42 glycolysis diagram for kids
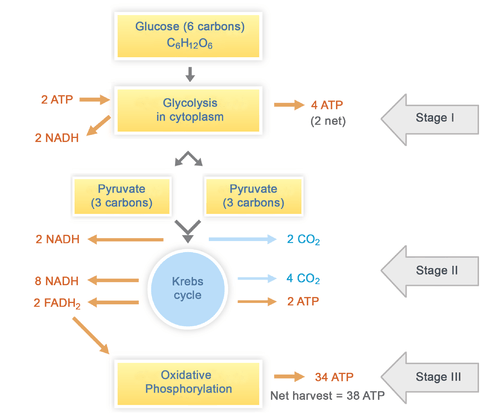
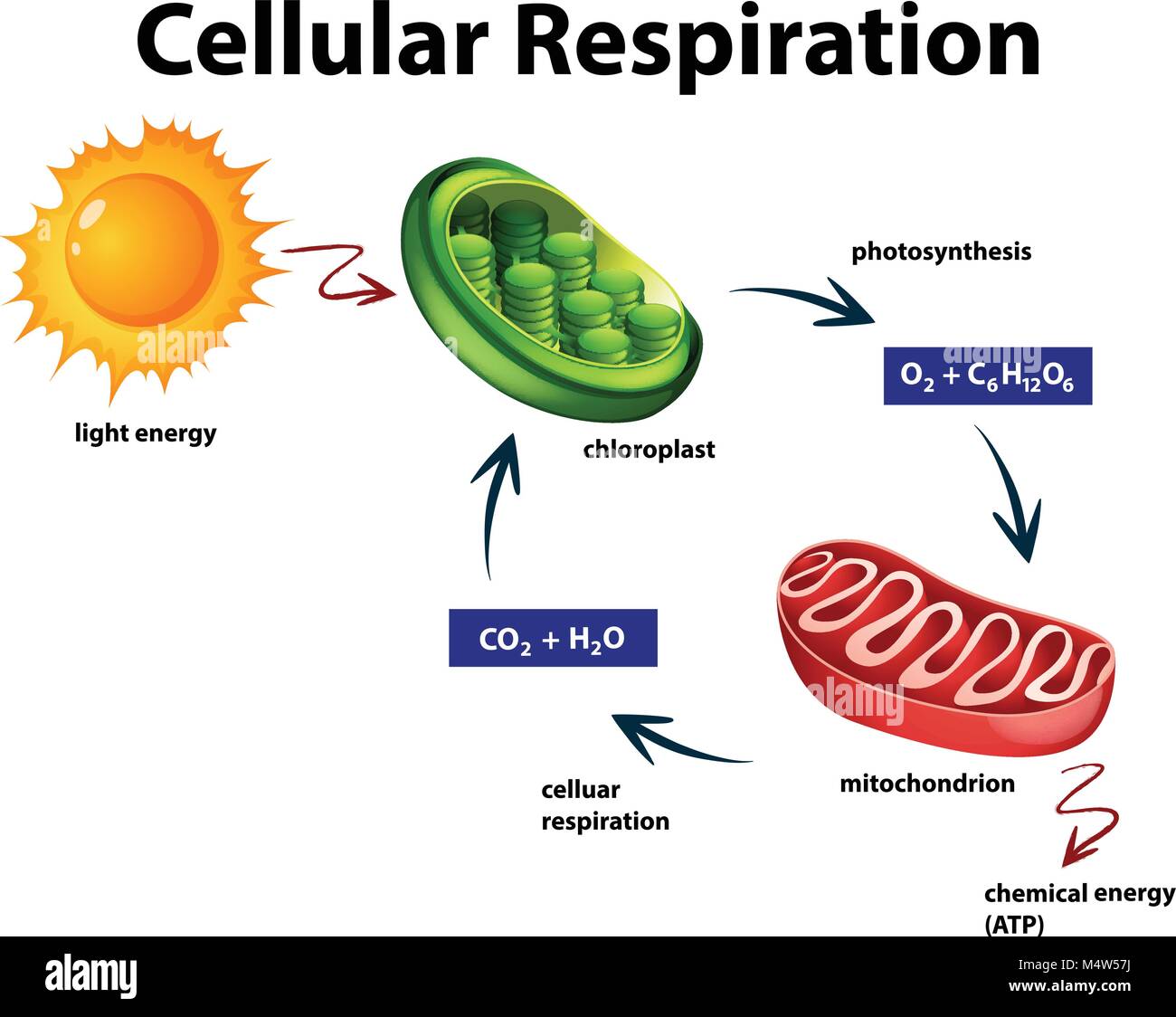
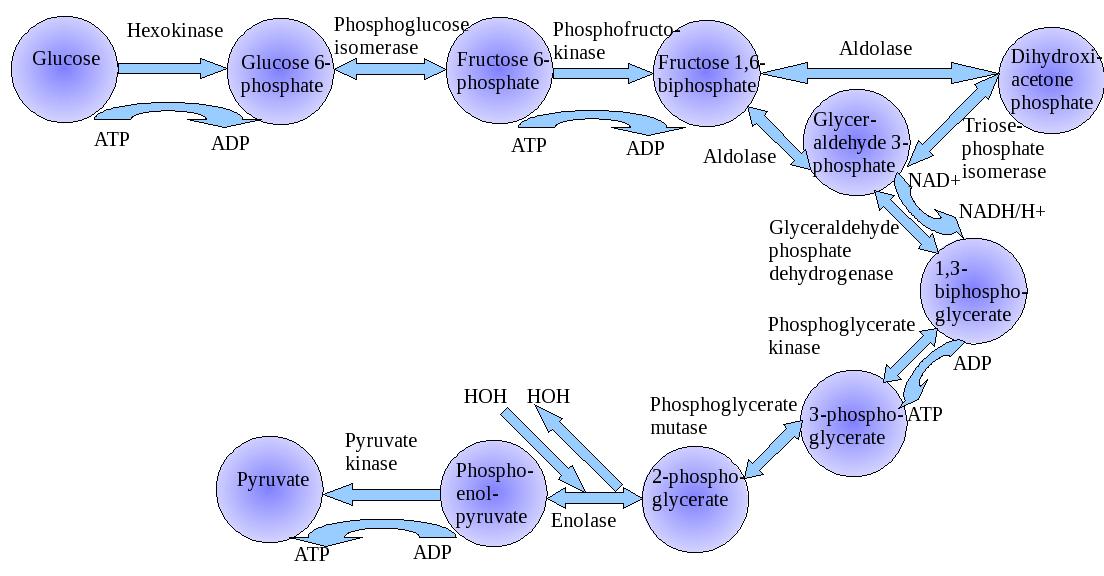
Glycolysis During glycolysis, two NADH molecules are produced. Because glycolysis does not require oxygen, the process is considered to be anaerobic. Glycolysis is a somewhat inefficient process because much of the cellular energy remains in the two molecules of pyruvic acid that are created. Glycolysis overview | Biology Drawing | Biology | Glycolysis Cycle... "Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)."
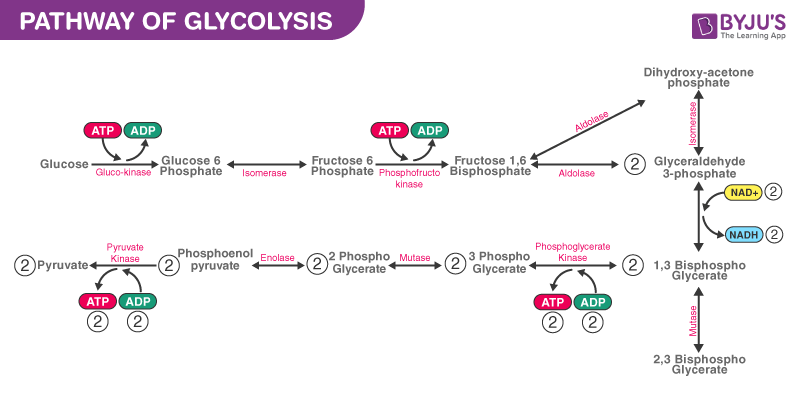
Glycolysis Cycle - Steps and Enzymes (with Diagrams) In-Detail Glycolysis is the process by which the sugar is split and the energy within the sugar is released. It splits two molecules of three carbon sugar pyruvate. (1, 2). Image 1: The glycolysis cycle as shown in the diagram. Picture Source: botanystudies.com. Picture 2: The glycolysis process with emphasis...

Glycolysis diagram for kids
Glycolysis - Wikipedia Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvic acid, CH3COCOOH. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. Diagram of Glycolysis pathway Glycolysis, an overview. Glycolysis (a sweet splitting process) is a central pathway for the catabolism of carbohydrates in which the six-carbon sugars are split to three-carbon compounds with subsequent release of energy used to transform ADP to ATP. Glycolysis can proceed under anaerobic (without...
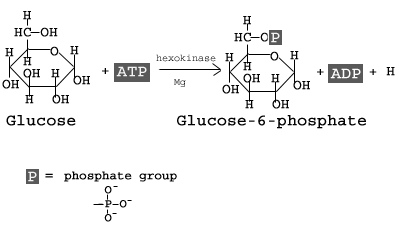
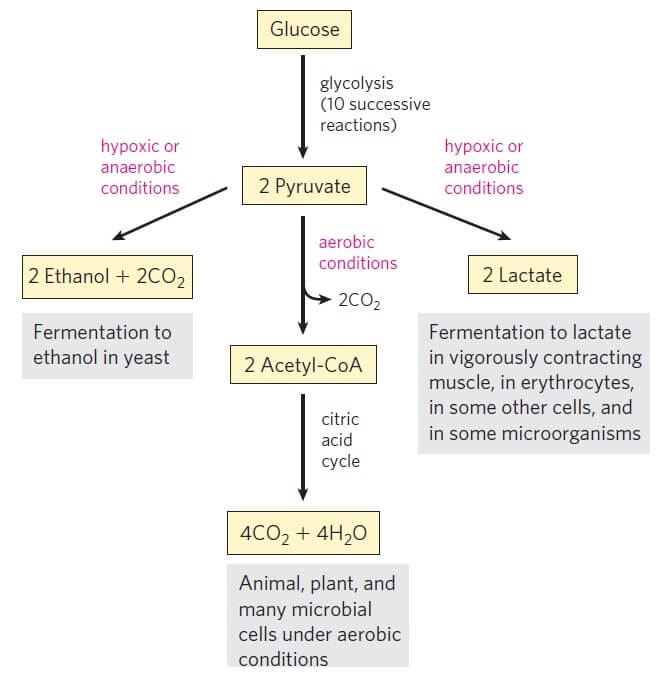
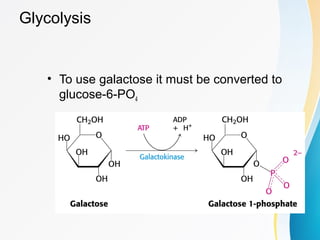
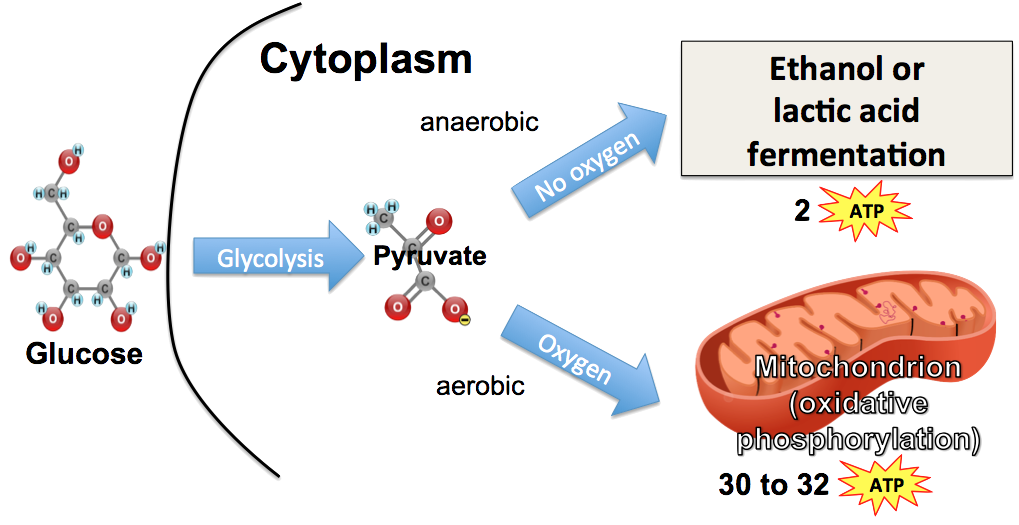
Glycolysis diagram for kids. Glycolysis, steps, diagram, regulation - The Virtual Notebook Glycolysis is the major pathway for glucose metabolism in which glucose will convert to pyruvate (under aerobic condition) or lactate (anaerobic). Glycolysis is both the principal route for glucose metabolism and also the main pathway for the metabolism of fructose, galactose, and other... Glycolysis Facts for Kids Glycolysis is a metabolic process in most organisms. It is the first stage in cellular respiration. It allows both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Glycolysis releases only a small amount of energy. Glycolysis is thought to be the archetype of a universal metabolic pathway. Glycolysis Summary Introduction to Glycolysis: The most pressing need of all cells in the body is for an immediate source of energy. Some cells such as brain cells have severely limited storage capacities for either glucose or ATP, and for this reason, the blood must maintain a fairly constant supply of glucose. Glycolysis - What You Need to Know (Diagram) : Mcat Also, Heres my Anki for glycolysis: Glycolysis - Net yield = {{c7::2 ATP and 2 NADH}}. Hexokinase - enzyme that {{c6::traps}} glucose in cells by converting it to {{c6::glucose-6-phosphate}} via the addition of a phosphate from {{c6::ATP}}. It is inhibited by {{c6::its product (G6P)}}.
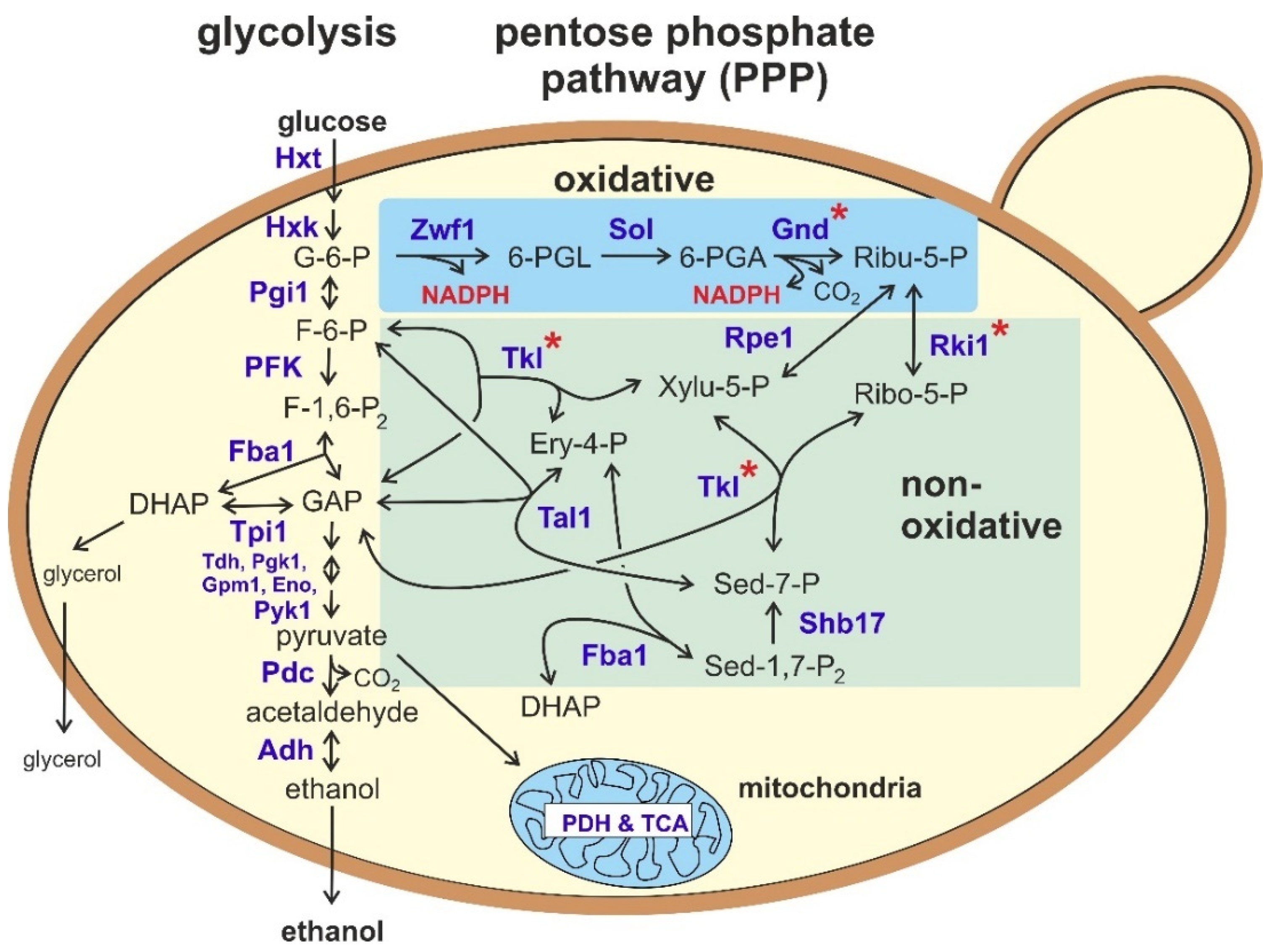
Glycolysis Interactive Lyrics and Flashcards - learn-biology Really want to learn about glycolysis? Go to my glycolysis tutorial, which will take you through the whole process (and which is my new, improved version of what's below). Here's some other sciencemusicvideos links that you might find useful. Glycolysis: steps, enzymes, and products - Tuscany Diet Glycolysis: where the pathway takes place in the cell, steps, enzymes, and products. Other carbohydrates besides glucose, both simple and complex, can be catabolized via glycolysis, after enzymatic conversion to one of the glycolytic intermediates. Glycolysis : All Steps with Diagram, Enzymes... - Laboratoryinfo.com Glycolysis can be defined as the sequence of reactions for the breakdown of Glucose (6-carbon molecule) to two molecules of pyruvic acid (3-carbon Hexokinase is a key glycolytic enzyme. Hexokinase catalyses a regulatory step in glycolysis that is irreversible. However, for hexokinase's... glycolysis diagram for kids - Google Search This is a 4 page hands-on activity that focuses on glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Included are two pages that have diagrams, a cut-n-paste sheet, and an analysis sheet (5 questions). The digital version uses drag and drop for the answers instead of cut and paste!
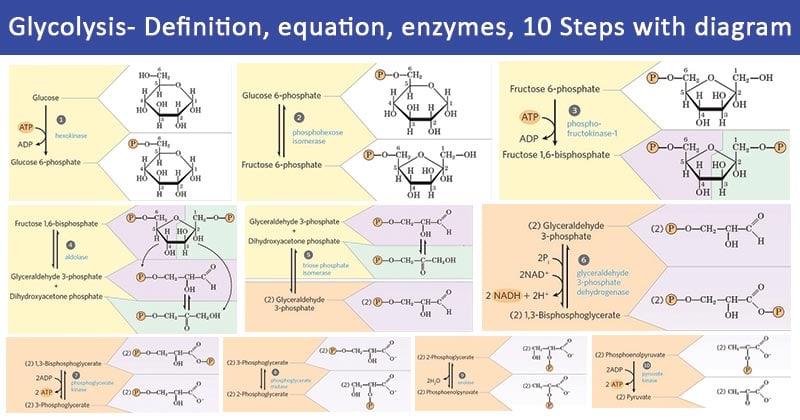
Glycolysis - Diagram, Steps, Pathway (Cycle), Products, Enzymes Picture 4: Regulating Steps of Glycolysis Diagram source :quizlet.com. As for any chemical reaction, when the reactant (Glucose) is available in excess, there is an increase in the Also, increased amount of Glucose results in insulin secretion which in turn increases the glycolytic enzyme activities. Glycolysis Diagram Flashcards | Quizlet Only RUB 193.34/month. Glycolysis Diagram. STUDY. Flashcards. Glycolysis As noted above, glycolysis is only the first stage of glucose degradation. Under aerobic conditions, most of the pyruvate formed in glycolysis undergoes complete oxidative degradation to CO2 and H2O. Pyruvate destined for complete degradation is transported to the mitochondria... Glycolysis 10 Steps with Diagram and ATP Formation Glycolysis refers to the biochemical pathway by which glucose breaks down into pyruvate and produces energy in the form of ATP. The process of glycolysis is divided into two phases. Firstly, the Preparatory phase consists of five different reactions. During this phase, the glucose molecule...
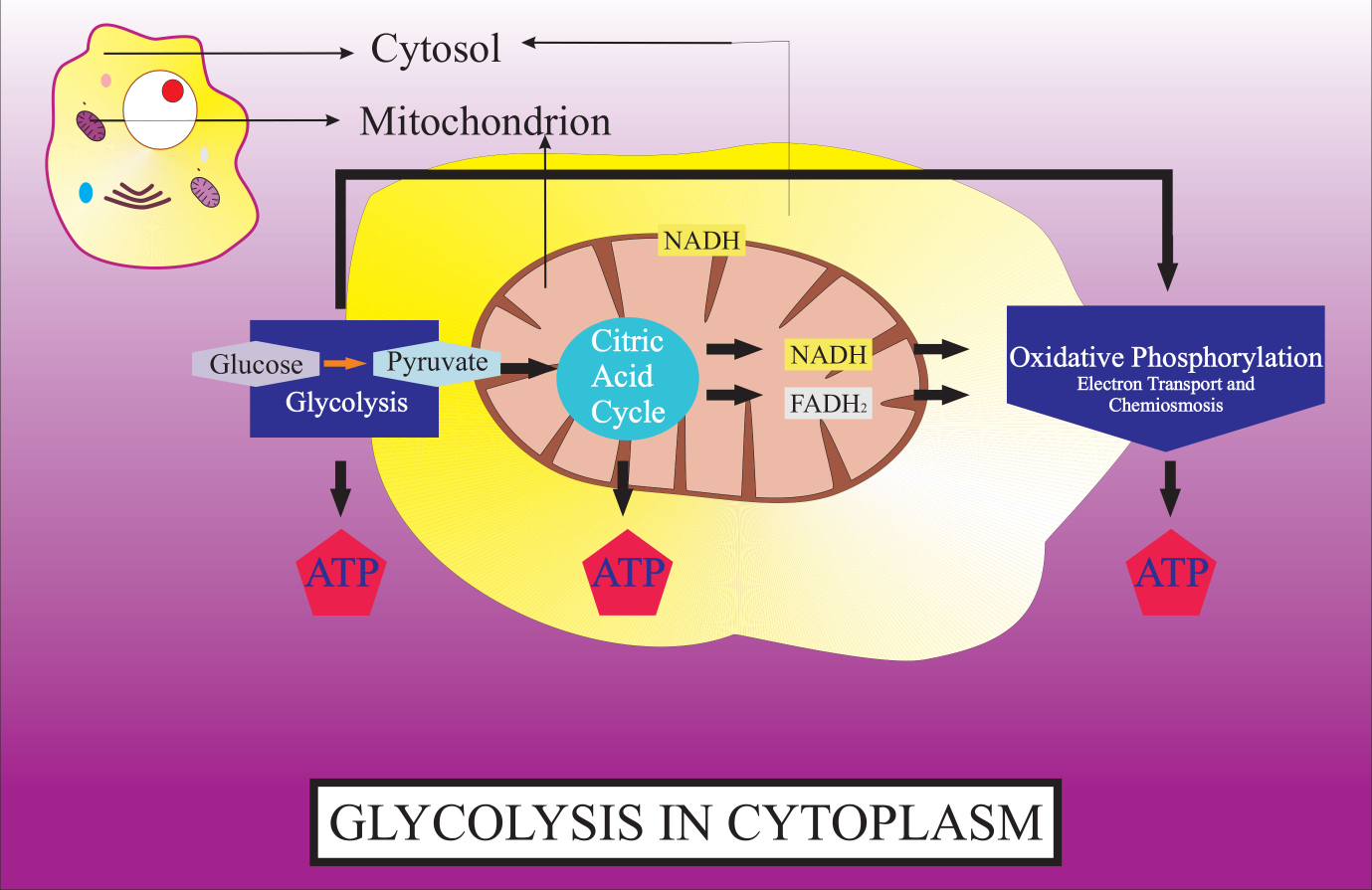
What is Glycolysis?, Where does it take place?, Pathway and Products Glycolysis (or the glycolytic pathway) may be described as the metabolic breakdown of glucose (a 6 carbon sugar) in order to release energy. Where does Glycolysis Take Place? Glycolysis is the first phase of cellular respiration. It takes place in the cytoplasm where associated enzymes and factors...
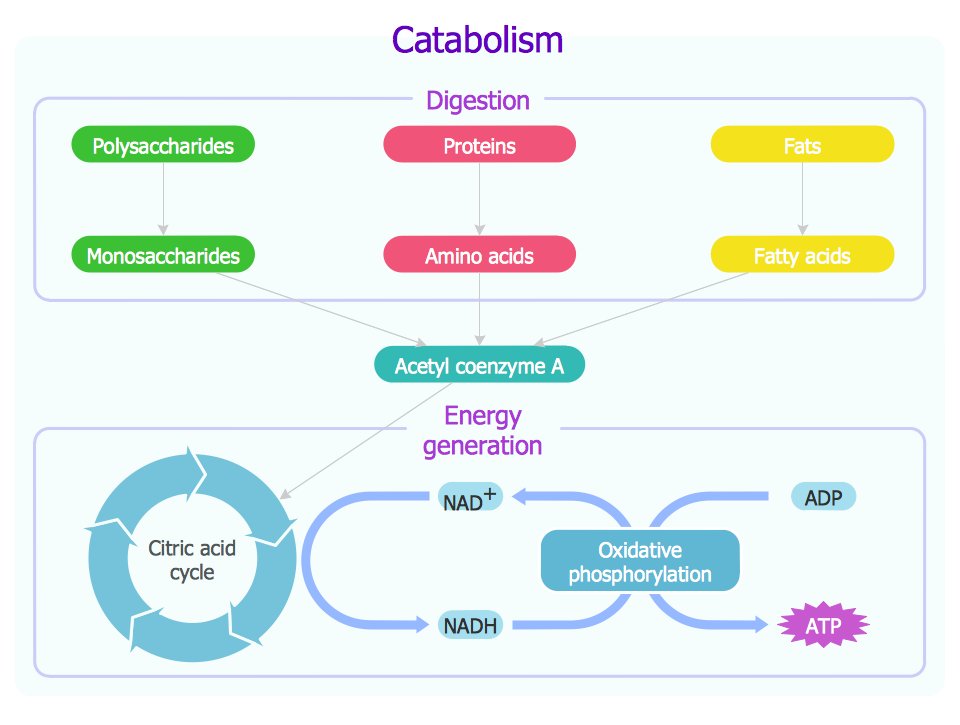
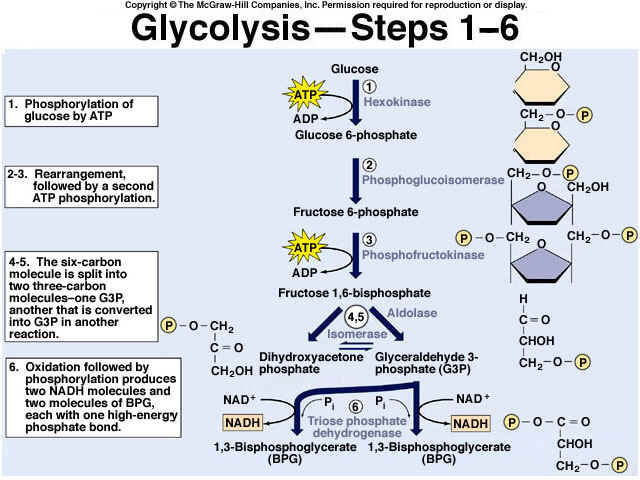
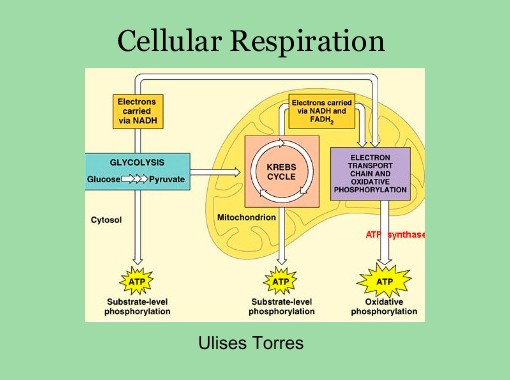
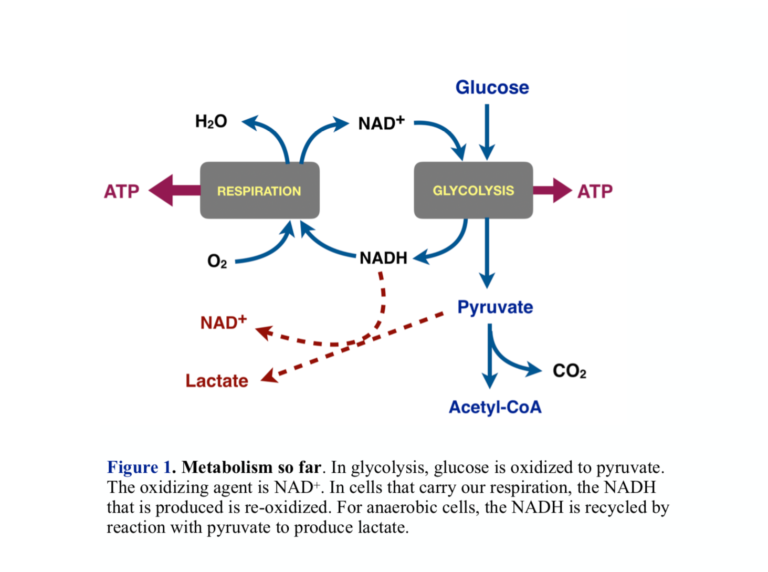
Glycolysis | Biochem.co - Biochem & Science Notes Outline to Glycolysis. The diagram above shows the process and points where ATP is released or consumed during Glycolysis. It is important to remember that this pathway is only the first section of a larger process (metabolism), as Pyruvate from this chain is used later in Krebs cycle etc.
Glycolysis | Definition, What Is It? | A-Level Biology Revision Notes Glycolysis is the first pathway used to derive energy from carbohydrates.It is a complex process requiring the activity of various enzymes and Glycolysis consists of two parts: The first part requires ATP is invested to provide energy to separate glucose into two 3 carbon sugars. separation.
Kids.Net.Au - Encyclopedia > Glycolysis Glycolysis is the only metabolic pathway common to nearly all living organisms, suggesting great antiquity; it may have originated with the first The first step in glycolysis is phosphorylation of glucose by hexokinase. This reaction consumes 1 ATP molecule, but the energy is well spent...
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps (With Diagrams) Glycolysis is the metabolic process that serves as the foundation for both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. In glycolysis, glucose is converted into pyruvate. All of the glycolytic enzymes are found in the cytosol.
Glycolysis | Introduction, Pathway , Diagram & Summary Introduction of Glycolysis: Glycolysis is a process in which glucose divided into two pyruvate molecules. However, it is assumed as a linear pathway of ten enzyme meditation steps. This pathway has two stages or phases; the energy investment phase and the energy generation phase.
Glycolysis: Pathway, Cycle, Reaction, Diagram Glycolysis: Pathway, Reaction, Diagram. Glycolysis is a metabolic mechanism that transforms glucose (C6H12O6) to pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) without the use of oxygen. Glycolysis is also Known as EMP. Glycolysis Reaction Diagram.
Glycolysis! (Mr. W's Music Video) - YouTube Glycolysis! (Mr. W's Music Video). Смотреть позже.
Glycolysis- Definition, Equation, Enzymes, 10 Steps, Diagram Glycolysis is the central pathway for glucose catabolism in which glucose is converted into pyruvate through a sequence of 10 steps. The glycolytic sequence of reactions differs from one species to the other in the mechanism of its regulation and the subsequent metabolic fate of the pyruvate formed at...
Glycolysis: steps, diagram and enzymes... - Online Biology Notes During glycolysis some of the free energy is released and conserved in the form of ATP and NADH. Glycolysis is an almost universal central pathway of glucose catabolism. Glycolytic breakdown of glucose is the sole source of metabolic energy in some mammalian tissues and cells (RBCs, Brain...
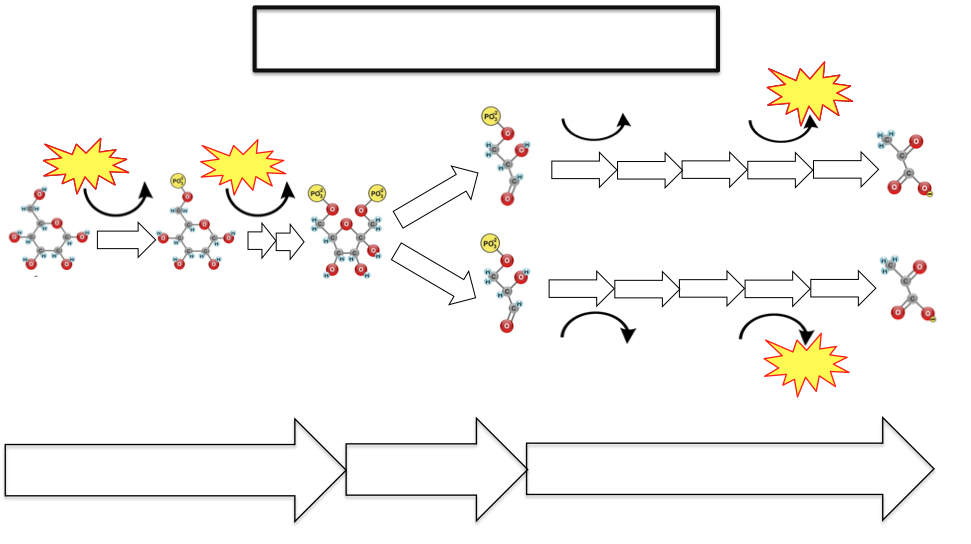
The 10 Steps of Glycolysis Glycolysis can take place with or without oxygen. Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm. There are 10 enzymes involved in breaking down sugar.
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Glycolysis.ppt Glycolysis. • The Glycolytic pathway describes the oxidation of glucose to pyruvate with the generation of ATP and NADH. The 3 stages of Glycolysis. • Stage 1 is the investment stage. 2 mols of ATP are consumed for each mol of glucose.
Diagram of Glycolysis pathway Glycolysis, an overview. Glycolysis (a sweet splitting process) is a central pathway for the catabolism of carbohydrates in which the six-carbon sugars are split to three-carbon compounds with subsequent release of energy used to transform ADP to ATP. Glycolysis can proceed under anaerobic (without...
Glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase.
Glycolysis - Wikipedia Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvic acid, CH3COCOOH. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH).















0 Response to "42 glycolysis diagram for kids"
Post a Comment