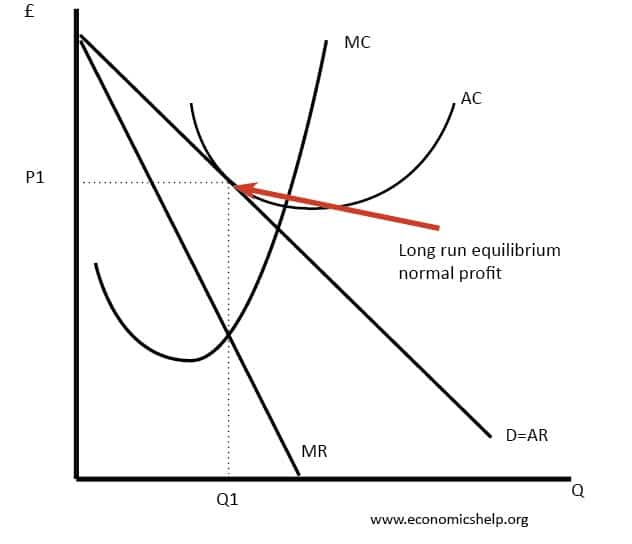
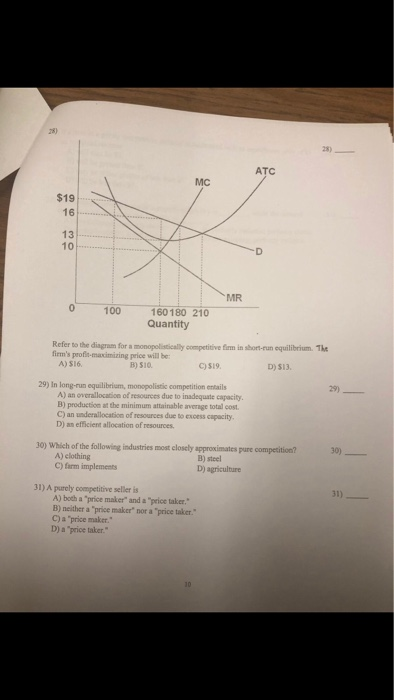
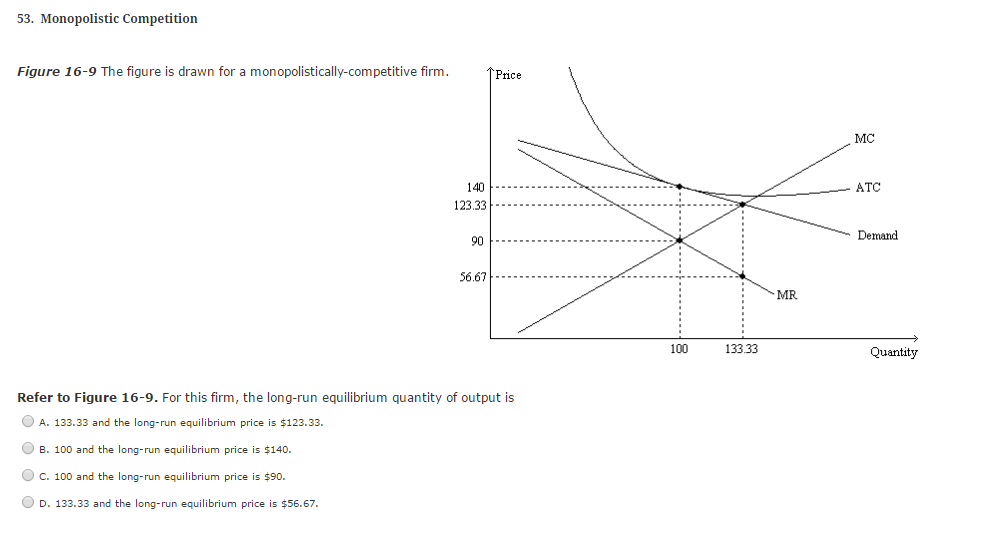
37 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
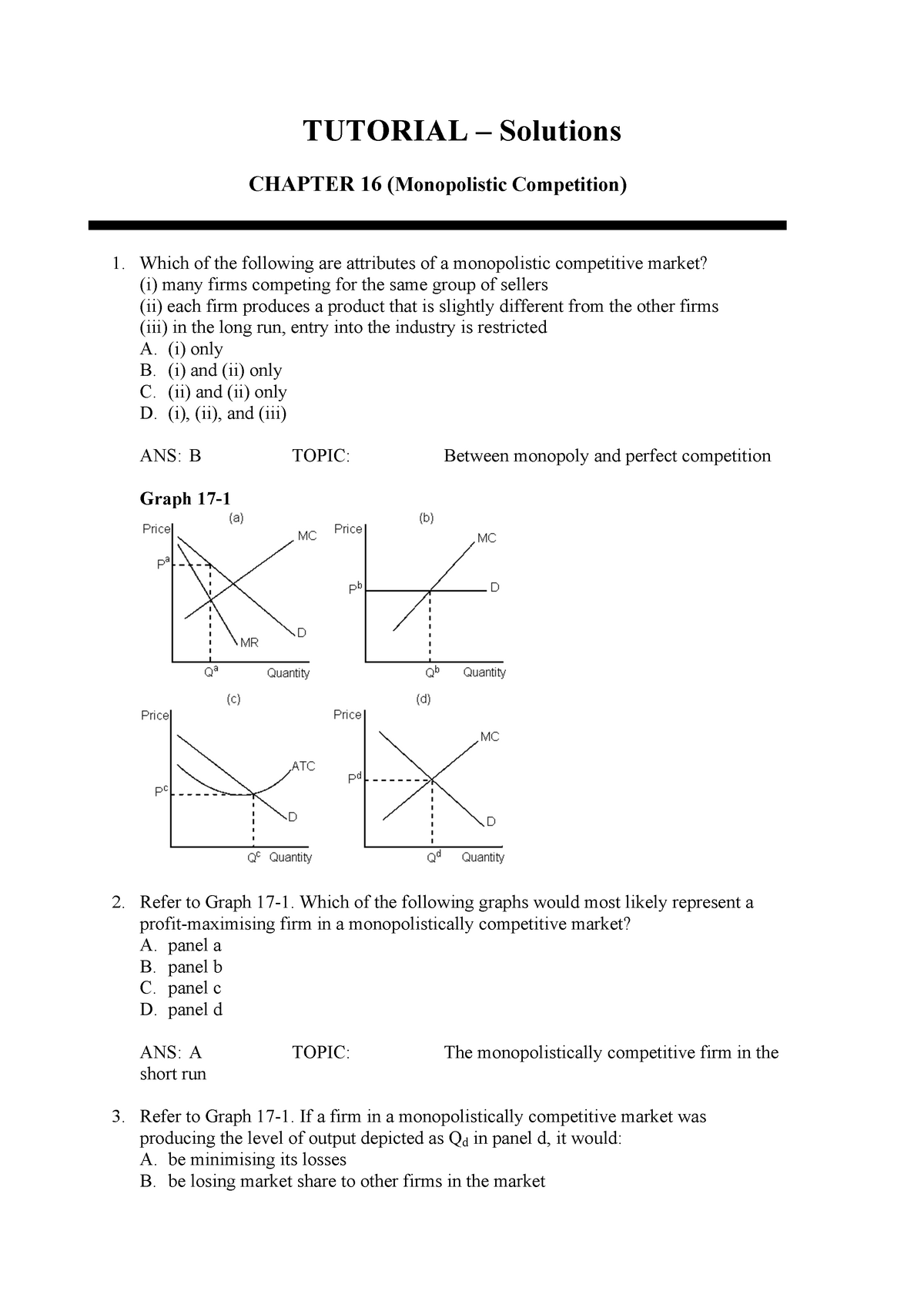
The diagram below shows demand and cost curves for a monopolistically competitive firm. 38) Refer to Figure 11-3. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will A) produce Q2 at Price P1. B) produce Q1 at Price P2. C) produce Q1 at Price P1. D) produce Q2 at Price P2. E) produce the output where AC is at its minimum. 39) Refer to ... C) differential between price and marginal costs which characterizes monopolistically competitive firms. D) fact that most monopolistically competitive firms encounter diseconomies of scale. E) fact that firms produce more than the socially optimal output 9. When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium:
Refer to the above diagram where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars. 4both diagrams b and c. Long run equilibrium price will be. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. P mc atc.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
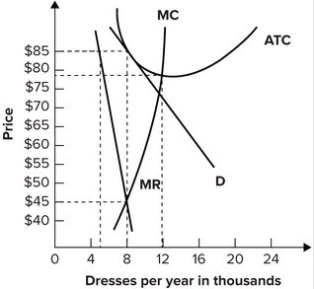
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Long run equilibrium price will be. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is. In the short run a monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profit or minimizes losses by producing that quantity that corresponds to when marginal ... Option d is correct. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm, the long run price will be a …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: $ MC ATC A Demand MR DE Quantity Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be Multiple Choice above A EF 8. SR Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Given the short run equilibrium described, why does entry occur? As entry occurs, demand shifts leftward until profit equals zero. Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Diagram at right shows long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm. economic profits? price mark-up (P vs ...
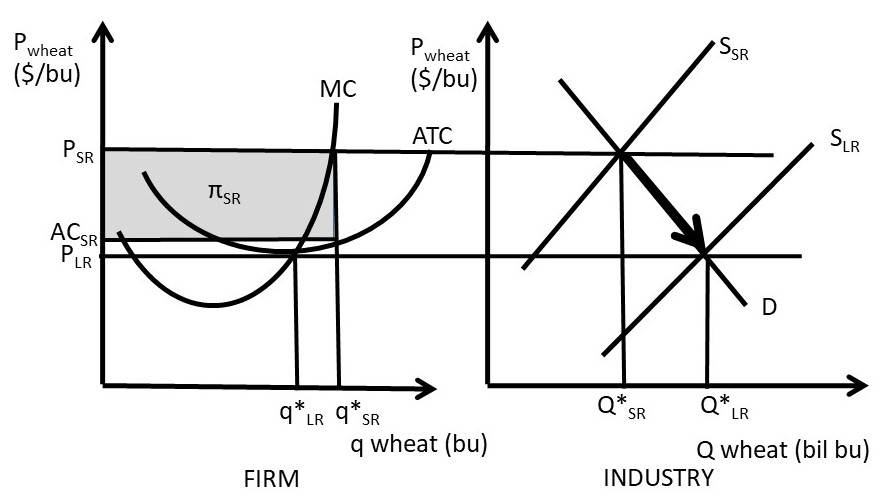
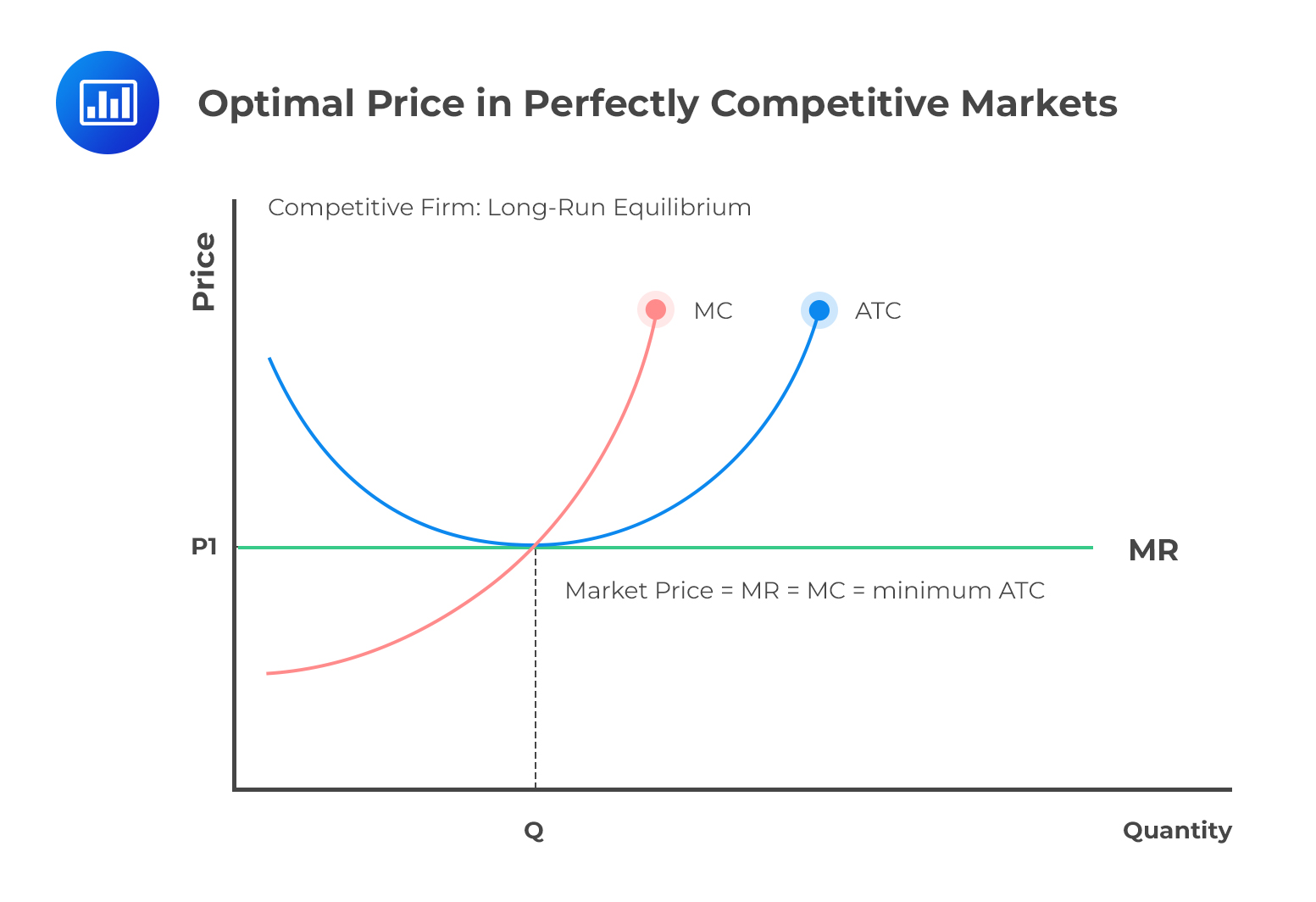
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be. Long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from. ... refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. this firms profit-maximizing price will be. 16. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect firms to leave the industry, market supply to fall, and product price to rise. Therefore, at the long-run equilibrium output at the MR = LMC point, we have, for the monopolist, p > LMC. In other words, in the long-run equilibrium, price is equal to marginal cost for the competitive firm and price is greater than marginal cost for the monopolistic firm. c. Assuming identical long-run costs as in the diagram above, compare graphically the prices and outputs that would result in the long run under pure competition and under monopolistic competition. The reference point corresponding to the long-run price and output for a monopolistically competitive firm is . d.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will: In the long run, economic theory predicts that a monopolistically competitive firm will have excess production capacity. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. 19. Long-run equilibrium for firms in monopolistically competitive industries is similar to that for firms in perfect competition in that A. price equals average cost. B. price equals marginal cost. C. marginal revenue equals average cost. D. price equals minimum possible average cost. 20. Under oligopoly A. there are many sellers in the industry. 6. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: 1. diagram a only. 2. diagram b only. 3. diagram c only. 4. both diagrams b and c. 7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be: 1. above A. 2. EF. 3. A. 4. B. 8.
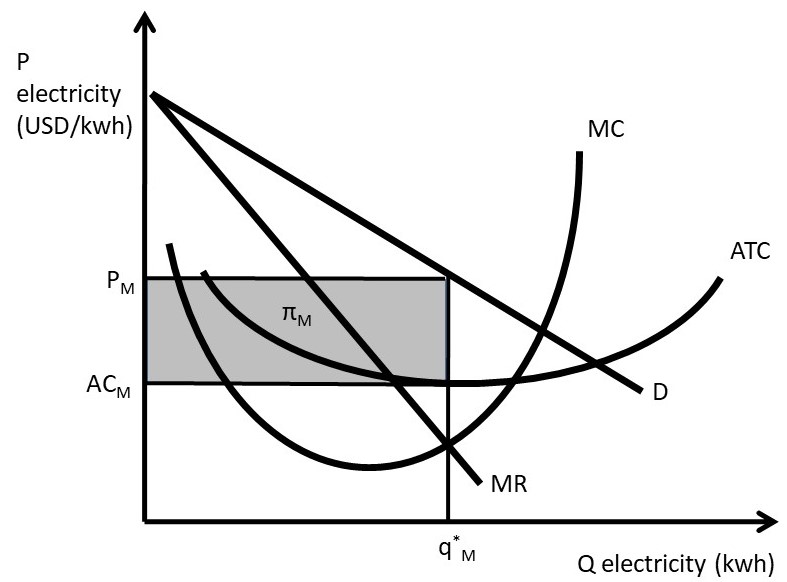
Graph of a monopolistically competitive firm in long run equilibrium firms earn a normal (zero) profit because of few barriers to entry (P=ATC means zero profit) therefore there is no incentive for other firms to enter; Are they efficient? NO. Neither allocative or productive efficiency will be achieved by monopolistically competitive firms in ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. The firm is: A. minimizing losses in the long run. B. minimizing losses in the short run. C. realizing a normal profit in the long run. D. about to leave the industry. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be. e. Nonprice competition refers to. price increases by a firm that are ignored by its rivals. This monopolistically competitive firm is earning economic profits in the short run and. 33) In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms produce where . A) excess capacity exists . B) the markup is equal to zero . C) the demand curve has shifted so that it intersects the minimum average total cost point . D) average total cost is minimized . Answer: A . 34) In monopolistic competition, in the long run firms produce
Long run equilibrium is shown by. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics 4both diagrams b and c. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium price will be. Refer to the above diagram wherein the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars.

Suppose That A Firm Produces Footballs In A Monopolistically Competitive Market The Following Graph Shows Its Demand Curve Marginal Revenue Curve Marginal Cost Curve And Long Run Average Total Cos Study Com
82. Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: A.diagram a only. B. diagram b only. C. diagram c only. D. both diagrams b and c. Difficulty: Medium Learning Objective: 12-02 Explain why monopolistic competitors earn only a normal profit in the long run.
The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist. A monopolistic competitor, like a monopolist, faces a downward-sloping demand curve, and so it will choose some combination of price and quantity along its perceived demand curve.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium output will be. In the short run chamberlins model of monopolistic competition comes closer to monopoly. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. 4both diagrams b and c.
In short run equilibrium the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price. 2refer to the diagram. 13 02 explain why monopolistic competitors earn only a normal profit in the long run. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium.
11) The diagram below shows selected cost and revenue curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry. FIGURE 11-4 Refer to Figure 11-4. How is the excess-capacity theorem demonstrated in this diagram? 11) A) The long-run equilibrium occurs where the firm is producing output at q 1, which is the same as for a perfectly competitive ...
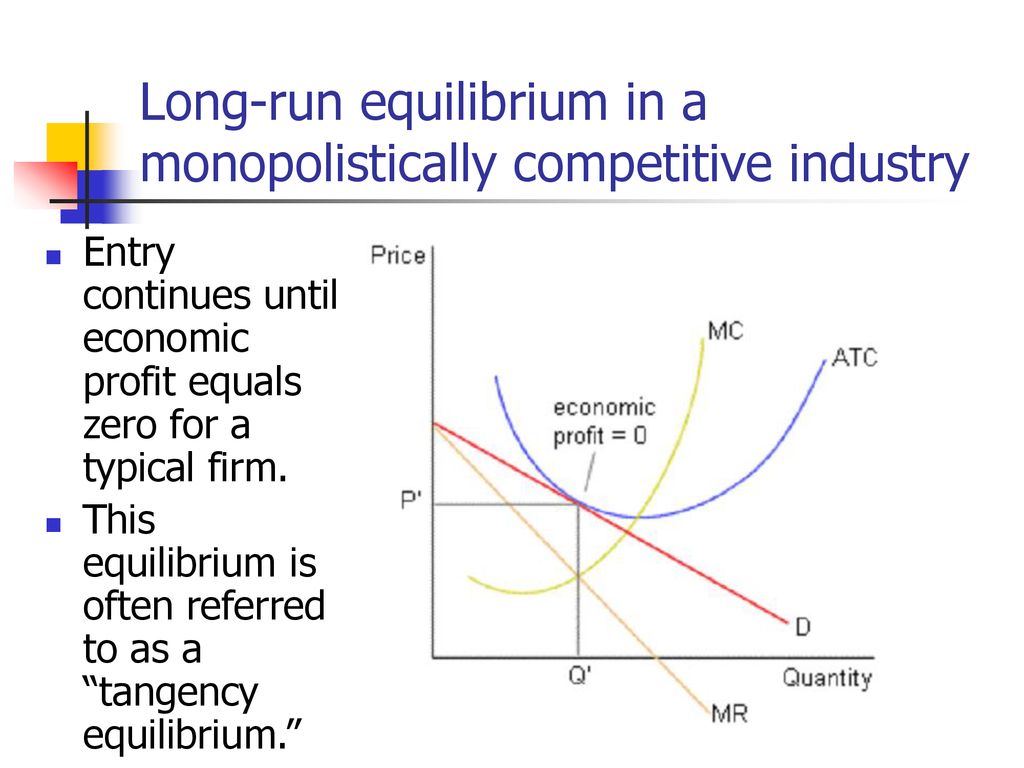
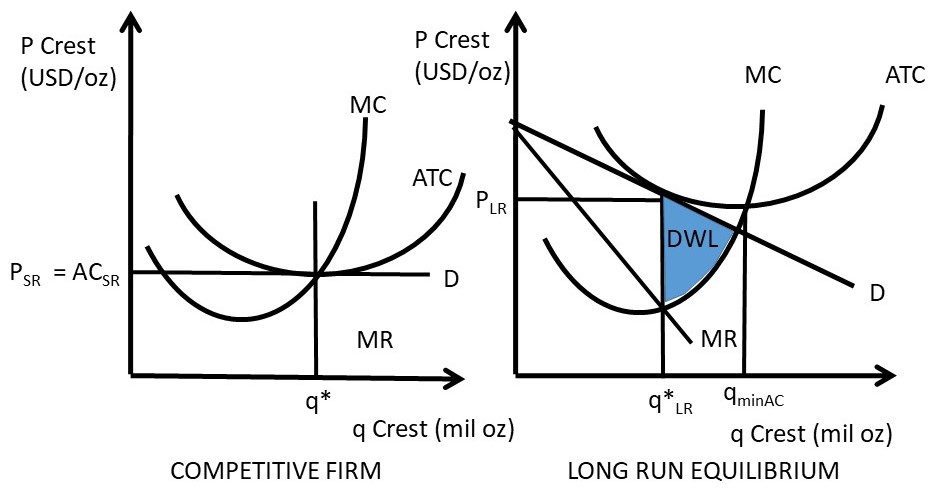
Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn zero economic profits in the long run. Long run equilibrium of monopolistic competition. The price will be set where the quantity produced falls on the average revenue ar curve. In long run equilibrium a monopolistically competitive firm sets it price.
0 is the long-run equilibrium in the market, just as it is in perfect completion. The graph below shows a monopolistically competitive firm in long-run equilibrium with zero profit. Use the graph above and compare to long-run equilibriums in perfect competition and monopoly. The graph will also be used to evaluate monopolistic competition with
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
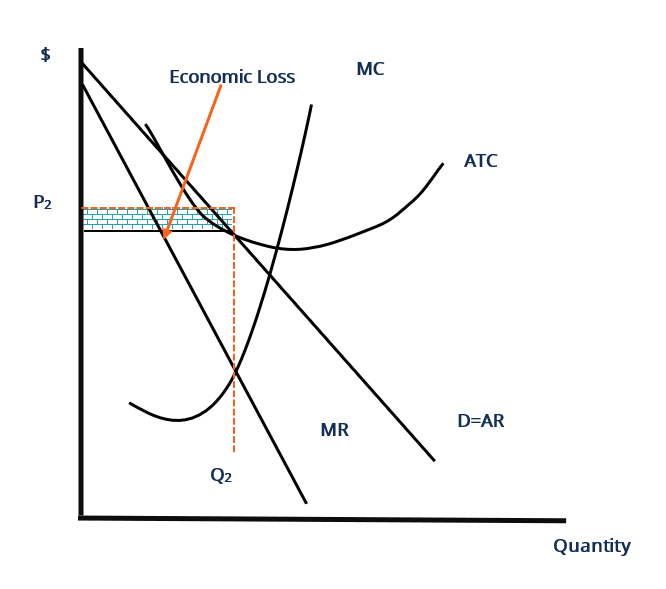
A) equilibrium output would rise and equilibrium price would fall. B) the demand curve would become more elastic. C) equilibrium output would decline and equilibrium price would rise. D) none of these above. B. Refer to the diagram below for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically. Long run equilibrium output will be. Production takes place where atc is minimized. Monopolistic competition in the long run. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. The same price and produce the same output as a competitive firm.
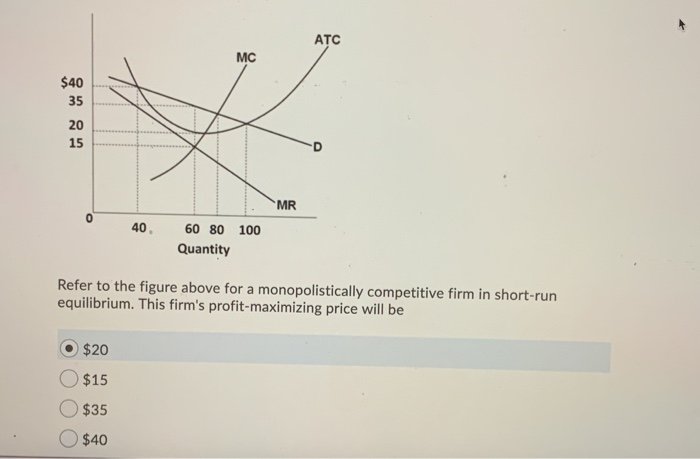
The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be If some firms leave a monopolistically competitive industry, the demand curves of the remaining firms will shift to the right.
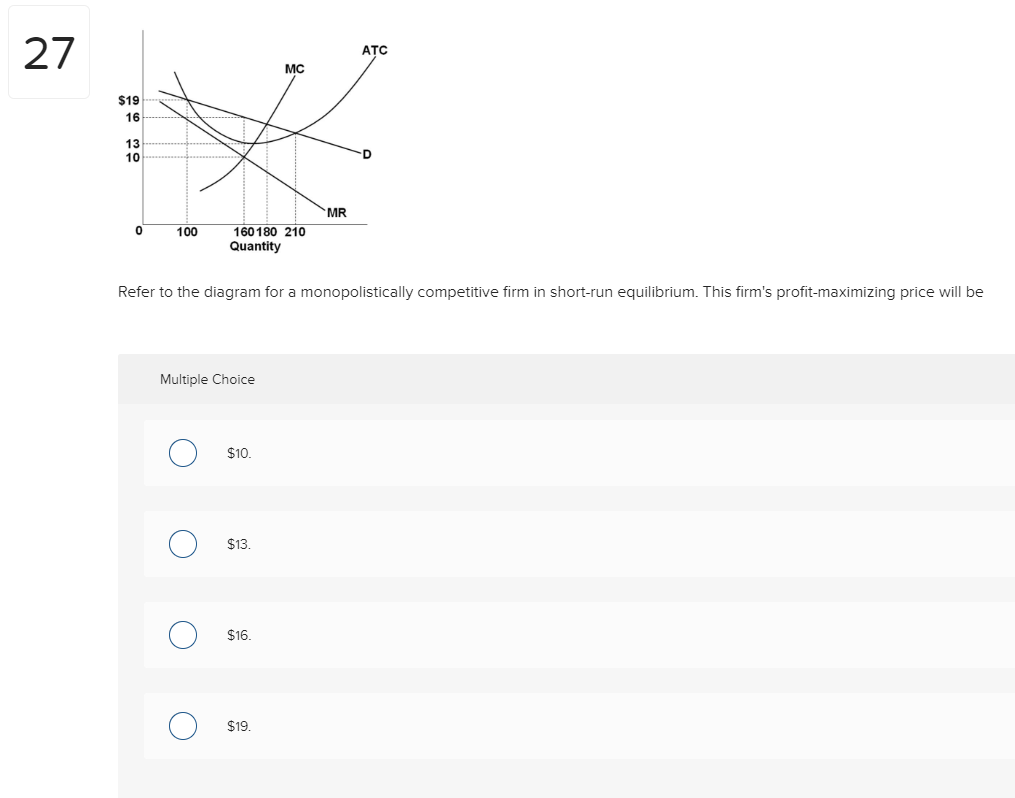
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030 ... In long-run equilibrium a monopolistically competitive firm will: A. earn an economic profit. ...
a) 0.1 b) 0.167 c) 0.25 d) 6 e) Impossible to calculate. 2 7. The diagram above shows the residual demand, marginal revenue and long-run cost curves for a monopolistically competitive producer. In the long-run, the monopolistically competitive firm will: a) continue to earn economic profit. b) earn normal profit like perfectly competitive firms.
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be. A. Long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm where economic profits are zero results from. relatively easy entry.
In the long run, what price will this firm charge for its output? a) $10. b) A price less than $10 and greater than $6. c) $6. d) A price less than $6 and greater than $4. The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 3. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm? a) Figure 1 ...
Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown - will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. - cannot operate at a loss. - is in long-run equilibrium. - is realizing an economic profit.
The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure .. The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the supply of differentiated products, which causes the firm's market demand curve to shift to the left. As entry into the market increases, the firm's demand curve will continue shifting to the left until it is just tangent to the average total ...
SR Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Given the short run equilibrium described, why does entry occur? As entry occurs, demand shifts leftward until profit equals zero. Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Diagram at right shows long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm. economic profits? price mark-up (P vs ...

1 A Monopolistically Competitive Sneaker Firm Is Currently In Long Run Equilibrium A Graph The Firm Homeworklib
Option d is correct. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm, the long run price will be a …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: $ MC ATC A Demand MR DE Quantity Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium price will be Multiple Choice above A EF 8.
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Long run equilibrium price will be. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is. In the short run a monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profit or minimizes losses by producing that quantity that corresponds to when marginal ...













0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be"
Post a Comment