40 law of diminishing returns diagram
Law of Diminishing Returns (Dijelaskan Dengan Diagram) Hukum pengembalian menurun menjelaskan bahwa ketika semakin banyak unit input variabel dipekerjakan pada jumlah tertentu dari input tetap, total output awalnya dapat meningkat pada tingkat yang meningkat dan kemudian pada tingkat yang konstan, tetapi pada akhirnya akan meningkat pada ... Diminishing returns, law of. Sometimes also referred to as the law of variable proportions, this "law" is really a generalization economists make about the nature of technology when it is possible to combine the same factors of production in a number of different proportions to make the same product.The law states: When increasing amounts of one factor of production are employed in production ...
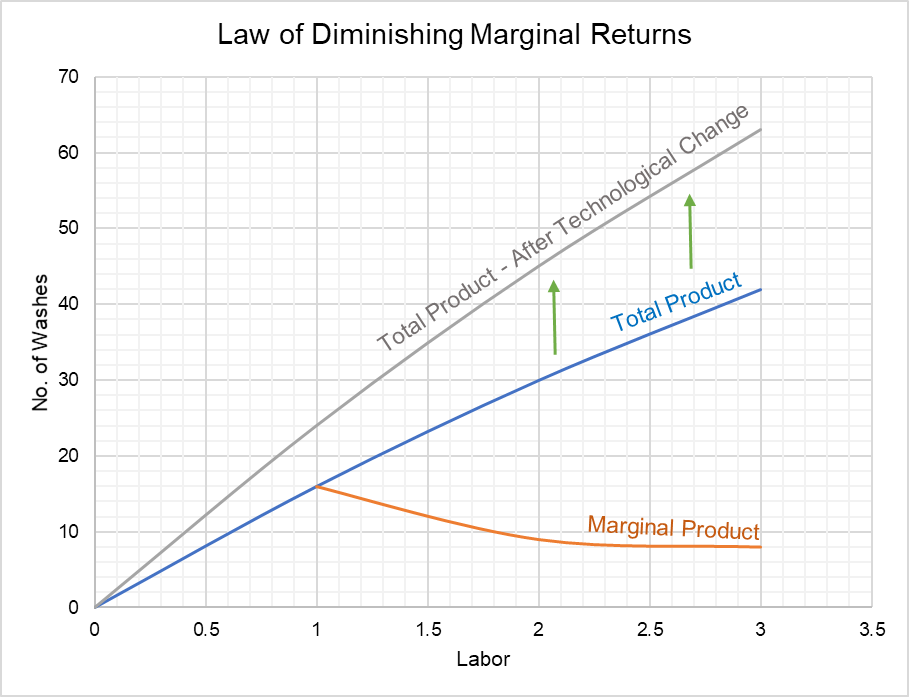
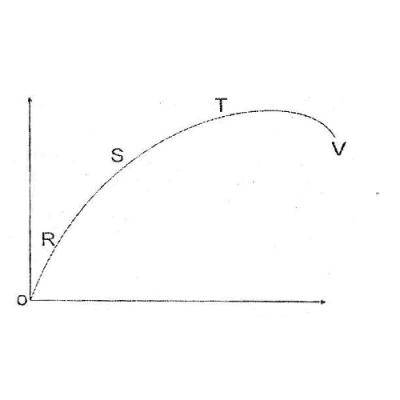
Graphical Representation of the Law of Diminishing Returns. In the diagram OX represents the number of labourers (the variable factor). OY denotes the size of output. TP is the total product curve. MP is the Marginal product curve, AP is the average product curve. At point 'C' Marginal product and average product are equal.

Law of diminishing returns diagram
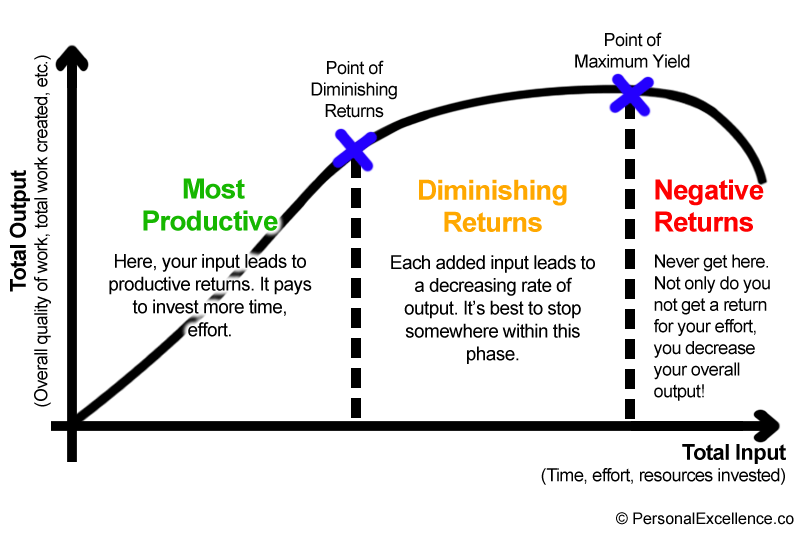
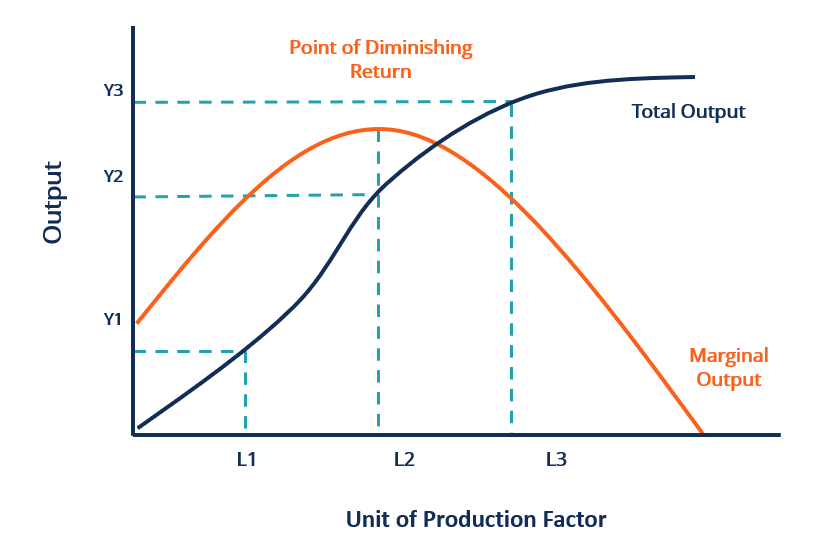
It is known as the point of diminishing returns. At such a point, the marginal output is maximized but will decrease if the units of a production factor continue to increase. As the diagram above shows, the point of diminishing return is at L2. In economics, diminishing returns is the decrease in marginal (incremental) output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, holding all other factors of production equal (ceteris paribus). The law of diminishing returns (also known as the law of diminishing marginal productivity) states that in productive processes, increasing a factor ... Law of diminishing returns, also referred to as the law of diminishing marginal returns, is a concept in economics that if one factor of production (e.g. number of workers) is increased while other factors (e.g. work area or equipment) are held constant, the output per unit of the variable factor will eventually diminish.
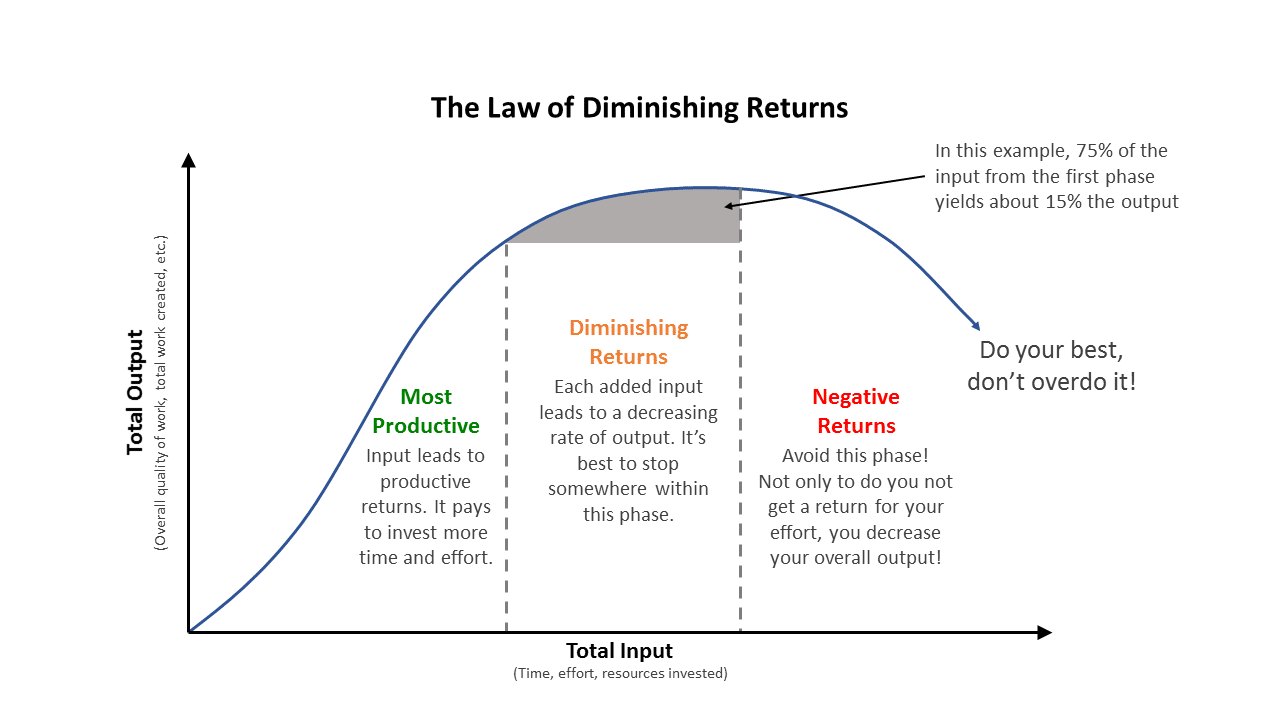
Law of diminishing returns diagram. The law is also known as the law of increasing costs. It is one of the important laws of microeconomics. The law of diminishing return indicates that if the number of variable inputs is increased with some fixed inputs, the total output will first increase but then start to decline. It is the third stage of the law of variable proportions. The law of diminishing returns states that results do not increase at the same rate of the effort put in. As your results get better, you need to put in more energy to improve results further. A more formal definition of the law indicates, if you increase the input while holding all other factors constant, the corresponding returns will start ... This tendency of marginal productivity to decrease as successive units of variable factors are employed to fixed factor is called the law of diminishing returns. Diagram: Application: The law of diminishing returns has its wide application. But is is especially applicable to agricultural sector. In this sector, there is the supremacy of nature ... The law of variable proportions is a new name for the law of diminishing returns, a concept of classical economics. But before getting on with the law, there is a need to understand the total product (TP), marginal product (MP) and average product (AP). Total Product: Total product is the total output obtained from the combined efforts of all ...
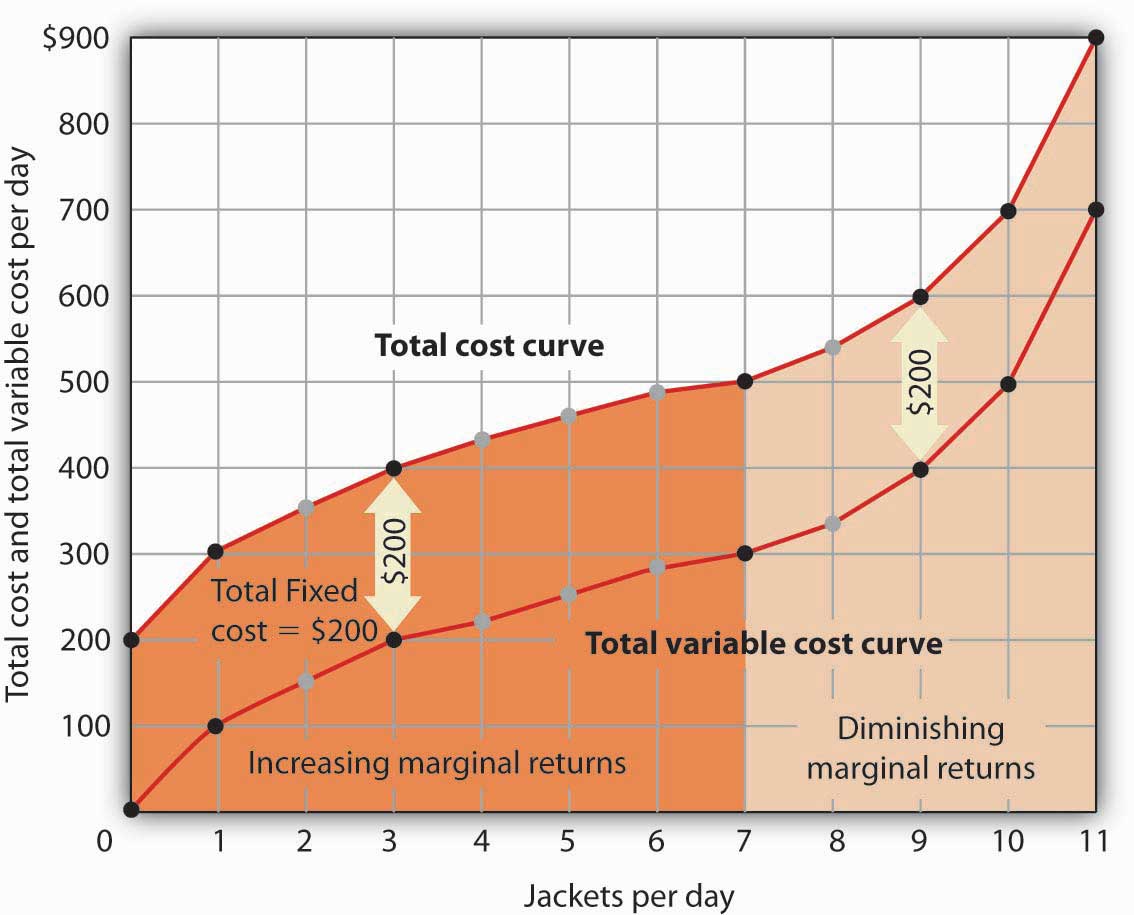
The law of diminishing returns, also referred to as the law of diminishing marginal returns, states that in a production process, as one input variable is increased, there will be a point at which ... the law of diminishing returns indicates that as extra units of a variable resource are added to a fixed resource, marginal product will decline beyond some point. in the diagram, curves 1, 2, & 3 represent the Table 35.9 explains diminishing returns with labour as the variable factor. The table shows that after more than 4 workers are employed, though the output units increase, the average output per worker reduces and so illustrates the law of Diminishing Returns with reference to labour. The law can be expressed in terms of costs too: Increasing returns mean lower costs per unit just as diminishing returns mean higher costs. Thus, the law f of increasing return signifies that cost per unit of the marginal or additional output falls with the expansion of an industry.
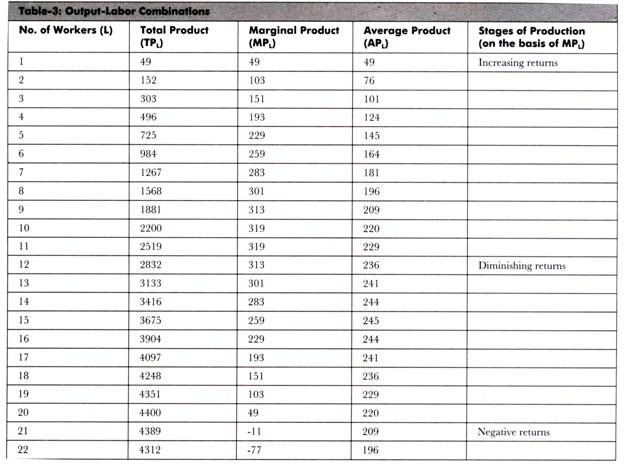
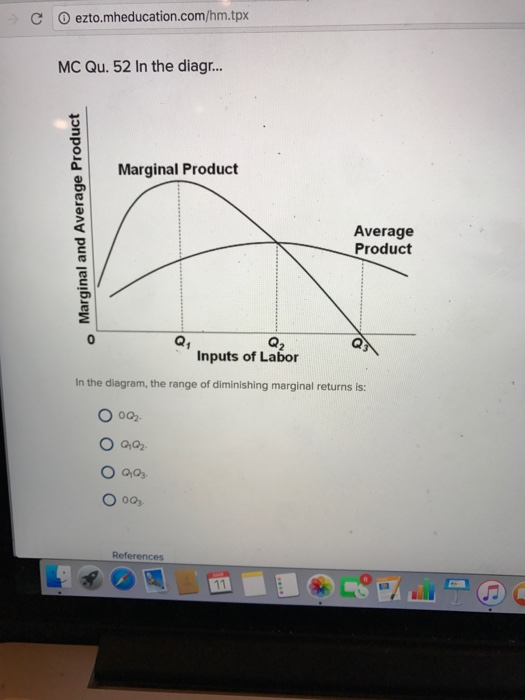
In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. In the above diagram total product will be at a maximum at. Law of diminishing returns helps mangers to determine the optimum labor required to produce maximum output. B in the long run all resources are variable while in the short run at least one resource is fixed. Diminishing returns to labour in the short run. As more of a variable factor (e.g. labour) is added to a fixed factor (e.g. capital), a firm will reach a point where it has a disproportionate quantity of labour to capital and so the marginal product of labour will fall, thus raising marginal cost and average variable cost. The law of diminishing returns is therefore, also called the law of variable proportions. In agriculture, the law of diminishing returns sets in at an early stage because one very important factor, i.e., land is a constant factor there and it cannot be increased in right proportion with other variable factors, i.e., labor and capital. After the 5 th worker, diminishing returns sets in, as the MP declines. As extra workers produce less, the MC increases. Diagram of diminishing returns . In this example, after three workers, diminishing returns sets in. After employing 4 workers or more - the marginal product (MP) of the worker declines and the marginal cost (MC) starts to rise.
Hence, it is called the stage of diminishing returns. In this example, Stage II runs between four to six units of labour (between the points L and M). This stage reaches a point where TPP is maximum (18 in the above example) and MPP becomes zero (point R). ... Diagram of Law of Variable Proportion in terms of TPP.
Diminishing Marginal Returns Diagram. As we can see from the diagram, at 3 workers, the gap between marginal profit and marginal cost is at its maximum. However, at 4 workers, the marginal cost of producing an additional unit starts to become more expensive. At this point, we start to see diminishing marginal returns.
Law of Diminishing Returns (Explained With Diagram) Law of diminishing returns explains that when more and more units of a variable input are employed on a given quantity of fixed inputs, the total output may initially increase at increasing rate and then at a constant rate, but it will eventually increase at diminishing rates. In other words ...
The law of diminishing marginal returns states that additional inputs will eventually lead to a negative impact on outputs. For it to be valid, some assumptions need to be made: All the technology involved is constant. Changing the technological tools used in production would change the marginal and average cost and value of a product.
Definition: The law of diminishing returns is an economic concept that shows that there is a point where an increased level of inputs does not equal to an equal increase level of outputs.In other words, after a certain point of production each input will not increase outputs at the same rate. There will be a diminishing effect where each input contributes less in proportion to the overall ...
Law of diminishing returns states that an additional amount of a single factor of production will result in a decreasing marginal output of production. The law assumes other factors to be constant. What this means is that if X produces Y, there will be a point when adding more quantities of X will not help in a marginal increase in quantities of Y.
Aug. 1,1933 Law of Diminishing Returns in Agriculture 169 It is obvious that this curve represents diminishing output per unit of additional input and that exact expression can be given it. In each of these experiments, especially those performed by Mitscherlich, productions were obtained with the variation of a single element of plant growth.
Law of Variable Returns (Explained With Diagram) It is the business of the entrepreneur to combine factors of production to make the maximum profits from their use. He can use the factors in varying proportions but for any business there is one combination that is the most efficient.
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns: The law of diminishing marginal returns is a law of economics that states an increasing number of new employees causes the marginal product of another employee ...
Q (1) Explain and illustrate with diagrams the differences between diminishing marginal returns and decreasing economies of scale and cite causes and examples. Ans. The law of diminishing returns is also called the law of variable proportion, as the proportions of each factor of production employed keep changing as more of one factor is added.
Law of diminishing returns, also referred to as the law of diminishing marginal returns, is a concept in economics that if one factor of production (e.g. number of workers) is increased while other factors (e.g. work area or equipment) are held constant, the output per unit of the variable factor will eventually diminish.
In economics, diminishing returns is the decrease in marginal (incremental) output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, holding all other factors of production equal (ceteris paribus). The law of diminishing returns (also known as the law of diminishing marginal productivity) states that in productive processes, increasing a factor ...
It is known as the point of diminishing returns. At such a point, the marginal output is maximized but will decrease if the units of a production factor continue to increase. As the diagram above shows, the point of diminishing return is at L2.
































0 Response to "40 law of diminishing returns diagram"
Post a Comment