40 refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be
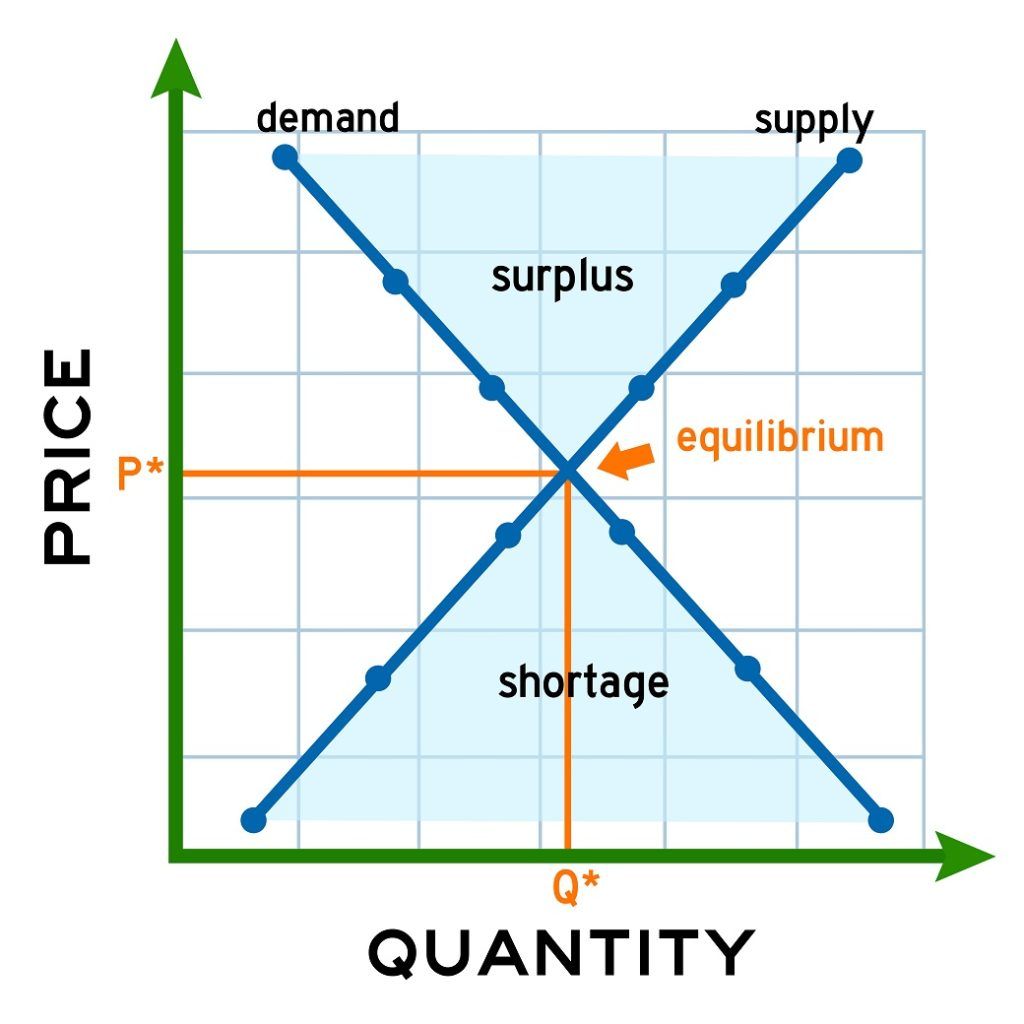
The market for coffee is in equilibrium. Unless the demand or supply curve shifts, there will be no tendency for price to change. The equilibrium price in any market is the price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price in the market for coffee is thus $6 per pound. Refer to the diagram. Rent controls are best illustrated by Price A. 92. Refer to the diagram. A price of $60 in this market will result in A surplus of 100 units. 93. The law of demand states that, other things equal, Price and quantity demanded are inversely related.
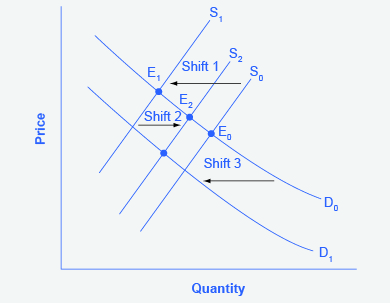
a) A lower equilibrium quantity and a higher equilibrium price. b) A lower equilibrium quantity and a lower equilibrium price. c) A higher equilibrium quantity and a higher equilibrium price. d) A higher equilibrium quantity and a lower equilibrium price. The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 15.

Refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be
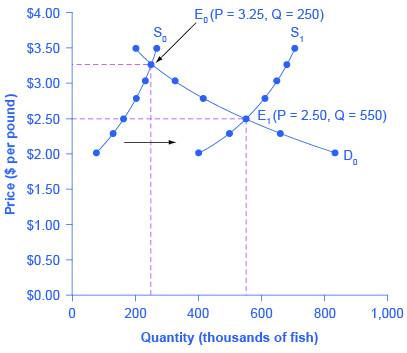
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Supply $1.60 21.00 1.00 o. 50 Demand 130 200 Quantity 290 Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be Multiple Choice $1.00 and 200. $1.60 and 130. $0.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. Step 1. Draw a demand and supply model to illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began. The demand curve D 0 and the supply curve S 0 show that the original equilibrium price is $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity is 250,000 fish. (This price per pound is what commercial buyers pay at the fishing docks. Q. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: answer choices . $1.00 and 200. $1.60 and 130. $.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. Tags: Question 5 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Report an issue . Q. An effective ceiling price will.
Refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be. Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: (Pic29) $1.00 and 200. $1.60 and 130. $0.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. $1.00 and 200. A market is in equilibrium: provided there is no surplus of the product. at all prices above that shown by the intersection of the supply and demand curves. 71. Refer to the above diagram for the milk market. In this market, the equilibrium price is ____ and equilibrium quantity is ___. A. $1.50 per gallon; 28 million gallons B. $1.50 per gallon; 30 million gallons C. $28 per gallon; 150 million gallons D. $1.00 per gallon; 35 million gallons 72. Refer to the above diagram for the milk market. 27. A market for a product is in equilibrium when: A) Product price equals demand B) The supply curve remains fixed C) Quantity supplied equals quantity demanded D) Supply is equal to the price 28. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity for milk in this market are: A) $1.50 and 28 million gallons B) $1.50 and 30 million ... Refer to the diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if the price was. $1.60. Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be. $1.00 and 200. If there is a surplus of a product, its price. is above the equilibrium level.
Step 1. Draw a demand and supply model to illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began. The demand curve D 0 and the supply curve S 0 show that the original equilibrium price is $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity is 250,000 fish. (This price per pound is what commercial buyers pay at the fishing docks; what consumers pay at the ... May 07, 2014 · The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A) $1.00 and 200. B) $1.60 and 130. C) $.50 and 130. D) $1.60 and 290. 16. Refer to the above diagram. A surplus would be encountered if price was in the following range: A) $0.01 - $0.50. B) $0.51 - $1.00. C) Exactly $1.00. D) $1.01 and higher. 17. Refer to the above diagram. At equilibrium level of output OX, price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the MR curve from below. The firm enjoys normal profits. Now, suppose demand increases from DD to D 1 D 1 and the industry is in equilibrium at point E 1 which determines the price OP 1 The new price OP 1 is less than the new market price i.e ... Refer to the above diagram. A decrease in quantity demanded is depicted by a: A. Move from point x to point y ... The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200 B. $1.60 and 130 C. $0.50 and 130 D. $1.60 and 290. B. Refer to the above diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if price was:
The equilibrium price and | Chegg.com. Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $0.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. If there is a surplus of a product, its price: A. is below the equilibrium level. B. is above the equilibrium level. D. will rise in the near future. Chapter 03 - Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium Difficulty: Easy Learning Objective: 03-04 Relate how supply and demand interact to determine market equilibrium. Topic: 03-17 Market Supply 158. Refer to the diagram below for the market for corn. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market are: A. $4 and 10,000 bushels. B. $3 and 8,000 bushels. C. $2 and 4,000 bushels. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $0.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 14. Refer to the above diagram. A surplus of 160 units would be encountered if the price was: A. $1.10, that is, $1.60 minus $.50. B. $1.60. Money market equilibrium occurs at the interest rate at which the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied. All other things unchanged, a shift in money demand or supply will lead to a change in the equilibrium interest rate and therefore to changes in the level of real GDP and the price level.
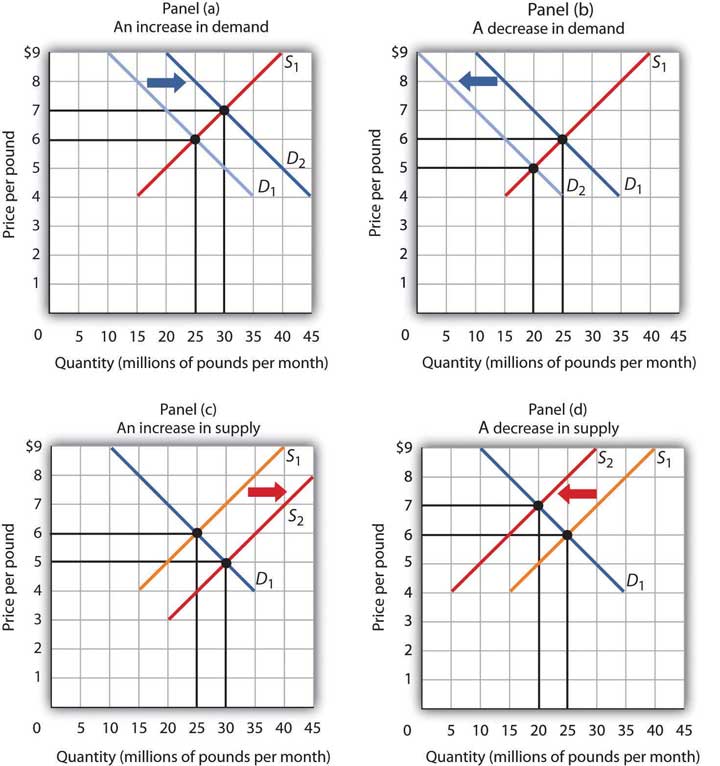
D. price and equilibrium quantity must both decline. A Refer to the diagram, in which S1 and D1 represent the original supply and demand curves and S2 and D2 the new curves.
The market for coffee is in equilibrium. Unless the demand or supply curve shifts, there will be no tendency for price to change. The equilibrium price in any market is the price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. The equilibrium price in the market for coffee is thus $6 per pound.
Refer to the diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If the initial demand and supply curves are D0 and S0, equilibrium price and quantity will be: 0F and 0C, respectively.

Electricity Balancing As A Market Equilibrium An Instrument Based Estimation Of Supply And Demand For Imbalance Energy Sciencedirect
Equilibrium Practice Assignment 1. The price at which there is neither surplus nor shortage is called a. the adjustment price. b. the equal price.c. the fair price. d. equilibrium price. 2. If both the demand curve and supply curve move to the left, we can predict that a. price will fall, but we cannot predict quantity. b.
Refer to the above diagram. The Equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: If two products are complementary goods, how will a decrease in the price of one affect the other?
Begin by considering a market with the demand and supply equations: where is the quantity demanded and is the quantity supplied. There is currently no tax applied to this market. This market is depicted in the supply and demand diagram below. We solve for the equilibrium price and quantity by equating demand and supply such that: Solving for ...
Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. B. $1.60 and 130. C. $.50 and 130. D. $1.60 and 290. 7. R-2 F03090. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. equilibrium. B. a shortage of 50 units. C. a surplus of 50 units. ...
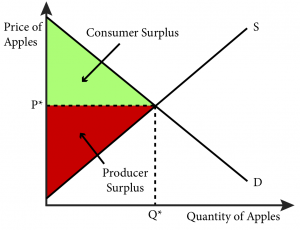
Consider our diagram of a negative externality again. Let’s pick an arbitrary value that is less than Q 1 (our optimal market equilibrium). Consider Q 2.. Figure 5.1b. If we were to calculate market surplus, we would find that market surplus is lower at Q 2 than at Q 1 by triangle e.. The market surplus at Q 2 is equal to area a+b. [(a+b+c) – (c)].
Q. A new substitute enters the market causing a shift in the demand curve in the graph. What is the new equilibrium point after the substitute enters the market? ... Q. Refer to the diagram. A price of $15 in this market will result in: answer choices ... The equilibrium price and quantity for this product will be: answer choices . $60 and 2,600.
According to the figures in the given table, Market Equilibrium quantity is 150 and the Market equilibrium price is 15. It is the point where QD = QS, of the given figures. Demand and Supply Curves. This is the way how economist use demand and supply curves to prove the market equilibrium.
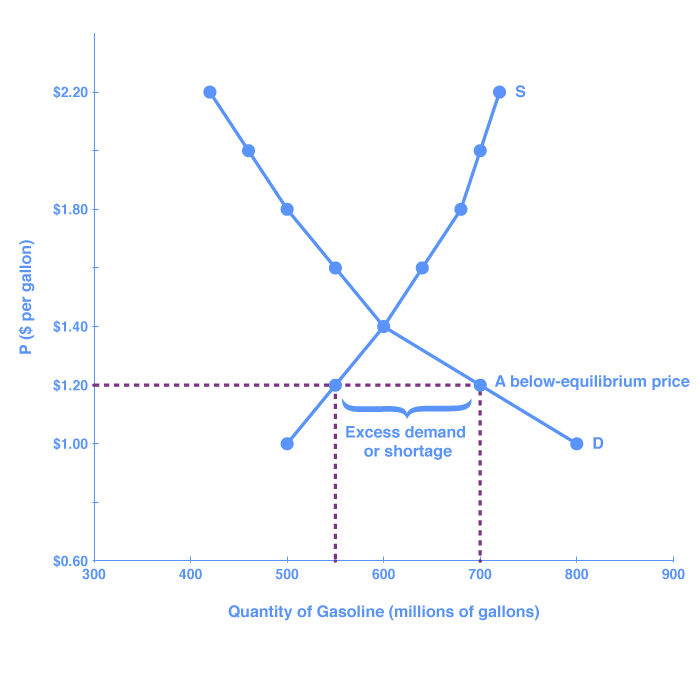
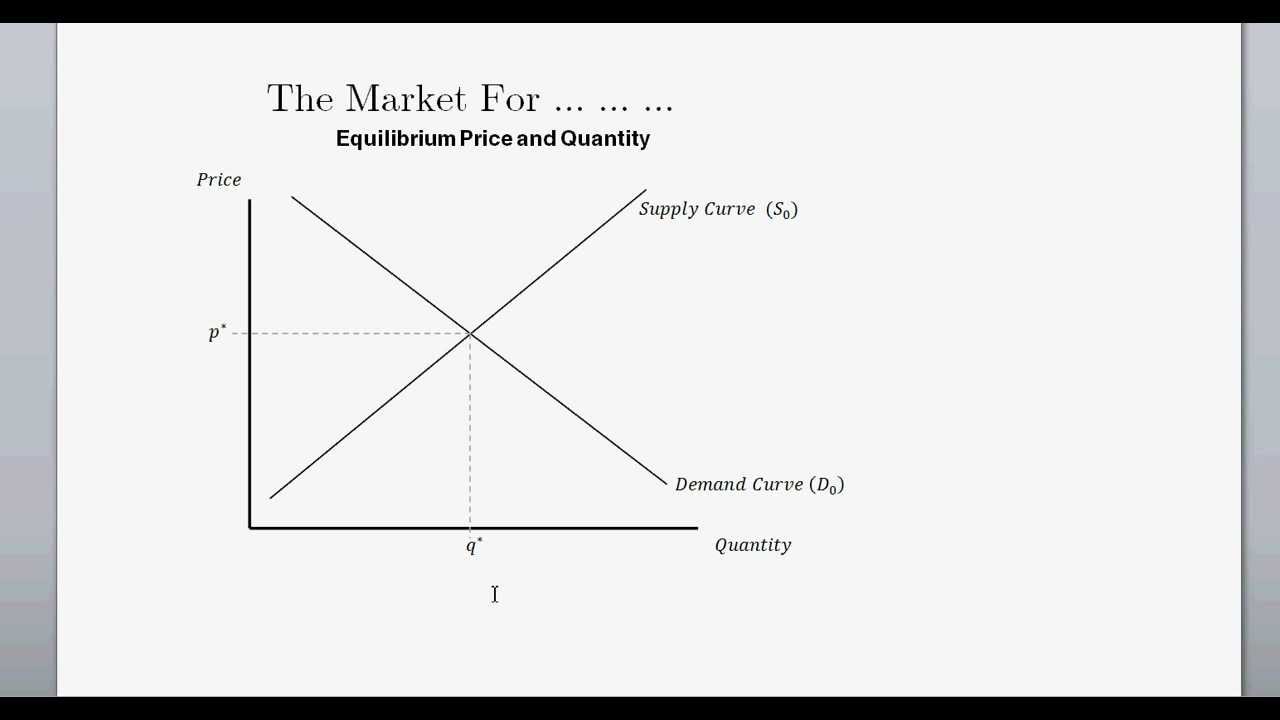
Market equilibrium. Market equilibrium can be shown using supply and demand diagrams. In the diagram below, the equilibrium price is P1. The equilibrium quantity is Q1. If price is below the equilibrium. In the above diagram, price (P2) is below the equilibrium. At this price, demand would be greater than the supply. Therefore there is a ...

Refer To The Figure Below Find The Equilibrium Price And Quantity Analyze The Market At A Price Of 9 And A Quantity Of 6 Study Com
Refer to the above diagram, which shows demand and supply conditions in the competitive market for product X. If the initial demand and supply curves are D0 and S0, equilibrium price and quantity will be:
##Key Terms Term | Definition -|- **market** | an interaction of buyers and sellers where goods, services, or resources are exchanged **shortage** | when the quantity demanded of a good, service, or resource is greater than the quantity supplied **surplus** | when the quantity supplied of a good, service, or resource is greater than the quantity demanded **equilibrium** | in a market setting ...
Q. Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: answer choices . $1.00 and 200. $1.60 and 130. $.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290. Tags: Question 5 . SURVEY . 30 seconds . Report an issue . Q. An effective ceiling price will.

Refer To The Figure Below The Equilibrium Price In The Market Before The Tax Is Imposed Is A 1 00 B 3 50 C 5 00 D 6 00 Study Com
Step 1. Draw a demand and supply model to illustrate the market for salmon in the year before the good weather conditions began. The demand curve D 0 and the supply curve S 0 show that the original equilibrium price is $3.25 per pound and the original equilibrium quantity is 250,000 fish. (This price per pound is what commercial buyers pay at the fishing docks.

Refer To The Graph Below At The Competitive Market Equilibrium Price Is Equal To Blank Units Of The Good Are Produced A 18 And 70 B 14 And 70 C 12 And
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Supply $1.60 21.00 1.00 o. 50 Demand 130 200 Quantity 290 Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be Multiple Choice $1.00 and 200. $1.60 and 130. $0.50 and 130. $1.60 and 290.

7 Refer To The Diagram The Equilibrium Price And Quantity In This Market Will Be A 1 00 And Brainly Com

Draw A Graph Depicting The Equilibrium In This Market Without International Trade Assume That The Equilibrium Price Is 4 Lb And The Equilibrium Quantity Is 2 Million Lbs Label Your No Trade Equili
/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)




















/EquilibriumQuantity-3d51042295814ceda425f70c182d9e76.png)
0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram. the equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be"
Post a Comment