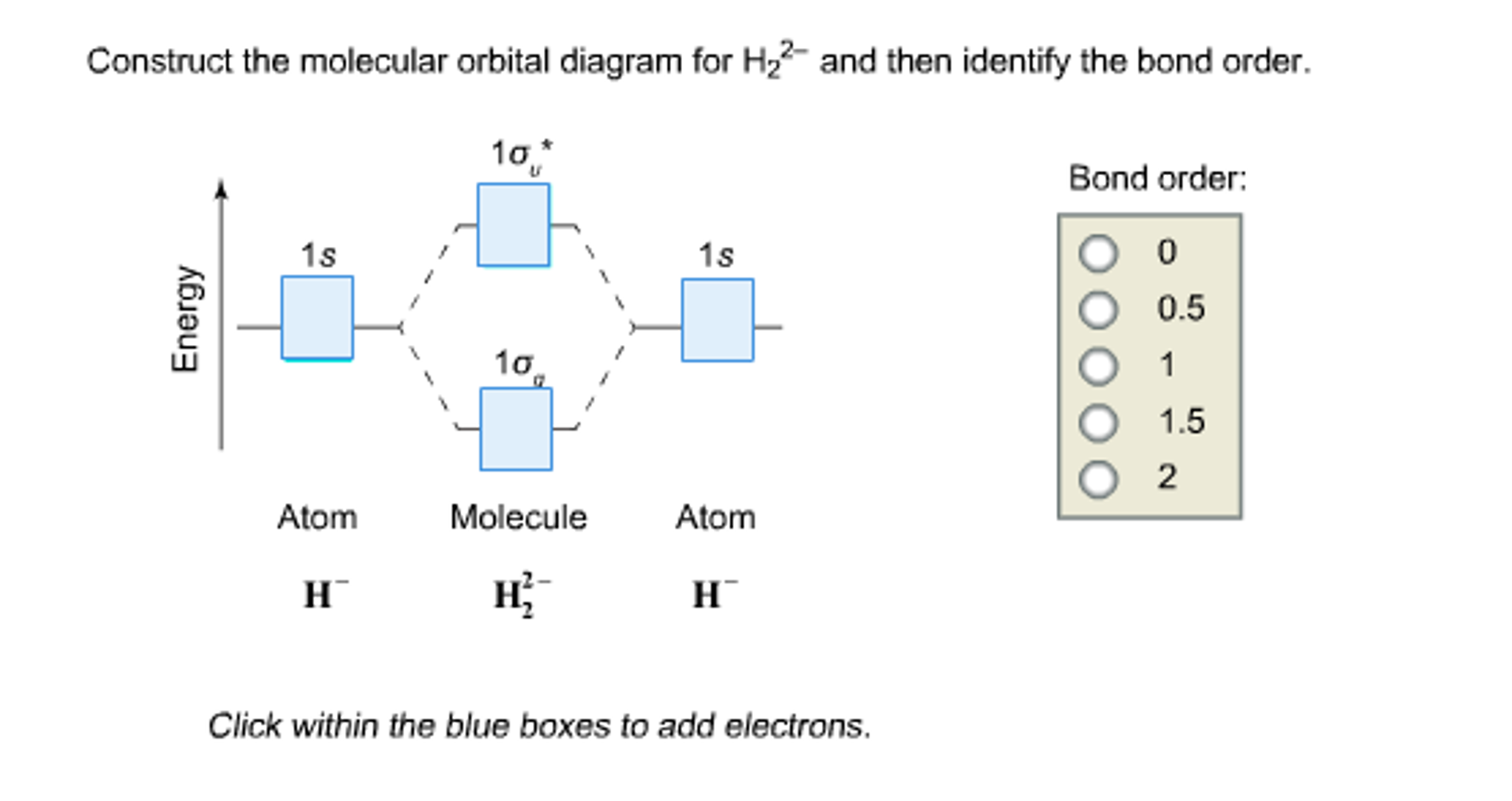
2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b - Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero.
Bond order is the number of possible bonds between two atoms. As the bond order of diatomic nitrogen is 3 i.e. two nitrogen atoms are connected with a triple bond (N≡N). The bond order signifies the strength of the bonding between atoms. The bond is stronger when the bond order is high and vice versa. The bond order also tells about the ...
Bond order=1/2 (bonding−anti-bonding) According to molecular orbital diagram, the bond order of CO+ is 3.5. The highest occupied molecular orbital is sigma*2s MO. In the case oc CO, the 2s atomic orbital on oxygen is much lower than the energy than the 2s atomic orbital of carbon. This discrepancy of energy allows the pi2px & pi2py BMO to ...
Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram. To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is:
Problem Details. Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H 2− exists. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO Theory: Bond Order Practice Problems. Q. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+, CN, and CN-. According to the Lewis model, which species is ...
Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. Molecular orbitals: Molecular orbitals are gotten by joining the nuclear orbitals on the particles in the atom.
The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Two are placed in the bonding orbital, the other two in antibonding orbital. The bond order = 1/2 x (Number of Bonding Electrons - Number of Antibonding Electrons) = .
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Bond order of B2 molecule. So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
_ Select] Without 28 -2p mixing With 2s - 2p mixing op 2p 2P Energy 17 625 Without 2s - 2p mixing With 2s - 2p mixing X 20 TE 20 Energy 2 n 2s 028 AO AO MO AO A MO energy levels for O2, F2, and Nez АО MO B MO energy levels for B2, C2, and N2 Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: • What is the bond order for F2 ...
What is the bond order of H2? Formula for bond order is: BO = 1/2 {no. of electron in bonding orbital - no. of electron in antibonding orbital} Since H2 has 2 electron {1 from both H} and both electron will be in 1s2 (bonding orbital) So, BO = 1/2 {2-0} =1 4.5K views View upvotes Related Answer Abhishek Singh , Carbon
The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. For instance, the bond order of diatomic nitrogen N≡N is 3 and bond order between the carbon atoms in H-H≡C-H is also three. The bond order describes the stability of the bond. The molecular orbital provides an easy understanding of the concept of the bond ...
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric.
A further example is given using the NH3 MO diagram. Here, they calculate the bond order as 3, ignoring the fact that the NH3 a1 orbital is weakly bonding. If we were to in theory calculate the MO diagram for NH3 in a trigonal planar geometry (same as for BH3), we would also get the bond order as 3.
In the article Bond order formula, you have grasped the formulas to find the bond order based on Molecular Orbital Theory and Lewis structure. You can explain the information conveyed by the bond order, such as stability, number of bonds, etc.
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of $ {N_2}$ or $ {O_2}$ with magnetic behavior and bond order. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond ...
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
The bond order in sulfur dioxide, for example, is 1.5 the average of an S-O single bond in one Lewis structure and an S=O double bond in the other. In molecular orbital theory, we calculate bond orders by assuming that two electrons in a bonding molecular orbital contribute one net bond and that two electrons in an antibonding molecular orbital ...
need to use a computer. But because the matrices are so simple, we can usually find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors very quickly. 4) Occupy the orbitals according to a stick diagram. At this stage, we note that from our N pz orbitals we will obtain N π orbitals. Further, each carbon atom has one free valence electron to contribute, for a
Answer (1 of 4): Hi guys let me tell u one short trick for finding bond order… First of all for the given molecule add up the total no of electrons present in that molecule.. For example here in N2 we have 7+7 =14 electrons. Now remember this table.. ELECTRONS = BOND ORDER 10 = 1 11 = 1.5 ...
We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H 2+. With a bond order of only 1/2 the bond in H 2+ should be weaker than in the H 2 molecule, and the H-H bond should be longer.
The bond order tells us the average number of bonds between the bonded atoms. In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]`
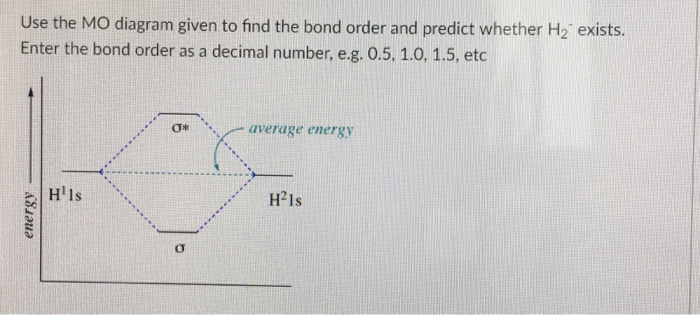
Chemistry questions and answers. Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists. Enter the bond order as a decimal number, eg. 0.5. 1.0, 1.5, etc ?* ???Y-average energy H2ls. Question: Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists.





















0 Response to "42 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order for h2-."
Post a Comment