41 brain diagram reticular formation
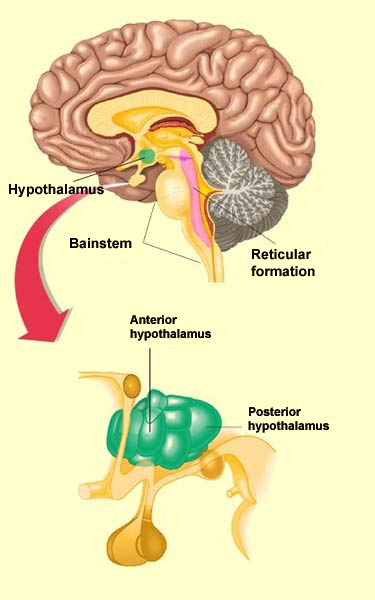
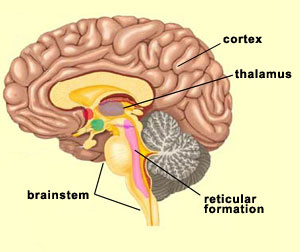
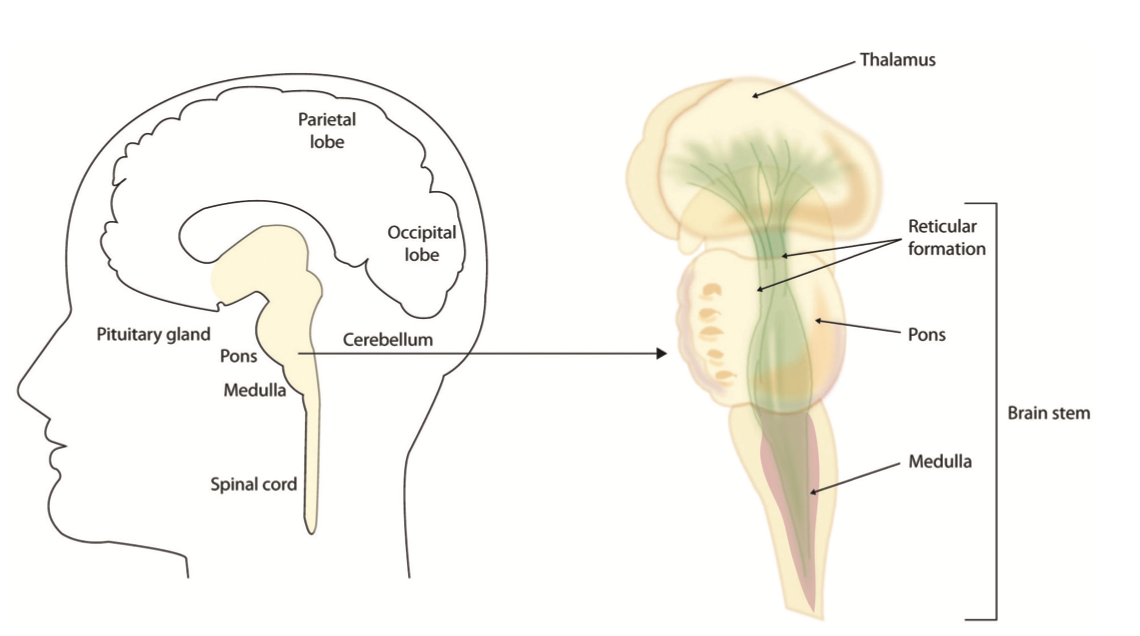
The Limbic System and the Reticular Formation. The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei. This "web of gray matter" runs vertically throughout the brainstem and has connections with the cerebrum. This has over 100 neural networks that use different neurotransmitters that function in: Somatic motor control, Cardiovascular ... The reticular formation is found in the brainstem, at the center of an area of the brainstem known as the tegmentum.The tegmentum is a heterogeneous section of neural tissue that extends vertically through the brainstem, making up the portion of the brainstem that sits between the ventricles and surface structures like the basal pons and the pyramids of the medulla.
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem.It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain.The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core of the brainstem that extend from the upper part of the midbrain to the lower part of the medulla oblongata.

Brain diagram reticular formation
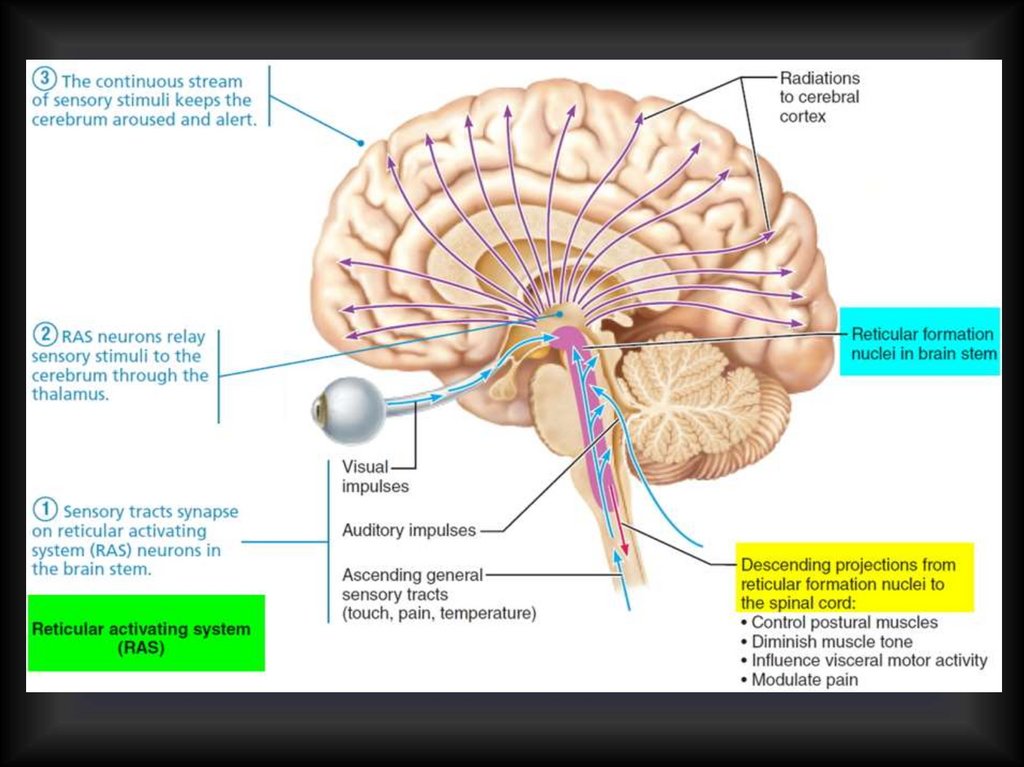
The reticular formation is a cluster of nerves within the brainstem that relay sensory and motor signals to and from the spinal cord and the brain. It aids in the control of autonomic and endocrine functions, as well as muscle reflexes and sleep and awake states. The red nucleus is a mass of cells that aids in motor function. Substantia nigra ... Controls/regulates heartbeat and breathing To and from brain Reticular Formation Helps control arousal, responds to change in monotony Thalamus Relays sensory information, switchboard between sensory neurons and higher brain regions Deals with sight, hearing, touch, taste. Transmits replies from higher brain to cerebellum and medullam The reticular activating system connects the brain stem, to the cerebral cortex, through various neural paths. The stem controls most of the involuntary functions, as well as reflexes of the body, while the cerebral cortex is the seat of consciousness and thinking abilities. The system forms a link between these two different regions, helping ...
Brain diagram reticular formation. reticular formation and the disorders of the reticular formation. Historical reviews The term ''reticular formation'' was coined in the late 19th century, coinciding with Cajal (1909) who commented on the extensive multiple branching of the reticular formation neurons as the fibers ascended and descended through the middle of the brain stem. Papez The reticular formation is found bilaterally in the brain and is therefore able to provide motor control to both sides of the brain when a person laughs or smiles. Since these fibers do not integrate with the corticobulbar fibers (also involved in facial expression), a patient may still smile symmetrically even if they have suffered a ... Brain Diagram Reticular Formation Like the spinal cord, the brain is made of mainly gray matter and white matter and hypothalamus); limbic system; reticular activating system. The reticular formation is a cluster of nerves within the brainstem that relay sensory and motor signals to and from the spinal cord and the brain. Reticular formation, as the name suggests, is a network of neurons and nerve fibers, present in the brain. Earlier, no particular function was known to be associated with the reticular formation. Today, the reticular formation is considered to play a very important role in different activities of the brain and the nervous system.
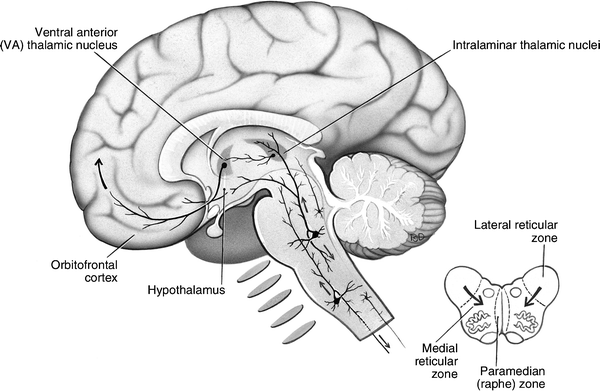
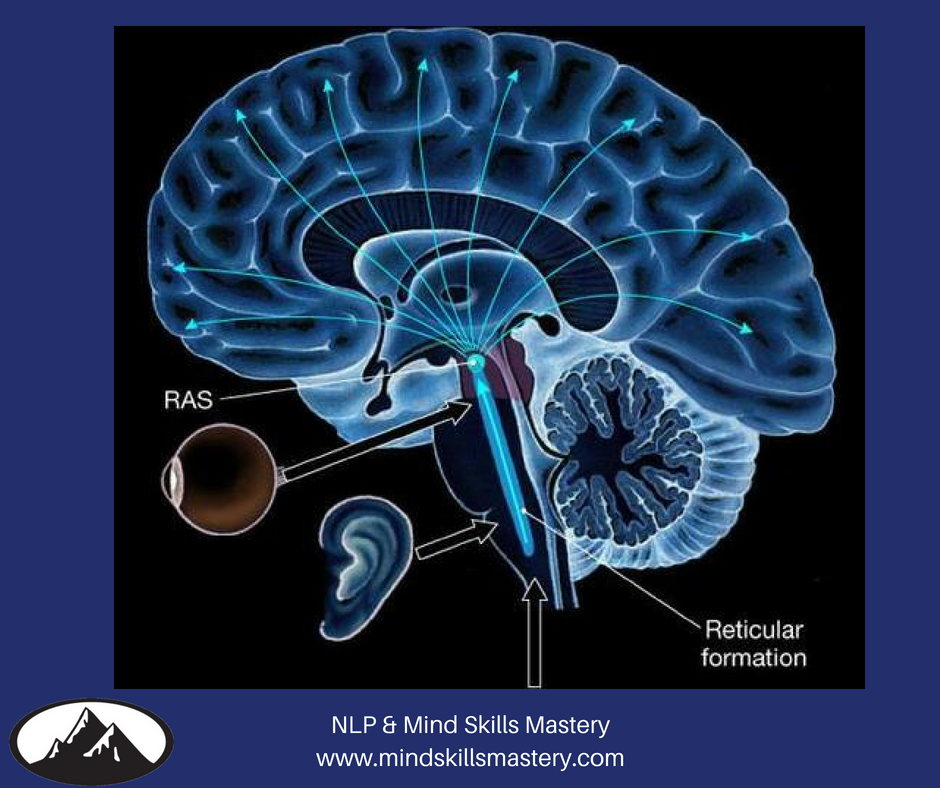
Reticular Activating System. The ARAS is part of the reticular formation, which consists of a network of neurons in the central portion or core of the brainstem from the medulla through the pons and midbrain and into the diencephalon. From: de Lahunta's Veterinary Neuroanatomy and Clinical Neurology (Fifth Edition), 2021. Related terms: Thalamus The reticular formation is a vast network of neurons that are involved in maintaining consciousness and initiating arousal. This neuronal tract extends from the spinal cord to the diencephalon and occupies different parts of the brainstem throughout. The nuclei of the reticular formation are situated deep within the brainstem along its vertical ... system) and brain stem nuclei (vestibular, red, reticular formation, etc.) • Convey instructions to spinal cord motor neurons and send a copy of that information to higher levels Segmental Level (lowest) • Spinal cord • Contains central pattern generators (CPGs) Internal feedback (b) Structures involved Precommand level • Cerebellum The reticular formation. In reality, if you look at its physiology, the reticular formation is a multineuronal post-synaptic formation. It has axons that are transversely and longitudinally arranged. However, it doesn't transmit any specific messages, such as sensitive, regional, or motor.
reticular formation. The white matter consists of myelinated tracts connecting the cerebrum with the spinal cord and various cranial nerve nuclei. Midbrain Anatomy The midbrain connects the pons and cerebel-lum with the forebrain and can be divided into a ventral part, the tegmentum, and a dorsal part, the tectal or quadrigeminal plate (Figs 2, 3). Define reticular formation. reticular formation synonyms, reticular formation pronunciation, reticular formation translation, English dictionary definition of reticular formation. n. A diffuse network of white longitudinal nerve fibers interspersed with gray matter, located in the brainstem, that regulates various autonomic functions,... Diagram showing the lobes of the brain. Image Source: Wikimedia Commons. ... the only important structure in the midbrain that you need to know is the reticular formation. The important structures in the hindbrain that you will need to know are the medulla, pons, and the cerebellum. The reticular formation is a complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival. The structure of the reticular formation forms a net-like connection of nuclei and neurons, hence its name "reticular," which correlates to its function of integrating, coordinating, and ...
This formation and some neurons in the thalamus, together with others from various sensory systems of the brain, make up the reticular activating system—the means by which we maintain consciousness. The reticular activating system also comes into play when we deliberately focus our attention, "tuning out" distractions to some degree.
Brain Diagram Reticular Formation. Like the spinal cord, the brain is made of mainly gray matter and white matter and hypothalamus); limbic system; reticular activating system. The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the The human reticular formation is composed of almost brain nuclei and contains ...
Reticular Formation Location. The reticular formation is located mainly in brain stem. The reticular formation cranial extension is upto the dienceph-alon (subthalamus, hypothalamus and thalamus) and caudally extended to the spinal cord in the cervical region. These extensions are either actual or projectional.
Reticular Formation Diagram. angelo. July 3, 2021. Pin By Jason Sun On Projets A Essayer Cholinergic Gene Therapy Hypothesis. Reticular Activating System Cholinergic Slow Wave Sleep. Reticular Formation The Reticular Formation Extends Through The Central Core Of The Medulla O Reticular Formation Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy ...
The reticular formation is a part of the brain which is involved in stereotypical actions, such as walking, sleeping, and lying down.It is absolutely essential for life. The reticular formation, phylogenetically one of the oldest portions of the brain, is a poorly-differentiated area of the brain stem, centered roughly in the pons, but with the ascending reticular activating system connecting ...
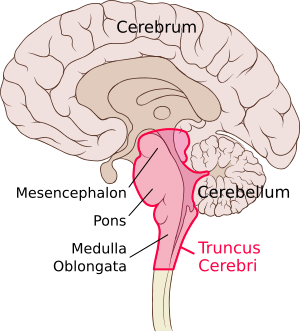
Brain Divisions . The forebrain is the division of the brain that is responsible for a variety of functions including receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function. There are two major divisions of forebrain: the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The diencephalon contains structures such as the ...
The reticular formation is a nerve network of nuclei clusters found in the human brain stem. The dorsal tegmental nuclei are in the midbrain, the central tegmental nuclei are in the pons, and the ...
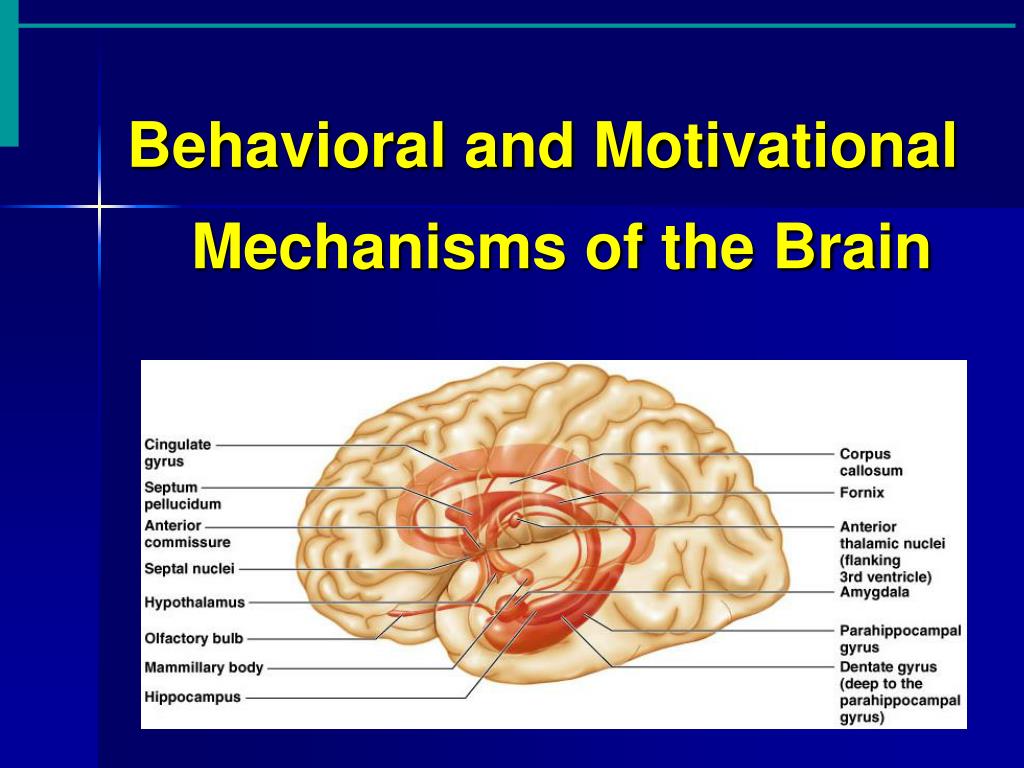
The limbic system and reticular formation are networks of neurons that function together even though they are widely separated. The limbic system is the "emotional brain" made of deep gray matter structures linked together by the fornix.. The fiber tracts have the appearance of oval fibers and looks like the corpus callosum but it's not the same.
Reticular Formation. core of brain stem; monitors incoming sensory information and attention. Thalamus. receives information and prioritizes and distributes it accordingly. ... Brain Diagrams. 75 terms. cmmontanye. Labeling Brain and Ventricles. 19 terms. mkcoleman PLUS. Brain Anatomy. 103 terms. Axelknows. YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE... Parts of the ...
Definition. The reticular formation is a neuron network in the brainstem that enables consciousness, sensory and motor function, and endocrine and neurotransmitter regulation. This part of the central nervous system, spread in three main columns from one end of the brainstem to the other, is a core relay point that connects the nerves of the spinal cord with the brain via efferent and afferent ...
The reticular formation controls muscle tone in the body and acts as the switch between consciousness and sleep in the brain. The medulla oblongata is a roughly cylindrical mass of nervous tissue that connects to the spinal cord on its inferior border and to the pons on its superior border.
The Reticular Activating System (RAS) of the brain stem is considered as one of the most important systems which facilitates the functioning of sensation and attention. This is made up of a net-like bundle of neurons that run through the hind-brain, mid-brain and a part of the fore-brain called the hypothalamus.
The reticular activating system connects the brain stem, to the cerebral cortex, through various neural paths. The stem controls most of the involuntary functions, as well as reflexes of the body, while the cerebral cortex is the seat of consciousness and thinking abilities. The system forms a link between these two different regions, helping ...
Controls/regulates heartbeat and breathing To and from brain Reticular Formation Helps control arousal, responds to change in monotony Thalamus Relays sensory information, switchboard between sensory neurons and higher brain regions Deals with sight, hearing, touch, taste. Transmits replies from higher brain to cerebellum and medullam
The reticular formation is a cluster of nerves within the brainstem that relay sensory and motor signals to and from the spinal cord and the brain. It aids in the control of autonomic and endocrine functions, as well as muscle reflexes and sleep and awake states. The red nucleus is a mass of cells that aids in motor function. Substantia nigra ...



















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11464/image5.png)




0 Response to "41 brain diagram reticular formation"
Post a Comment