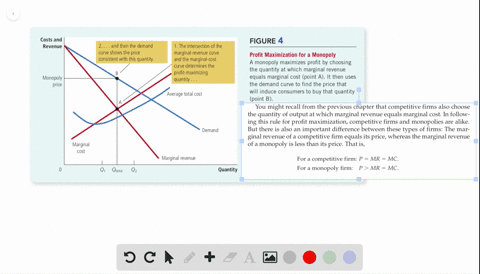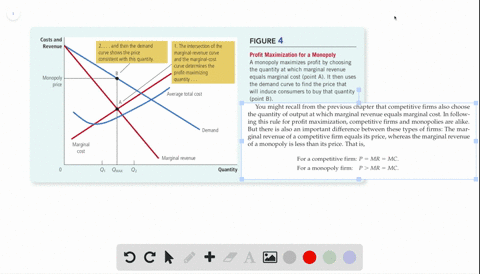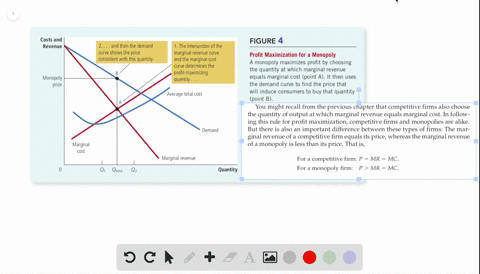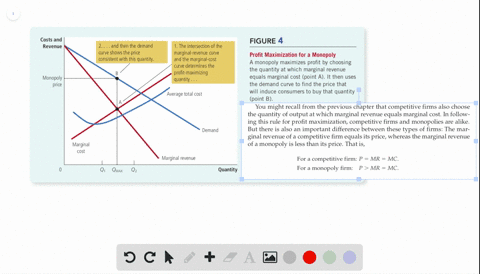
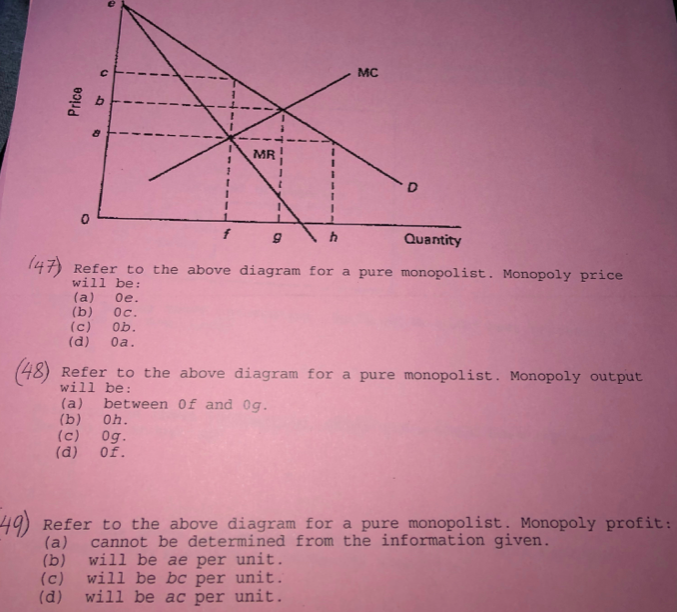
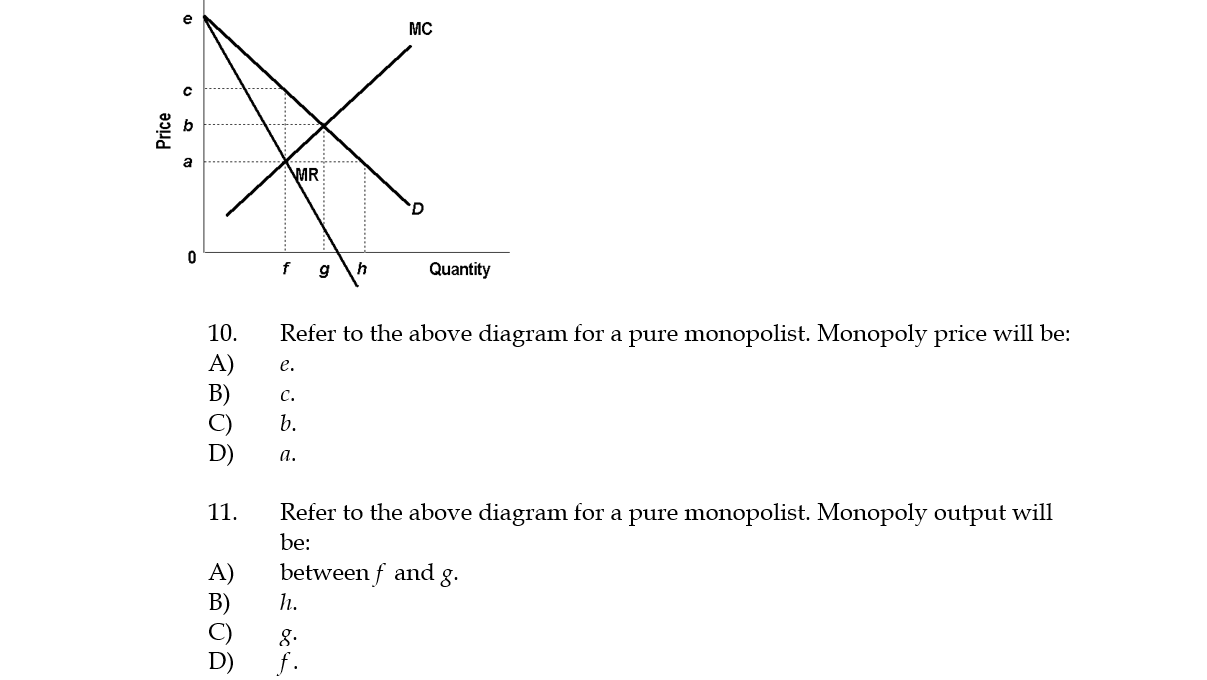
40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
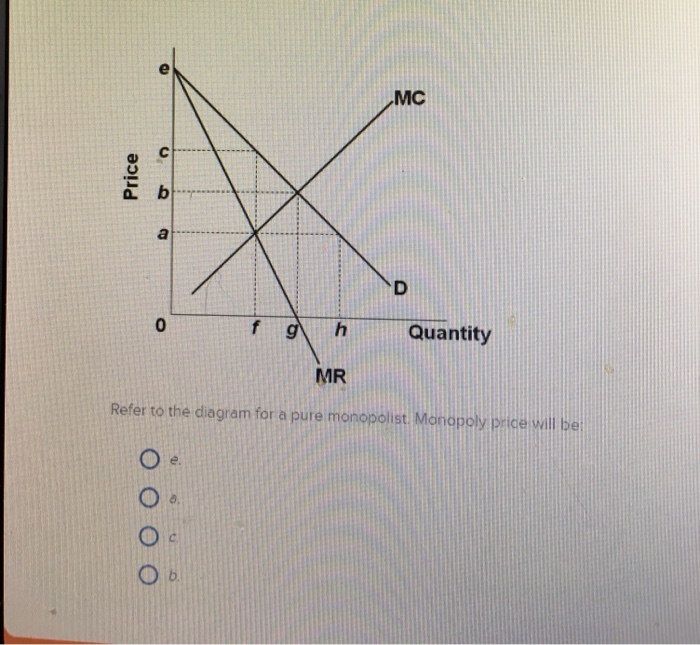
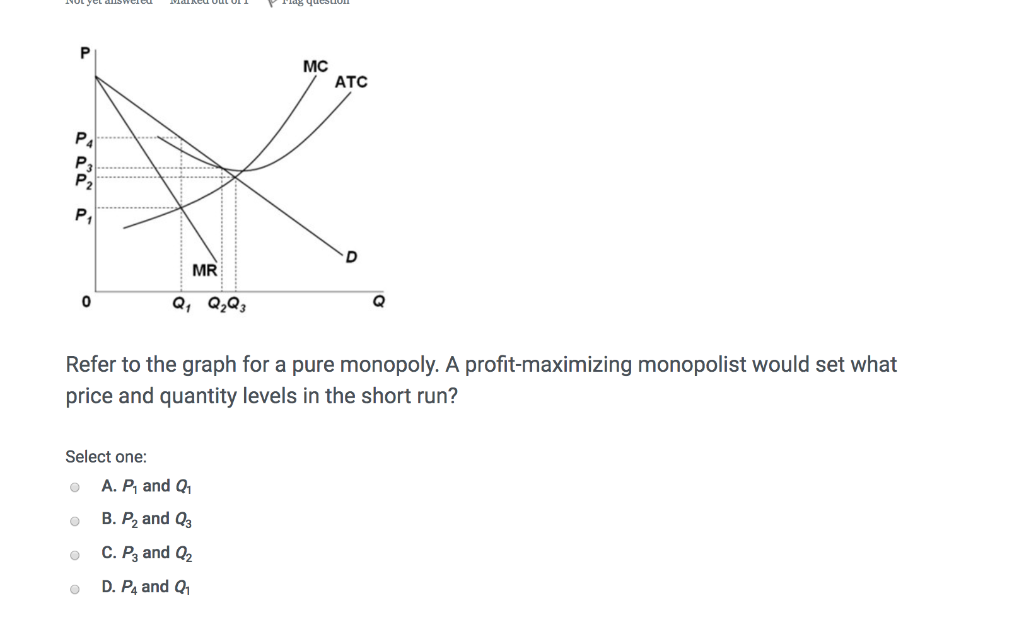
22. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: A. e. B. c. C ... Price (per Quantity demanded domestically Quantity supplied domesticall 1 answer This question: 3 point(s) possible Minnie's Salon is a single price monopoly The table shows the demand schedule for Minnie's Salon (columns 1 and 2) and the firm's total cost schedule (columns 2 and
5. A grocery store sells a bag of potatoes at a fixed price of $2.30. Which of the following is a term used by economists to describe the money received from the sale of an additional bag of potatoes? (Points : 1) marginal revenue gross earnings pure profit marginal costs net benefit 6.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be
8. (TCO 3) One feature of pure monopoly is that the monopolist is. 9. (TCO 3) Barriers to entry. 10. (TCO 3) The demand curve confronting a non discriminating, pure monopolist is. 11. (TCO 3) Which is the best example of price discrimination? 12. (TCO 3) Monopolistic competition is characterized by firms. 13. Change in the price of a good divided by the change in the quantity of that good demanded. 10. For a monopolist, the price of a product: Equals the marginal revenue. Equals the marginal cost. Is less than the marginal revenue. Exceeds the marginal revenue. 11. A perfectly competitive firm facing a price of $50 decides to produce 500 widgets. E units and charge price A. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: Refer to the above diagram to maximize profits or. 80. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: A. Eunits and charge price CB.Eunits and charge price AC.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be. setting a price higher than the market price results in increased profits. each firm's product is slightly different. each firm influences the price because it has a significant market share. each firm faces a relatively inelastic demand curve. setting a price higher than the market price results in zero sales.Question 43 (Multiple Choice Worth ... 40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be Price discrimination is a microeconomic pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different p... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly price will be A e B c from ECON 202 at Old Dominion University. Diagram of Profit Maximis at ion. To understand this principle look at the above diagram. If the firm produces less than Output of 5, MR is gre at er than MC. The refore, for this extra output, the firm is gaining more revenue than it is paying in costs, and to tal profit will increase. long as bL<aK. If bL>aK the n an increase in labor by one unit doesn't change output at all—in o the r ...
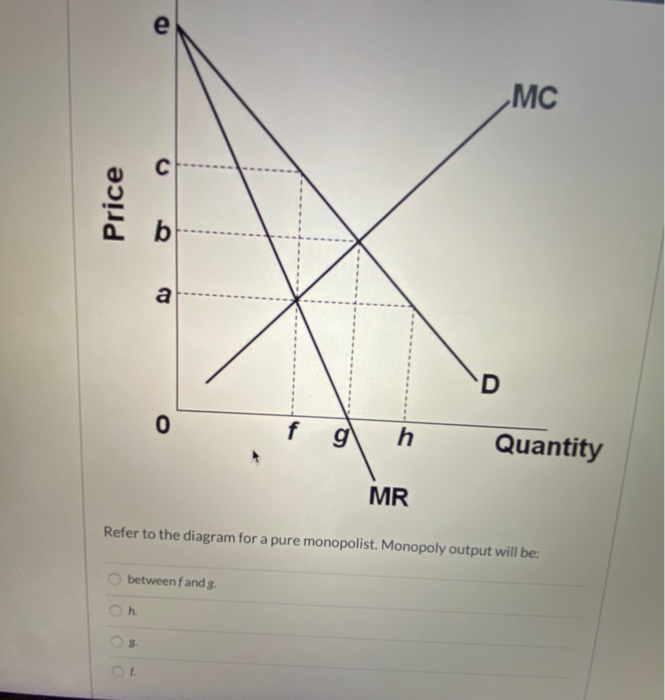
This is completely the opposite of VAT. The whole point of VAT is that it isn't double taxation -- if a business buys wholesale for $80 and sells retail for $100, they only have to collect VAT on the $20 difference and not the whole $100, because the wholesale seller already collected it on the $80. We offer students the best possible prices for legit assignment help services. Our experienced writers are adept at referencing your academic papers, which helps you get an A+ score in your subjects. You are sure to get 100% unique and spotless assignment write-ups. We help you stick to your deadlines with our swift deliveries. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g ... 8. (TCO 3) One feature of pure monopoly is that the monopolist is. 9. (TCO 3) Barriers to entry. 10. (TCO 3) The demand curve confronting a non discriminating, pure monopolist is. 11. (TCO 3) Which is the best example of price discrimination? 12. (TCO 3) Monopolistic competition is characterized by firms. 13.
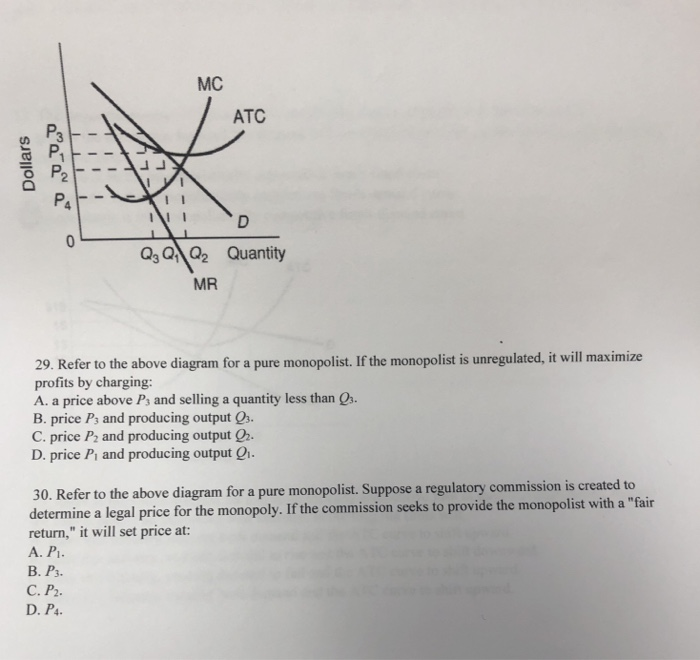
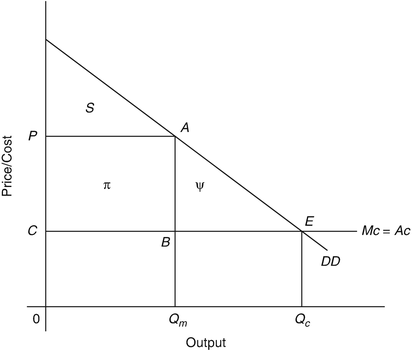
[Solved] The graph shows the relevant curves for a prot ... Solved: BYOB Is A Monopolist In Beer Production And Distri ... Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output ... ECON 312 Midterm Exam. 1. (TCO 1) As a student of economics, when you speak of scarcity, you are referring to the ability of society to 2. (TCO 1) The idea in economics that "there is no free lunch" means that 3. (TCO 1) (TCO 1) The law of increasing opportunity costs indicates that 4. (TCO 1) A tradeoff exists between two economic goals, X and Y. A pure monopolist determines that at the current level of output the marginal cost of production is $2, average variable costs are $2.75, and average total costs are $2.95. The marginal revenue is $2.75. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A) a price above P3 and selling a ...
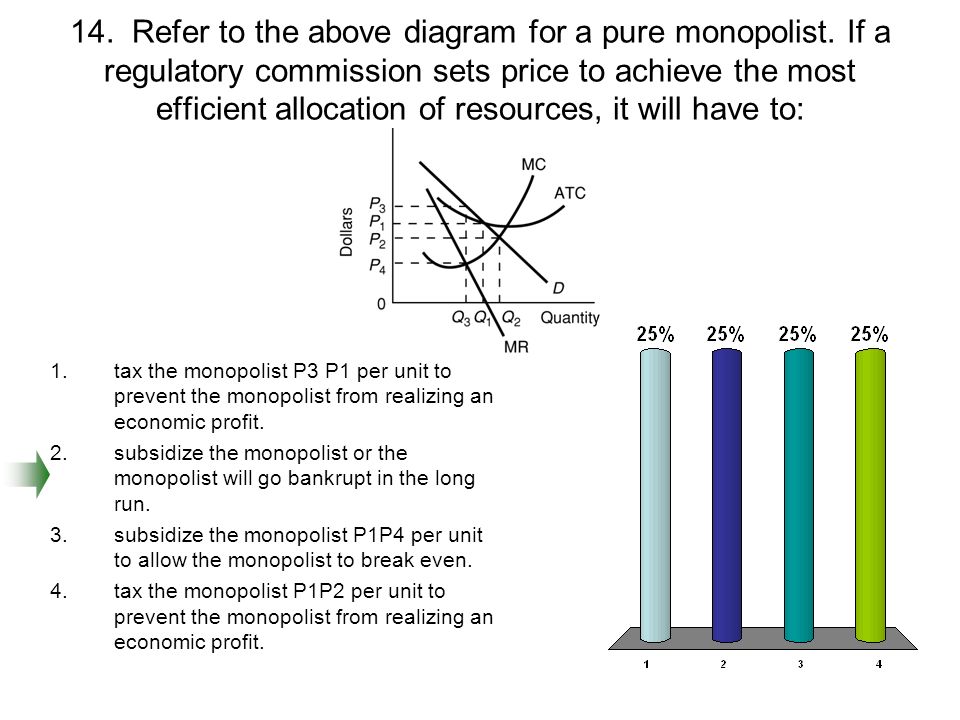
Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly.
View Screen Shot 2021-11-29 at 16.34.09.png from ECON 2302 at Austin Community College. Question 1 1 2.5 out of 2.5 points r7. Refer to the below graph. The pure monopolist firm will charge a price
They have the ability to set monopoly prices, produce a monopoly quantity, and allocate monopoly as inefficiently as it is in the monopoly market structure. A formal method of collusion usually common among international brings forth a cartel. Oligopoly graph. Different diagrams explain the oligopoly markets.
37 ford 4.0 sohc timing chain diagram. Written By Chelsea P. Mariano Saturday, November 20, 2021 Add Comment. Edit. This video covers the removal and installation of the timing drive system for applications with the Ford 4.0 L SOHC engine. 11 May 2011 — Background: The Ford 4.0 L single overhead camshaft ( SOHC) V6 engine manufactured in ...
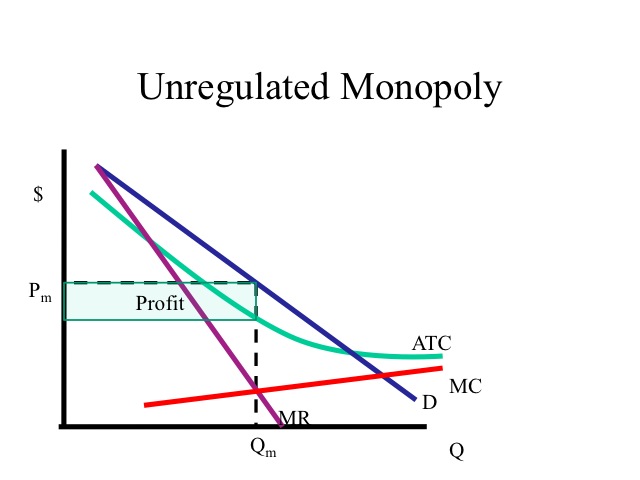
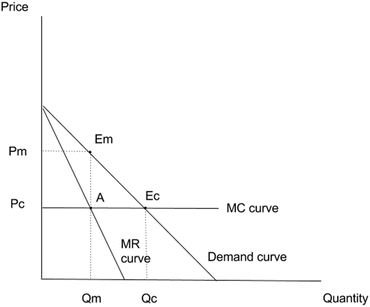
A monopoly occurs when a single seller can set market prices because it faces little to no competition. Monopolies are disastrous for consumers because the lack of competition allows monopolists to restrict market output and artificially increase prices. This reduces consumer surplus and economic welfare, which is why monopolies have been ...
ECON 312 Midterm Exam. 1. (TCO 1) As a student of economics, when you speak of scarcity, you are referring to the ability of society to 2. (TCO 1) The idea in economics that "there is no free lunch" means that 3. (TCO 1) (TCO 1) The law of increasing opportunity costs indicates that 4. (TCO 1) A tradeoff exists between two economic goals, X and Y.
Feb 25, 2019 - This Animal Cell includes: #Nucleus #Rough endoplasmic ... Diagram s are amazing because you can use your artistic abilities to learn! Plant Cell Color ing. An image of a plant cell needs to be color ed, make sure that you match the color with the appropriate organelle; ribosome, chloroplast ... Nov 9, 2015 - Students will use the color code chart to color each cell organelle ...
Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. Chapter 011 Pure Competition in the Short Run AACSB: Reflective Thinking Type: Graph Refer To: 8_28 [Question] 29. Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm.
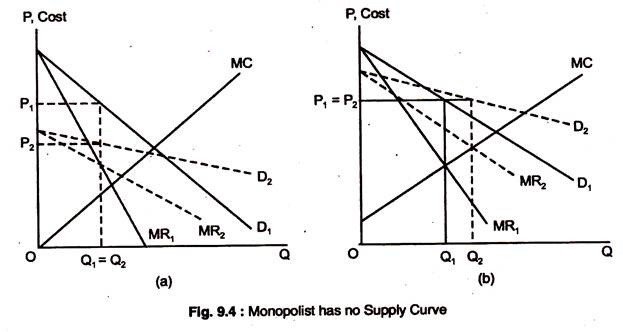
The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is: -$1. Which of the diagrams correctly portrays a nondiscriminating pure monopolist's demand (D) and marginal revenue (MR) curves? The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is A. -$1. Correct B. $1. C. $4. D. $24. Why is it A?
60. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: c.
Monopoly price will be: A) e. B) c. C) b. D) a. 11. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A) between f and g.
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, a price system, private property and the recognition of property rights, voluntary exchange and wage labor. In a capitalist market economy, decision-making and investments are ...
Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers. ... If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A) lose P1P 2ba ...
19.11.2021. Internet and its effects on competition - Europa
Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . B) g. Ch. D) between fand g. 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR. 60.
ECON 312 Midterm Exam. 1. (TCO 1) As a student of economics, when you speak of scarcity, you are referring to the ability of society to 2. (TCO 1) The idea in economics that "there is no free lunch" means that 3. (TCO 1) (TCO 1) The law of increasing opportunity costs indicates that 4. (TCO 1) A tradeoff exists between two economic goals, X and Y.
At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's to tal revenue: 400 Refer to the diagram. at output level q, average fixed cost In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the to tal cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented, the cost of producing additional quantity.
Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output ... Refer To The Diagram For A Pure Monopolist Monopoly Output ... Pure Monopoly; ... Solved: 8. Price-discriminating Monopolist Aa Aa Daesun, A ... Business Game: Monopolist App for iPhone - Free Download ...
E units and charge price A. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue will be: Refer to the above diagram to maximize profits or. 80. Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: A. Eunits and charge price CB.Eunits and charge price AC.
Change in the price of a good divided by the change in the quantity of that good demanded. 10. For a monopolist, the price of a product: Equals the marginal revenue. Equals the marginal cost. Is less than the marginal revenue. Exceeds the marginal revenue. 11. A perfectly competitive firm facing a price of $50 decides to produce 500 widgets.
8. (TCO 3) One feature of pure monopoly is that the monopolist is. 9. (TCO 3) Barriers to entry. 10. (TCO 3) The demand curve confronting a non discriminating, pure monopolist is. 11. (TCO 3) Which is the best example of price discrimination? 12. (TCO 3) Monopolistic competition is characterized by firms. 13.









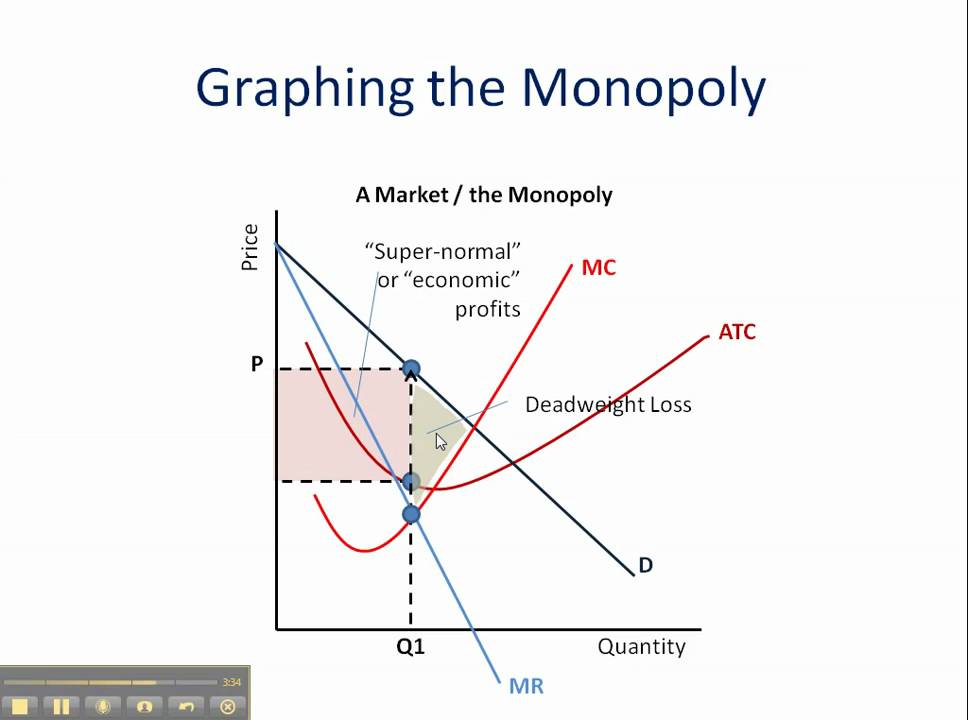
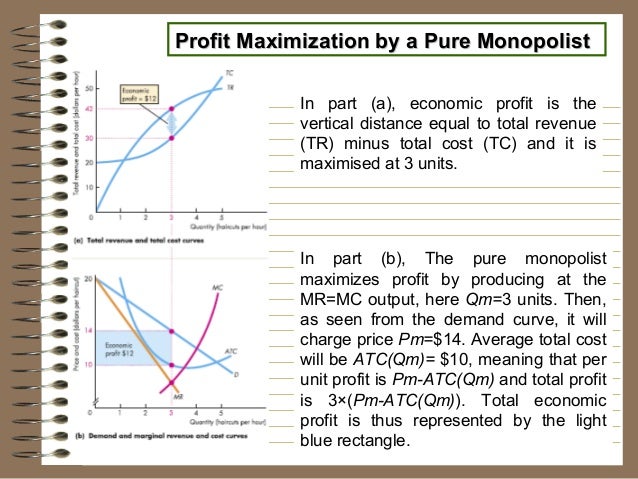




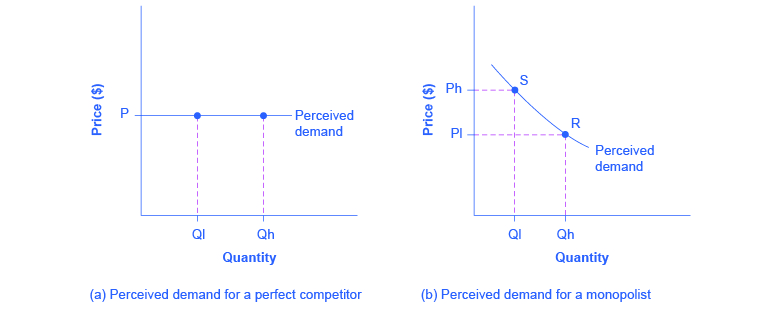

0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly price will be"
Post a Comment