41 pacemaker cell action potential diagram
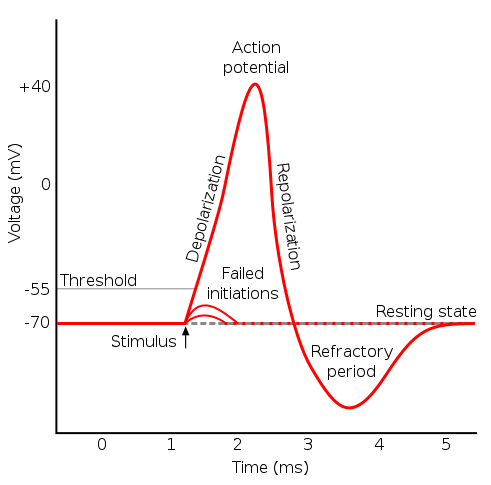
Action Potential - The Resting Membrane Potential ... An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs. The membrane action potential of pacemaker cells and the ... Download scientific diagram | The membrane action potential of pacemaker cells and the mechanism of action of several bradycardic drugs. In SA cells, when the membrane potential is repolarized to ...
Cardiac electrophysiology: action potential, automaticity ... Figure 1. The action potential in the sinoatrial node and in contractile myocardial cells. Phase 4 of the action potential in the sinoatrial node is called 'pacemaker potential', because it is responsible for the spontaneous repetitive depolarization. The depolarization spreads from the sinoatrial node to the atrial and ventricular myocardium.

Pacemaker cell action potential diagram
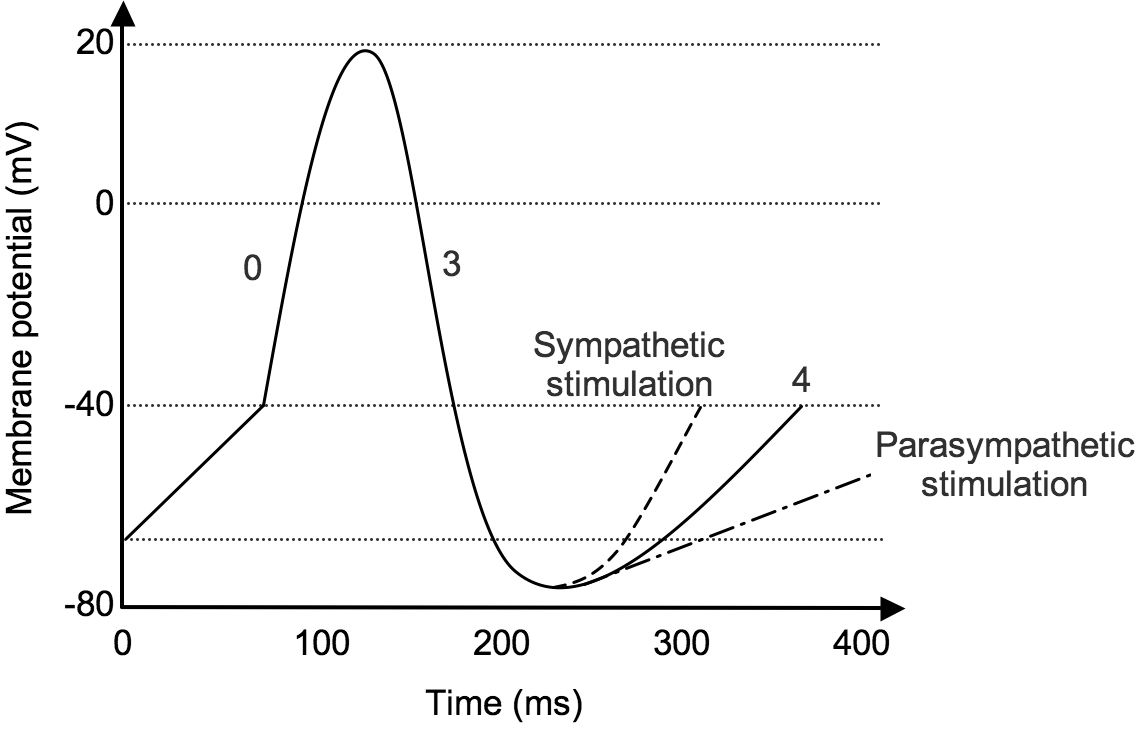
Action Potential in Cardiac Pacemaker Cells ... Feb 06, 2021 · Fig 2 – Diagram showing the action potential in cardiac pacemaker cells and the main ion movements at each stage. Control by the Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system (ANS) alters the slope of the pacemaker potential, in order to alter heart rate. Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac ... Start studying Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac Pacemaker Cells. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. PDF Possible Essay Questions: total points from essay will be ... the pacemaker of the heart. Explain how action potentials in autorhythmic (pacemaker) cells are produced and include a labeled diagram of the action potential for these cells. Describe how the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate. Explain how action potentials in myocardial contractile cells are produced and include ...
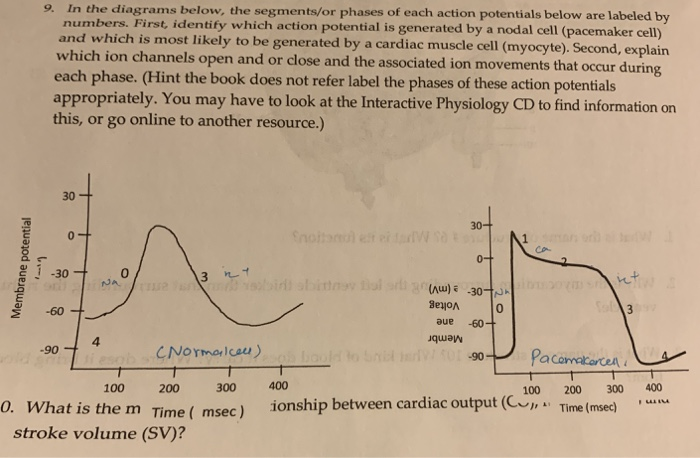
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. Cardiac Action Potentials - The Student Physiologist Cardiac action potentials differ from the APs found in other areas of the body. Typical neural AP duration is around 1ms and those of skeletal muscle are roughly 2-5ms, whereas cardiac action potentials range from 200-400ms. Nervous and muscle cells (as well as non-pacemaker cardiac cells) use the opening of Na channels to facilitate the depolarisation phase, whereas cardiac pacemaker cells ... Non-Pacemaker Action Potentials - CV Physiology Transformation of non-pacemaker into pacemaker cells. It is important to note that non-pacemaker action potentials can change into pacemaker cells under certain conditions. For example, if a cell becomes hypoxic, the membrane depolarizes, which closes fast Na + channels. At a membrane potential of about -50 mV, all the fast Na + channels are ... Cardiac action potential - All About Cardiovascular System ... Action potential of ventricular myocardial cell. Action potential of pacemaker cells. Action potential of the pacemaker cell is different from that of ventricular myocardial cell. It is characterized by lower slope of phase 0 (lower Vmax) and the presence of diastolic depolarization mediated by the funny current (I f), also known as pacemaker ... Action Potentials Made Easy: Cardiac Myocyte ... - EZmed The inherent pacemaker rate of the SA node is faster than the other pacemaker cells, and for that reason the SA node generates the initial action potential in a normal functioning heart. If the SA node becomes suppressed, then the other pacemaker cells are capable of generating spontaneous action potentials but at a slower heart rate.
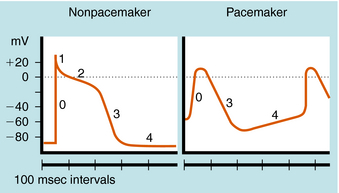
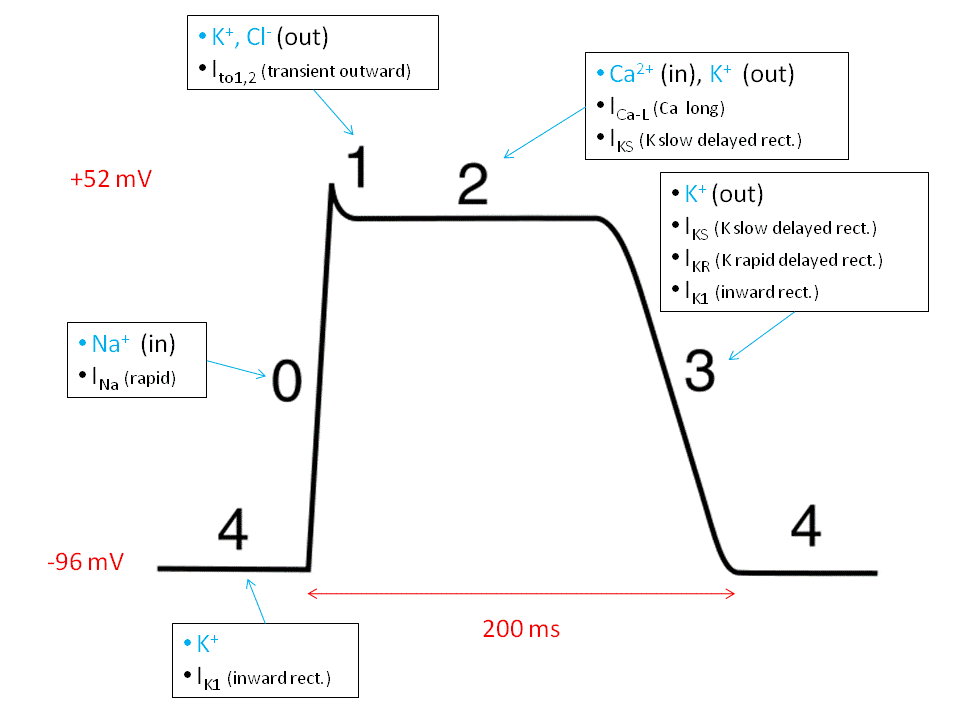
Physiology, Action Potential - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The action potential is then dispersed throughout the heart by myocardiocytes, cardiac muscle cells that contract while they conduct the current to neighboring cells. Similar to action potential initiation in neurons, and in contrast to pacemaker cells, myocardiocytes initiate rapid depolarization through voltage-gated sodium channels. Phases of the Cardiac Action Potential - Sciencing The cardiac cell action potential, like action potentials in nerves, is divided into five phases, numbered 0 through 4. Two of these, phase 2 (the plateau phase) and phase 4 (the diastolic interval) are marked by little to no change in voltage. Sodium, potassium and calcium are the primary ions. Cardiac Action Potential, Animation. - YouTube (USMLE topics, cardiology) Cardiac action potential in pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes, electrophysiology of a heartbeat. Purchase PDF (script of th... BIO 2982 Action Potentials of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells ... Start studying BIO 2982 Action Potentials of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
PDF CV 1. HEART ELECTRICAL ACTIVTY - Duke University phase of depolarization occurs (Fig 2). At the peak of the action potential, K+ channels open, K+ rushes out of the cell and the cell repolarizes. Figure 2. Slow action potential has 3 phases (0, 3 and 4). The pacemaker cells set the rate of the heart beat. They are anatomically distinct from the PDF 6.3.4 Action potential - Stanford University ular node, and action potentials for non-pacemaker cells such as atrial or ventricular muscle cells. Pacemaker cells are capable of spontaneous action potential generation, whereas non-pacemaker cells have to be triggered by depolarizing currents from adja-cent cells. To compare non-oscillatory and oscillatory cells, it is convenient to rewrite Normal processes of cardiac ... - Deranged Physiology This chapter is relevant to Section G2(ii) of the 2017 CICM Primary Syllabus, which asks the exam candidate to "describe the normal and abnormal processes of cardiac excitation and electrical activity". Almost all the SAQs on this topic ask for a comparison between the action potentials of a normal cardiac myocyte and a specialised pacemaker cell, and so this chapter should probably be ... Factors Controlling Pacemaker Action in Cells of the ... length) A and B. In C recording is from a Intent or subsidiary pacemaker cell (upper) and true pacemaker (lower), rate of drive 300/min or 200 msec cycle length. Note the decrease in amplitude of pacemaker cell spike and the greater than normal duration of pacemaker cell action potentials after drive.
Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential • LITFL • BSCC Examination Cardiac Myocyte Action Potential. This diagram is a diagram of a cardiac myocyte - a ventricular muscle cell as apposed to a cardiac pacemaker cell. The resting membrane potential (RMP) is -90mv. A membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and the exterior of the cell membrane.
File:Pacemaker potential.svg - Wikipedia Pacemaker cell action potential diagram. Licensing. I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license: Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no ...
Physiology of cardiac conduction and contractility ... An action potential in one cell will cause all neighbouring cells to depolarize, allowing the heart chambers to act as a unit. Dominance : the cell with the highest inherent rate of pacemaker activity will therefore also set the heart rate, as all other pacemaker cells will be depolarized and rendered inactive by this stimulus.
Cardiac pacemaker - Wikipedia The contraction of cardiac muscle (heart muscle) in all animals is initiated by electrical impulses known as action potentials.The rate at which these impulses fire controls the rate of cardiac contraction, that is, the heart rate.The cells that create these rhythmic impulses, setting the pace for blood pumping, are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate.
Conduction System of the Heart: Step-By-Step ... - EZmed The pacemaker cells within the Purkinje fibers produce action potentials at 20-40 beats per minute. Practical Application Abnormalities within the conduction system can lead to diseases such as heart blocks, sick sinus syndrome, arrhythmias, etc which will be discussed in other EZmed posts.
Assembly of the Cardiac Pacemaking Complex: Electrogenic ... This would support pacemaker cell excitability by preventing current dissipation during the slow diastolic and/or upstroke phase of pacemaker action potential generation. Thus, by creating a unique microenvironment, sinoatrial node fibrosis may provide direct biophysical support for pacemaker myocardium.
Cardiac Electrophysiology Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations ... Figure 17.2 Graph depicting the action potential of a pacemaker cell. ACTION POTENTIALS IN MYOCYTES osms.it/myocyte-action-potentials Myocytes Receive signal from from pacemaker cells causing them to contract Able to depolarize, spread action potentials Action potential phases: Phase 0 (depolarization phase): rapid influx of sodium into cell (inward current); responsible for rapid ...
PDF Cardiac Action Potential - interactivephysiology.com 1. Pacemaker Potential • An autorhythmic cell has the unique ability to depolarize spontaneously, resulting in a pacemaker potential. 2. Depolarization and Reversal of the Membrane Potential • Once threshold is reached, an action potential is initiated, which begins with further depolarization and leads to reversal of the membrane potential ...
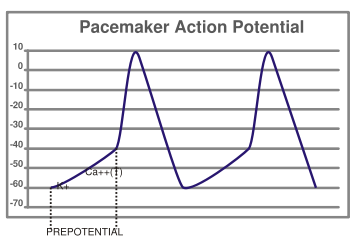
PDF The Cardiovascular System Part II: Heart - Dr. Scott Croes ... myocyte action potentials. 4. Pacemaker potential phase: Pacemaker potentials are slow spontaneous depolarization's to threshold that triggers an action potential. They involve the movement of Na+, K+, and Ca2+ ions. • During diastole the cell starts out as being hyperpolarized (-60 mV) as a result of the preceding action potential.
Phases - PhysiologyModels.info The three sections of the pacemaker action potential are labeled and color coded on the graph. The y-axis of the graph shows the membrane potential in millivolts (mV) and the x-axis is time. how the membrane potential changes over time. Depolarization is also called phase 0, repolarization is called phase 3and
Sinoatrial Node Action Potentials - CV Physiology Cells within the sinoatrial (SA) node are the primary pacemaker site within the heart. These cells are characterized as having no true resting potential, but instead generate regular, spontaneous action potentials.Unlike non-pacemaker action potentials in the heart, and most other cells that elicit action potentials (e.g., nerve cells, muscle cells), the depolarizing current is carried into ...
Action potentials in pacemaker cells - Osmosis Action potentials are the really rapid electrical changes that occur across the membrane of certain cells, and often propagates from one cell to an adjacent cell. Cells in the heart communicate this way. That signal’s gotta start somewhere, so some of these cells, called pacemaker cells, have the responsibility of setting the rhythm and the ...
PDF Possible Essay Questions: total points from essay will be ... the pacemaker of the heart. Explain how action potentials in autorhythmic (pacemaker) cells are produced and include a labeled diagram of the action potential for these cells. Describe how the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate. Explain how action potentials in myocardial contractile cells are produced and include ...
Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac ... Start studying Pacemaker and Action Potentials of Typical Cardiac Pacemaker Cells. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Action Potential in Cardiac Pacemaker Cells ... Feb 06, 2021 · Fig 2 – Diagram showing the action potential in cardiac pacemaker cells and the main ion movements at each stage. Control by the Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system (ANS) alters the slope of the pacemaker potential, in order to alter heart rate.


























0 Response to "41 pacemaker cell action potential diagram"
Post a Comment