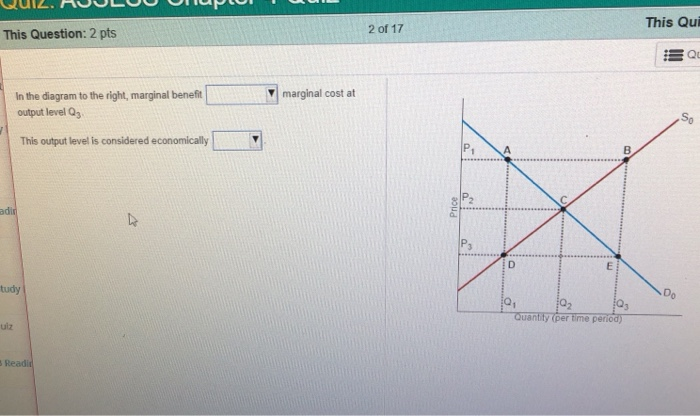
40 in the diagram to the right, marginal benefit
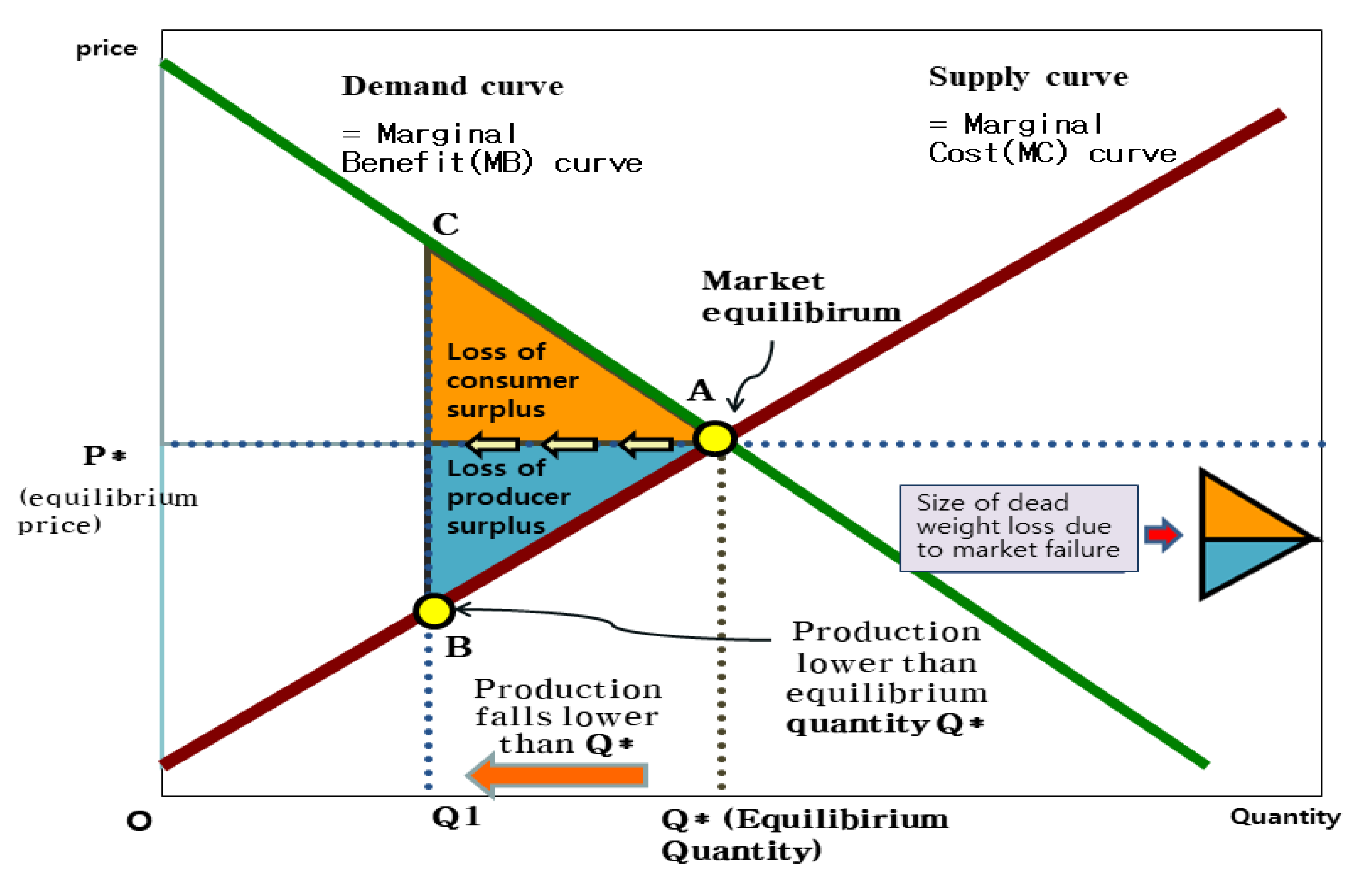
b) Always buy at additional unit if its marginal net benefit is positive. c) Keep buying more units if marginal cost is greater than marginal benefit. d) Always buy at additional unit if its marginal benefit is positive. 8. Refer to the supply and demand diagram below. Another difference that the externality diagram has to an ordinary supply and demand diagram is the vertical axis which is labelled costs/benefits rather than price. Whenever drawing an externality diagram, it is always the social curve that is moved, whether that is marginal social cost or marginal social benefit.
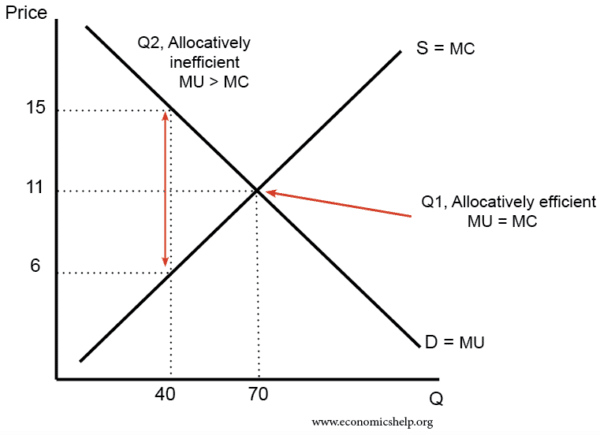
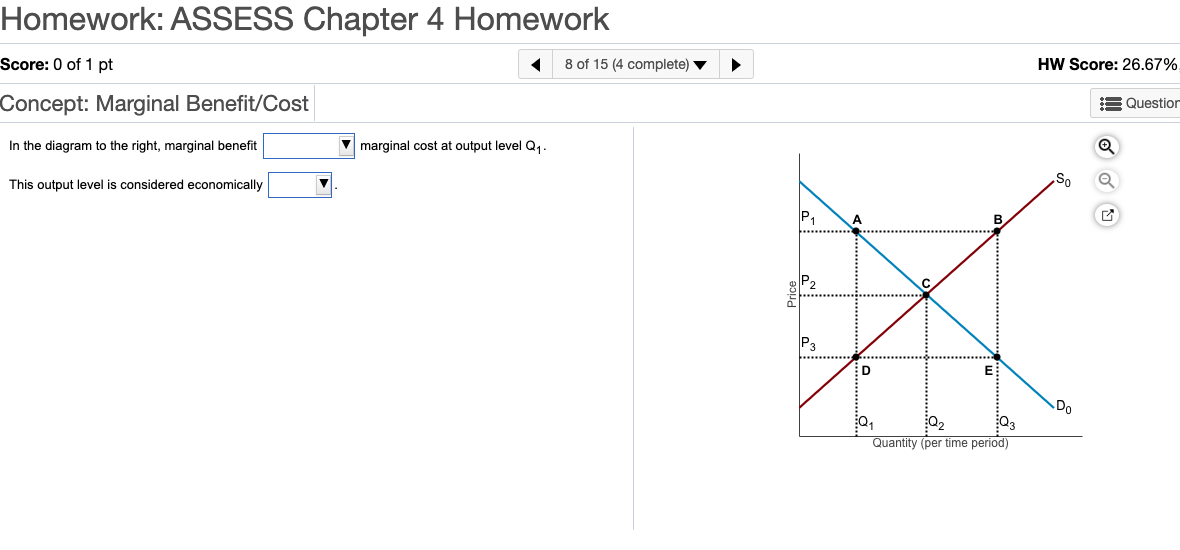
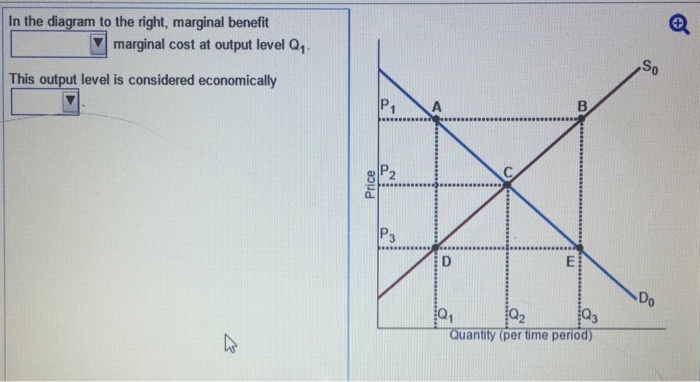
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit is equal to is less than is greater than marginal cost at output level Upper Q 3 Q3. This output level is considered economically neutral efficient inefficient ....
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit
Marginal benefit and marginal cost are two measures of how the cost or value of a product changes. While the former is a measurement from the consumer side of the equation, the latter is a ... Transcribed image text: In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit marginal cost at output level Q1 This output level is considered economically : D Do ... In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit _____ marginal cost at output level Q3. This output level is considered economically _____. is less than; inefficient-At Q3, supply is greater than demand.
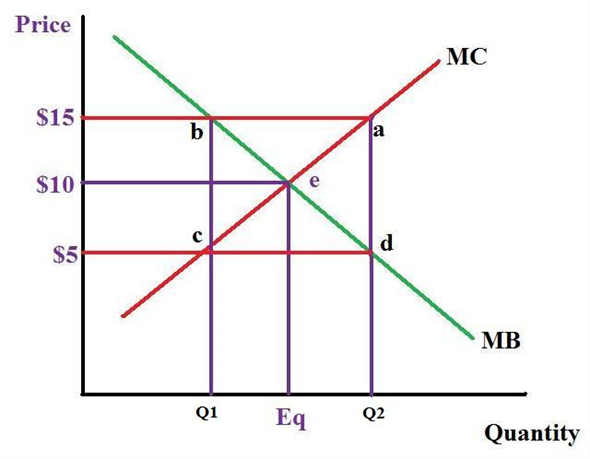
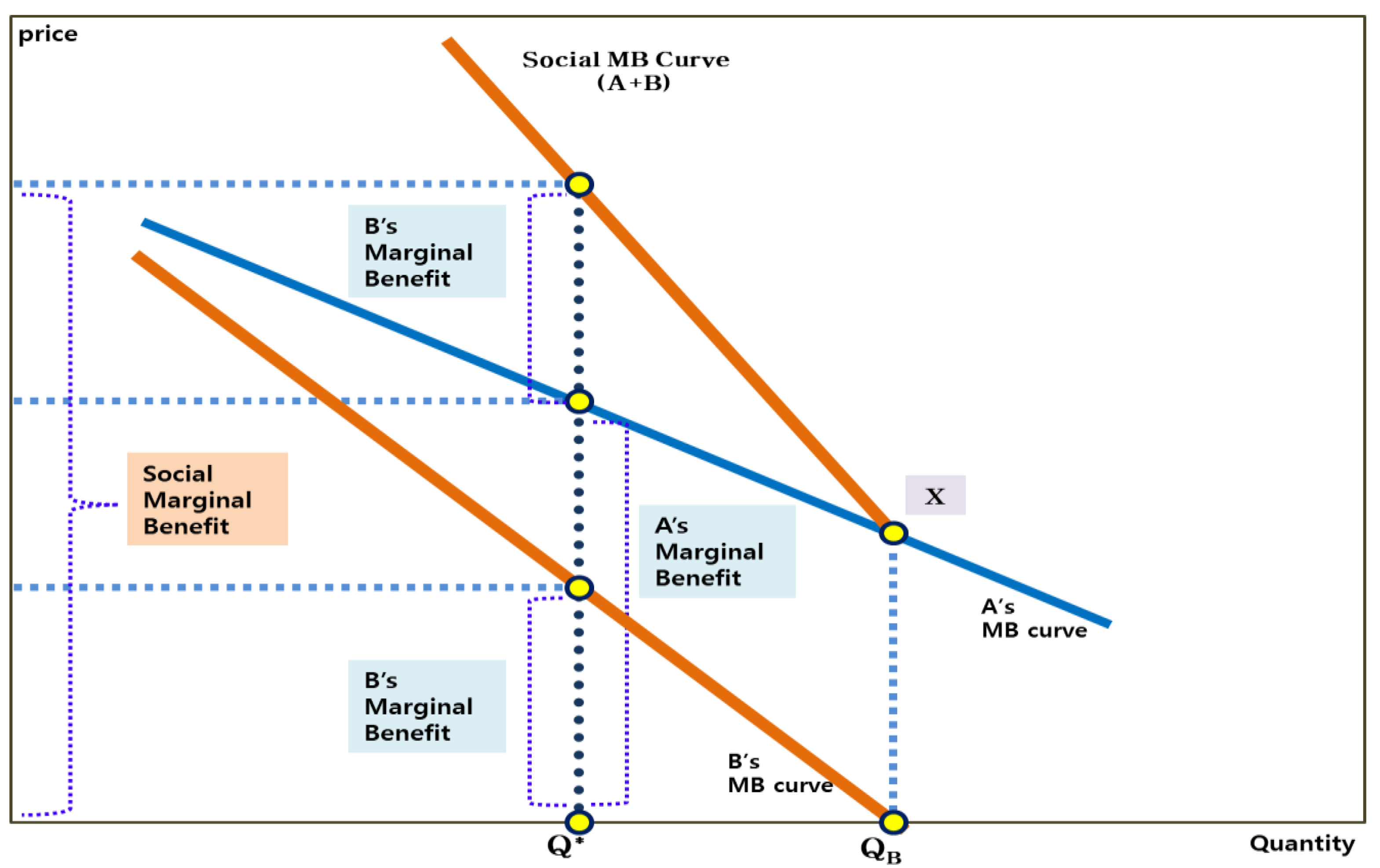
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit. 2 The diagram shows the private and social marginal costs and benefits curves for the antibiotics market. The market equilibrium is at point X. P1 QQ1 P O MPC = MSC MSB MPB X output cost benefit Why does market failure occur? A There is overconsumption and overpricing. B There is overproduction and under-pricing. C There is underconsumption and ... Consumer and producer surplus measure the net benefit rather than the total ... In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost ... In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit marginal cost at output level . is equal to Q This output level is considered economically . efficient Quantity (per time period) Price C B A D E In the diagram to the right, illustrating a binding price ceiling at P 3, the amount of producer surplus transferred to consumers is represented by area ... A negative consumption externality as shown in the diagram below, leads to marginal social benefit which is below the marginal private benefit, and a socially optimal quantity of output (Q2) that is below the competitive market equilibrium output(Q1) (private optimal output). Thus, we say that there is overconsumption of Q1-Q2.
a) Taking actions whenever the marginal benefit is positive. b) Taking actions only if the marginal cost is zero. c) Taking actions whenever the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost. d) All of the above. 2. Jane's marginal benefit per day from drinking coke is given in the table below. marginal benefit (for consumers) marginal benefits curve net benefits market (or aggregate) benefits market consumer surplus producer surplus marginal cost.12 pages Marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost at… View the full answer Transcribed image text : In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit ーー | marginal cost at output level Q1 This output level is considered economically As firms and consumers consider only private costs and benefits, the divergence between the marginal social benefit and the marginal private benefit of healthcare results in under-consumption. In the above diagram, due to external benefits, the marginal social benefit (MSB) is higher than the marginal private benefit (MPB).
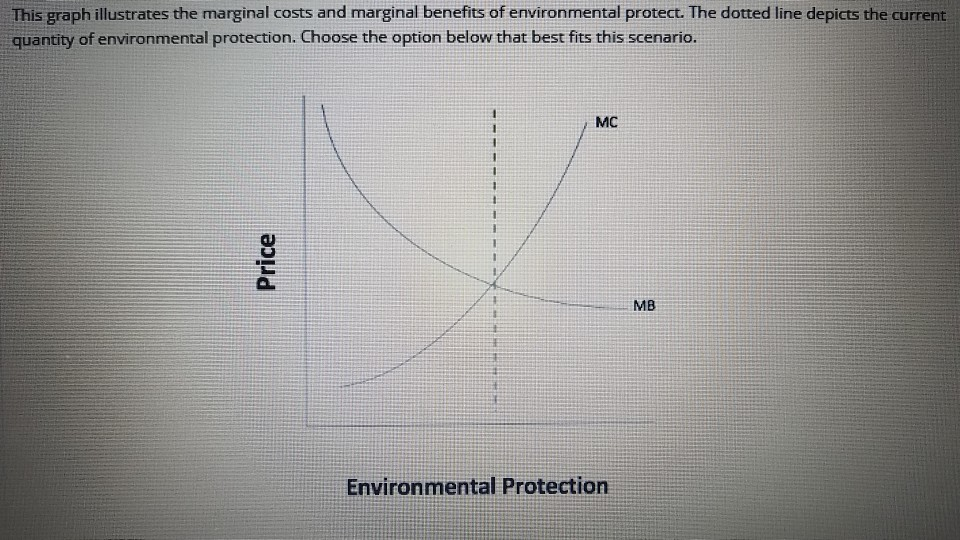
Draw a box diagram to show linkages between Nature and economy. ... the greater the marginal abatement cost. At its right end, the curve starts from the maximum level of emissions with no abatement efforts, ... MD can be interpreted as the marginal benefit of reducing emissions (damages saved), and MAC is the marginal cost of reducing emissions As we move toward the right along the horizontal axis, pollution is reduced through the application of environmental controls. Industrial emissions are entirely eliminated at 100%. The diagram indicates that as pollution is reduced the marginal benefit from an additional percentile reduction in air pollution declines. In the above diagram, the marginal social benefit (MSB) curve slopes downward from left to right. This indicates that the social benefit derived out of public expenditure is reducing at a diminishing rate. When the public expenditure was OM 1, the margina social benefit was OB ... Consider our diagram of a negative externality again. Let's pick an arbitrary value that is less than Q 1 (our optimal market equilibrium). Consider Q 2.. Figure 5.1b. If we were to calculate market surplus, we would find that market surplus is lower at Q 2 than at Q 1 by triangle e.. The market surplus at Q 2 is equal to area a+b. [(a+b+c) - (c)].
The accompanying diagram shows the marginal social cost curve and the marginal social benefit curve of music. The socially optimal volume of music is the volume at which marginal social benefit and marginal social cost are equal (point O in the diagram). This is the case at a volume of 95 dB. b.
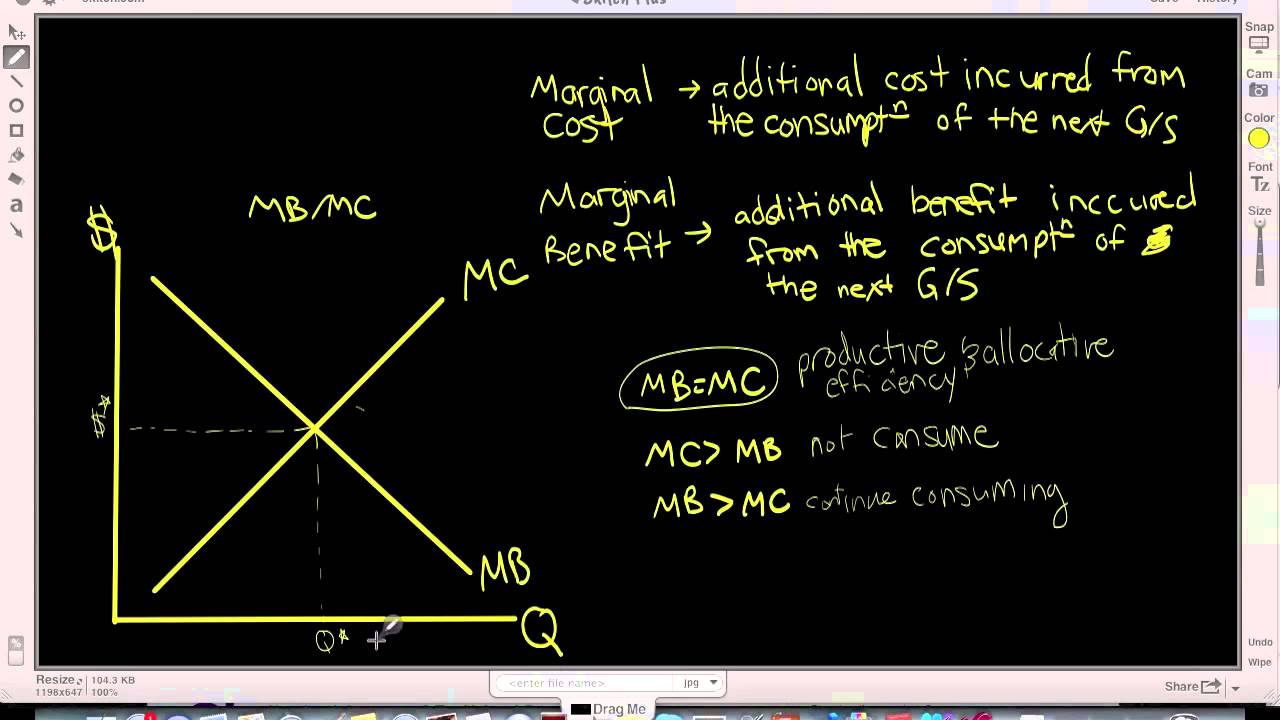
marginal benefit and marginal cost are equal. No resources beyond that point should be allocated to production. Theory: Resources are efficiently allocated to any product when the MB and MC are equal. Essential Graph: Application: External Costs and External Benefits External Costs and Benefits occur when some of the costs or the benefits of the
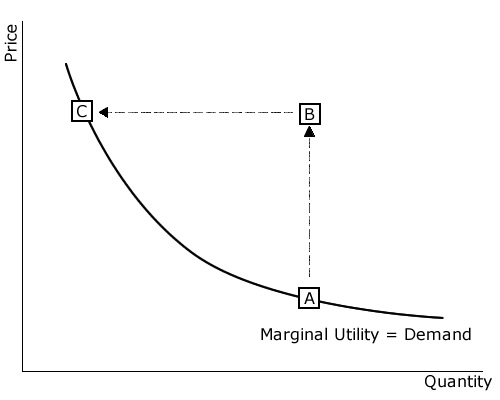
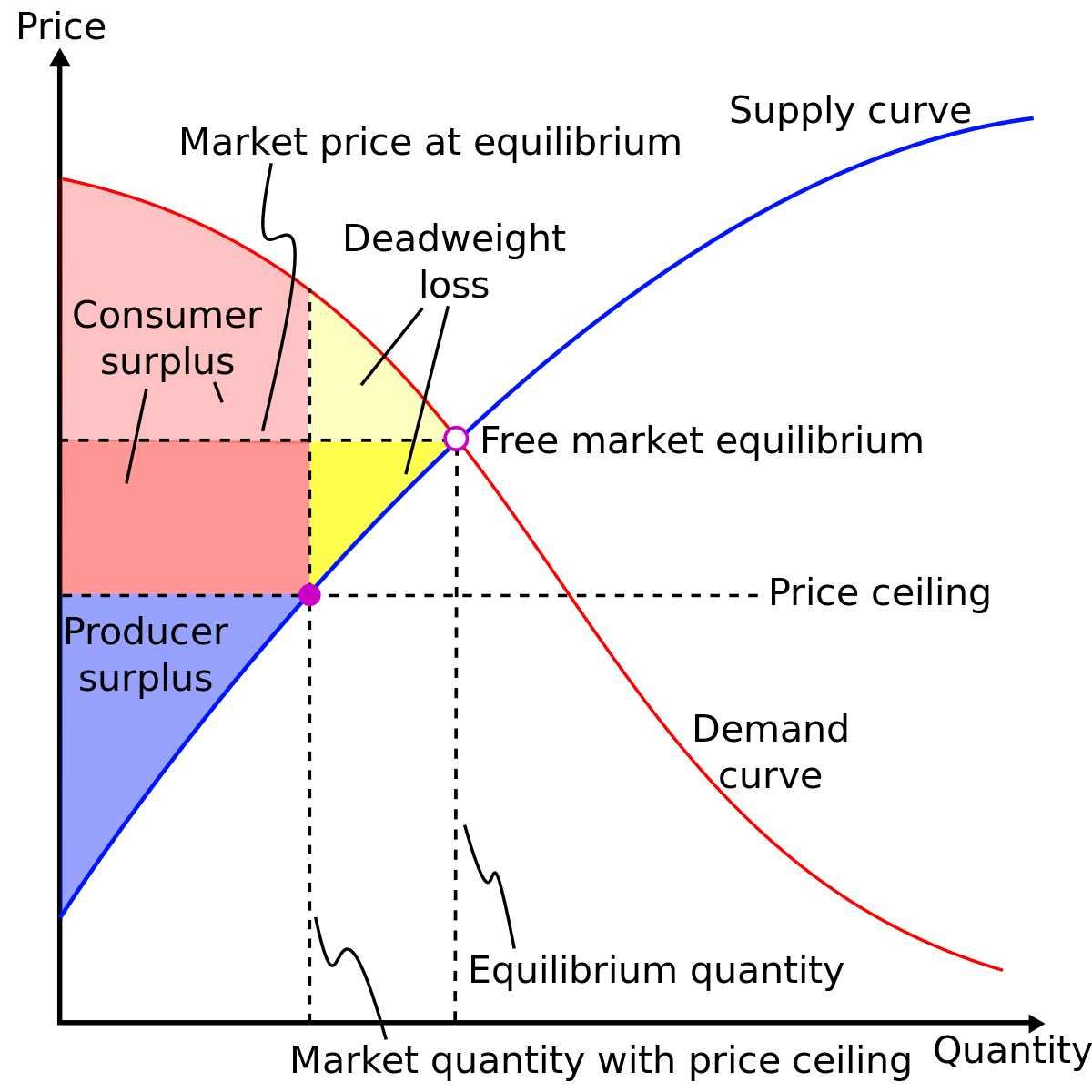
Marginal benefit is the additional benefit to a consumer from consuming one more unit of a good or service. The height of a market demand curve at a given quantity measures the marginal benefit to someone from consuming that quantity. Consumer surplus refers to the difference between this marginal benefit and the market price the consumer pays.
Consider the market for a public good such as dams along a river, illustrated in the figure to the right where S 1 represents marginal private costs and D 1 represents marginal private benefits. The dashed green line represents the corresponding marginal social benefit. The private market tends to underprovide public goods.
Marginal Cost vs. Marginal Benefit (With Examples) The differences between marginal cost and marginal benefit are important for companies to understand when developing operational plans for products. Regardless of the product type, these variables may influence company profits. Balancing marginal costs and benefits is valuable for maintaining ...
The diagram on the left shows a situation where the MSB (marginal social benefit) is higher than the MPB (marginal private benefit). What this means, is that the social benefit of using the good or service is higher than the private benefit of doing so (e.g. Education).
n the diagram to the right, marginal benefit is greater than is less than is equal to marginal cost at output level Upper Q 1. This output level is considered economically inefficient neutral efficient. is greater than, insufficient.
(i.e., that they are a series of appropriate vertical distances added ... “marginal cost and marginal benefit” diagram, which of course is the same diagram.
The diagram to the right illustrates a common economic relationship. Economists know this relationship as marginal cost (MC). The diagram illustrates the relationship between the change in total cost and quantity produced. There are three lines (A, B, and C) drawn tangent to the MC curve. At line A, the MC curve has a _____ slope.
(1) is less than is equal to is greater than (2) inefficient efficient neutral In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit (1) marginal cost at output level. Q This output level is considered economically (2) Quantity (per time period) Price C B A D E D 0 S 0 Q 2 P 2 Q 3 P 1 Q 1 P 3 1.
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit _____ marginal cost at output level Q1 (the lowest) The output level is considered economically _____. answer. is greater than. Inefficient. question. Consider the market for eggs illustrated in the figure to the right. Suppose the market is perfectly competitive and initially in equilibrium at a ...
marginal benefit and marginal cost are equal. No resources beyond that point should be allocated to production. Theory: Resources are efficiently allocated to any product when the MB and MC are equal. Essential Graph: Application: External Costs and External Benefits External Costs and Benefits occur when some of the costs or the benefits of the
C The marginal product of labour is maximised at ON 2. D The marginal product of labour is maximised at ON 3. 16 What would cause a perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue product of labour curve to shift to the right? A a higher rate of sales tax B a rise in the price of the final product C an increase in labour supply
Refer to the diagram. Which one of the following might shift the marginal benefit curve from MB1 to MB2? asked Jun 16, 2019 in Economics by anman. A - major new studies strongly linking cancer to pollution Correct. B - improved technology for reducing pollution.
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit-----marginal cost at output level Upper Q 2 This output level is considered economically---is equal to efficient.
In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit _____ marginal cost at output level Q3. This output level is considered economically _____. is less than; inefficient-At Q3, supply is greater than demand.
Transcribed image text: In the diagram to the right, marginal benefit marginal cost at output level Q1 This output level is considered economically : D Do ...
Marginal benefit and marginal cost are two measures of how the cost or value of a product changes. While the former is a measurement from the consumer side of the equation, the latter is a ...
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13352/zTUB0lRGW6c3TC5xKyjRBQ_Arteria_marginalis_dextra_01_copy.png)







/producer_surplus_final-680b3c00a8bb49edad28af9e5a5994ef.png)










0 Response to "40 in the diagram to the right, marginal benefit"
Post a Comment