40 diagram of facial nerves
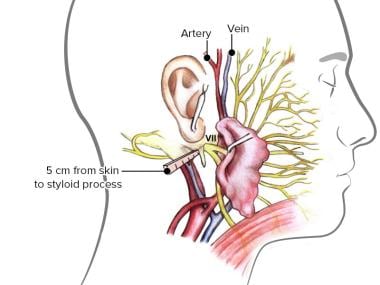
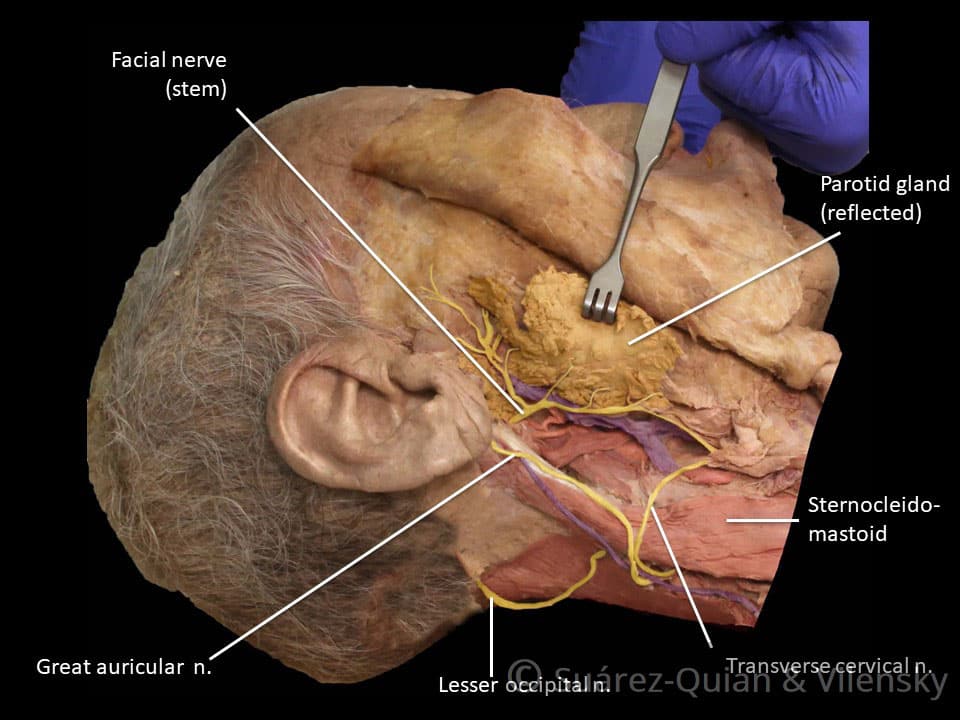
The Facial Nerve (CN VII) | Cranial Nerves | Anatomy ... The internal auditory meatus is approximately 1 cm long, and the facial nerve roots leave this meatus via the Z-shaped facial canal. The facial canal begins at the internal auditory meatus and continues for 3 cm before opening at the stylomastoid foramen. The facial canal is a point of convergence of the motor and sensory roots of the facial nerve. Facial Nerve: Function, Anatomy & Branches The facial nerve: Starts in your brainstem. Travels through the base of your skull near the vestibulocochlear nerve, the eighth cranial nerve, which helps you hear and maintain balance. Enters your face through an opening in a bone near the base of your ear. Branches out through an opening near your parotid gland, a major salivary gland.
Facial nerve - Wikipedia The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: intracranial (cisternal) segment meatal (canalicular) segment (within the internal auditory canal) labyrinthine segment (internal auditory canal to geniculate ganglion) tympanic segment (from geniculate ganglion to pyramidal eminence)
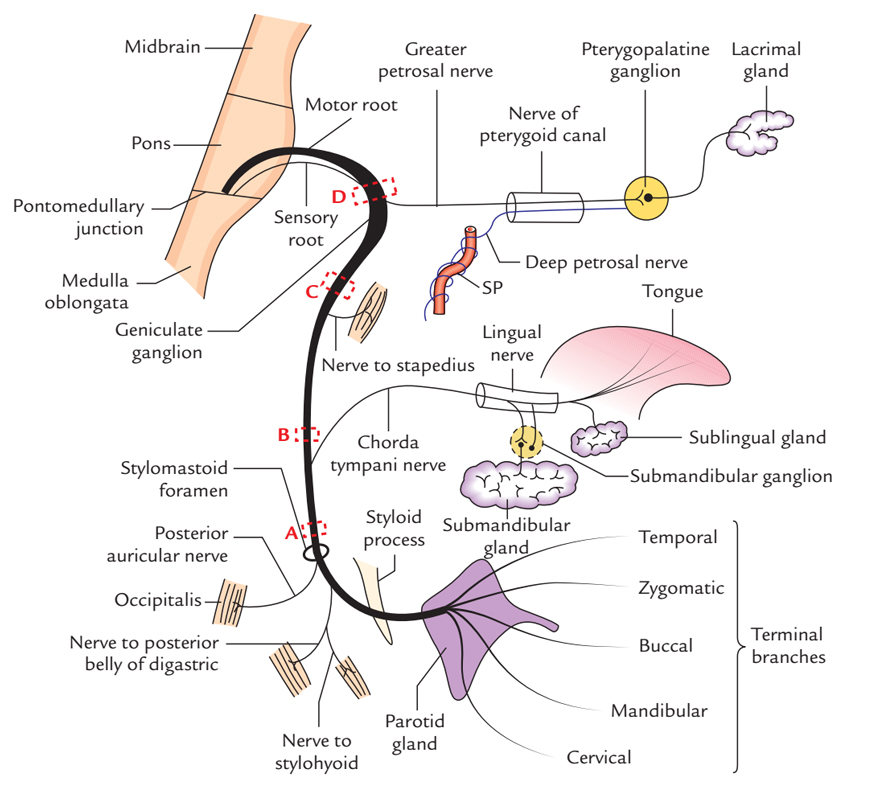
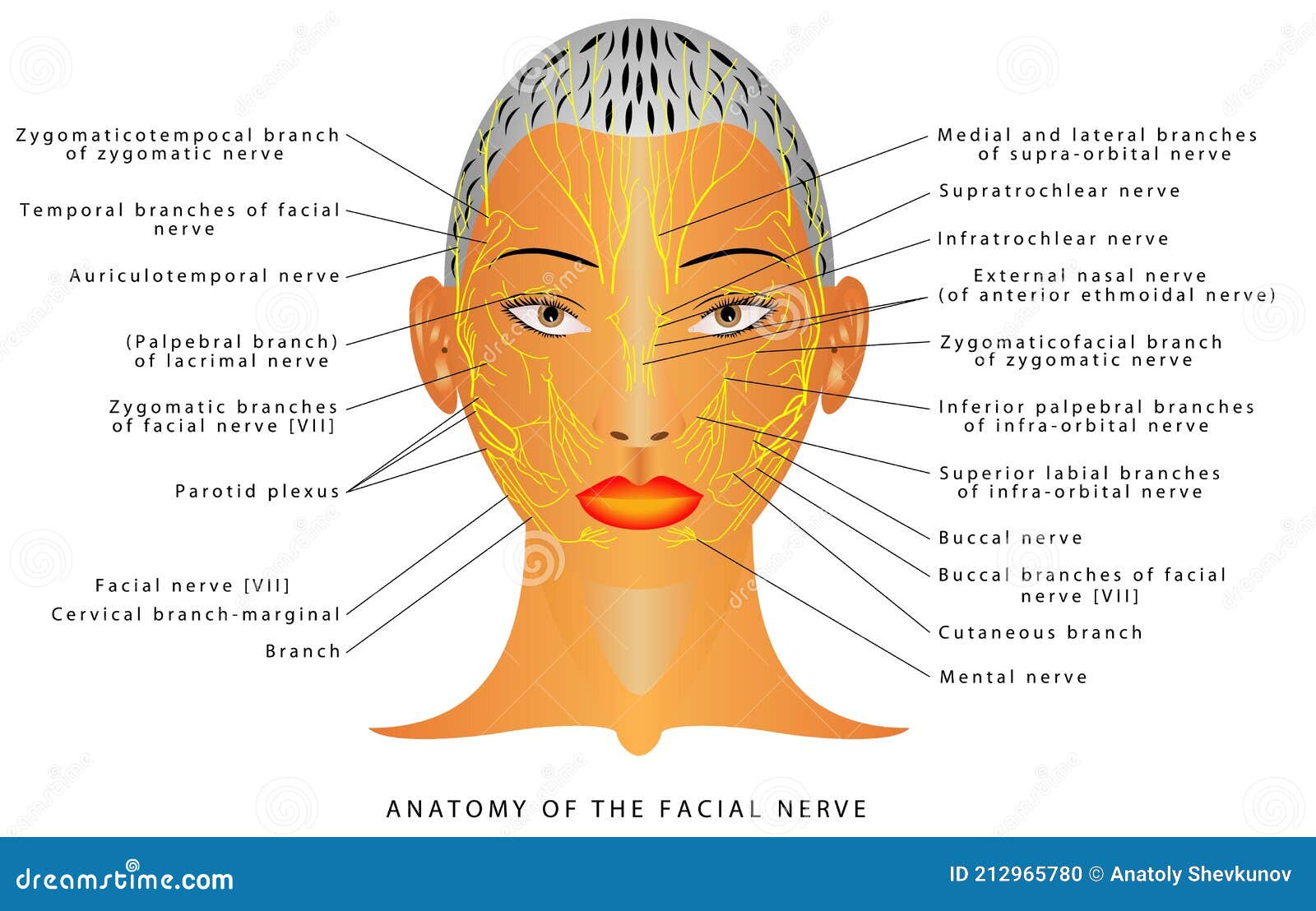
Diagram of facial nerves
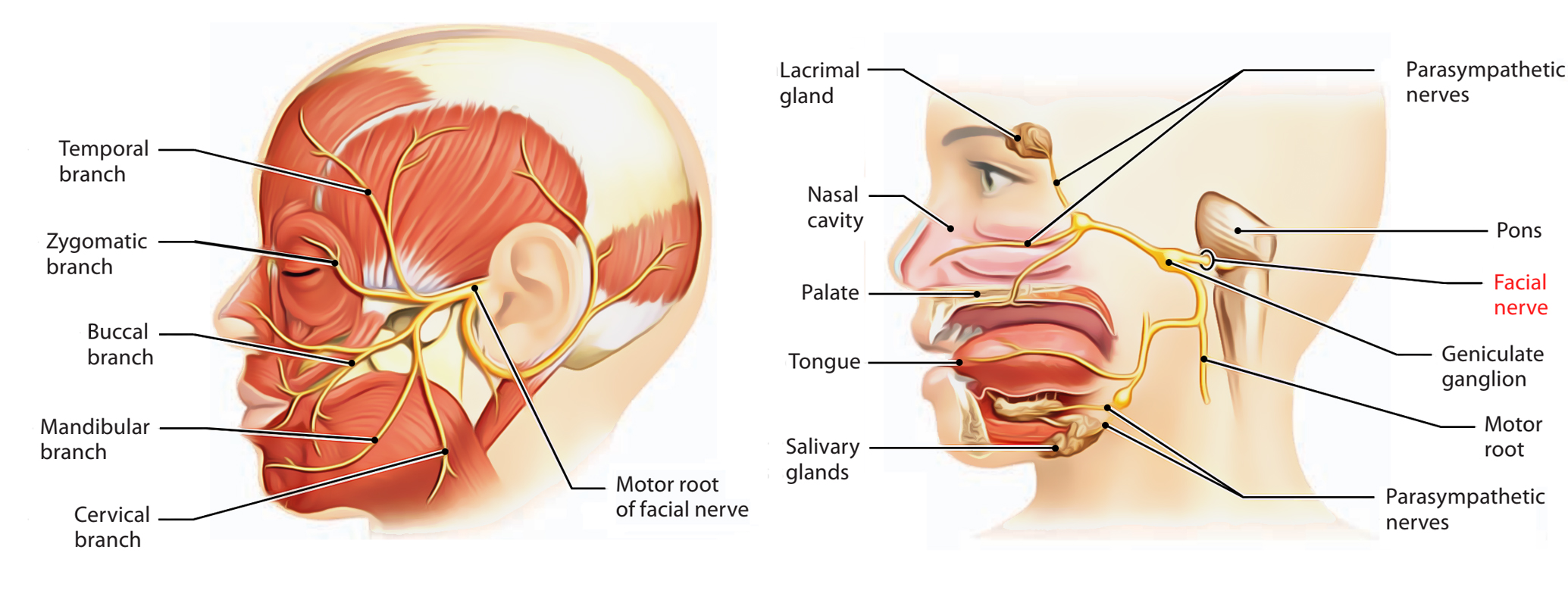
Facial Nerve - Human Body Diagrams - Medical Art Library The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve, and has two roots. A large motor root, and a much smaller sensory and parasympathetic root. The smaller root contains sensory fibers for taste, sensation in parts of the ear, throat and palate, and parasympathetic fibers which control the various secretory glands in the face, such as the salivary ... Facial nerve: Origin, function, branches and anatomy | Kenhub The 12 paired cranial nerves include: the olfactory nerve (CN I) the optic nerve (CN II) the oculomotor nerve (CN III) the trochlear nerve (CN IV) the trigeminal nerve (CN V) the abducens nerve (CN VI) the facial nerve (CN VII) the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) the vagus nerve (CN X) National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information
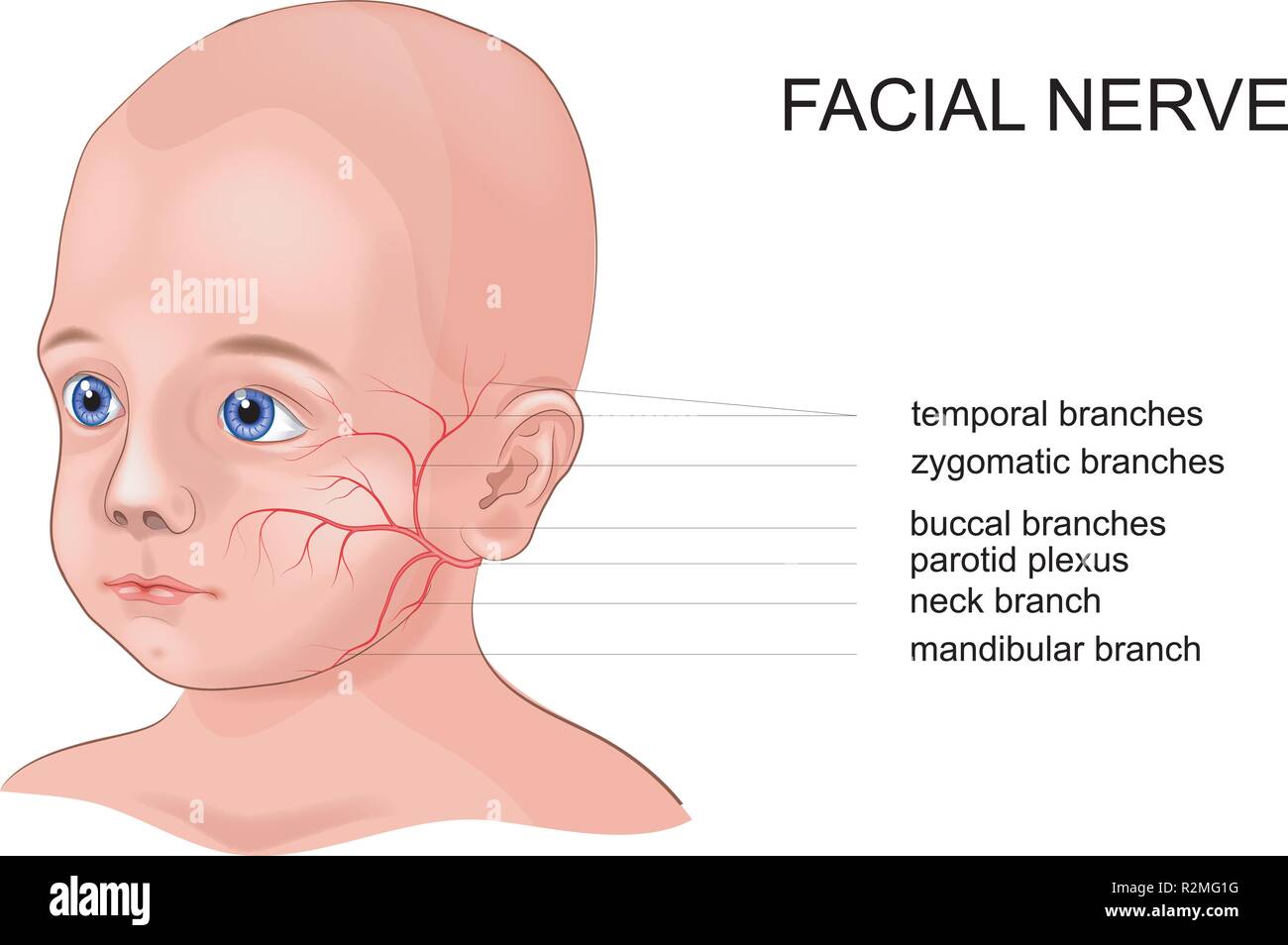
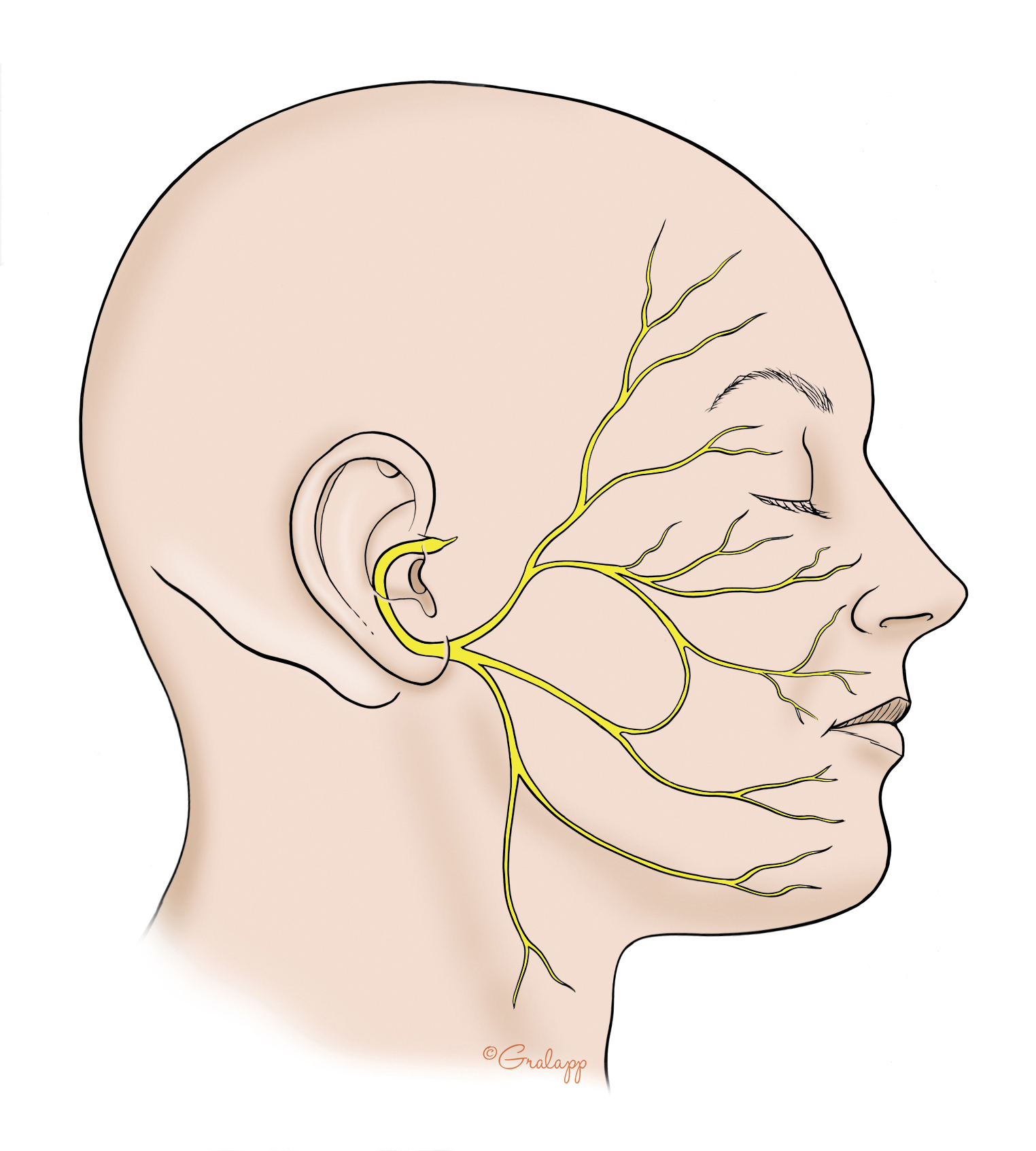
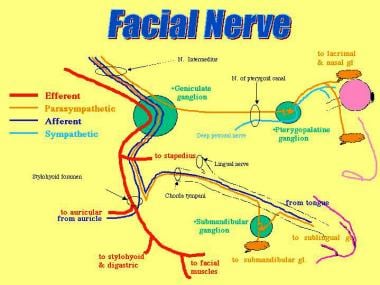
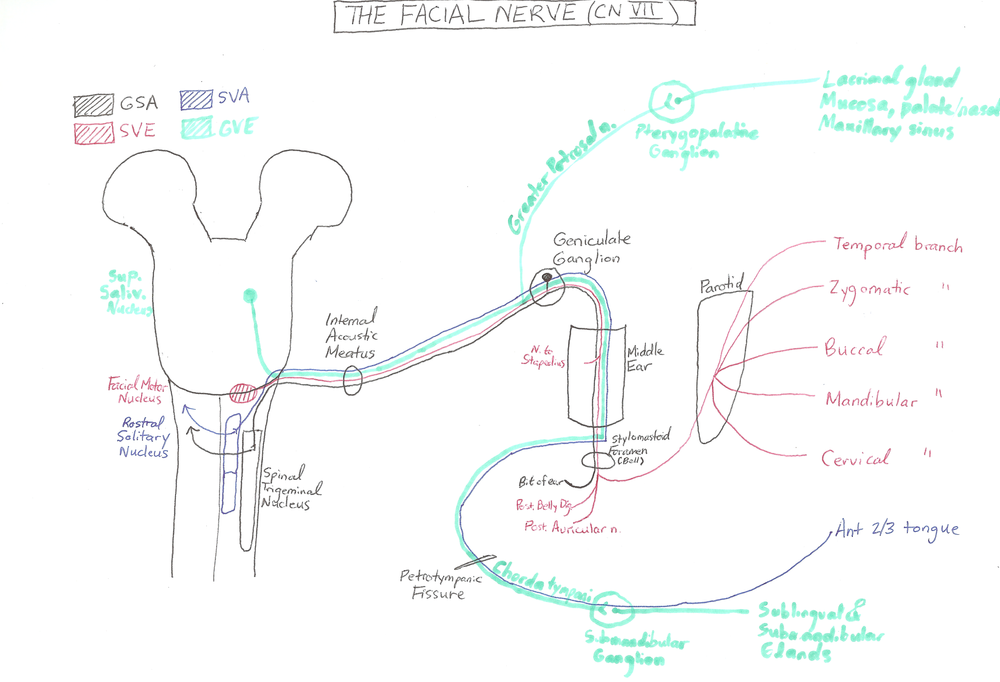
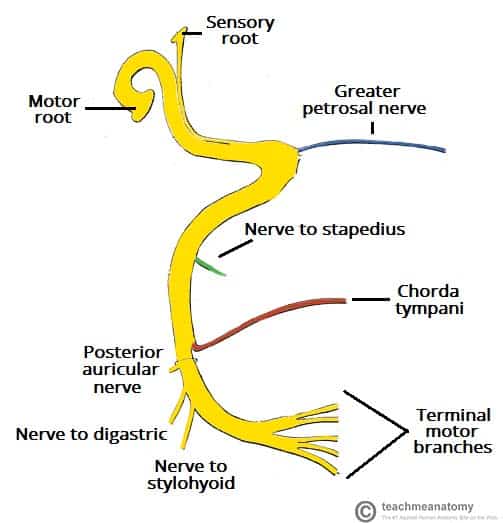
Diagram of facial nerves. The Facial Nerve (CN VII) - Course - Functions ... Fig 2 - Schematic of the course and branches of the facial nerve. Extracranial After exiting the skull, the facial nerve turns superiorly to run just anterior to the outer ear. The first extracranial branch to arise is the posterior auricular nerve. It provides motor innervation to the some of the muscles around the ear. What are the 12 cranial nerves? Functions and diagram The facial nerve functions to produce facial expressions. The facial nerve also has both motor and sensory functions. The facial nerve is made up of four nuclei that serve different functions:... Facial Nerve - Physiopedia Facial nerve The Facial Nerve is the seventh Cranial Nerve. It is composed of approximately 10,000 neurons which comprise 2 roots: 7,000 myelinated, innervating the muscles of facial expression (motor root). 3,000 fibres, being mixed sensory, taste and parasympathetic root, known as the Nervus Intermedius. Facial Nerve Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps The facial nerve is also known as the seventh cranial nerve (CN7). This nerve performs two major functions. It conveys some sensory information from the tongue and the interior of the mouth....
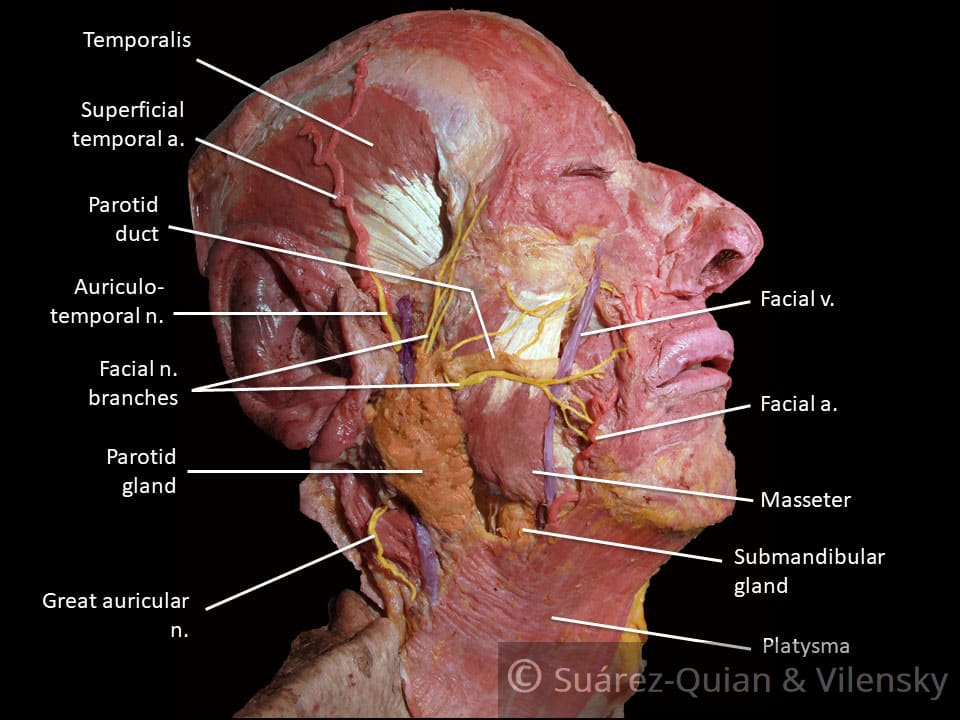
Cranial Nerves of Face & Mouth | Overview, Sensations ... The Trigeminal nerve, also known as cranial nerve V, is best known as the cranial nerve for chewing and facial sensation. It is also the largest cranial nerve and contains three divisions. The... Seventh Cranial Nerve - normal cranial nerves image, id ... Seventh Cranial Nerve. Here are a number of highest rated Seventh Cranial Nerve pictures upon internet. We identified it from well-behaved source. Its submitted by direction in the best field. We assume this kind of Seventh Cranial Nerve graphic could possibly be the most trending subject bearing in mind we allowance it in google help or facebook. How to Memorize the Entire Facial Nerve Using a Memory ... View fullsize. In this 20-minute video, I walk through how I memorized the entire facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) using a memory palace. The facial nerve is a key player in neuroanatomy and pops up repeatedly during gross anatomy in medical school. I explain how I capture the nuclei, branches, and key practical points in an efficient way. Nerves of the Head and Neck | Interactive Anatomy Guide The muscles of the head and neck are also controlled by various cranial nerves including the facial nerve (facial expression) and accessory nerve (head and neck movements). Wandering through the neck and torso, the vagus nerve communicates vital information from the brain to the heart and intestines.
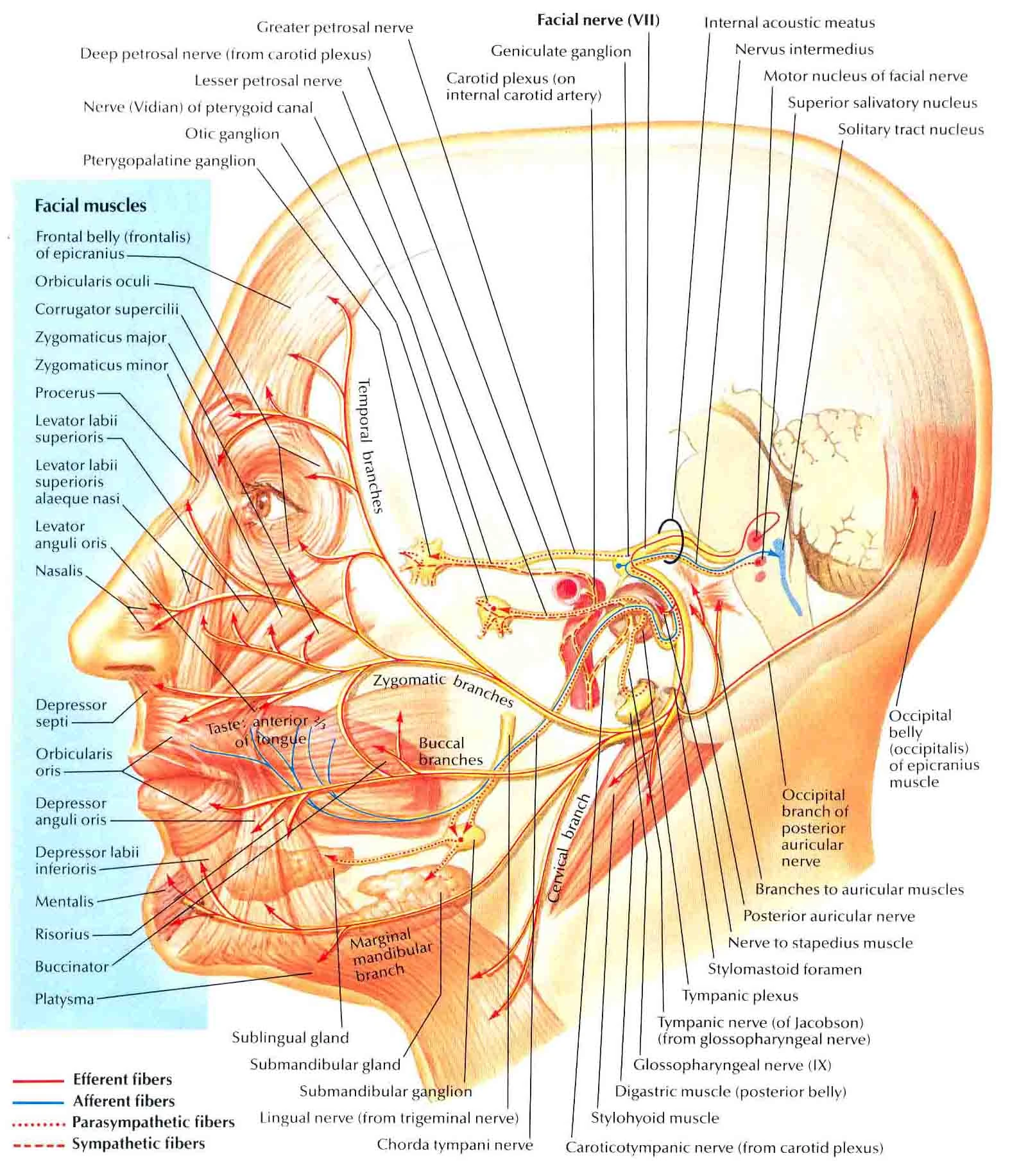
Facial nerve | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org The facial nerve emerges from the lower lateral pons, lateral and rostral to the abducens nerve, and medial and caudal to the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) 9. Nervus intermedius emerges immediately lateral to the main trunk and the two travel laterally through the cerebellopontine angle to the internal acoustic meatus. Facial Nerve Diagram from Grants Atlas of Anatomy Facial Nerve Scheme--From Grants Atlas of Anatomy Facial Nerve: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment The facial nerve emerges at the pontine level of the brainstem. The brainstem is the part of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord. It includes three sections, the medulla (right above the spinal cord), the pons (above the medulla), and the midbrain, (which is the uppermost region of the brainstem).
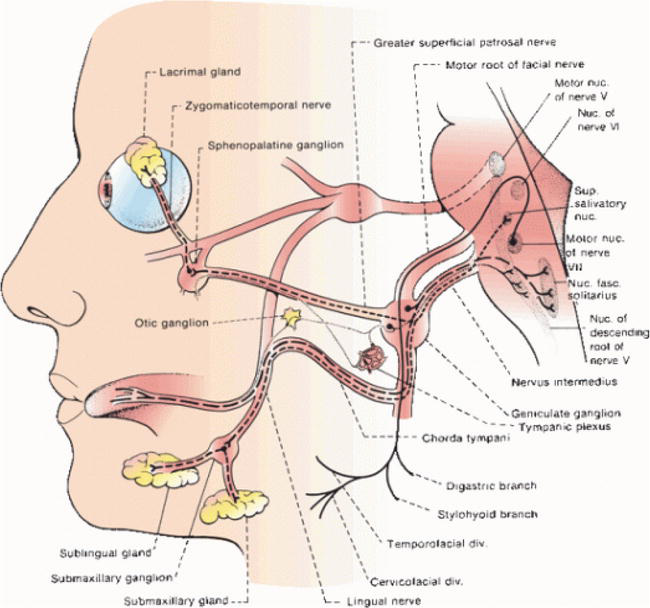
Facial nerve anatomy - Washington University in St. Louis 1. Facial nerve nucleus 2. Trigeminal nerve: Spinal nucleus 3. Superior salivary nucleus 4. Solitary tract 5. Porus acusticus internus 6. Meatal foramen 7. Greater petrosal nerve 8. Sphenopalatine ganglion 9. Maxillary nerve 10. Lacrimal gland 11. Deep petrosal nerve 12. Vidian nerve 13. Nerve to glands of nose and palate (motor fibers to ...
12 Cranial Nerves: Functions & Diagram of Locations ... The trigeminal nerve is the largest of the cranial nerves and can be further divided into three divisions: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. The ophthalmic division sends information from the scalp, forehead, and upper eye lids (the upper parts of the head) and is sensory in modality, of the general somatic sensory variety.
PDF Muscles of the Face - Exploring Nature 1 4 9 3 2 10 4 7 11 6 8 5 12 13 Muscles of Facial Expression Blood Supply: External Carotid Artery Motor Innervation: Facial Nerve (Vll) Sensory Innervation: Trigeminal Nerve (V) 1) Frontalis (worry muscle): a. Actions: Raises eyebrows, furrows brow b. Innervation: Facial Nerve (Vll) c. Origin: from galea aponeurotica d. Insertion: to skin above the eyebrows 2) Occipitalis - not shown on ...
Facial nerves anatomy - Graph Diagram Facial Nerves Anatomy. Posted on January 22, 2022 by admin. This human anatomy diagram with labels depicts and explains the details and or parts of the Facial Nerves Anatomy. Human anatomy diagrams and charts show internal organs, body systems, cells, conditions, sickness and symptoms information and/or tips to ensure one lives in good health.
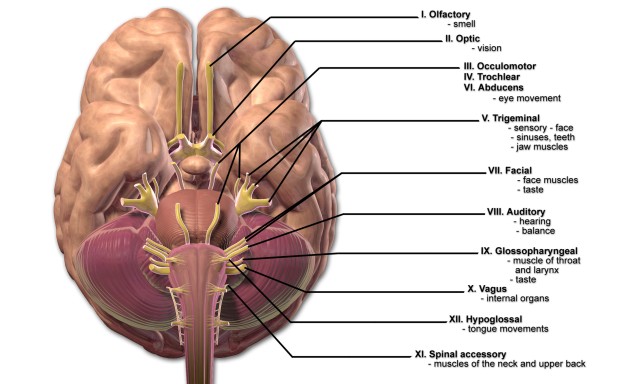
These Are the 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions These Are the 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions The 12 Cranial Nerves I. Olfactory nerve II. Optic nerve III. Oculomotor nerve IV. Trochlear nerve V. Trigeminal nerve VI. Abducens nerve VII....
Facial Nerve - Washington University in St. Louis Bilateral VII weakness. General. Definition: 2nd facial nerve paresis occuring within 30 days of 1st. Frequency: 0.3% to 2% of patients with facial paralysis. VII nerve lesions. Hereditary. Amyloidosis: Gelsolin. Melkersson syndrome. Möbius syndrome & Congenital facial paresis.
Cranial nerves: Anatomy, names, functions and mnemonics ... 12 cranial nerves list Mnemonics Olfactory nerve (CN I) Optic nerve (CN II) Oculomotor nerve (CN III) Trochlear nerve (CN IV) Trigeminal nerve (CN V) Abducens nerve (CN VI) Facial nerve (CN VII) Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) Vagus nerve (CN X) Accessory nerve (CN XI) Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) Sources + Show all
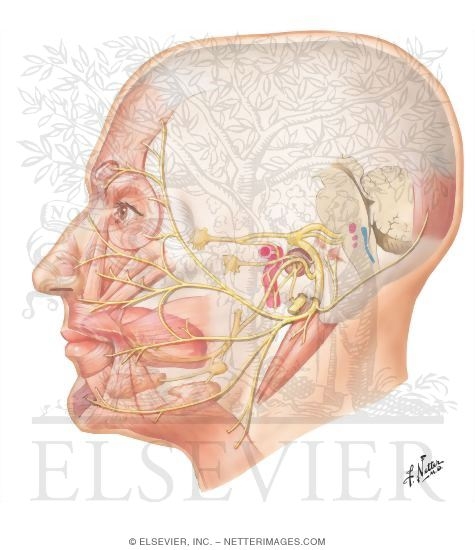
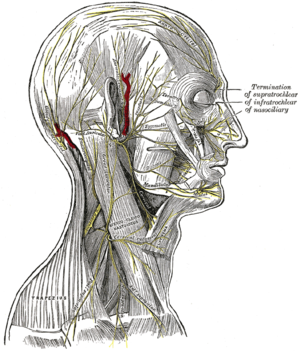
Facial Nerve Anatomy - ENT USA The pictures and diagrams below show the anatomy of the facial nerve. These pictures were submitted by Dr. Kedar K. Adour, M.D. and drawn by Edith Steadman and K K Adour, M.D. Diagram of the facial nerve and structures it innervates. Tearing -- Lacrimal Gland. Taste -- Anterior 2/3 of the Tongue. Saliva Production -- Sublingual Gland ...
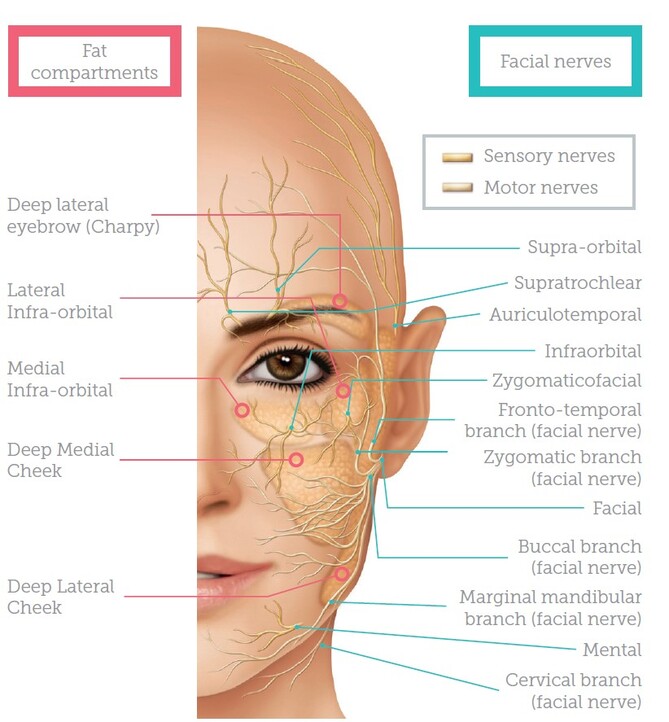
Facial anatomy at-a-glance | theaestheticguide.com MUST-KNOW: "The folds are very interesting area of the face," he says. "Outside the folds, we have skin, subcutaneous tissue, SMAS [Superficial muscular aponeurotic system], muscle, periosteum, bone. On the inside of the fold, we have skin, SMAS, muscle, and it is very tightly bound."
facial nerves Diagram | Quizlet facial nerves Diagram | Quizlet facial nerves STUDY Learn Write Test PLAY Match + − Created by vincent_alaniz PLUS Terms in this set (10) facial nerve ... long buccal nerve ... submandibular ganglion ... sublingual gland ... mental nerve ... inferior alveolar nerve ... submandibular gland ... mylohyoid nerve ... chorda tympani nerve ...
National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information
Facial nerve: Origin, function, branches and anatomy | Kenhub The 12 paired cranial nerves include: the olfactory nerve (CN I) the optic nerve (CN II) the oculomotor nerve (CN III) the trochlear nerve (CN IV) the trigeminal nerve (CN V) the abducens nerve (CN VI) the facial nerve (CN VII) the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) the vagus nerve (CN X)
Facial Nerve - Human Body Diagrams - Medical Art Library The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve, and has two roots. A large motor root, and a much smaller sensory and parasympathetic root. The smaller root contains sensory fibers for taste, sensation in parts of the ear, throat and palate, and parasympathetic fibers which control the various secretory glands in the face, such as the salivary ...




:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11477/pasted_image_0.png)



:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12550/HeadCadavar.png)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-141483691-4cc225237a5945f8ab949d936f52c48e.jpg)
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nervus-facialis-7/0IuCKamYnn0XjUHp5CNtZQ_facial_nerve.png)
/GettyImages-141483691-4cc225237a5945f8ab949d936f52c48e.jpg)






0 Response to "40 diagram of facial nerves"
Post a Comment