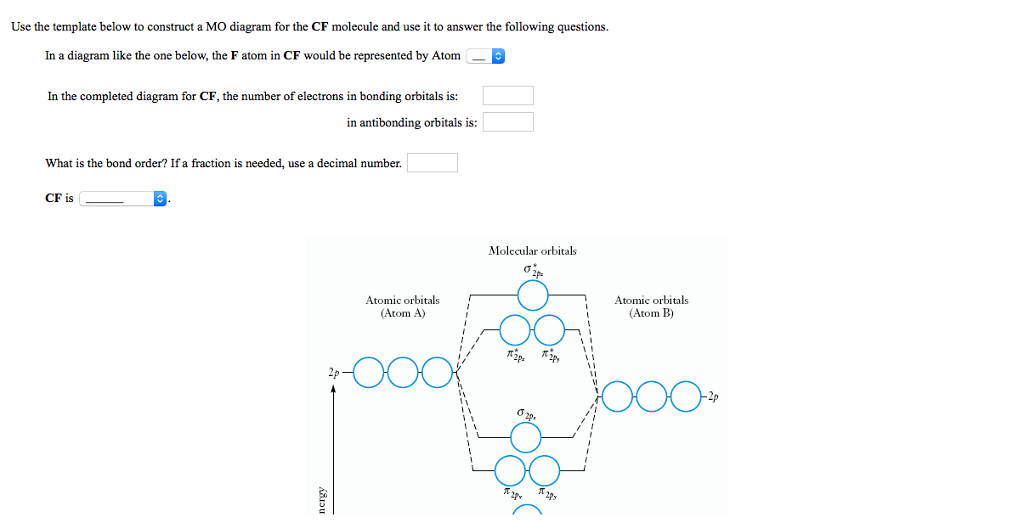
41 cf molecular orbital diagram
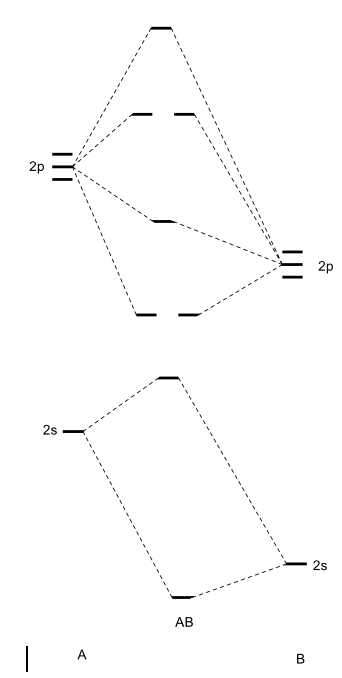
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding. For heteroatomic dinuclear molecule, energy of BMO closely matches with those of more electronegative atom & energy of ABMO closely matches with those of less electronegative atom. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. ( i have no faqing idea man, how do u determine this For a diatomic molecule, the molecular orbital diagram will contain: the atomic orbitals of each atom the molecular orbitals that result from the...
Summary Molecular orbitals editor allows to build, analyze and graphically edit molecular/Kohn-Sham orbitals diagrams from the results of for analysis/editing, e.g. by selecting Orbital/Peak Selection tool and clicking on the molecular orbital energy level of interest you will see in AO Coefficients window...

Cf molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital (MO) theory describes the behavior of electrons in a molecule in terms of combinations of the atomic wavefunctions. Application: Computational Chemistry in Drug Design. Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. Bond Order. Bonding in Diatomic Molecules. Notes on. Molecular Orbital ~ a l c u l aitons. Notes on molecular orbital calculations. First printing, 1961 Second printing, with corrections, 1962 Third 'Cf. C. A. Coulson, Q u a r t e r l y Reviews, 144 (1947). 2 ~ P.auling, "Nature of the Chemical Bond, " pp. 14-15... Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in LaTeX by means of the package MOdiagram. For information about the more traditional molecular structure...
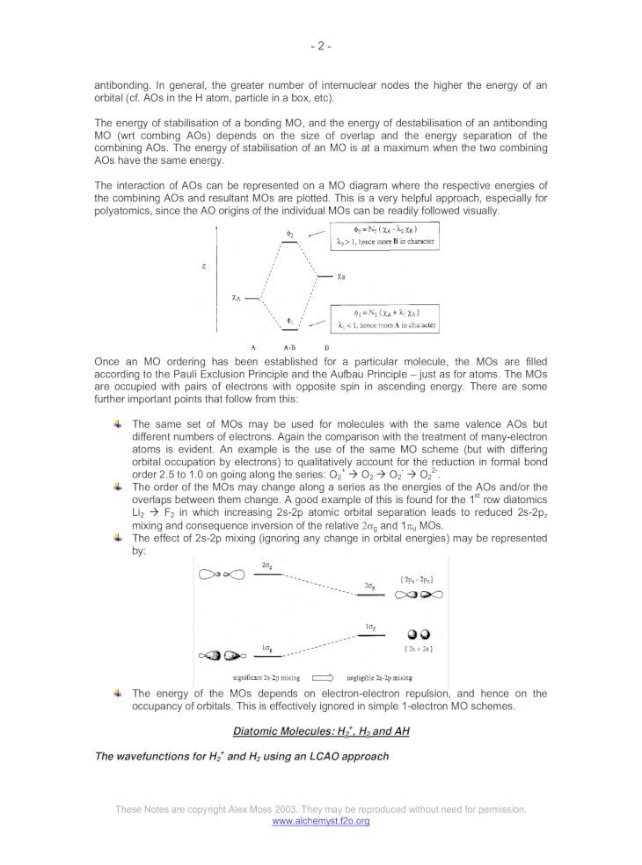
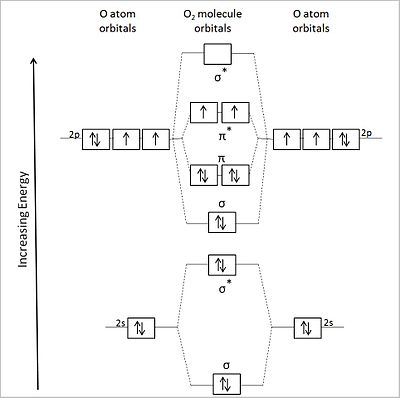
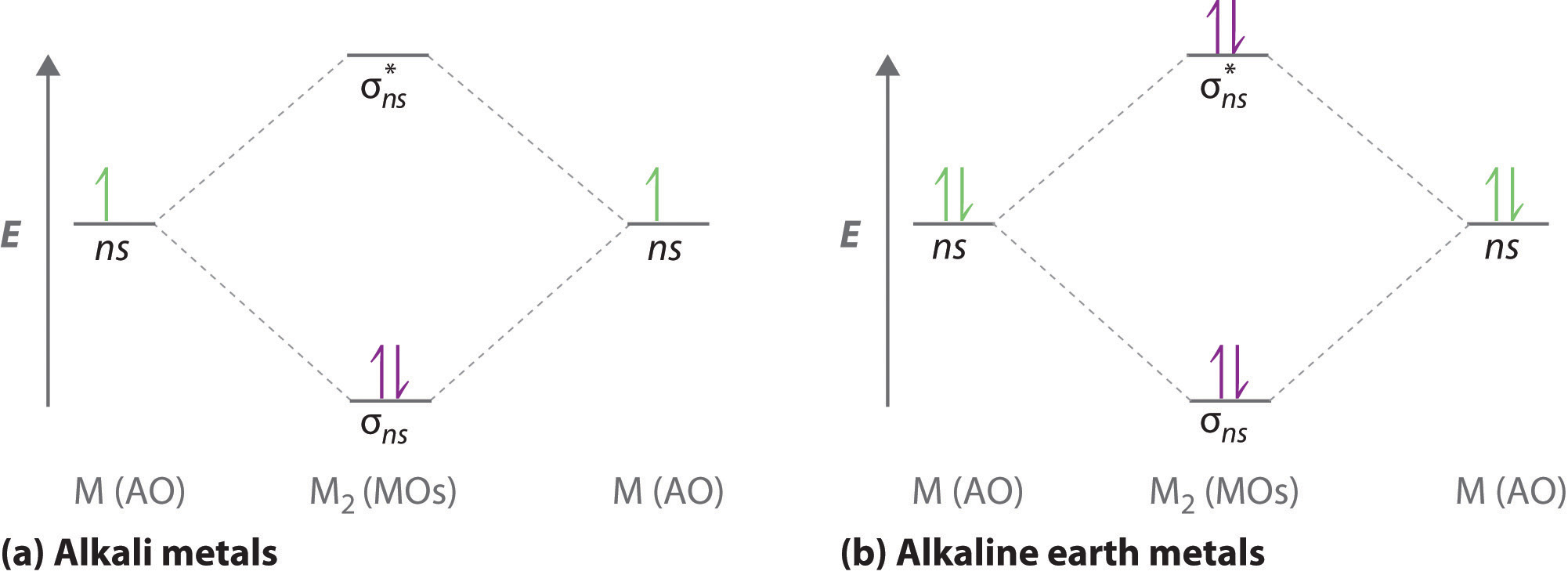
Cf molecular orbital diagram. The molecular orbital of the hydrogen molecule encompasses both nuclei. They are separated by an optimum distance, the bond length, which results from a balance between attractive and repulsive forces. The nuclei attract the bonding electrons, but repel each other. • Molecule orbital theory (Robert Mullikan). • Electrons are delocalised - Different to Lewis and hybridisation (these are not MO). • Energy level diagram represents this interaction. - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital. ... corresponding molecular orbital diagrams, depicting the dominant atomic orbital characters of the occupied and some of the low-lying unoccupied In particular, the GOS profile of the C 1s→σC-Cl∗ [lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)] transition of CF3Cl was found to contain relatively... The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. Figure 10. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons.
For chem videos, quizzes and more download Chemistry X for free on the App Store! Correlation Diagrams - by considering the positions and energies of... Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules This energy diagram for the molecular orbitals is shown in Fig.1 However, experimental evidence for oxygen and heavier diatomic molecules have... The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable. Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are similar (as in NO or CN mole-cules, for example), we can modify the diagram of Figure 9-5 by skewing it slightly.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. u Stable electronic configurations: MO Energy Level Diagrams Reviewed u Electron count preference u Electron count and Oxidation States u Ligands. • Carbon Monoxide • Phosphines • Cyclopentadienide and arenes • Hydrides and dihydrogen. The terms atomic orbital and molecular orbital[a] were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean one-electron orbital wave functions.[2] At an The qualitative approach of MO analysis uses a molecular orbital diagram to visualize bonding interactions in a molecule. In this type of diagram... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive...
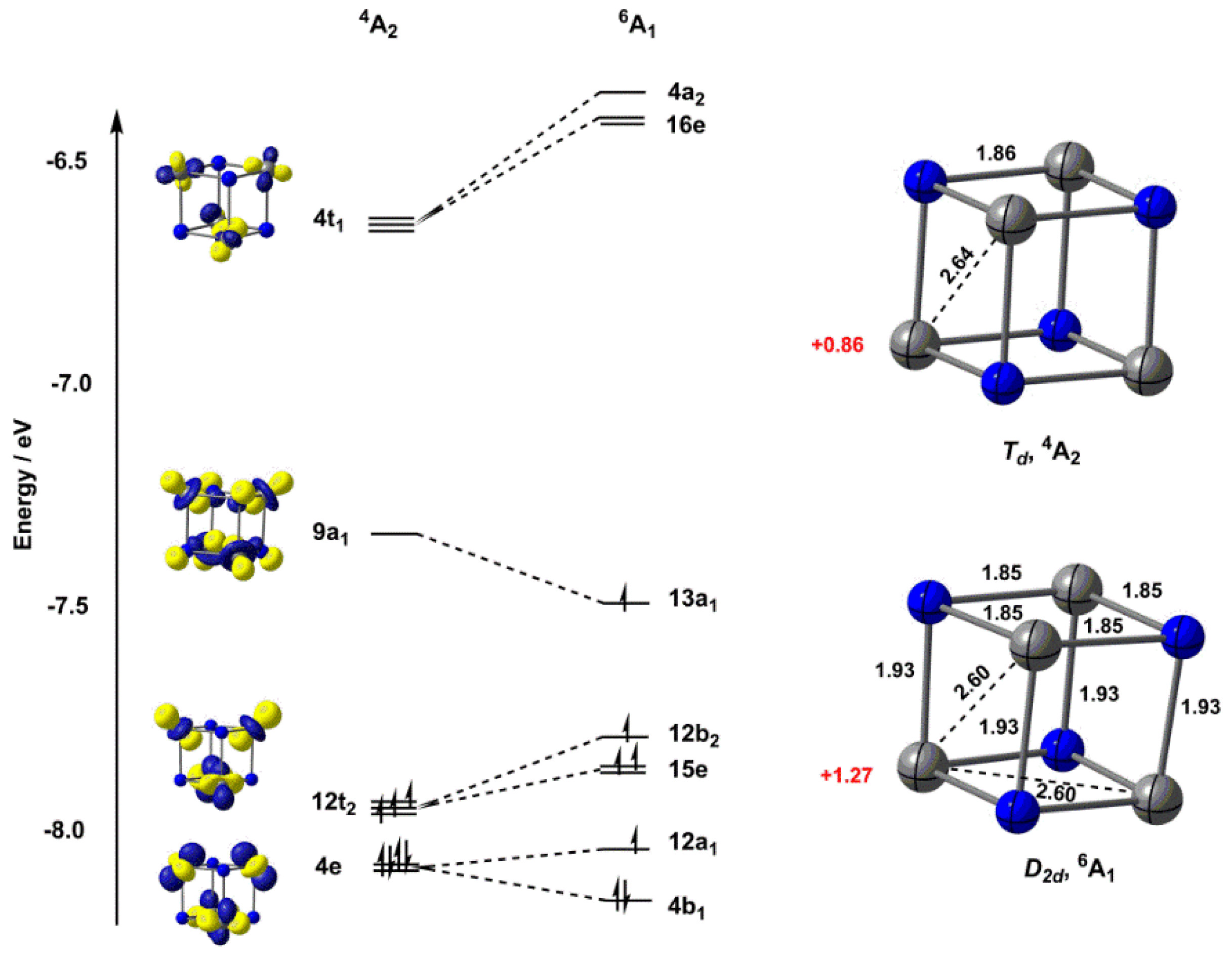
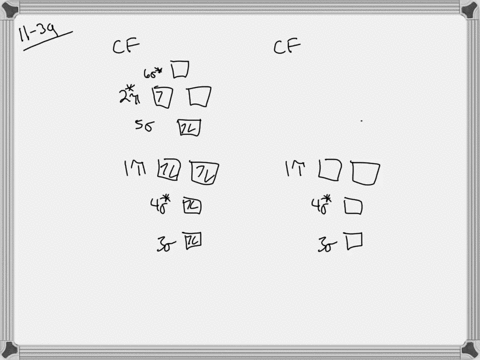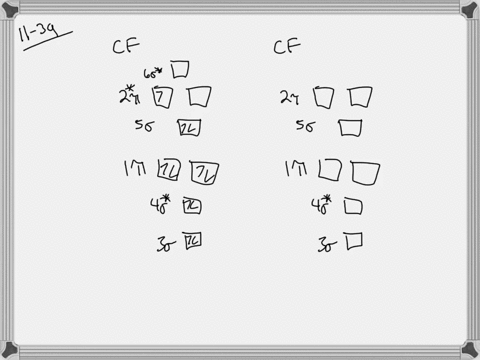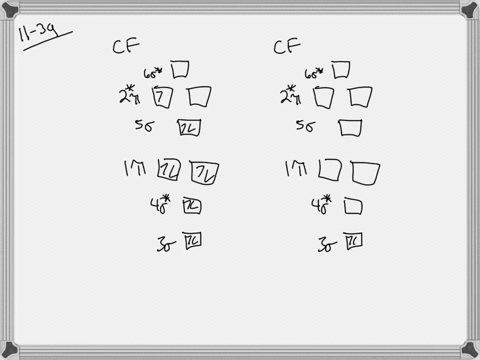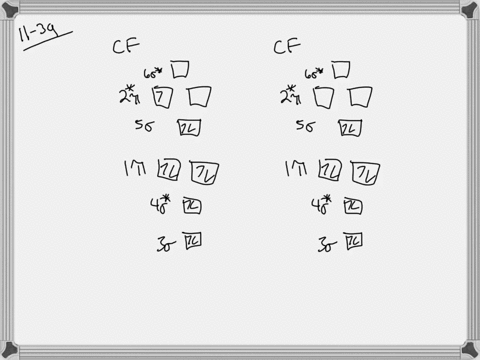
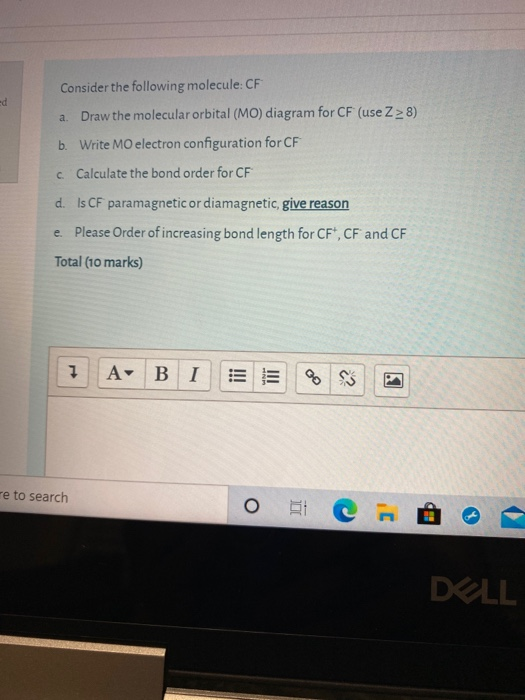
Problem 39 Medium Difficulty. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for CF. Would you expect the bond length of $\mathrm{CF}^{+}$ to be longer or shorter than that of CF? To both CF and CF' ions, CF' has shorter bond length than CF. This is because CF' bond order more than CF molecule.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram for short, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the Linear combination of atomic orbitals molecular orbital method (LCAO method) in particular.[1][2][3] A...
Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. However, with more atoms, computers are required to calculate how the atomic orbitals combine. See three-dimensional drawings of the...
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence On the other hand, Molecular Orbital Theory visions the electrons of a covalent bond to be delocalized over the entire molecule.
The molecular orbital must describe the motion of the electron for all values of the internuclear separation; from R = ∞ for the separated atoms, through By carrying out this correlation procedure for every orbital we may construct a molecular orbital correlation diagram (Fig. 8-4) which relates each...
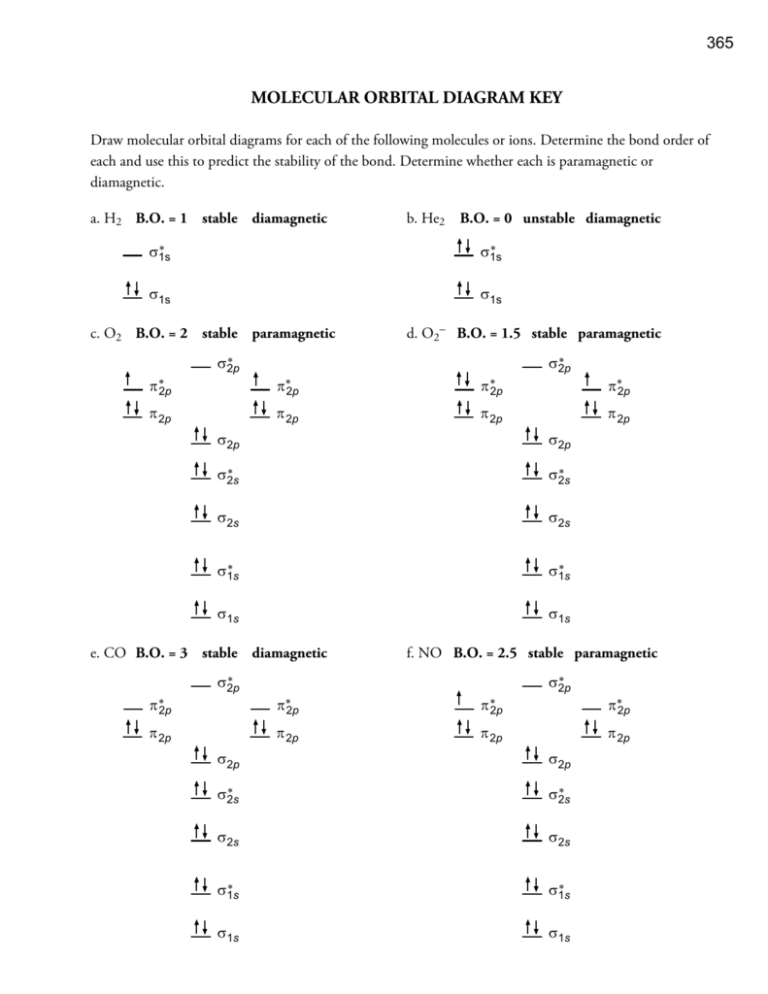
365 MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions. C8H18 or CH4 h. CF4 or PF3 Hydrogen bonds stronger than dipole-diplole The larger molecule has the stronger London forces.
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Molecular orbital theory is more powerful than valence-bond theory because the orbitals reflect the The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both...
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in LaTeX by means of the package MOdiagram. For information about the more traditional molecular structure...
Notes on. Molecular Orbital ~ a l c u l aitons. Notes on molecular orbital calculations. First printing, 1961 Second printing, with corrections, 1962 Third 'Cf. C. A. Coulson, Q u a r t e r l y Reviews, 144 (1947). 2 ~ P.auling, "Nature of the Chemical Bond, " pp. 14-15...
Molecular orbital (MO) theory describes the behavior of electrons in a molecule in terms of combinations of the atomic wavefunctions. Application: Computational Chemistry in Drug Design. Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. Bond Order. Bonding in Diatomic Molecules.



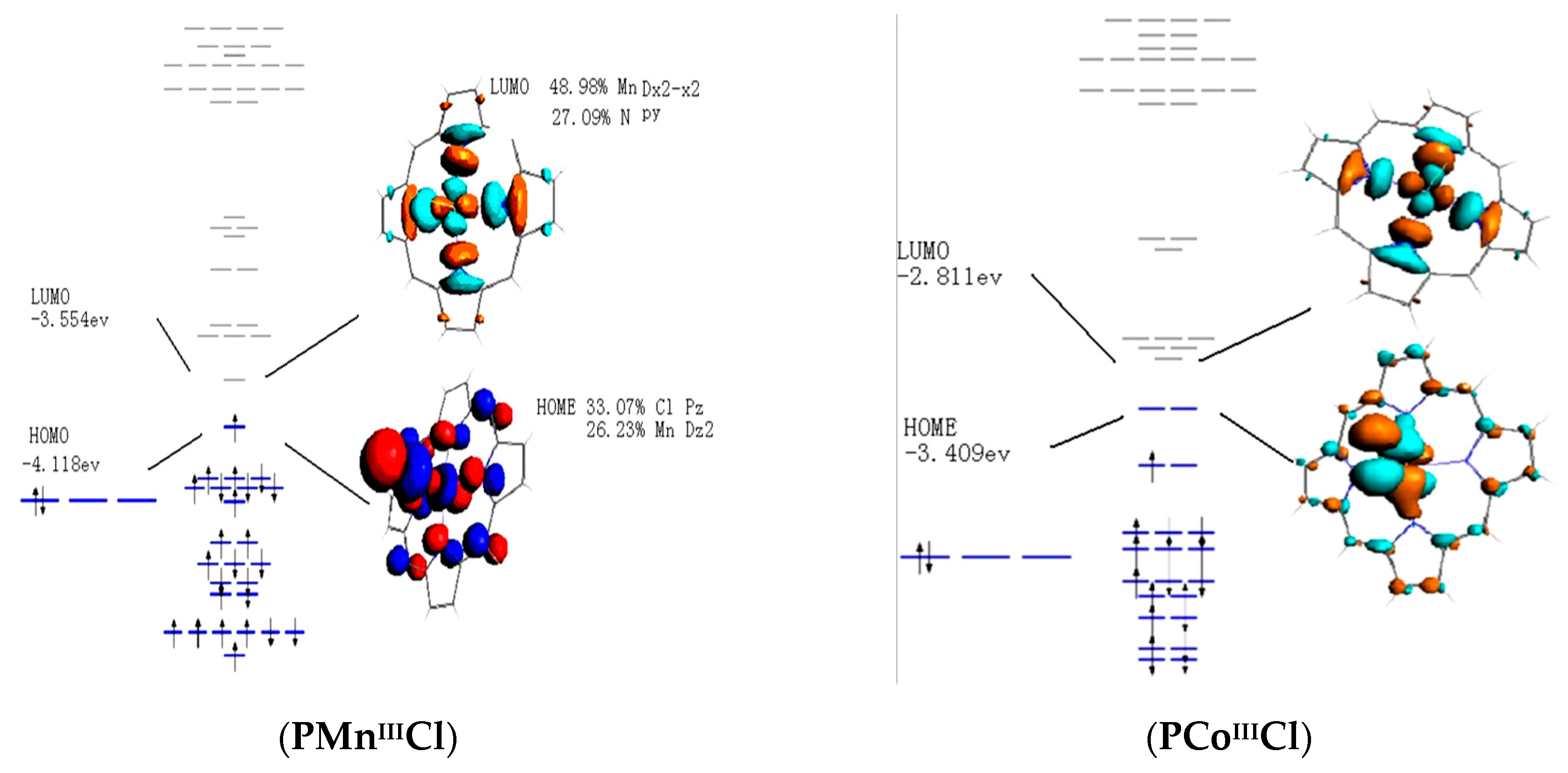

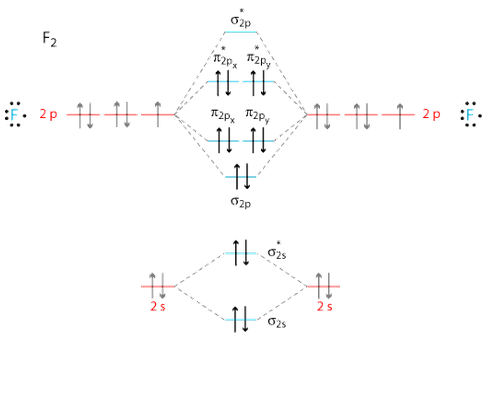


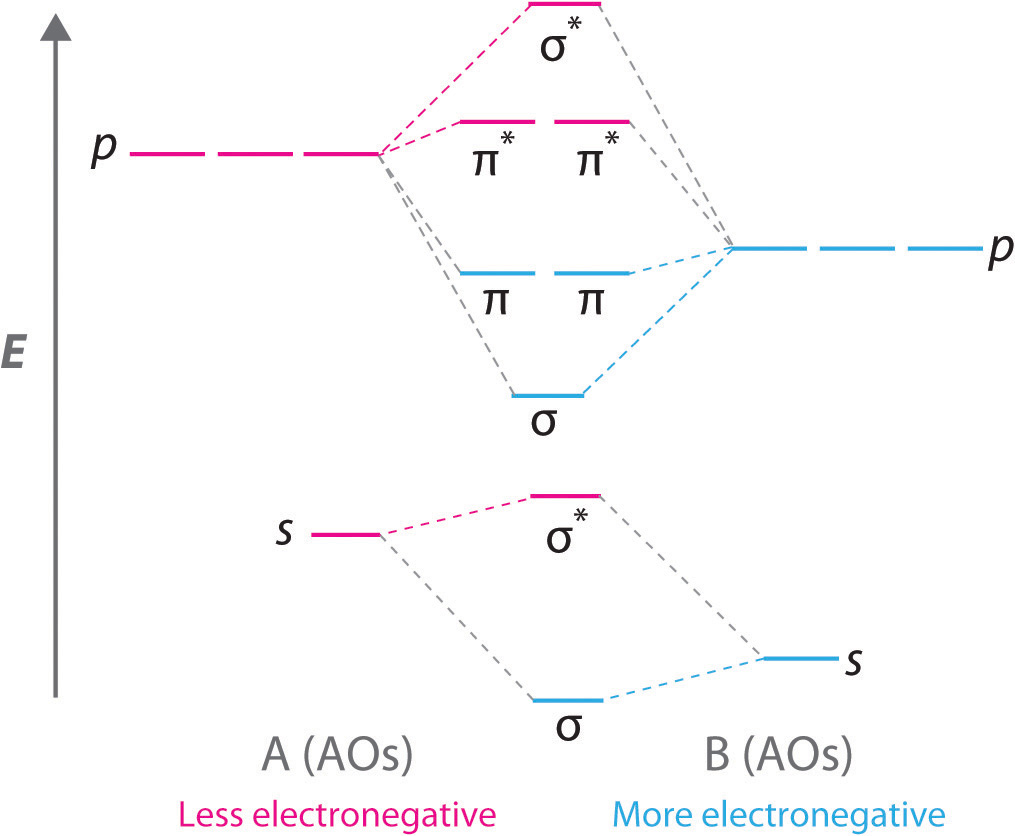
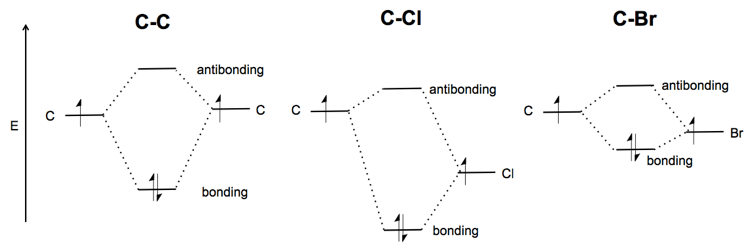













0 Response to "41 cf molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment