41 transition states energy diagram
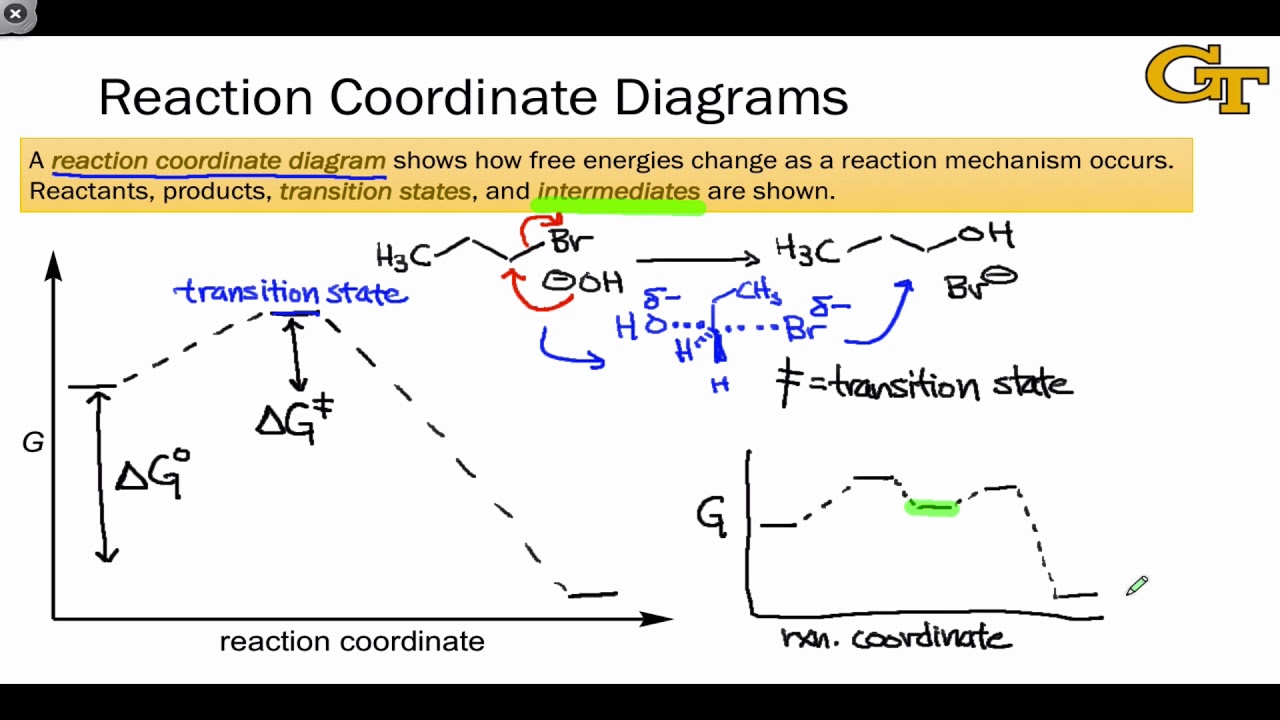
Transition state - Wikipedia The transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate.It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger ‡ symbol.. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the S N 2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxyl anion: What is the Difference Between a Transition State and an ... the energy curve describing the energy states of the components at a certain point in the reaction. the transition states (TS) and an intermediate (I). Among other things that you typically see in these diagrams are the change in energy and the activation energy, which are not too important for us at the moment.
Learn About Transition State In Energy Diagram | Chegg.com An energy diagram refers to the plot which shows the reactants' relative potential energies, its transition states, as well as the products progression of the reaction with time. It is a plot between potential energy and reaction progress or time. It tells us about the reaction whether it is endothermic or exothermic.

Transition states energy diagram
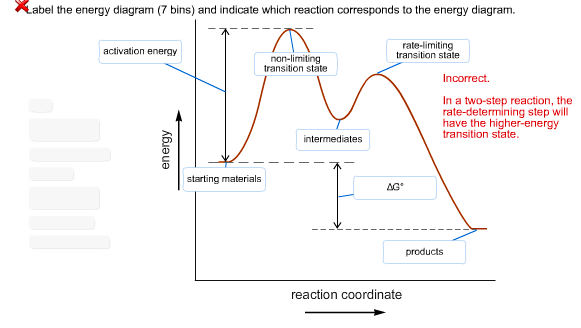
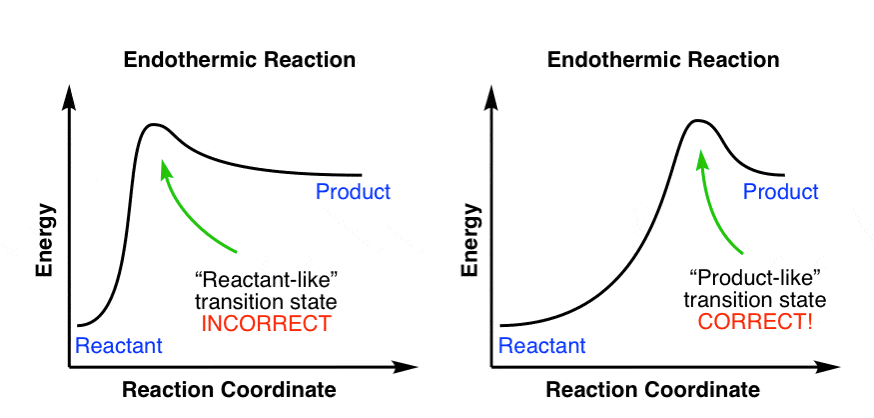
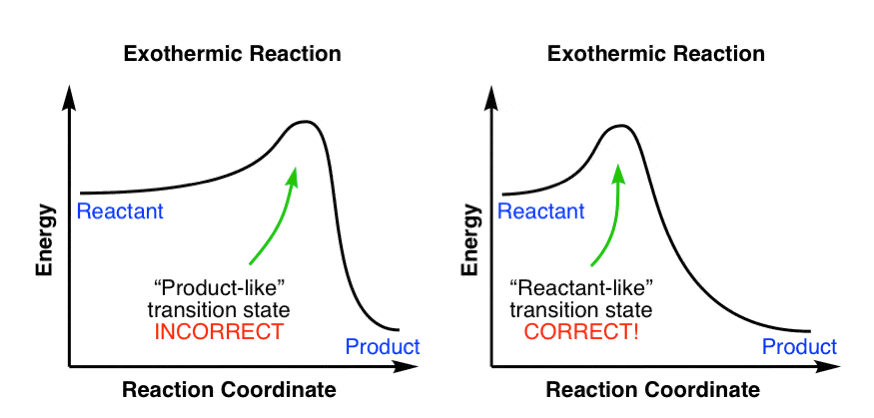
Exothermic Energy Diagram: Activation Energy, Transition ... In this video, I go over how to properly label and explain a reaction mechanism diagram which is also referred to as an energy diagram or energy graph. I'll ... PDF Energy/Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Energy Diagrams # Transition States! • An intermediate occurs at an energy minimum.! Intermediates often exist long enough to be observed.! Bonds are NOT in the process of breaking or forming. ! Energy Diagrams # Intermediates! 6! For each of the diagrams below, will the transition state PDF Structure of the Transition State the beginning state. The energy of the TS≠ must be closer to the beginning state. There's just no other way to draw the diagram. We call this TS≠ "early" since the structure of the transition state has not evolved far from its starting point. Case 2: the ending state is higher than the beginning state - In this case
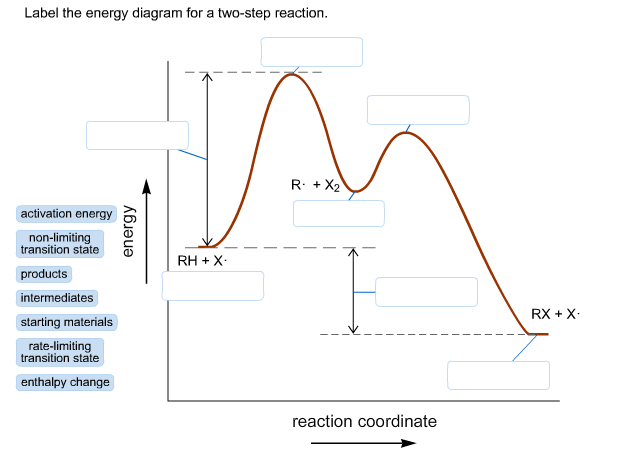
Transition states energy diagram. › embedWelcome to CK-12 Foundation | CK-12 Foundation FlexBook® Platform, FlexBook®, FlexLet® and FlexCard™ are registered trademarks of CK-12 Foundation. Solved How many intermediates and transition states are in ... Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (57 ratings) Transcribed image text: How many intermediates and transition states are in the mechanism represented by the following free energy diagram? energy profiles - chemguide The second diagram where the bonds are half-made and half-broken is called the transition state, and it is at this point that the energy of the system is at its maximum.This is what is at the top of the activation energy barrier. But the transition state is entirely unstable. Arrhenius Theory and Reaction Coordinates The transition state is the higher energy point between two minima along the reaction coordinate. Each step in a mechanism will have a transition state. The transition states are often very difficult to identify and during a reaction the molecules exist in this state for essentially zero time.
physics.bu.edu › ~duffy › semester2Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from a particular state to a lower state, it is losing energy. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Molecular_vibrationMolecular vibration - Wikipedia A molecular vibration is a periodic motion of the atoms of a molecule relative to each other, such that the center of mass of the molecule remains unchanged. The typical vibrational frequencies range from less than 10 13 Hz to approximately 10 14 Hz, corresponding to wavenumbers of approximately 300 to 3000 cm −1 and wavelengths of approximately 30 to 3 µm. Solved Use the energy diagram for the reaction A D to ... Use the energy diagram for the reaction A D to answer the questions. How many transition states are there in the reaction? transition states: Potential energy How many intermediates are there in the reaction? intermediates: Reaction progress Which step of the reaction is the fastest? Which step of the reaction has the smallest rate constant? Transition state theory - Wikipedia Transition state theory. Transition state theory ( TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes. TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place.
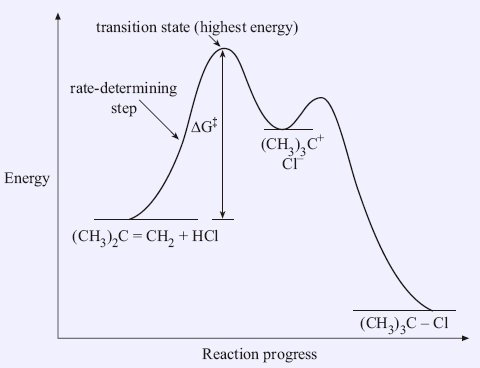
Reaction Energy Diagrams Activation Energy Transition ... Reaction Energy Diagrams, Activation Energy, Transition States… 40. Which point as labeled by an asterisk (*) on the following energy profile is the transition state? 7.2 SN2 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and ... The energy changes for the above reaction can be represented in the energy diagram shown in Fig. 7.1. S N 2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram has only one curve. The products CH 3 OH and Br - are in lower energy than the reactants CH 3 Br and OH - , indicates that the overall reaction is exothermic and the products are more stable. Transition State Theory - Concept, Formation, Formula and ... Now the diagram above shows the transition state of a chemical reaction taking place. It is basically a potential energy graph that shows the minimum energy required to convert reactants into products. From this curve, it is clear that that activation energy is a hurdle that the reactants need to overcome during the chemical reaction to get ... Transition State Theory The active intermediate is shown in transition state at the top of the energy barrier. A class of reactions that also goes through a transition state is the S N2 reaction. A. The Transition State ... The entire energy diagram for the ABC system is shown in 3-D in Figure PRS.3B-3.
› science › chemistryPhase diagrams (video) | States of matter | Khan Academy So what I've drawn here is a phase diagram. Let me write that down. And there are many forms of phase diagrams. This is the most common form that you might see in your chemistry class or on some standardized test, but what it captures is the different states of matter and when they transition according to temperature and pressure.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Phase_(matter)Phase (matter) - Wikipedia When a substance undergoes a phase transition (changes from one state of matter to another) it usually either takes up or releases energy. For example, when water evaporates, the increase in kinetic energy as the evaporating molecules escape the attractive forces of the liquid is reflected in a decrease in temperature.
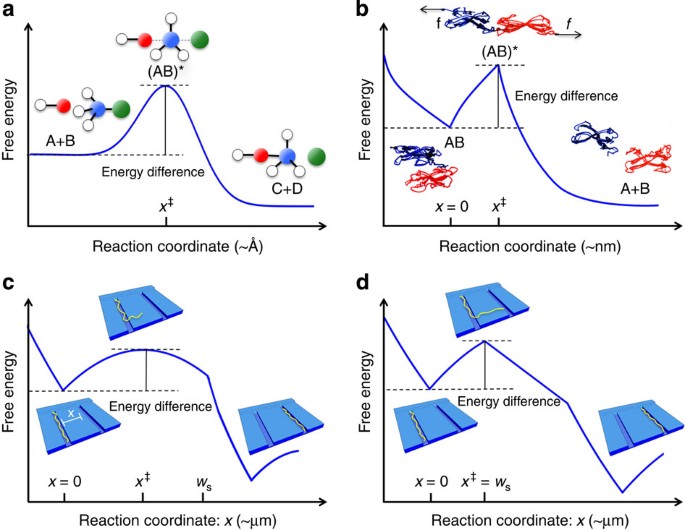
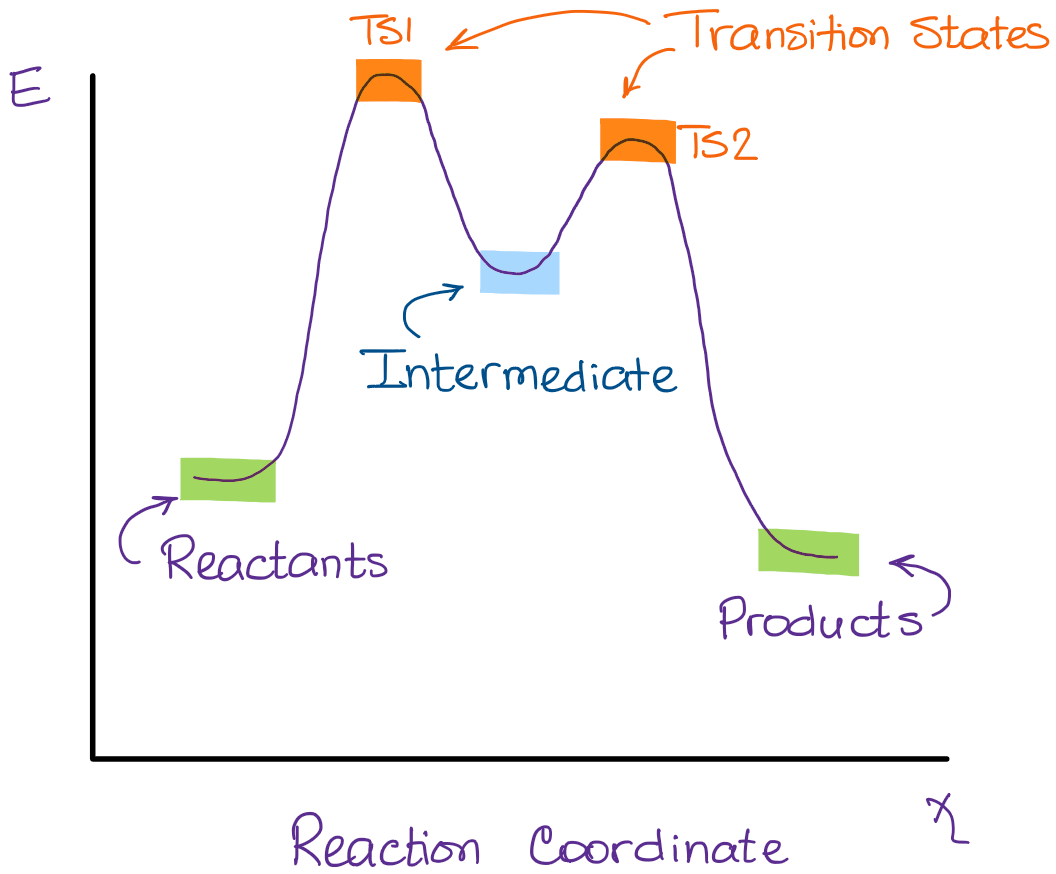
Energy profile (chemistry) - Wikipedia The saddle point represents the highest energy point lying on the reaction coordinate connecting the reactant and product; this is known as the transition state. A reaction coordinate diagram may also have one or more transient intermediates which are shown by high energy wells connected via a transition state peak.
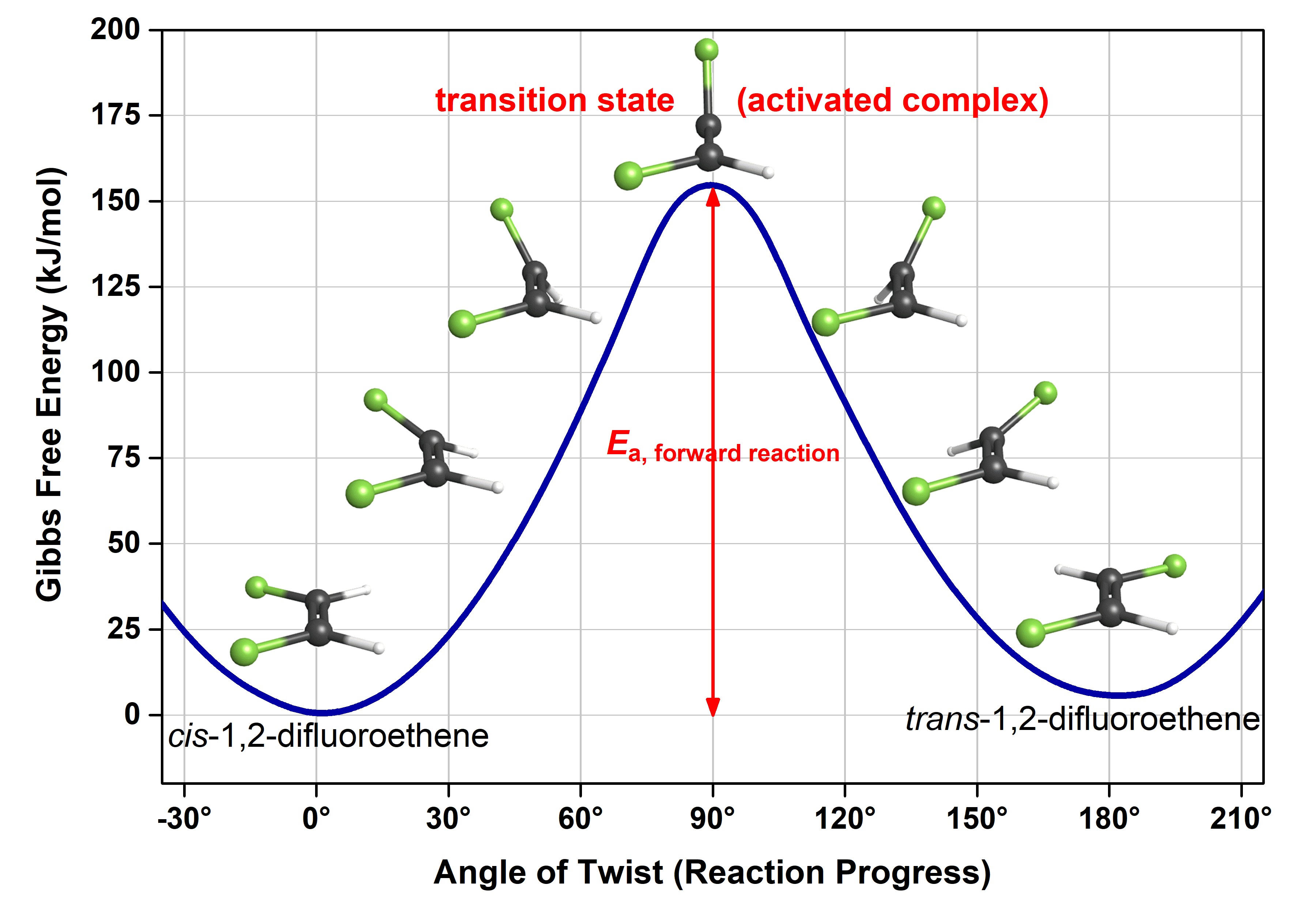
Energy Diagrams, Transition States, and Reactive ... Peaks on the energy diagram represent the transition states, whereas the valleys represent the reactive intermediates. As the reaction progresses, the reactants pass through an unstable state of maximum free energy, called the activated complex, or the transition state. They last for less than one picosecond and cannot be isolated.
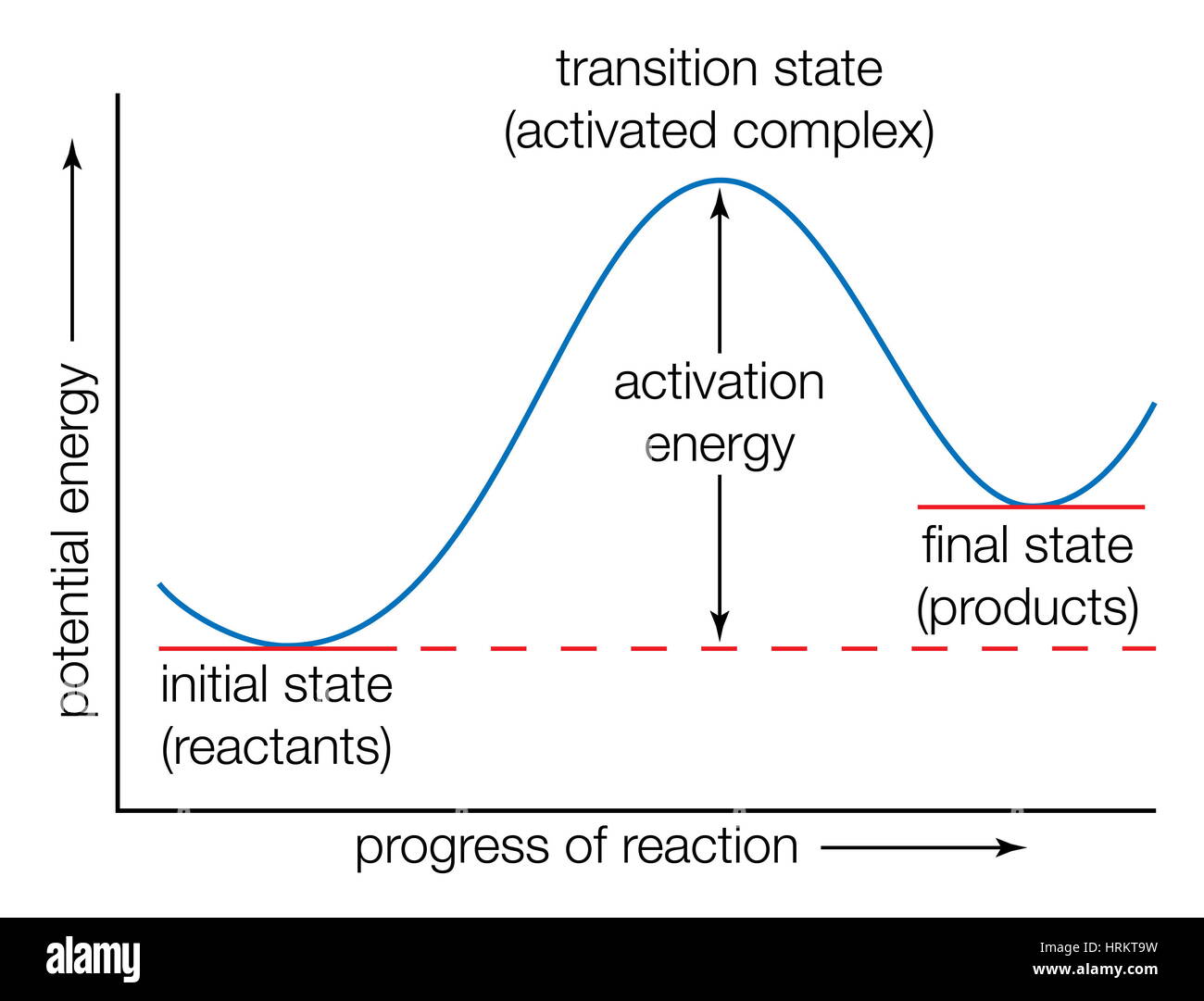
Potential Energy Diagrams - Kentchemistry.com In this diagram, the activation energy is signified by the hump in the reaction pathway and is labeled. At the peak of the activation energy hump, the reactants are in the transition state, halfway between being reactants and forming products. This state is also known as an activated complex.
chem.libretexts.org › Bookshelves › Physical_andFundamentals of Phase Transitions - Chemistry LibreTexts Feb 16, 2021 · A Brief Explanation of a Phase Diagram. Phase transition can be represented with a phase diagram. A phase diagram is a visual representation of how a substance changes phases. This is an example of a phase diagram. Often, when you are asked about a phase transition, you will need to refer to a phase diagram to answer it.
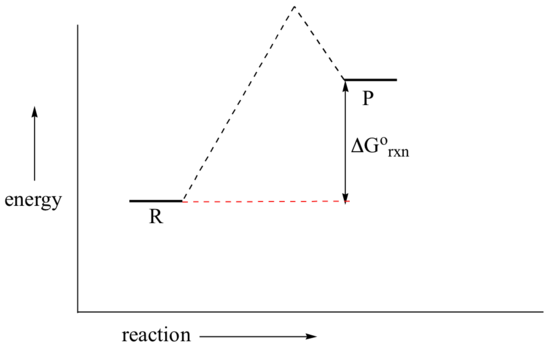
Understanding Energy Diagrams - Concept - Chemistry Video ... That's the energy it takes for the reaction to occur. So it's from the reactants to the highest point on the curve in the transition state. So up here we have the transition state. And so the difference between the reactants and the transition state, as in 1, this difference, is what we call the activation energy. You might see that as E sub a.
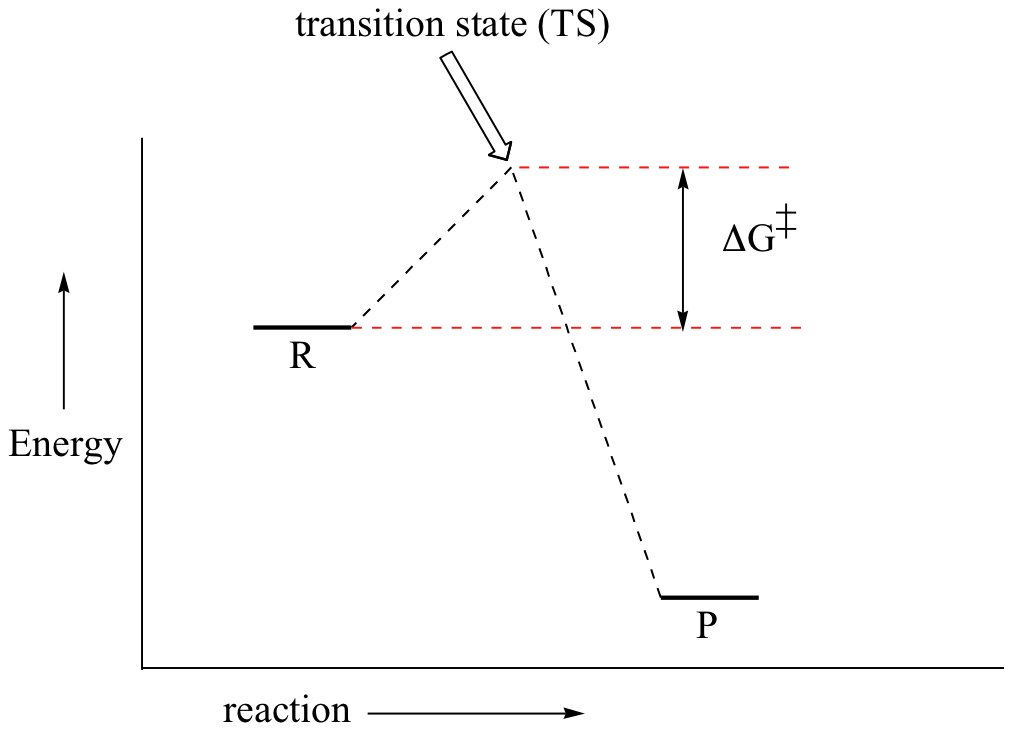
Transition states and activation energy | Open Textbooks ... A reaction starting from reactants that change into products must pass through an unstable state at the highest energy level; this is called a transition state.A certain amount of energy is required to overcome the energy barrier, and this energy, called activation energy, is represented by ΔG ‡.The magnitude of ΔG ‡ determines the rate of a chemical reaction.
Answered: An energy diagram showing two peaks… | bartleby Transcribed Image Text: An energy diagram showing two peaks suggests that there are two steps and three transition states in the reaction mechanism. Select one: O True O False Given a reaction with an activation energy of 2.3 x 104 J/mol. The rate constant will increase by a factor of when the reaction temperature is increased from 200 °C to 250 °C.
PDF Teacher's Guide to "Visualizing the Transition State and ... Transition state theory (TST), also called activated complex theory, is often introduced in general chemistry courses when discussing kinetics. A reaction energy diagram is used to follow the progress of the reaction from reactants through a transition state to products (see figure 1). The reaction energy diagram plots the
PDF Structure of the Transition State the beginning state. The energy of the TS≠ must be closer to the beginning state. There's just no other way to draw the diagram. We call this TS≠ "early" since the structure of the transition state has not evolved far from its starting point. Case 2: the ending state is higher than the beginning state - In this case
PDF Energy/Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Energy Diagrams # Transition States! • An intermediate occurs at an energy minimum.! Intermediates often exist long enough to be observed.! Bonds are NOT in the process of breaking or forming. ! Energy Diagrams # Intermediates! 6! For each of the diagrams below, will the transition state
Exothermic Energy Diagram: Activation Energy, Transition ... In this video, I go over how to properly label and explain a reaction mechanism diagram which is also referred to as an energy diagram or energy graph. I'll ...
















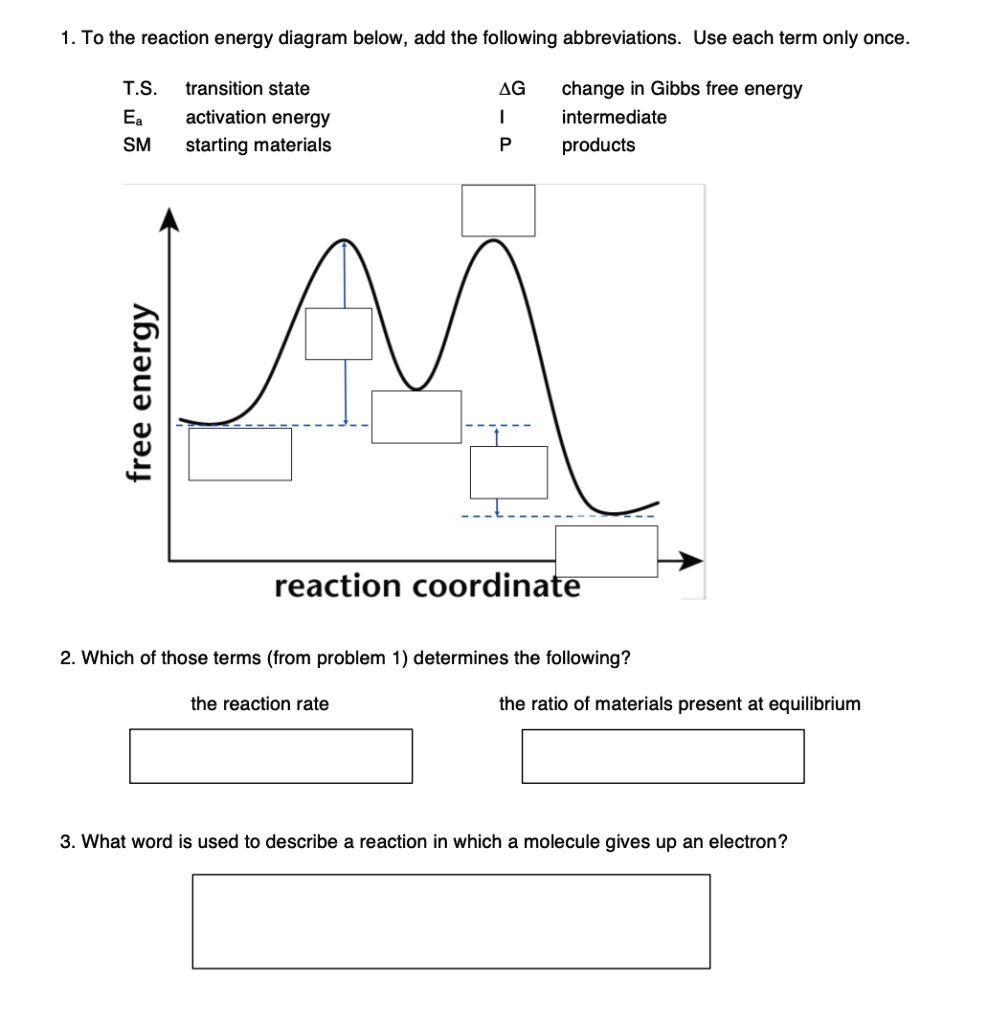
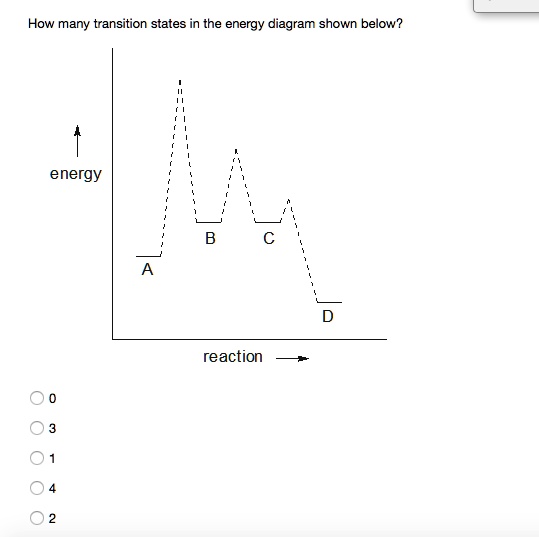
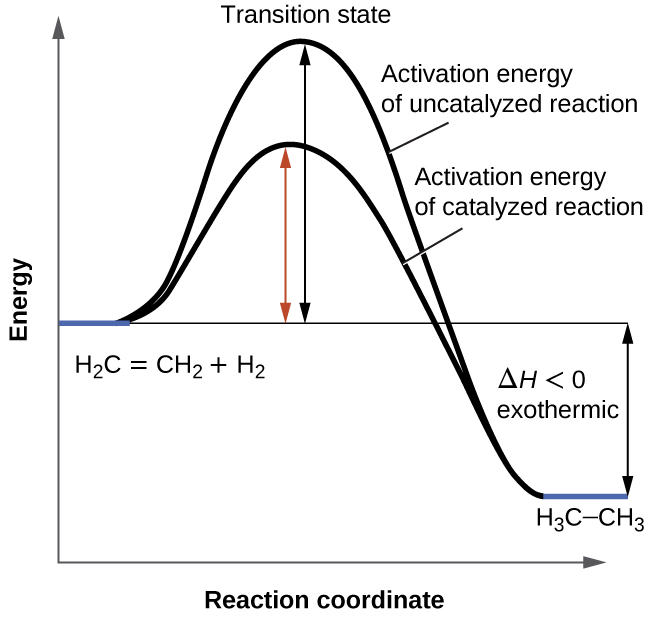

0 Response to "41 transition states energy diagram"
Post a Comment