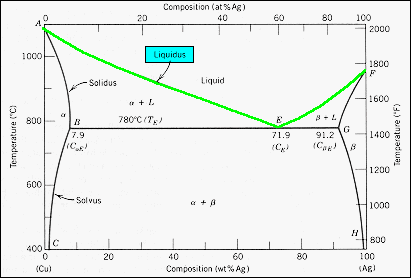
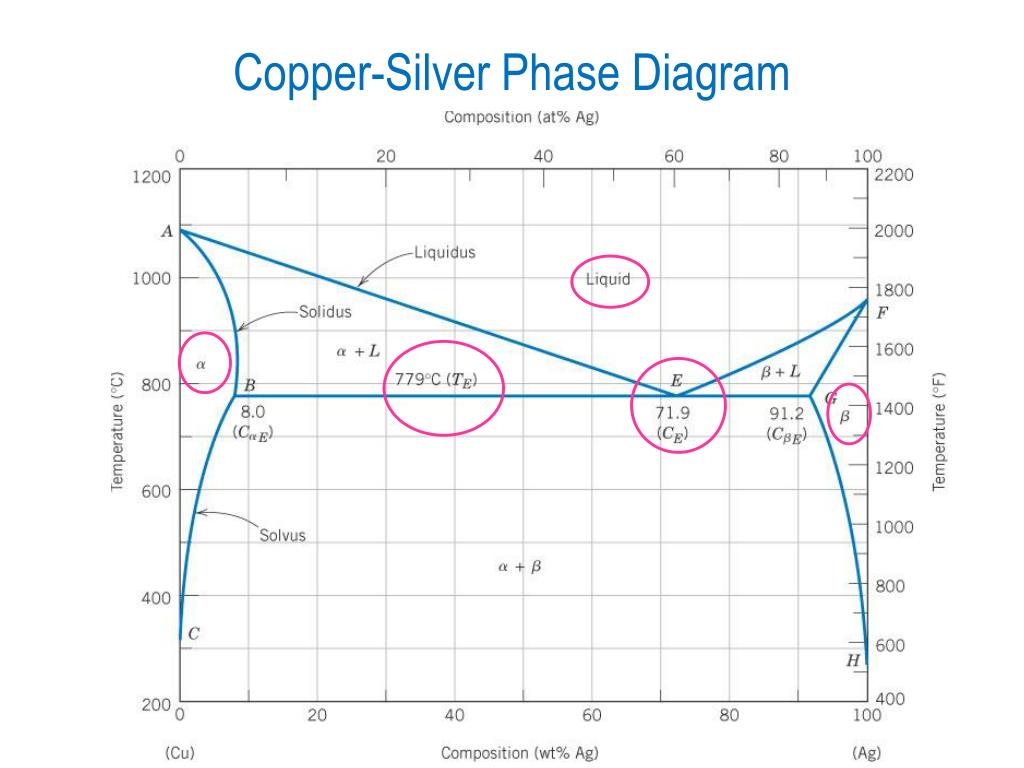
41 silver copper phase diagram
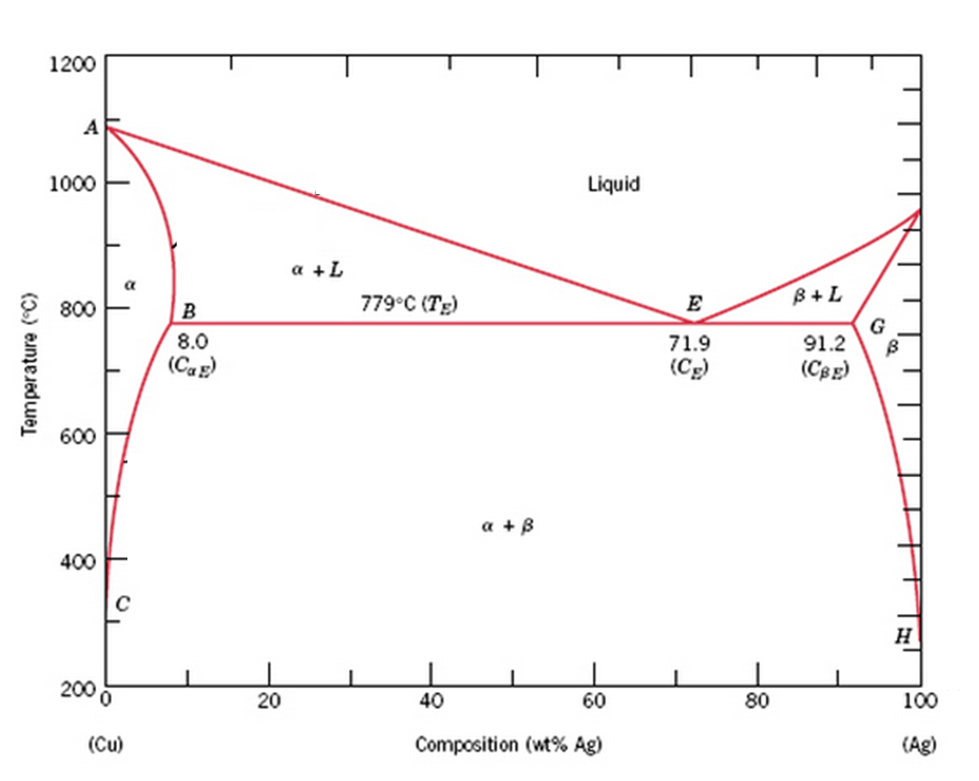
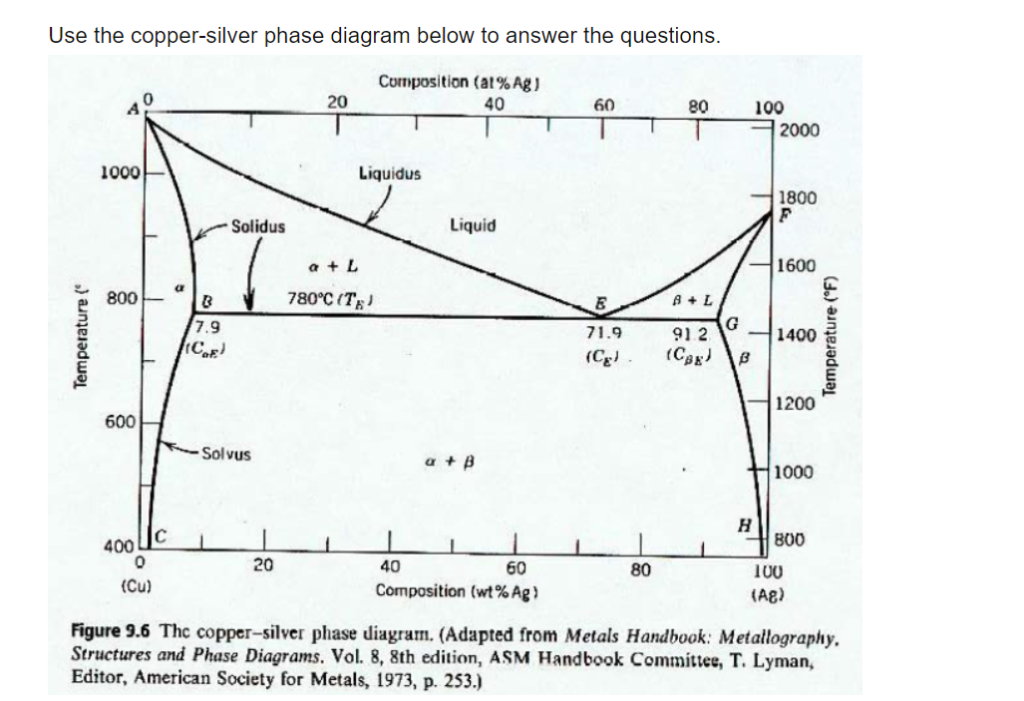
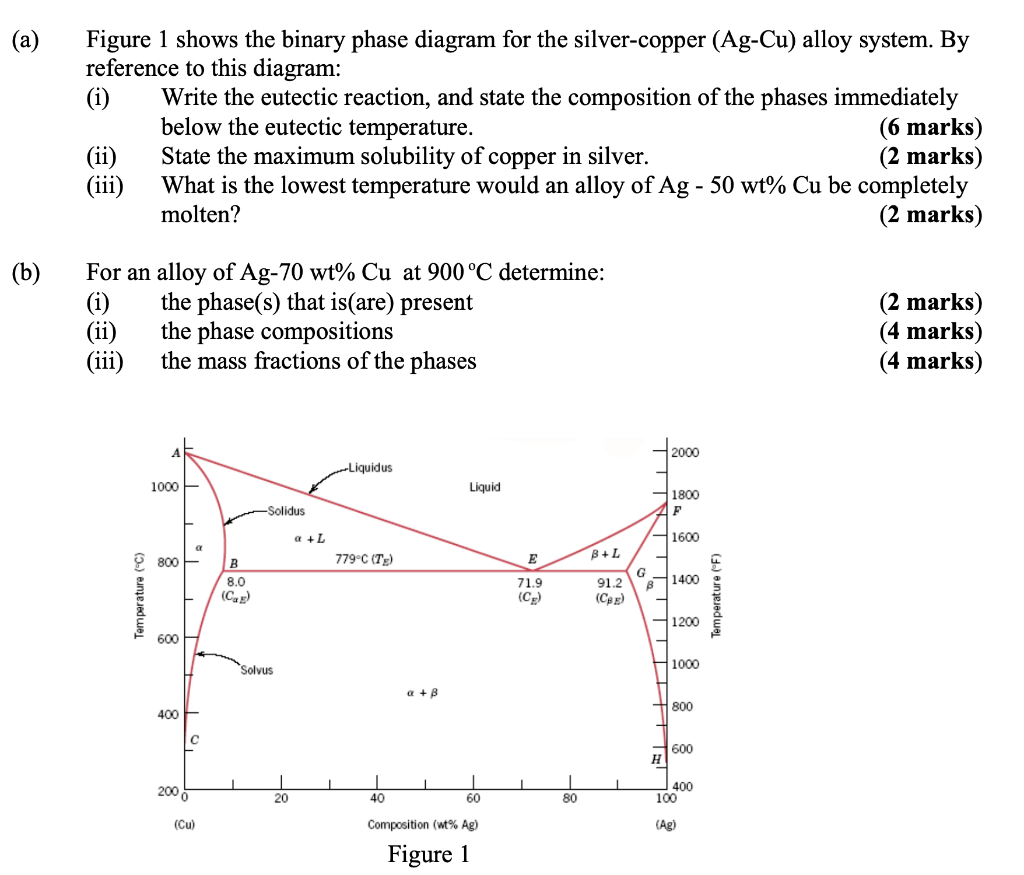
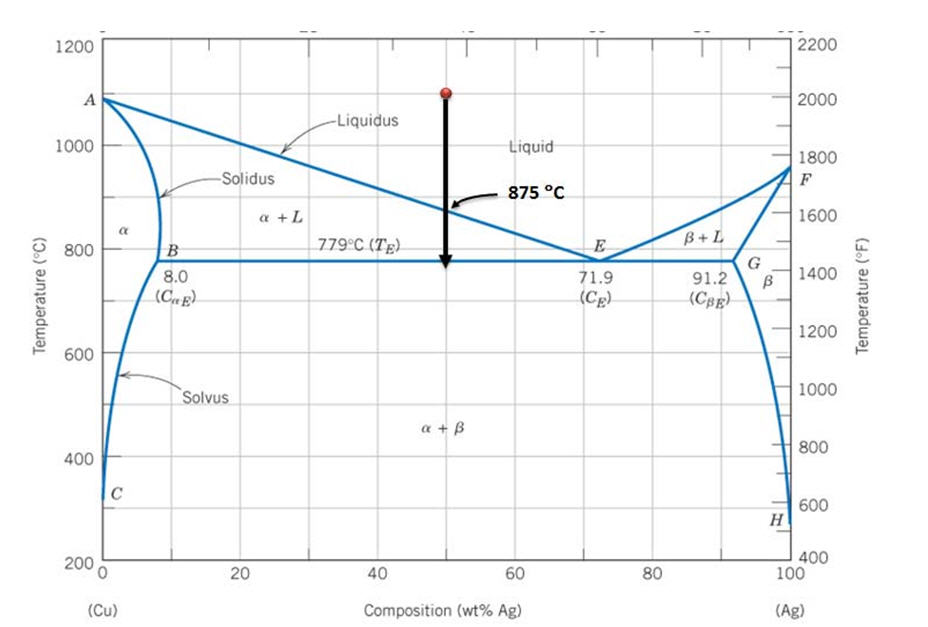
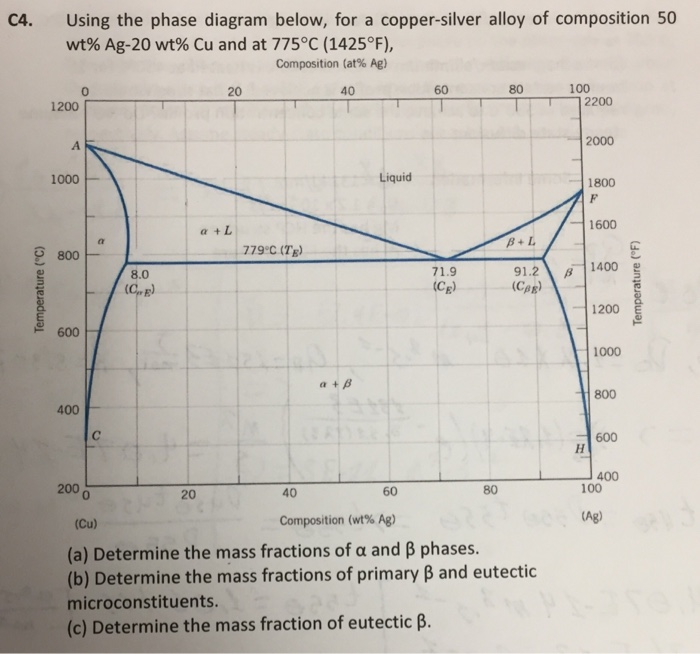
For a copper-silver alloy of composition 25 wt% Ag-75 wt% Cu and at 775°C (1425°F) do the following: (a) Determine the weight fractions of a and 3 phases. Phase diagram of Cu-Ag ( for both question) 20 40 60 80 100 2200 1200 А 2000 Liquidus 1000 1 Liquid 1800 F Solidus a 1600 800 BEL 779°C (7) B 8.0 G в 1400 Temperature (9 (CE) 71.9 (CE ... For instance, melting point of alloys of copper and silver is lower than melting point of either copper or silver. ... Figure 1 gives a general schematic of phase diagram of a single component system (Lue, 2009). The curves shown in the figure represent the coexistence of two phases. Melting curve is the curve in the phase diagram along which ...
Copper Silver Phase Diagram Phase Diagram Study For The Pbo Zno Cao Sio2 Fe2o3 System In Air. Copper Silver Phase Diagram Rewriting The Phase Diagram Of A Diamagnetic Liquid Crystal A. Copper Silver Phase Diagram Using The Phase Diagram For Silver Copper Ag Cu Chegg. Copper Silver Phase Diagram Solved Problem 2 05 Pt Max The Copper Silver Cu Ag ...
Silver copper phase diagram
Use the following silver-copper phase diagram for Problems 5-9. 5. What are the solubility limits of Ag in (Cu) and Cu in (Ag)? Recall that (Cu) and (Ag) are the same as α and β, respectively. The solubility limit of Ag in (Cu) is 7.9 wt. % Ag. The solubility limit of Cu in (Ag) is 8.8 wt.% Cu. Note that these Same is true for copper addition to silver. ii. Point E on the phase diagram it is called invariant point at this point an important reaction takes place at constant temperature Called Eutectic reaction where liquid (L) is directly converted to (α) and β phase. iii. Line CEG is called eutectic isotherm. Some gold-copper–aluminium alloys form a fine surface texture at heat treatment, yielding an interesting spangling effect. At cooling, they undergo a quasi-martensitic transformation from body-centered cubic to body-centered tetragonal phase; the transformation does not depend on the cooling rate. A polished object is heated in hot oil to 150–200 °C for 10 minutes then cooled below 20 °C ...
Silver copper phase diagram. Phase Diagrams • Indicate phases as function of T, Co, and P. • For this course:-binary systems: just 2 components.-independent variables: T and Co (P = 1 atm is almost always used). • Phase Diagram for Cu-Ni system Adapted from Fig. 9.3(a), Callister 7e. (Fig. 9.3(a) is adapted from Phase Diagrams of Binary Nickel Alloys , P. Nash The binary phase diagram shown for the copper-nickel alloy indicates that these materials can form both liquid and solid solutions over the full range of composition from Cu to Ni. Above 1728 K, the melting point of pure Ni the alloys ar in the liquid phase. Between 1728 K and 1357 K (the melting point of Cu) the alloys can be either solid or ... PHASE DIAGRAM OF COPPER SILVER SYSTEM | Dr. Kiran Rohit |SISTec Gandhinagar A region of the copper-zinc phase diagram that has been enlarged to show eutectoid and peritectic invariant points , C, 74 wt% Zn) and P (598 C, 78.6 wt% Zn), respectively. Figure by MIT OCW. Note that each single-phase field is separated from other single-phase fields by a two-phase field. Lecture 19 – Binary phase diagrams 6 of 16 11/23/05
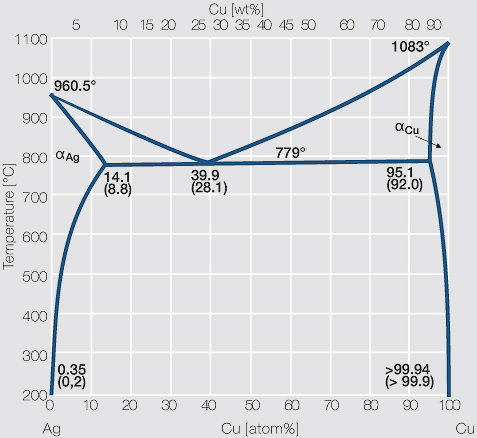
Engineering; Chemical Engineering; Chemical Engineering questions and answers; A phase diagram for Copper (Cu) - Silver (Ag) alloys is shown below: Composition (at% Ag) 20 40 60 80 100 1200 2200 А 2000 -Liquidus 1000 Liquid 1800 F -Solidus a +L 1600 ar 800 B+L 779°C (Tg) B 8.0 E 71.9 (Ce) G B 1400 Temperature (°C) 91.2 (Cag) (CB) Temperature (°F) 1200 600 Solvus 1000 800 400 с 600 H 2006 ... Download scientific diagram | Cu-Ag Phase Diagram. The eutectic composition is 28.1 wt% Cu-71.9 wt% Ag and the solid solubility limit of silver in copper is 8 wt% Ag (after Hansen and Anderko 1958 ... Download scientific diagram | Silver–copper phase diagram. from publication: Direct method for determining the segregation in silver-copper solid solutions not prone to brittle breakage of grain ... 9.32 For a copper-silver alloy of composition 25 wt% Ag-75 wt% Cu and at 775 °C (1425 °F) do the following: ... The illustration below is the Cu-Zn phase diagram (Figure 9.19). A vertical line at a composition of 68 wt% Zn-32 wt% Cu has been drawn, and, in addition, horizontal arrows at the four temperatures called for in the ...
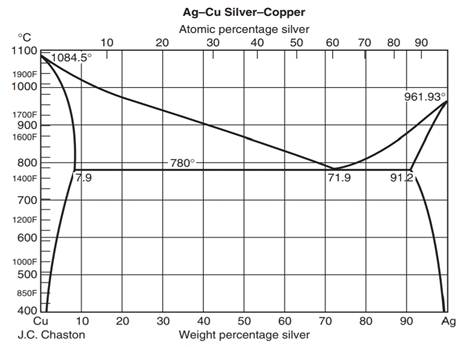
On the phase diagram, the value of either \(T\) or \(p\) has been fixed, so there are two other independent intensive variables. For example, on a temperature–composition phase diagram, the pressure is fixed and the temperature and composition can be changed independently within the boundaries of the one-phase area of the diagram. Transcribed image text: Use the copper-silver phase diagram below to answer the questions. Composition (at %Ag ) 0 20 40 60 80 100 2000 Liquidus 1800 Liquid Solidus 1600 800 780°C (T 7.9 91 2 71.9 1400 1200 600 Solvus 1000 800 100 AB) 400 20 40 (Cu) Composition (wt% Ag) Figure 9.6 Thc copper-silver phase diagram. Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from Latin: cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity.A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color.Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling ... Feb 24, 2012 · Copper Conductor is the most common material used for electrical wiring. Gold Conductor is used for high-quality surface-to-surface contacts. Silver is the best conductor on the Conductors list. Impure Water is listed in the Conductor List but it has less conductivity. What is the Charge of a Conductor During Carrying Electricity?
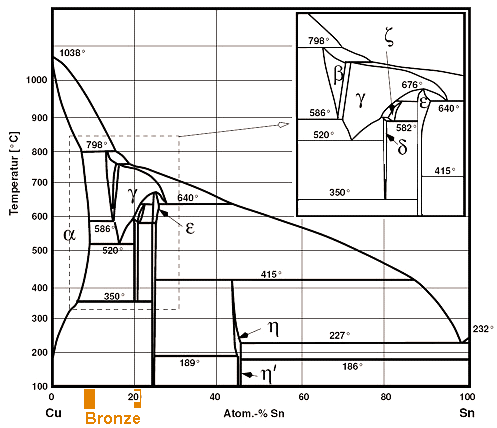
This representation is called a phase diagram. The phase diagrams of some binary systems relevant to bronze show the behavior of alloying elements that typically results in one of the three cases mentioned previously. The copper-tin equilibrium phase diagram (Figure 3) illustrates Cases (1) and (2).
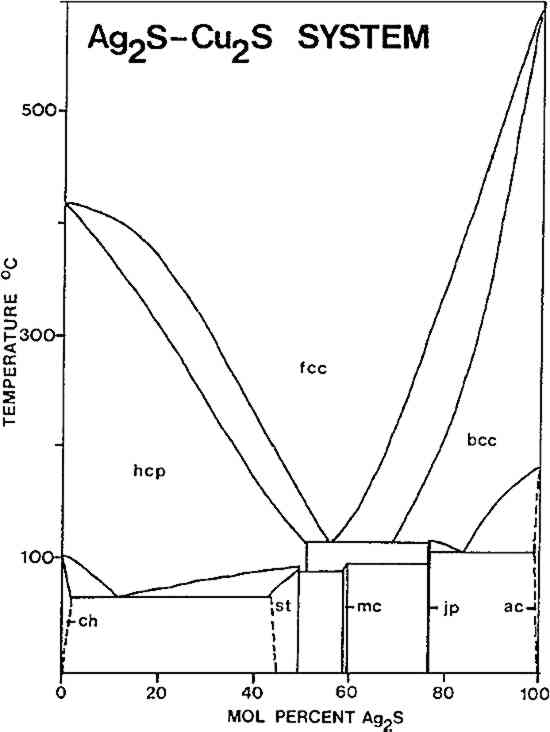
phase) Components and Phases Aluminum-Copper Alloy. ... Sugar/Water Phase Diagram S u g a r T e m p e r a t u r e ... concentrations, such as the gold-silver system, have no eutectic. An alloy system that has a eutectic is often referred to as a eutectic system, or eutectic alloy.
Some gold-copper–aluminium alloys form a fine surface texture at heat treatment, yielding an interesting spangling effect. At cooling, they undergo a quasi-martensitic transformation from body-centered cubic to body-centered tetragonal phase; the transformation does not depend on the cooling rate. A polished object is heated in hot oil to 150–200 °C for 10 minutes then cooled below 20 °C ...
Same is true for copper addition to silver. ii. Point E on the phase diagram it is called invariant point at this point an important reaction takes place at constant temperature Called Eutectic reaction where liquid (L) is directly converted to (α) and β phase. iii. Line CEG is called eutectic isotherm.
Use the following silver-copper phase diagram for Problems 5-9. 5. What are the solubility limits of Ag in (Cu) and Cu in (Ag)? Recall that (Cu) and (Ag) are the same as α and β, respectively. The solubility limit of Ag in (Cu) is 7.9 wt. % Ag. The solubility limit of Cu in (Ag) is 8.8 wt.% Cu. Note that these







.png)









0 Response to "41 silver copper phase diagram"
Post a Comment