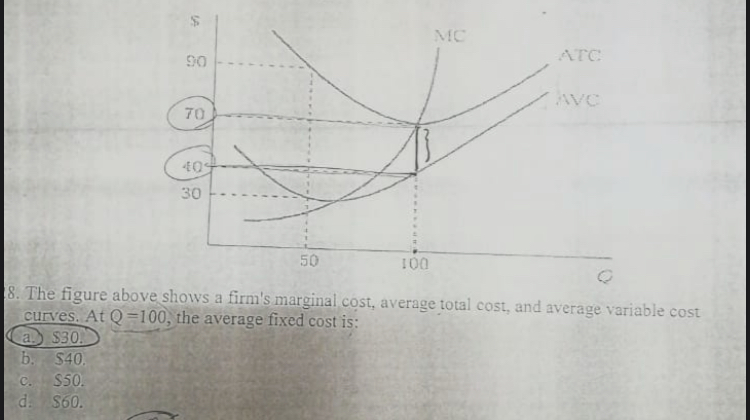
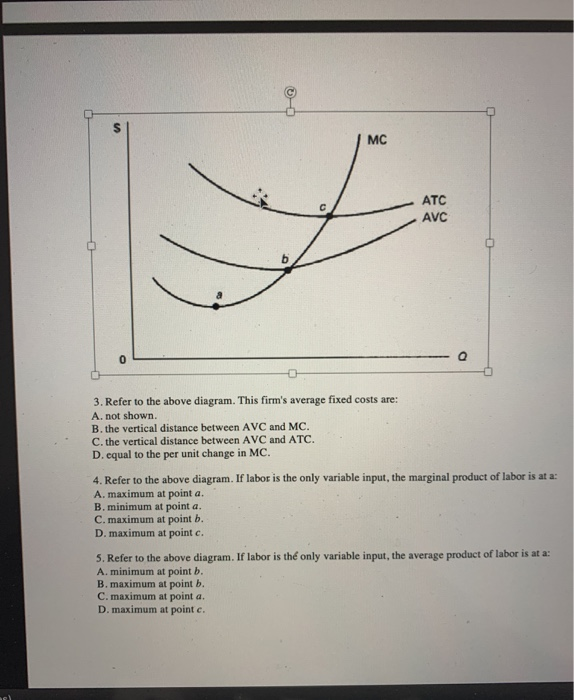
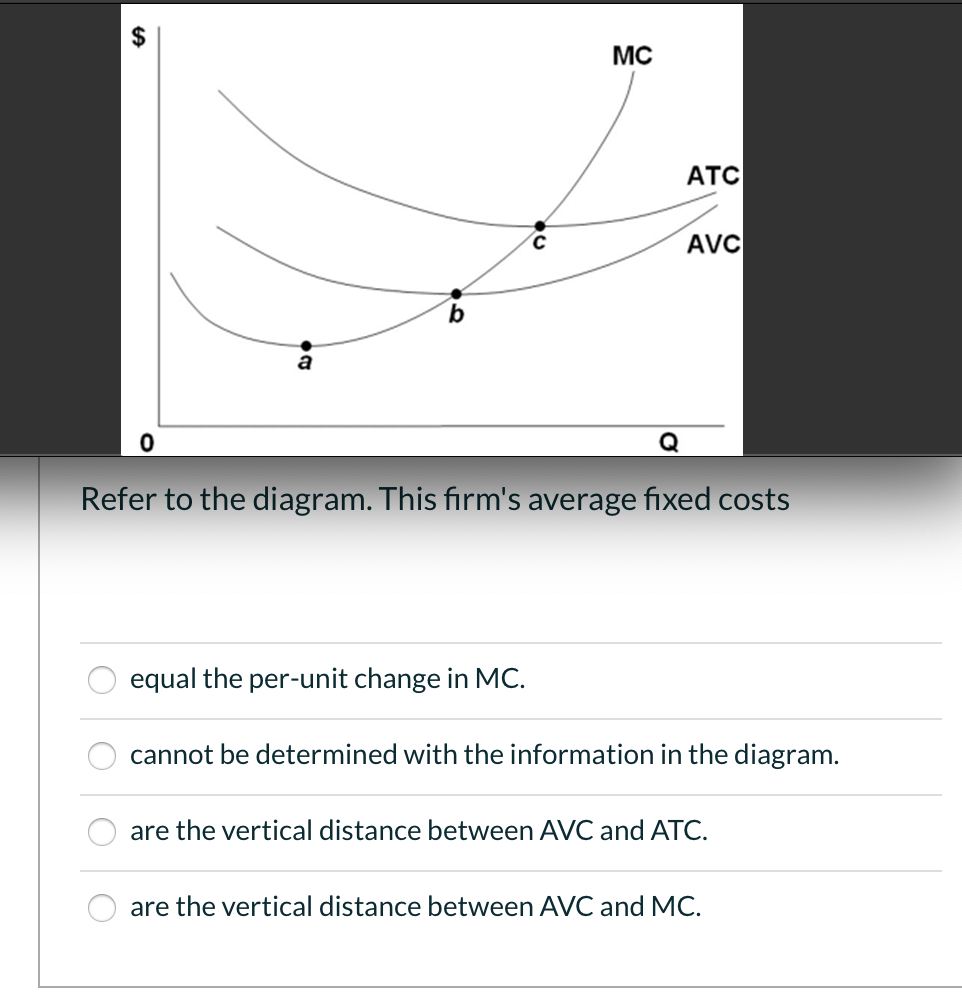
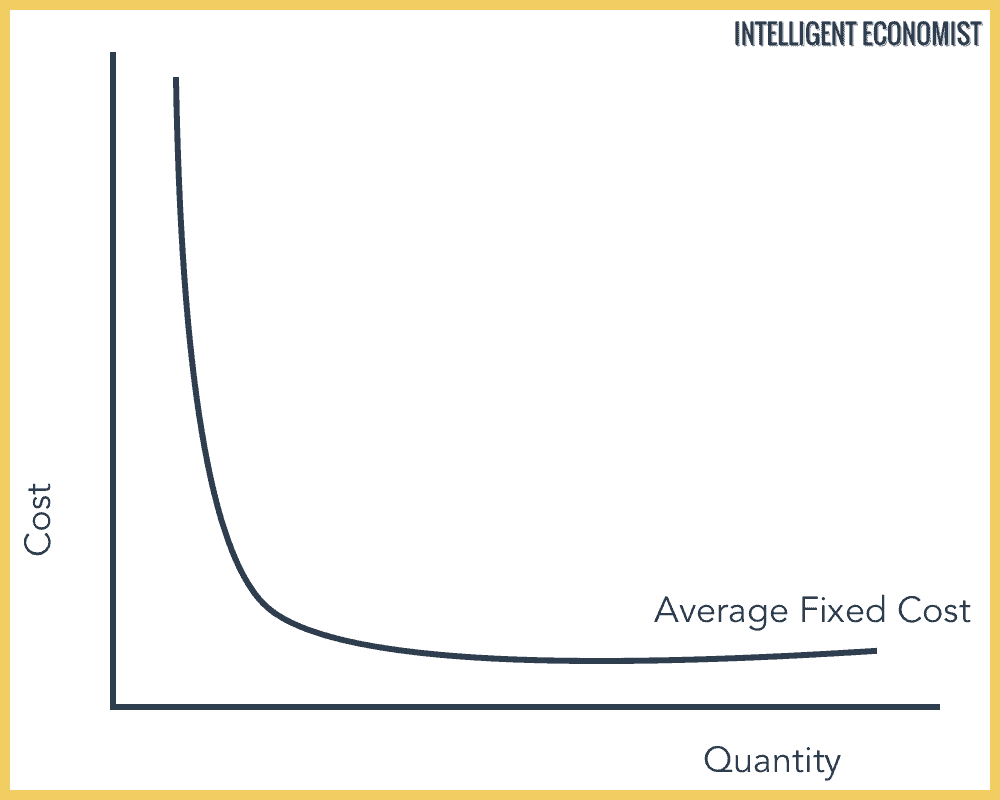
41 refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs
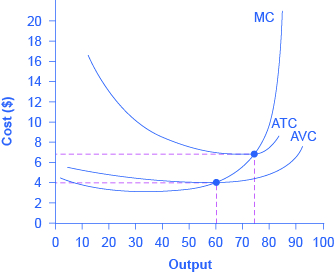
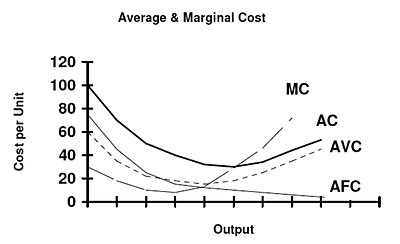
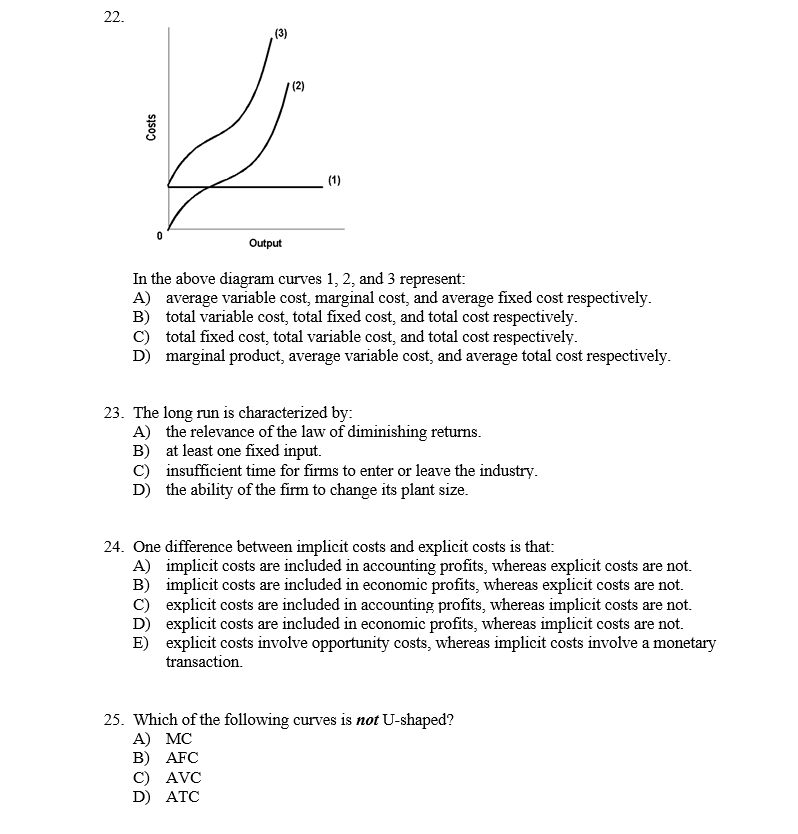
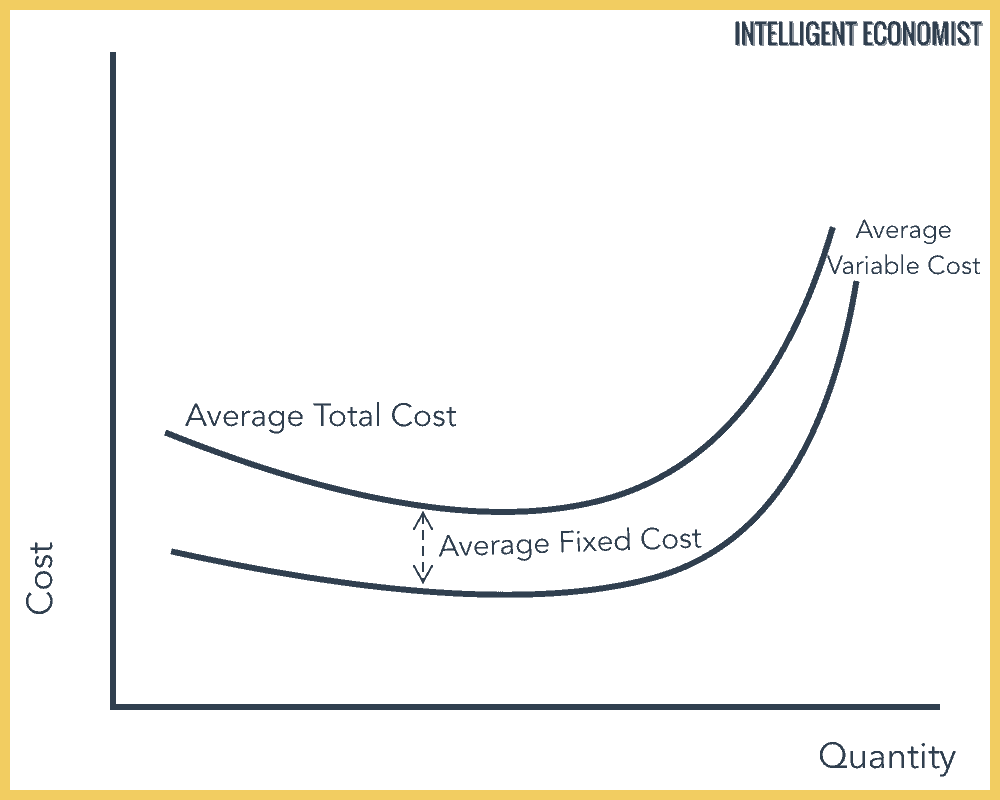
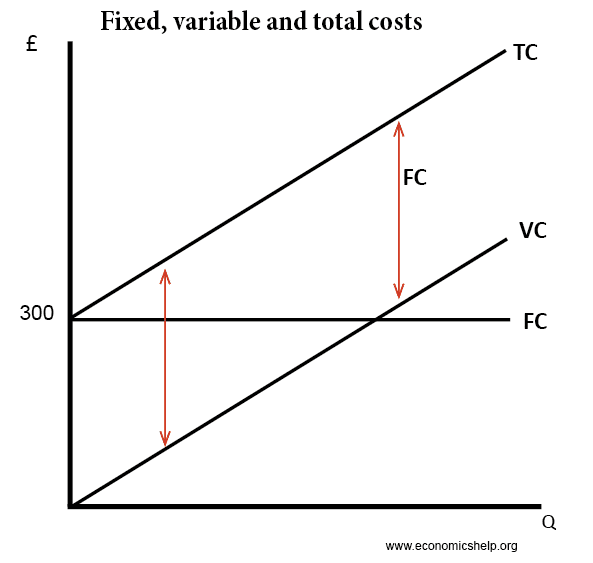
Refer to the above diagram. The vertical distance between ATC and AVC reflects: A) the law of diminishing returns. B) the average fixed cost at each level of output. C) marginal cost at each level of output. D) the presence of economies of scale. 25. In the above figure, curves 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the: A) ATC, MC, AFC, and AVC curves ... Average total cost curve is typically U-shaped i.e. it decreases, bottoms out and then rises. A firm's total cost is the sum of its variable costs and fixed costs. Variable costs are costs which vary with change in output level. Fixed costs, on the other hand, do not change with change in output.
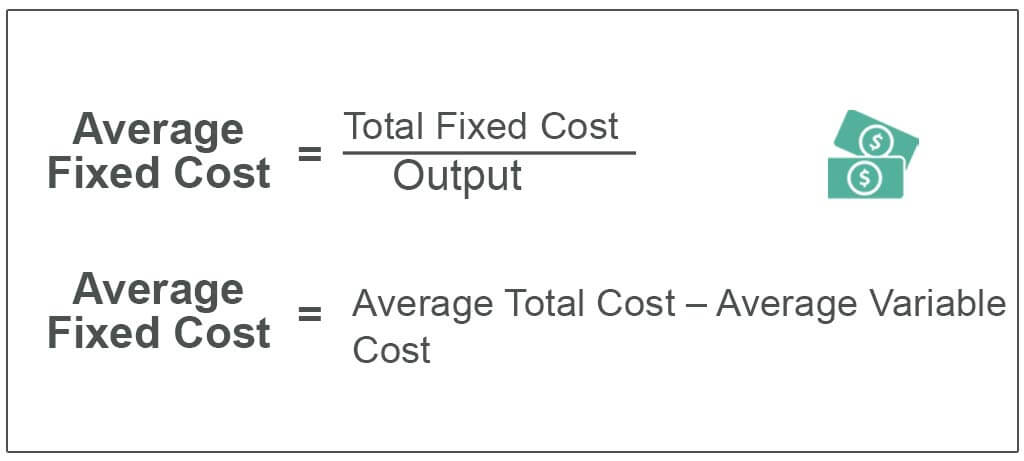
Average variable cost is calculated by taking variable cost and dividing by the total output at each level of output. Average variable costs are typically U-shaped. If a firm's average variable cost of production is lower than the market price, then the firm would be earning profits if fixed costs are left out of the picture.

Refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs
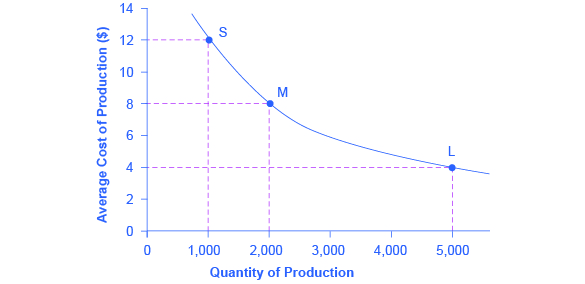
The structure of costs in the short run. The cost of producing a firm's output depends on how much labor and physical capital the firm uses. A list of the costs involved in producing cars will look very different from the costs involved in producing computer software or haircuts or fast-food meals. Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: is $400. 161. Refer to the table and information. The fixed cost of the firm is $500. The firm's total variable cost is indicated in the table. The average variable cost of the firm when 5 units of output are produced is:
Refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs. Microeconomics: Chapter 9. Refer to the diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: is equal to <i>QE</i>. Refer to the data. Diminishing returns begin to occur with the hiring of the _________ unit of labor. Nice work! $35, what is the firm's average fixed cost at that level of output? A) $65 B) $50 C) $15 D) It is impossible to determine without additional information. 30. If a firm produces 20 units of output and incurs a total cost of $1,000 and a variable cost is $700, calculate the firm's average fixed cost of production if it expands output to 25 units. (Table: Competitive Firm 2) Refer to the table that shows the revenue and cost schedules for a competitive firm. What is the average fixed cost at the profit-maximizing quantity? A) $54.30 B) $4.28 C) $50 D) $80 So average variable cost I'll do in this orange color. So, at an output of 25, our average variable cost is $240. Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: 400
Economics questions and answers. ATC AVC Refer to the diagram. This firm's average fixed costs Multiple Choice - o cannot be determined with the information in the diagram. | I II o are the vertical distance between AVC and MC. o are the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. o equal the per-unit change in MC. Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: A) not shown. C) the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. B) the vertical distance between AVC and MC. D) equal to the per unit change in MC. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q average fixed cost: Select one: a. ... Assume that the amounts of all non-labor resources are fixed. Refer to the above data. Diminishing marginal returns become evident with the addition of the: ... and average variable costs of $150. The firm's total fixed costs are: Select one: a. 3. Average Total Cost (ATC) The average total cost is the sum of the average variable cost and the average fixed costs. That is, ATC = AFC + AVC. In other words, it is the total cost divided by the number of units produced. The diagram below shows the AFC, AVC, ATC, and Marginal Costs (MC) curves: It is important to note that the behaviour of ...
102. Refer to the above information. The marginal cost of the third unit of output is: A. $105.B. $25. C. $15. D. $20. 103. Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: A. not shown.B. the vertical distance between AVC and MC. C. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC.D. equal to the per unit change in MC. 104. A)implicit costs. B)costs of the firm's fixed inputs. C)costs that rise as output increases. D)costs associated with the production of goods. 45) 46)A firm's marginal cost is the increase in its total cost divided by the increase in its A)output. B)average cost. C)average revenue. D)quantity of labor. 46) 47)Marginal cost is A)all the costs of ... WRITE [9] A firm has $60 of fixed costs, and variable costs as indicated in the table below. Complete the table; check your calculations by referring to question 4 at the end of Chapter 7. Total product Total fixed cost Total variable cost Total cost AFC AVC ATC Marginal cost 0 $60 $0 $60 Refer to the above data. The average fixed cost of producing 3 units of output: A. is $8. B. is $7.40. C. is $5.50. ... why the firm's long-run average total cost curve is U-shaped. C. why the firm's short-run marginal cost curve cuts the short-run average variable cost curve at its minimum point. ... The above diagram shows the short-run ...
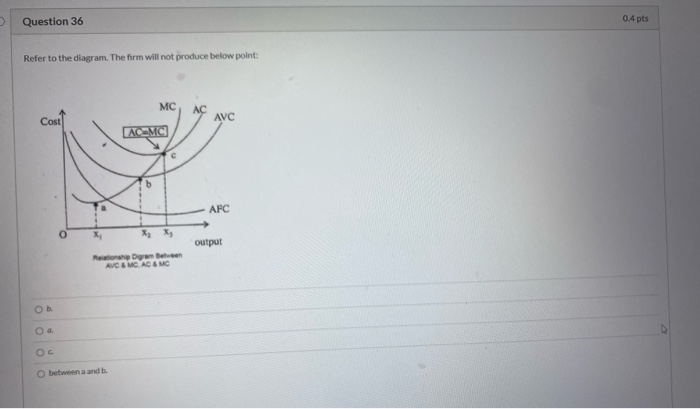
52. If marginal cost is rising in a competitive firm's short-run production process and its average variable cost is falling as output is increased, then . A. marginal cost is above average variable cost. B. marginal cost is below average fixed cost. C. marginal cost is below average variable cost. D. average fixed cost is constant.
Refer to the long-run cost curve for a firm. If the firm produces output Q1 at an average total cost of ATC1, then the firm is ... Refer to the Diagram. This firm's average fixed costs. are the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. In 2018, the United states. imported more goods than it exported.
the average fixed cost at each level of output. Refer to the above information. Average fixed cost is: TFC-----Q. ... Refer to the above diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. Refer to the above diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a: ...
41. Refer to the above diagram. At output C total variable cost is FGKJ. True False 42. Refer to the above diagram. At output C average fixed cost is GF. True False 43. Refer to the above diagram. At any price below R the firm will shut down in the short run. True False 44. Refer to the above diagram.
This firm's average fixed costs are: - FOORQUIZ. Refer to the diagram. This firm's average fixed costs are: A. not shown. B. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. C. the vertical distance between AVC and MC. D. equal to the per unit change in MC. ANSWER: B. the vertical distance between AVC and ATC.
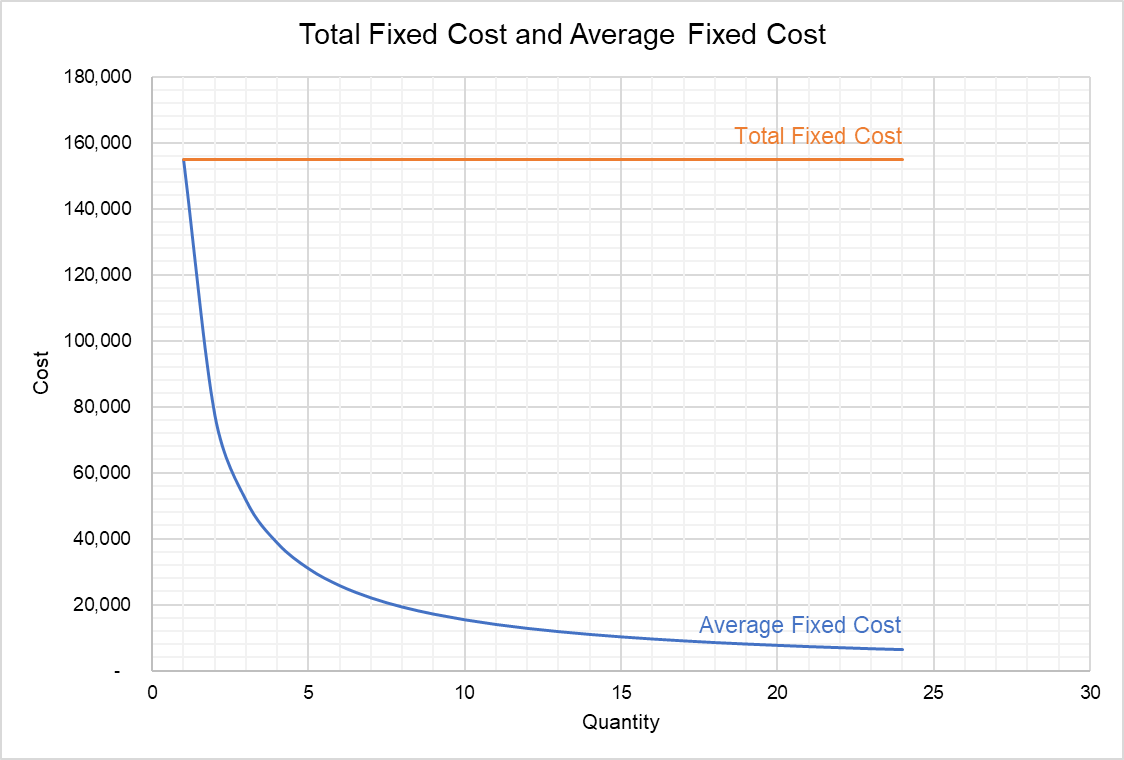
Now, the last thing that we didn't graph, and this is maybe the most intuitive, is the average fixed cost. And this is just going to asymptote down. At 25 units, we're at 200. 25 units, we are at 200. At 45 units, we are at 111. 45, 111, it's maybe right over there. At 58 units we're at 86. 58 units, 86.
This firm's average fixed costs A. cannot be determined with the information in the diagram. B. are the vertical distance between AVC and MC.C. are the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. D. equal the per-unit change in MC. 133. Refer to the diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a.
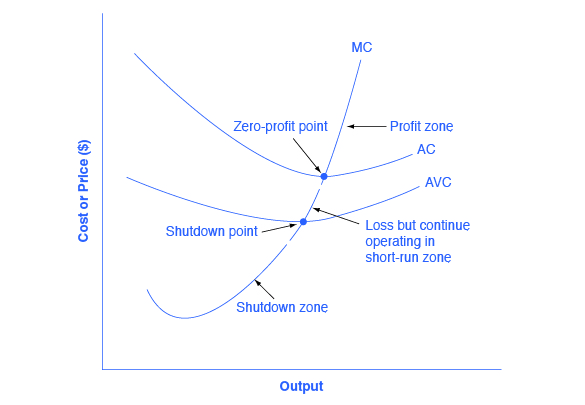
B) It must rise to offset the increased cost. C) The firm will shut down. D) It must fall. 12) Refer to Table 12 -1. The firm will not produce in the short run if the output price falls below 12) A) $8. B) $4. C) $3.20. D) $2.80. 13) If, for a given output level, a perfectly competitive firm's price is less than its average variable cost, the ...
This firm's average fixed costs are: A) not shown. B) the vertical distance between AVC and MC. C) the vertical distance between AVC and ATC. D) equal to the per unit change in MC. 144. Refer to the above diagram. If labor is the only variable input, the marginal product of labor is at a: A) maximum at point a. B) minimum at point a.
b. average total cost c. average variable cost d. average fixed cost ____ 28. Refer to Figure 13-4. Which curve is most likely to represent average total cost? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 29. Economies of scale occur when a firm's a. marginal costs are constant as output increases. b. long-run average total costs are decreasing as output increases.
13) Refer to Figure 13 -4. Should the firm represented in the diagram continue to stay in business despite its losses? 13) A) No, it is not able to cover its fixed cost. B) No, it should shut down. C) Yes, it should increase its revenue by raising its price. D) Yes, its total revenue covers its variable cost. Table 13 -3 Quantity Price (dollars ...
161. Refer to the table and information. The fixed cost of the firm is $500. The firm's total variable cost is indicated in the table. The average variable cost of the firm when 5 units of output are produced is:
Refer to the diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: is $400.
The structure of costs in the short run. The cost of producing a firm's output depends on how much labor and physical capital the firm uses. A list of the costs involved in producing cars will look very different from the costs involved in producing computer software or haircuts or fast-food meals.
















0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram. this firm's average fixed costs"
Post a Comment