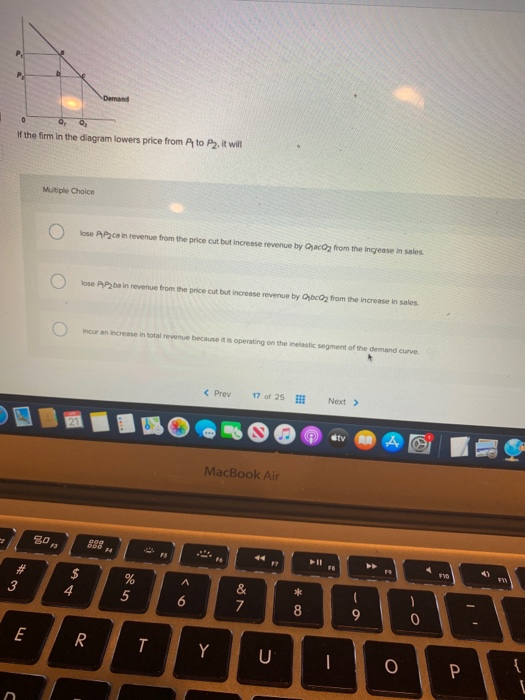
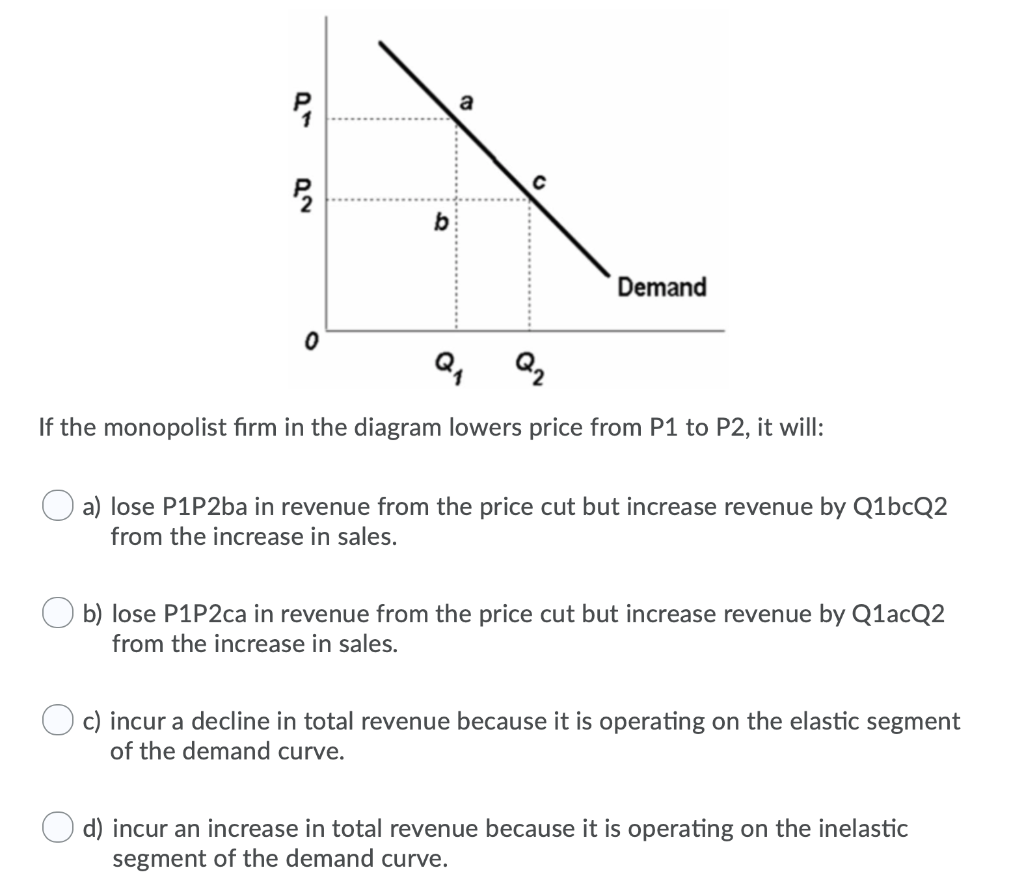
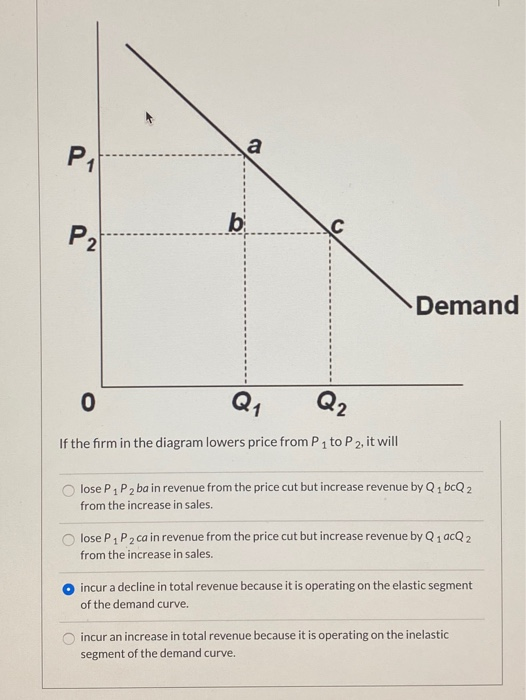
39 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
Get any needed writing assistance at a price that every average student can afford. Live Chat +1(978) 822-0999 Email WhatsApp. Order your essay today … maximising firm to charge a lower price (P2) but make higher total profits because of the fall in AC per unit Costs Output (Q) SRAC1 SRAC3 AR (Demand) MR MC1 MC2 P1 P2 Q1 Q2 Profit at Price P1 Profit at Price P2 Costs Output (Q) SRAC1 SRAC2 SRAC3 Q1 Q2 Q3 AC1 AC2 AC3 LRAC
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.

If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will
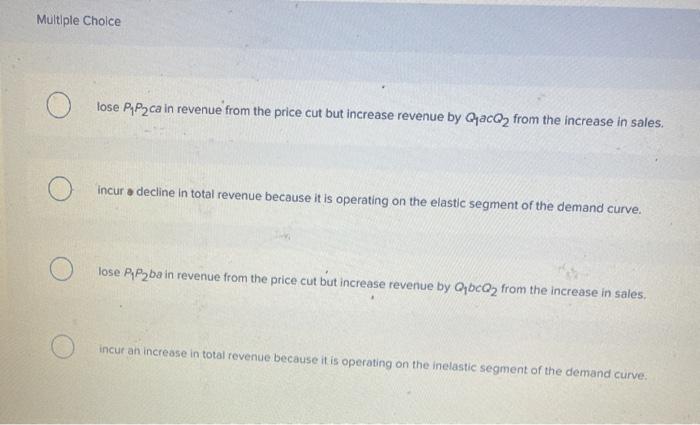
a single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. ... Refer to the above diagram. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, ... The quantitative difference between areas A and C for reducing the price from P1 to P2 measures: marginal revenue. Refer to the above diagram. This firm is selling in: an imperfectly competitive market. P2. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: will be less than $35. If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. A single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will. Lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales.
If the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will. The firm would have to lower its price to sell more than 10 units. ... price at P1, and suffer a loss . Q2, price at P2, and earn an economic profit . Q2, price at P2, and earn only a normal profit . Tags: Question 31 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . Q. For an unregulated monopolist, the profit-maximizing quantity will always be: If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A) lose P1P 2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B) lose P1P 2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales. solution-manual-mankiw-macroeconomics. Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. 17. If the firm in the above diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: A. lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. B. lose P1P2ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1acQ2 from the increase in sales.
Transcribed image text: Demand If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will lose P1 P2 ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ 2 from the increase in sales. lose P1 P2 ca in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q 1 acQ2 from the increase in sales. o incur a decline in total revenue because it is operating on the elastic segment of the ... If the company wants to realize a profit of P120,000, the selling price of each laundry hanger must be A. P2.50 B. P3.75 C. P4.50 D. P5.00 (Bobadilla) 130. An organization’s break-even point is 4,000 units at a sales price of P50 per unit, variable cost of … Every sweet feature you might think of is already included in the price, so there will be no unpleasant surprises at the checkout. 24/7/365 Support. You can contact us any time of day and night with any questions; we'll always be happy to help you out. Free Features. $15.99 Plagiarism report. $7.99 Formatting. If a firm is a price taker, then the demand curve for the firm's product is. perfectly elastic. ... If it lowers the price to $14, its total revenue increases by $22. This implies that its sold output increases by _____. ... Assuming equilibrium price P1 , …
A firm's marginal cost curve above the average variable cost curve is equal to the firm's individual supply curve. This means that every time a firm receives a … (Supposed to be a graph) In the accompanying diagram, if price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will a.) increase by A −C. b.) increase by C −A. c.) decrease by A −C. d.) decrease by C −A. A firm with monopoly power sells the same product in the US and Europe. The MC is $5 in both areas. The price elasticity is -1.5 in the US and -4 in Europe. What … If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales. The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist
The price paid by buyers declines by P1 - P2, shown in the figure as (PB. Sellers receive P2 and pay taxes of $1,000, receiving on net P2 - $1,000, a dcrease in what they receive by P1 - (P2 - $1,000), shown in the figure as (PS. Figure 2. Questions for Review. 1. An example of a price ceiling is the rent control system in New York City.
A single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. ... If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will. Lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales.
P2. If a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm is selling its 100th unit of output for $35, its marginal revenue: will be less than $35. If the firm in the diagram lowers price from P1 to P2, it will: lose P1P2ba in revenue from the price cut but increase revenue by Q1bcQ2 from the increase in sales.
a single firm producing a product for which there are no close substitutes. ... Refer to the above diagram. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, ... The quantitative difference between areas A and C for reducing the price from P1 to P2 measures: marginal revenue. Refer to the above diagram. This firm is selling in: an imperfectly competitive market.














/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)



0 Response to "39 if the firm in the diagram lowers price from p1 to p2, it will"
Post a Comment