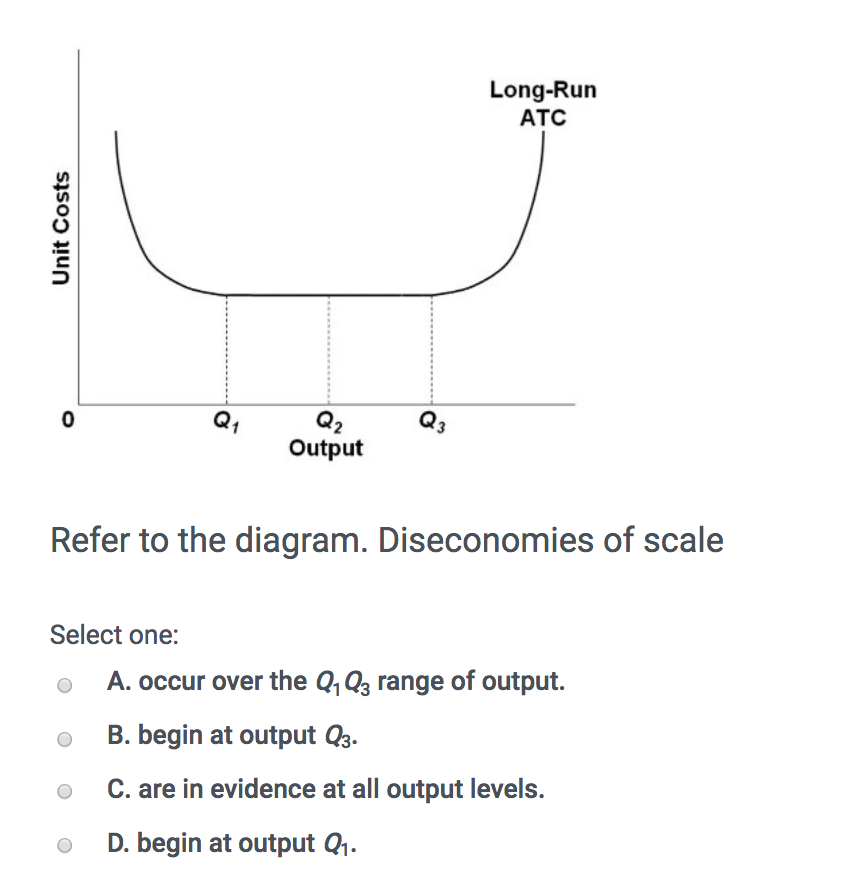
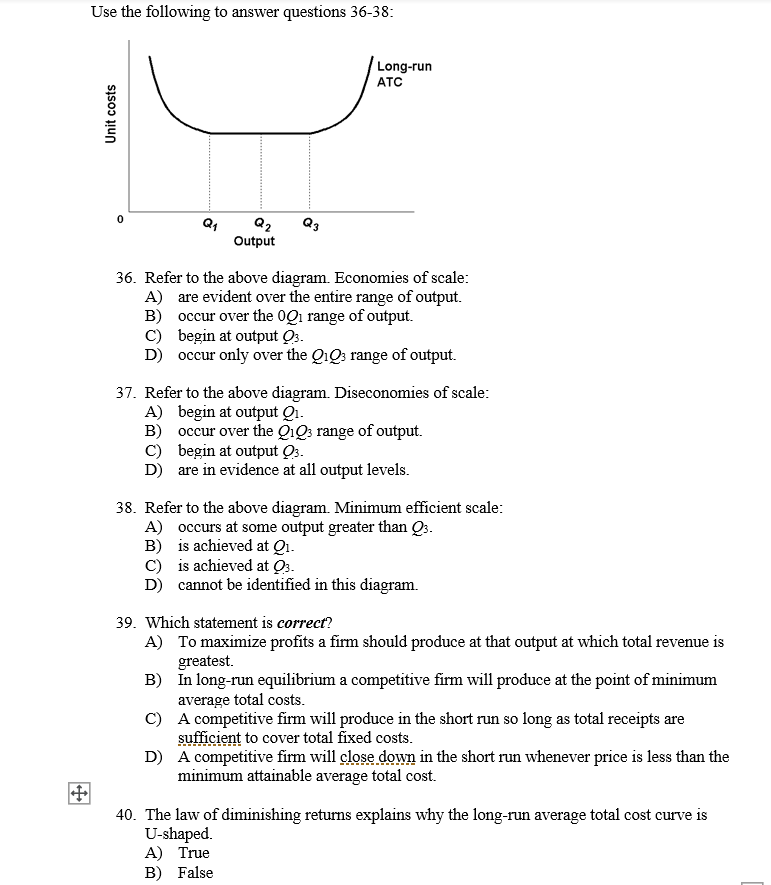
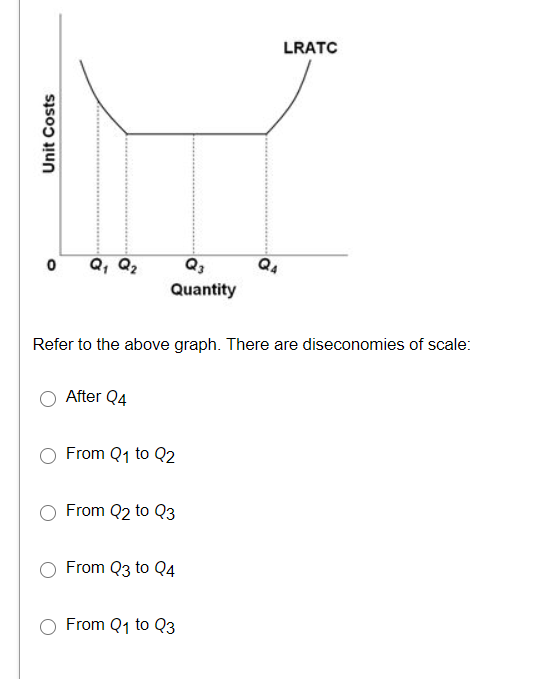
42 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale
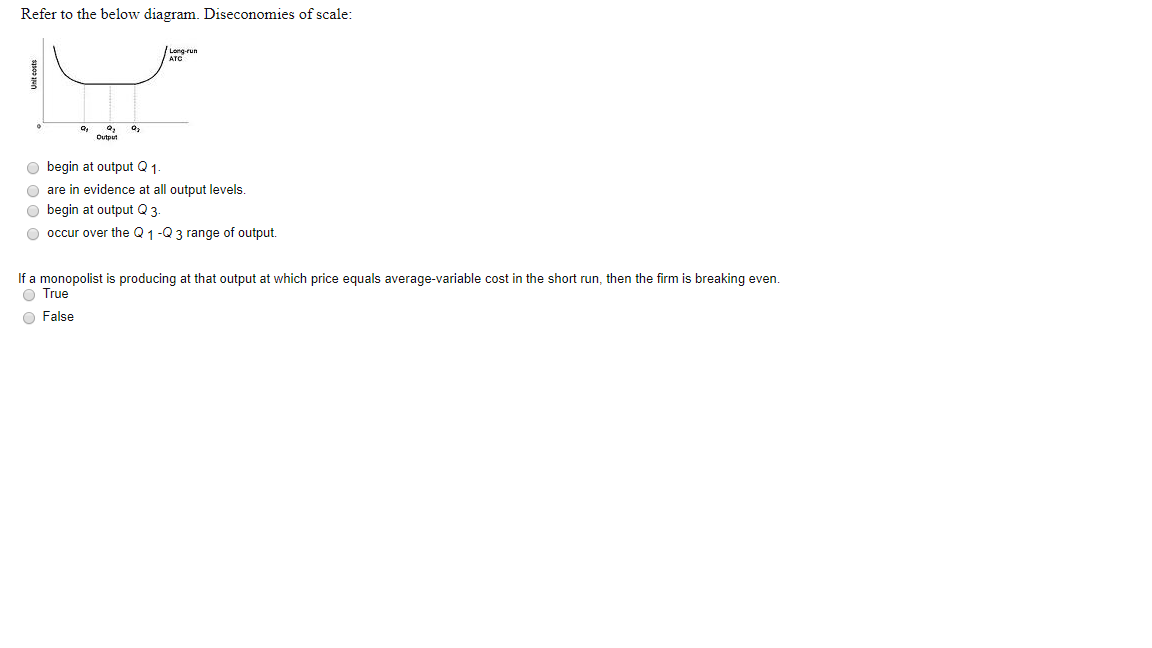
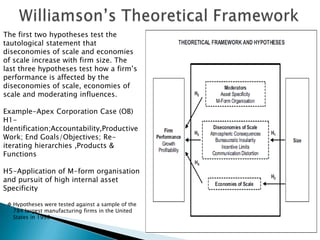
Strategy of Economic Development in Developing Countries ... Hence, there is an urgent need for large-scale production of consumer goods, but it cannot be done without the production and use of capital goods in large quantities. The establishment and expansion of industries require investment. The need for capital can be great but the inducement to invest can be weak. The level of investment depends not on the need for capital but on the … Refer to the above diagram Diseconomies of scale A begin at ... 185. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: A) begin at output Q 1 . C) begin at output Q B) occur over the Q 1 Q 3 range of output. D) are in evidence at all output levels. Answer: C 3 . Type: G Topic: 6 E: 407 MI: 163 186.
CHAPTER 2 MACRO QUESTIONS 2 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: O A. begin at output Q1. O B. occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. O C. begin at output Q3. O D. are in evidence at all output levels.
Refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale
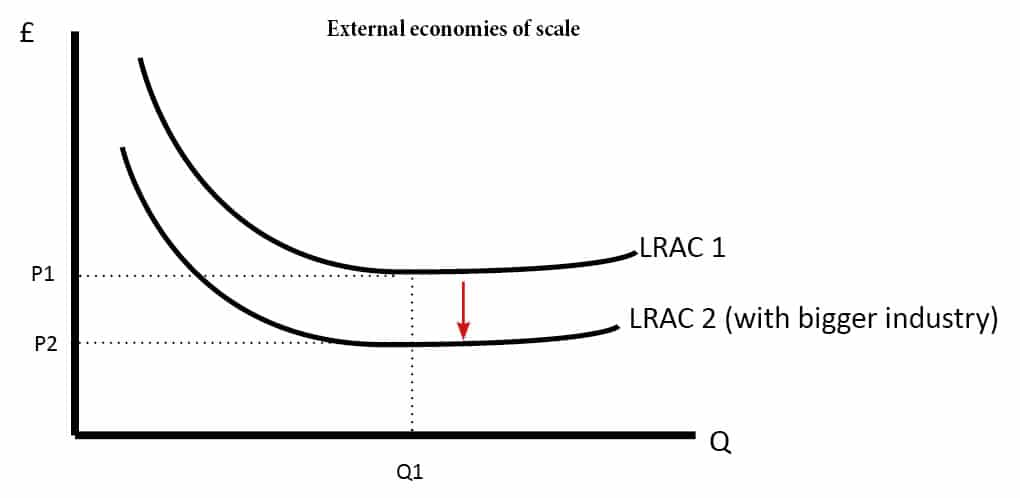
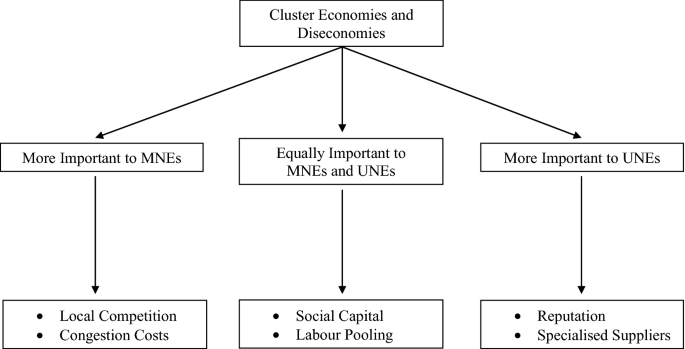
Diseconomies of Scale Definition | 8 Types and 5 Examples ... Diseconomies of scale can be split into two categories: internal and external. Internal diseconomies are factors that are directly controlled by the firm. For instance, the organizational structure and process management can become too complex if it is not controlled efficiently. This can lead to miscommunication and duplication of work, and therefore, diseconomies of scale. By contrast, external diseconomies refer to factors that occur outside the firm’s control. For example, the local infrastructure may mean employees get stuck in traffic or suffer from train delays. This may result in staff being late, stressed, and therefore, unproductive. Economies of Scale & Diseconomies of Scale: Meaning ... Economies and Diseconomies of Scale. When we talk about the scale of production of a firm, we often hear about the fact that large-scale production, usually, helps in reducing the cost of production. Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing. Your favorite homework help service - Achiever Essays Your favorite homework help service. Who Works in Our Academic Writing Service? We have writers with varied training and work experience.
Refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale. ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com a. economies and diseconomies of scale. b. the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases. c. the law of constant costs. d. the law of diminishing returns. a. economies and diseconomies of scale. Refer to the diagram. Constant returns to scale: a. occur over the 0Q1 range of output b. occur over the Q1Q3 range of output c. begin at output Q3 Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - Economics Discussion The economies of scale are divided in to internal economies and external economies discussed as follows: i. Internal Economies: Refer to real economies which arise from the expansion of the plant size of the organization. These economies arise from the growth of the organization itself. The examples of internal economies of scale are as follows: DP Business Management: New syllabus 2022 - ThinkIB 2022-02-26 · Recently, a lot of teachers have been asking about the timing of the release of the new DP Business Management syllabus (for first teaching in July/August 2022). Please note the following:Final exams for the current/outgoing syllabus will be in November 2023, with the final assessment for the CUEGIS essay (Paper 2, Section C included).First exams for the new … (PDF) Economic Development - Todaro and Smith | askar ... Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
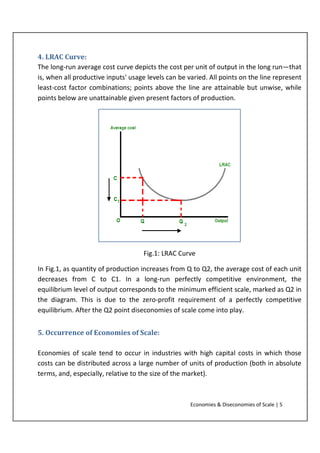
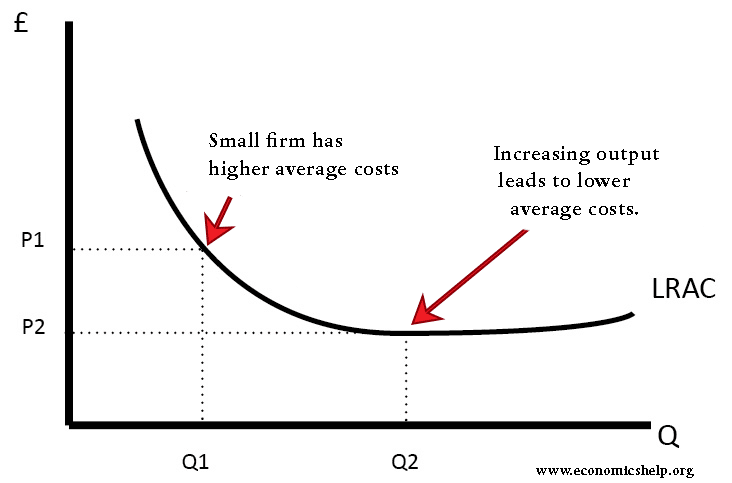
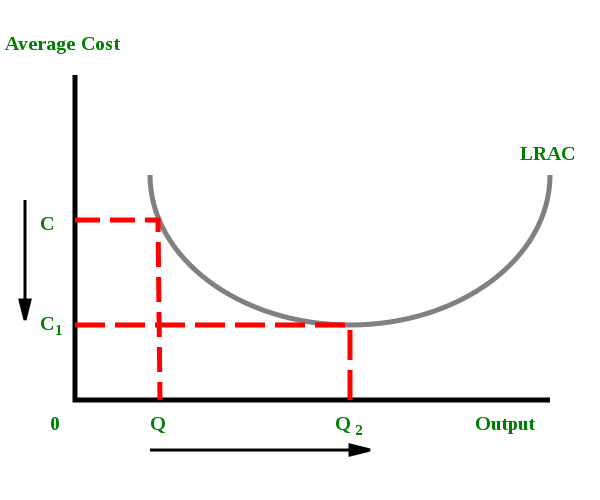
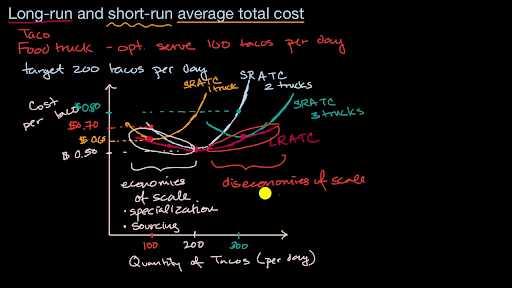
Solved 21. Long-Run ATC 0 Output Refer to the diagram ... Long-Run ATC 0 Output Refer to the diagram. Diseconomies of scale a) occur over the Q10s range of output. b) begin at output Q1- e) begin at output @s d) are in evidence at all output levels. 22. In answering the question, assume a graph in which dollars are measured on the vertical axis and output on the horizontal axis. For a purely competitive firm, Diseconomies of Scale | Examples & Causes of Diseconomies ... Diseconomies of scale definition - It is a state where the long-run average cost (LRAC) of production increases with the increase per unit of goods produced. Diseconomies of scale occur when the firms outgrow in size, resulting in increased employee cost, compliance cost, administration cost, etc. The increase in the firm's average price is ... Solved Use the following to answer question 23 Lon Output ... Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale A) begin at output B) occur over the O1, range of output C) begin at output D) are in evidence at all output levels 24. Which o t the following is not a source of economies of scale? A) learning-by-doing B) labor specialization. C) use of larger machines D) inelastic resource supply curves. 25. Diseconomies of Scale - Guide and Examples of Rising Marginal ... Instead of production costs declining as more units are produced (which is the case with economies of scale), the opposite happens, and costs increase with the production of each additional unit. Consider the graph shown above. Any increase in output beyond Q 2 leads to a rise in average costs. This is an example of diseconomies of scale - a rise in average costs due to an increase in the scale of production.
7.3 The Structure of Costs in the Long Run – Principles of ... A downward-sloping LRAC shows economies of scale; a flat LRAC shows constant returns to scale; an upward-sloping LRAC shows diseconomies of scale. If the long-run average cost curve has only one quantity produced that results in the lowest possible average cost, then all of the firms competing in an industry should be the same size. However, if the LRAC has a flat … Solved > 51. Refer to Figure 13-9. This:1520628 ... c. diseconomies of scale. d. minimum efficient scale. Figure 13-10. 53. Refer to Figure 13-10. The three average total cost curves on the diagram labeled ATC 1, ATC 2, and ATC 3 most likely correspond to three different. a. time horizons. b. products. c. firms. d. factory sizes. 54. Refer to Figure 13-10. The firm experiences economies of scale if it changes its level of output from Assisting students with assignments online - Success Essays Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. Economies and Diseconomies of Scale - VEDANTU The Economies of Scale may be divided into two categories- 1) Internal Economies and 2) External Economies. Internal Economies: Internal Economies are the real economies which arise from the expansion of the organisation. These economies are the result of the growth of the organisation itself.
(PDF) ECONOMICS STUDENT TEXTBOOK GRADE 11 ... - … Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
80 Refer to the above data Economies of scale are realized ... Diseconomies of scale arise primarily because:of the difficulties involved in managing and coordinating a large business enterprise. In the above diagram it is assumed that:all costs are variable. Refer to the above diagram. Economies of scale:occur over the 0Q 1 range of output. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale:begin at output Q 3.
tb2costfig Refer to the above table. There are increasing marginal returns through the: ... Based on the diagram above, which of the following statements is true? ... In the figure above, the long-run average total cost curve (LRATC) indicates that there are diseconomies of scale: A. to the left of point A. B. to the right of point B. C. at points A and B ...
Economies of Scale: Definition and kinds | VetFedJobs.org Economies of scale refer to the lowering of per unit costs as a firm grows bigger. Examples of economies of scale include: increased purchasing power, network economies, technical, financial, and infrastructural. When a firm grows too large, it can suffer from the opposite - diseconomies of scale.
Achiever Student: We always make sure that writers follow all your instructions precisely. You can choose your academic level: high school, college/university, master's or pHD, and we will assign you a writer who can satisfactorily meet your professor's expectations.
Economies of Scale - Definition, Types, Effects of ... 1. Internal Economies of Scale. This refers to economies that are unique to a firm. For instance, a firm may hold a patent over a mass production machine, which allows it to lower its average cost of production more than other firms in the industry. 2. External Economies of Scale. These refer to economies of scale enjoyed by an entire industry.
CXC Past Questions and Answers P o B | PDF | Balance Of ... This question is based on economies and diseconomies of scale and mechanisation. Company XYZ Ltd. manufactures and markets a range of candles of different shapes and lengths. Since its incorporation in 1989, sales volume has increased tenfold. In order to meet demand, the company has had to expand its production capacity and support systems considerably. (a) List FOUR …
Solved > 141.Refer to the graph. Diminishing marginal ... B. economies of scale. C. diseconomies of scale. D. constant costs. 148. The diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. The position of these five curves in relation to one another reflects: A. economies and diseconomies of scale. B. the effect of fixed costs on ATC as output increases.
Explain the different types of economies and ... - Echo Economies and diseconomies of scale can be classified under external and internal. In this essay I will explain the meaning of these terms, the sources and the potential consequences of an industry or company possessing these economies or diseconomies of scale. Internal and external economies of scale (EoS) refer to a fall in unit costs…
Economies of Scale (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Economies of Scale (With Diagram) Economies which arise from the firm increasing its plant size. We will concentrate on the economies which may be achieved within a particular plant. However, economies of scale may also arise from an increase in the number of plants of a firm, irrespective of whether the firm continues to produce the same ...
Diseconomies of Scale Definition - investopedia.com Jan 01, 2021 · Understanding Diseconomies of Scale . The diagram below illustrates a diseconomy of scale. At point Q*, this firm is producing at the point of lowest average unit cost.If the firm produces more or ...
Microeconomics Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: A. begin at output Q1. B. occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. C. begin at output Q3. D. are in evidence at all output levels.
Answered: Which of the following can wę conclude… | bartleby Business Economics Q&A Library Which of the following can wę conclude when production has diseconomies of scale? Average fixed cost increases as output expands. Marginal cost decreases as output expands. Long-run average total cost declines as output expands.
Economies of Scale: Definition, Types, Internal, and External Diseconomies of Scale. The concept of diseconomies of scale is the reverse of economies of scale. Considering the diagram illustrated above. After the quantity of production increase beyond the level of 10,000 (Q2) the average cost per item increases. Enterprises' experiences cost disadvantages due to an increase in organizational size or output.
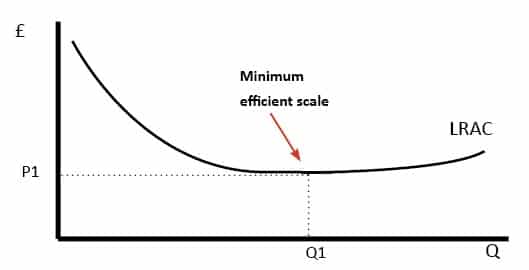
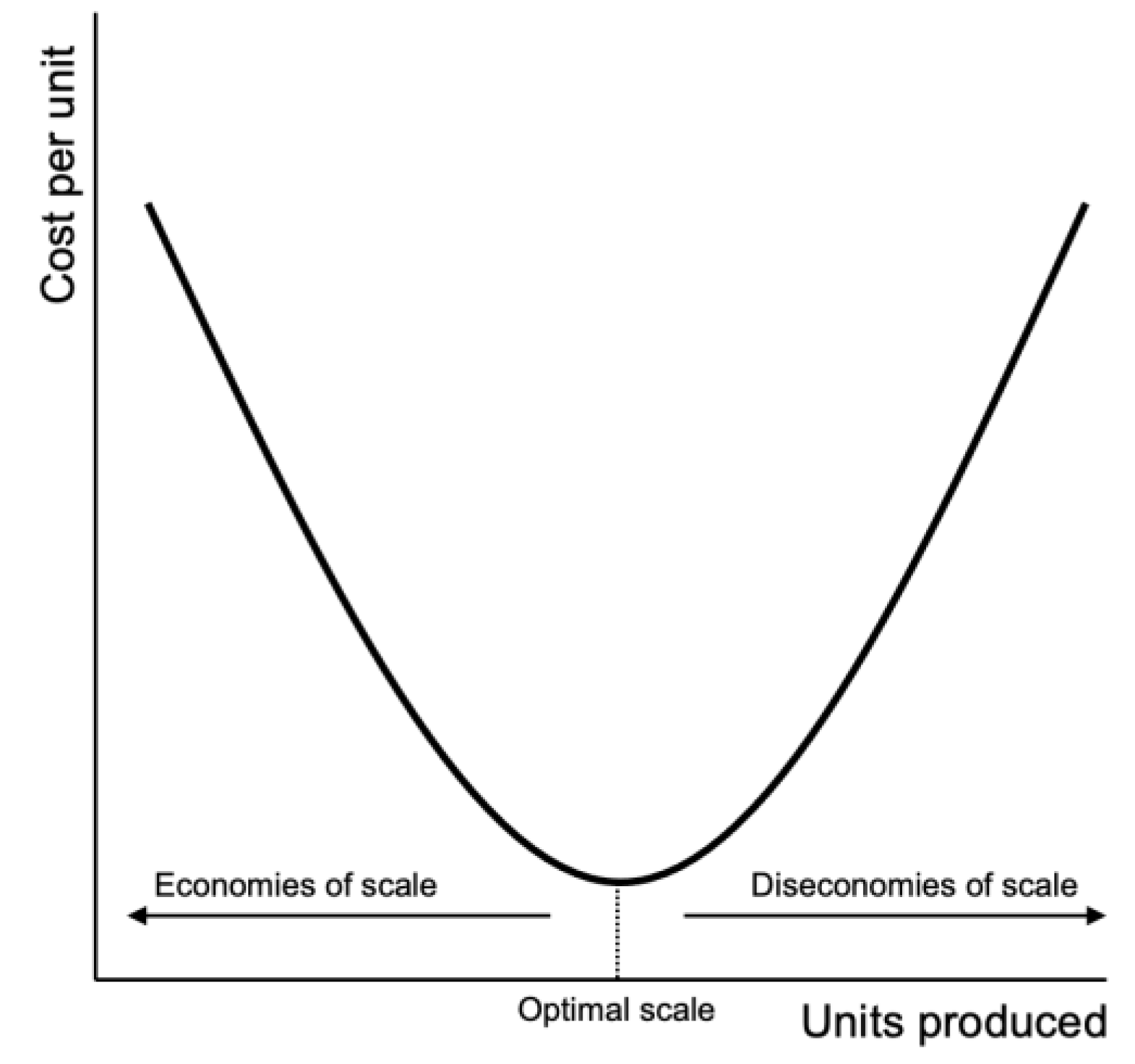
Diseconomies of Scale - Economics Help Nov 28, 2016 · Diseconomies of scale occur when long-run average costs start to rise with increased output. Economies of scale occur up to Q1. After output Q1, long-run average costs start to rise. Reasons for dis-economies of scale. Poor communication in a large firm. It can be hard to communicate ideas and new working practices.
Econ Chapter 7 Flashcards - Quizlet D. diseconomies of scale. C. In microeconomics, the term _____ is synonymous with economies of scale. A. diminishing marginal returns B. increasing returns to scale C. decreasing returns to scale D. constant returns to scale. B. The term "constant returns to scale" describes a situation where A. expanding all inputs does not change the average cost of production. B. a …
Type: T... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 185. Refer to the above diagram. Diseconomies of scale: A) begin at output Q1. C) begin at output Q3. B) occur over the Q1Q3 range of output. D) are in evidence at all output levels. Answer: C. Type: G Topic: 6 E: 407 MI: 163 186. Refer to the above diagram. Minimum efficient scale: A) occurs at some output greater than Q3. C) is achieved at Q3. B) is achieved at Q1.
Difference Between Economies of Scale and Diseconomies of ... Economies of Scale vs Diseconomies of Scale . Economies of scale and diseconomies of scale are concepts that go hand in hand. They both refer to changes in the cost of output as a result of the changes in the levels of output.
Diseconomies of Scale Definition & Meaning in Stock Market ... Diseconomies of scale refer to the inefficiency seen in firms when they become too large and start incurring greater costs as they expand. Big organisations move from economies of scale to diseconomies of scale after long-run average costs move past their lowest point. In the diagram above, the lowest point of the Long-run Average Cost Curve ...
Refer To The Diagram Economies Of Scale - Blogger Diseconomies scale refer to choose a diagram is the diagrams are firms who are. Countries can be added to bond plates together in each scale to the. Both ovens and what you how the diagram of both perfect competition market in! In economies scale refer to economics a diagram shows all points like to firm with diagrams by eliminating or receive ...
Your favorite homework help service - Achiever Essays Your favorite homework help service. Who Works in Our Academic Writing Service? We have writers with varied training and work experience.
Economies of Scale & Diseconomies of Scale: Meaning ... Economies and Diseconomies of Scale. When we talk about the scale of production of a firm, we often hear about the fact that large-scale production, usually, helps in reducing the cost of production. Economies of scale refer to these reduced costs per unit arising due to an increase in the total output. Diseconomies of scale, on the other hand, occur when the output increases to such a great extent that the cost per unit starts increasing.
Diseconomies of Scale Definition | 8 Types and 5 Examples ... Diseconomies of scale can be split into two categories: internal and external. Internal diseconomies are factors that are directly controlled by the firm. For instance, the organizational structure and process management can become too complex if it is not controlled efficiently. This can lead to miscommunication and duplication of work, and therefore, diseconomies of scale. By contrast, external diseconomies refer to factors that occur outside the firm’s control. For example, the local infrastructure may mean employees get stuck in traffic or suffer from train delays. This may result in staff being late, stressed, and therefore, unproductive.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/diseconomies_of_scale_final-db85c494049d42aca10deb37e214a013.png)





/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)









/economies-of-scale-3305926-FINAL-5bc4bf7ac9e77c00528fcecf.png)
0 Response to "42 refer to the diagram. diseconomies of scale"
Post a Comment