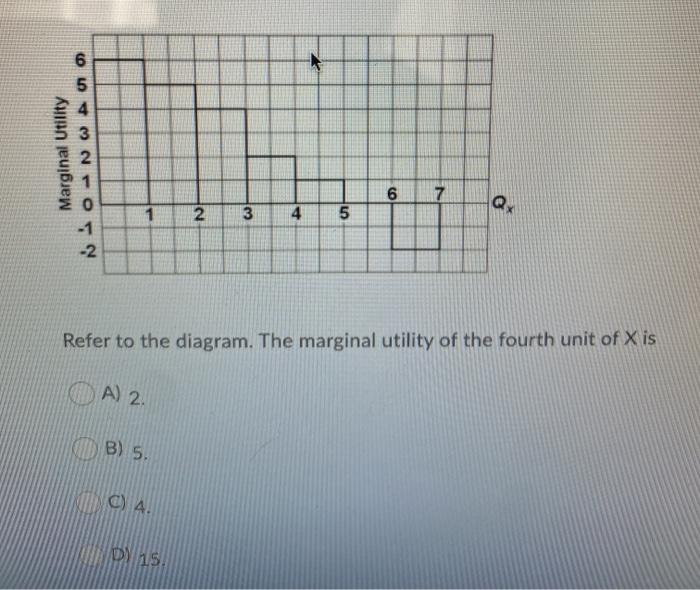
40 refer to the diagram. marginal utility
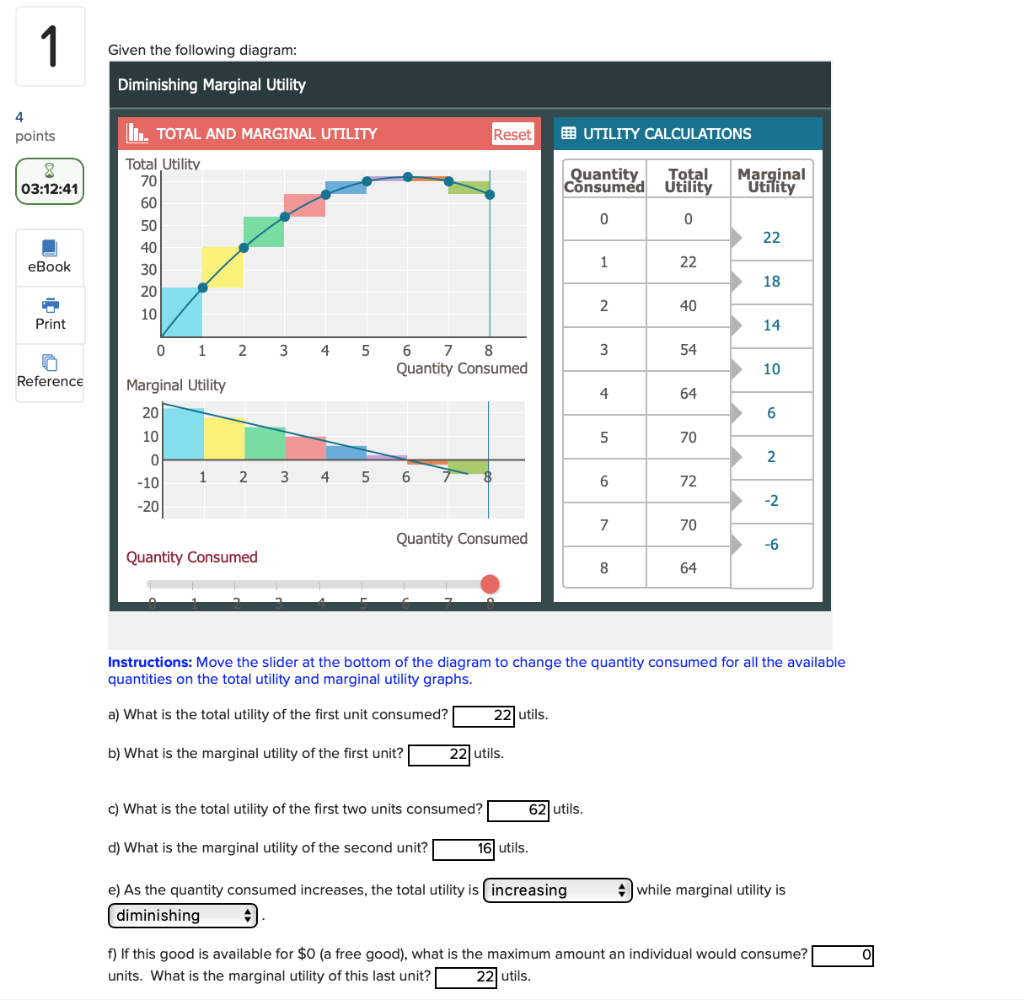
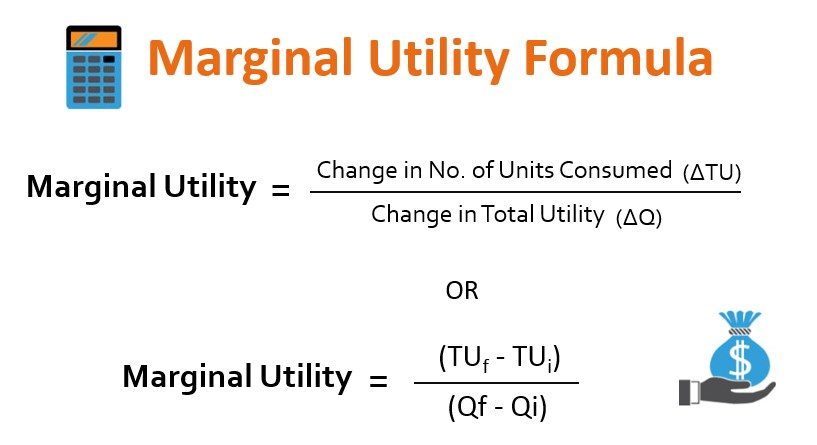
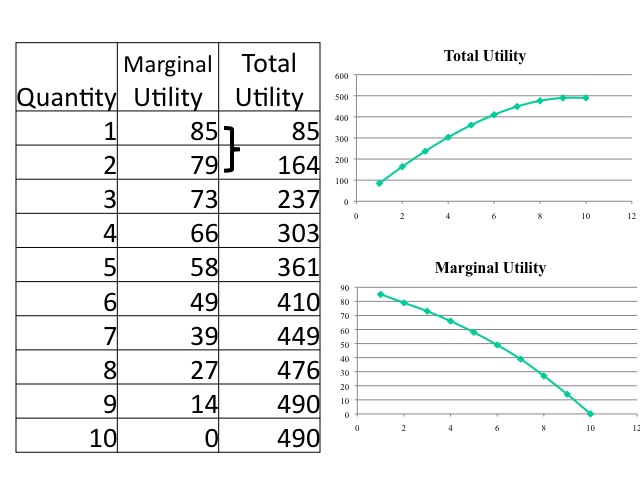
How to Calculate Marginal Utility Calculation *Marginal Utility - change in total utility divided by change in quantity. Marginal utility is measures the increase in satisfaction consumers gain from consuming an extra unit of a goods or services.Marginal utility is calculated by taking the difference in total utilities, and dividing by the... Multiscale Information Theory and the Marginal Utility of Information Utility of Information. Benjamin Allen 1,2,*, Blake C. Stacey 3,4 and Yaneer Bar-Yam 4. 1Department of Mathematics, Emmanuel College, Boston, MA 02115, USA. scales and a variety of information measures. We also introduce a new index, the marginal utility of.
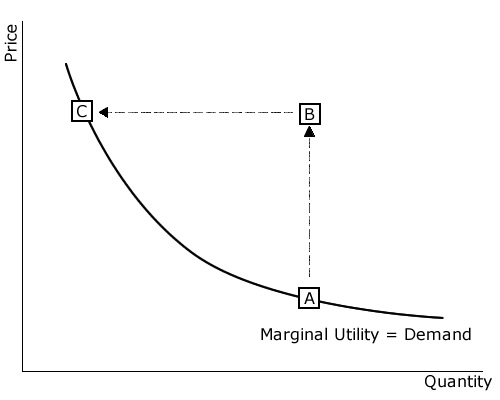
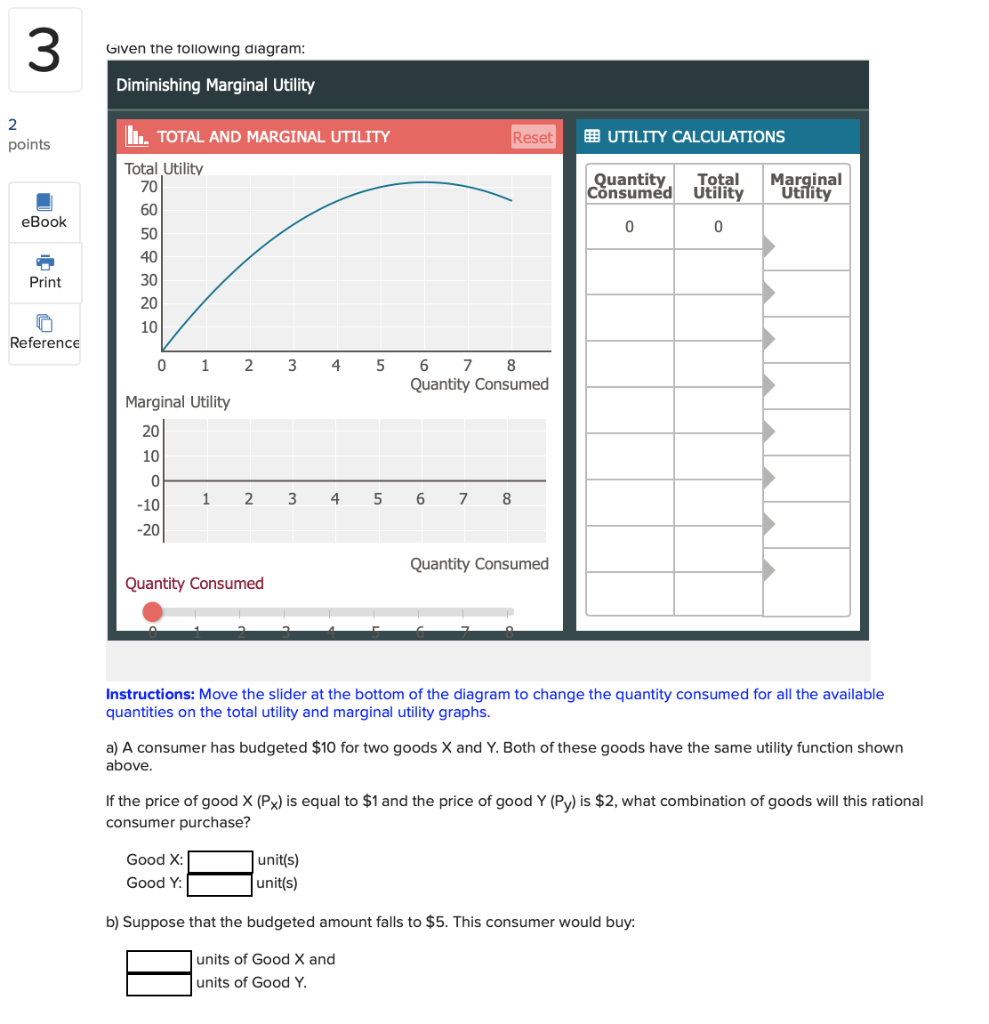
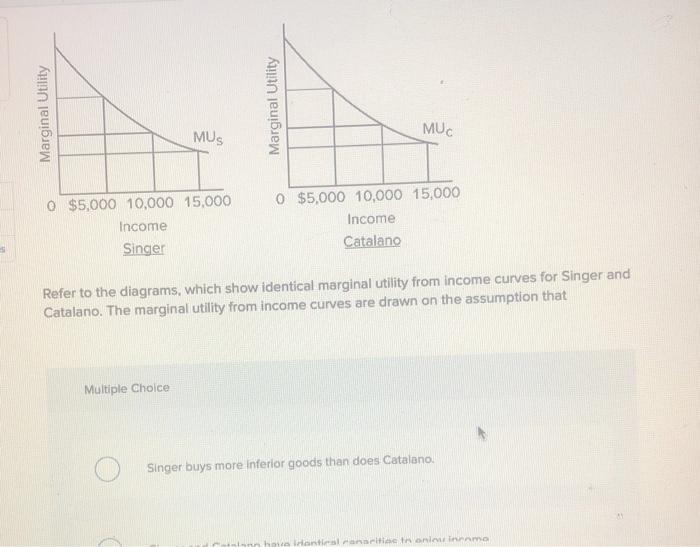
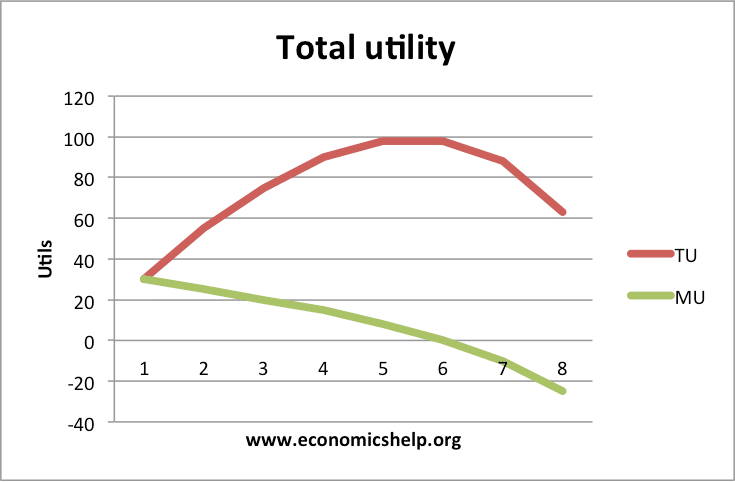
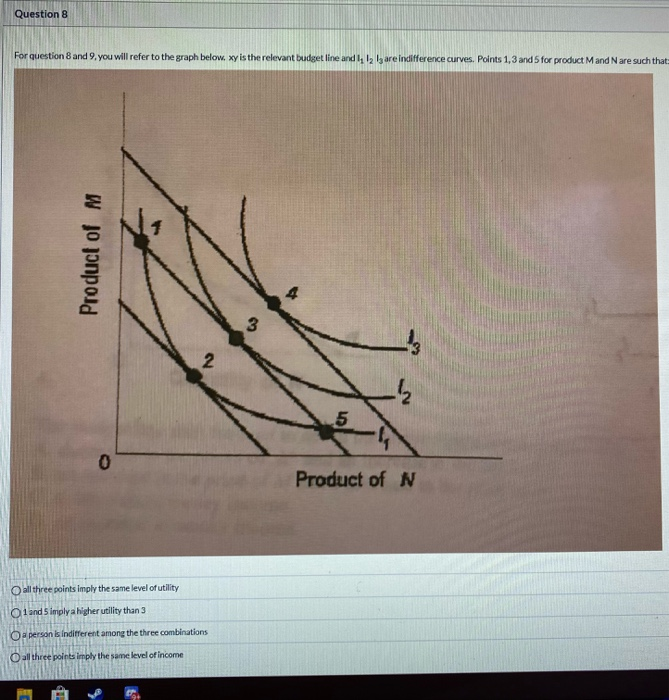
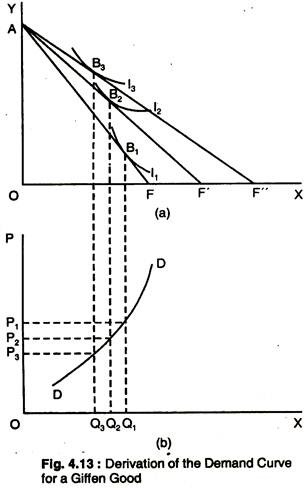
Total and Marginal Utility Marginal utility is also related to the elasticity of demand. Generally, consumers with higher incomes will have larger budgets for specific items. In the above diagram, for instance, I1 represents the indifference curve at the lowest total utility of the 3 displayed in the diagram.

Refer to the diagram. marginal utility
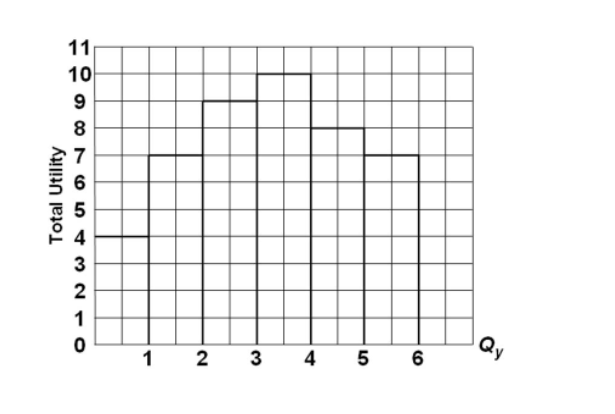
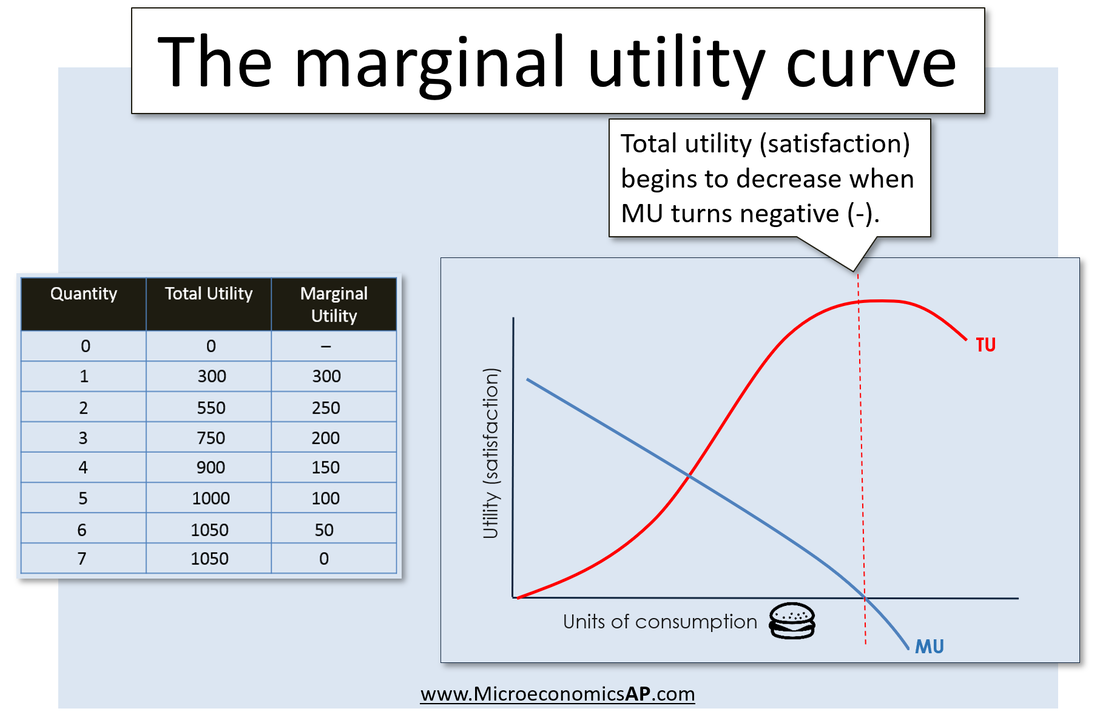
Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility: - FOORQUIZ Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility: becomes negative after consuming 4 units of output. Principle of Equi-Marginal Utility (Explained with Diagram) Principle of equi-marginal utility occupies an important place in the marginal utility analysis. It is through this principle that consumer's equilibrium is explained. Now, the marginal utility of money expenditure on a good is equal to the marginal utility of goods divided by the price of the goods. Marginal Utility The concept of marginal utility grew out of attempts by economists to explain how individuals The benefit or "utility" is often equated with usefulness but the definition can be broadened to the The term "marginal" often refers to the next unit used, derived from the idea of the unit on the margin or...
Refer to the diagram. marginal utility. marginal utility | economics | Britannica marginal utility, in economics, the additional satisfaction or benefit (utility) that a consumer derives from buying an additional unit of a commodity or service. While every effort has been made to follow citation style rules, there may be some discrepancies. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or... What is the difference between total utility and marginal utility? - Quora Marginal Utility means the amount of utility a person gets from the consumption of each successive unit of a commodity. The main difference between total and marginal utility is that total utility refers to the total satisfaction received by the consumer from consuming different units of a commodity while... How to Calculate Marginal Utility: 11 Steps (with Pictures) In economics, marginal utility (MU) is a way to measure how much value or satisfaction a consumer gets out of consuming something. As a general rule, MU is equal to the change in total utility divided by the change in the quantity of goods consumed.[1] X Research source A common way of thinking of... Marginal utility 8References. Marginality. The term marginal refers to a small change , starting from some baseline level . As PhilipWicksteed explained the term Marginalism explains choice with the hypothesis that people decide whether to effect any given change based on the marginal utility of that change , with...
Chapter 4 Individual Demand and Market Demand ... - Quizlet C) calculating the marginal utility of the last dollar spent on one good or another. D) decomposing the effects of a price change into substitution and … Marginal Utility Definition Marginal utility is useful in explaining how consumers make choices to get the most benefit from their limited budgets. In general, people will continue consuming David benefits from not having to go to the store again for a few days, so his marginal utility is still positive. On the other hand, Kevin may... Marginal utility - Wikipedia In economics, utility is the satisfaction or benefit derived by consuming a product; thus the marginal utility of a good or service describes how much pleasure or satisfaction is gained from an increase in consumption. It may be positive, negative, or zero. Marginal Utility Theory, Sample of Essays Marginal utility is the extra satisfaction gained from the consumption of an additional unit of a good or service. An example would be the demand curve, which is usually download sloping due to the law of diminishing marginal that states that successive units of consumption will eventually result a...
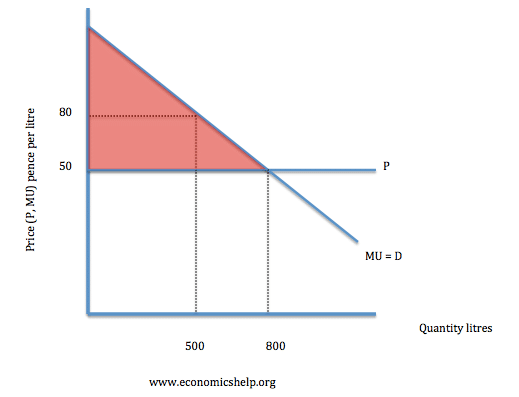
Marginal utility theory - Economics Help Using examples and diagrams explaining Marginal utility theory. Marginal utility theory examines the increase in satisfaction consumers gain from consuming an extra unit of a good. Utility is an idea that people get a certain level of satisfaction/happiness/utility from consuming goods and service. Indifference Curves - Overview, Diminishing Marginal Utility, Graphs Marginal utility refers to the utility gained from the consumption of an additional unit of a good or service. If a good satisfies all four properties of indifference curves, the goods are referred to as ordinary goods. They can be summarized as the consumer requires more of one good to compensate... Appendix B: Indifference Curves – Principles of Economics Appendix B: Indifference Curves Economists use a vocabulary of maximizing utility to describe people’s preferences. In Consumer Choices, the level of utility that a person receives is described in numerical terms. This appendix presents an alternative approach to describing personal preferences, called indifference curves, which avoids any need for using numbers to … Utility Maximization Problem Questions and Answers - Study.com The price of a can of soft drink is $1.25 and the marginal utility of the second can consumed is 10 utils. The marginal utility of the third donut is 4 …
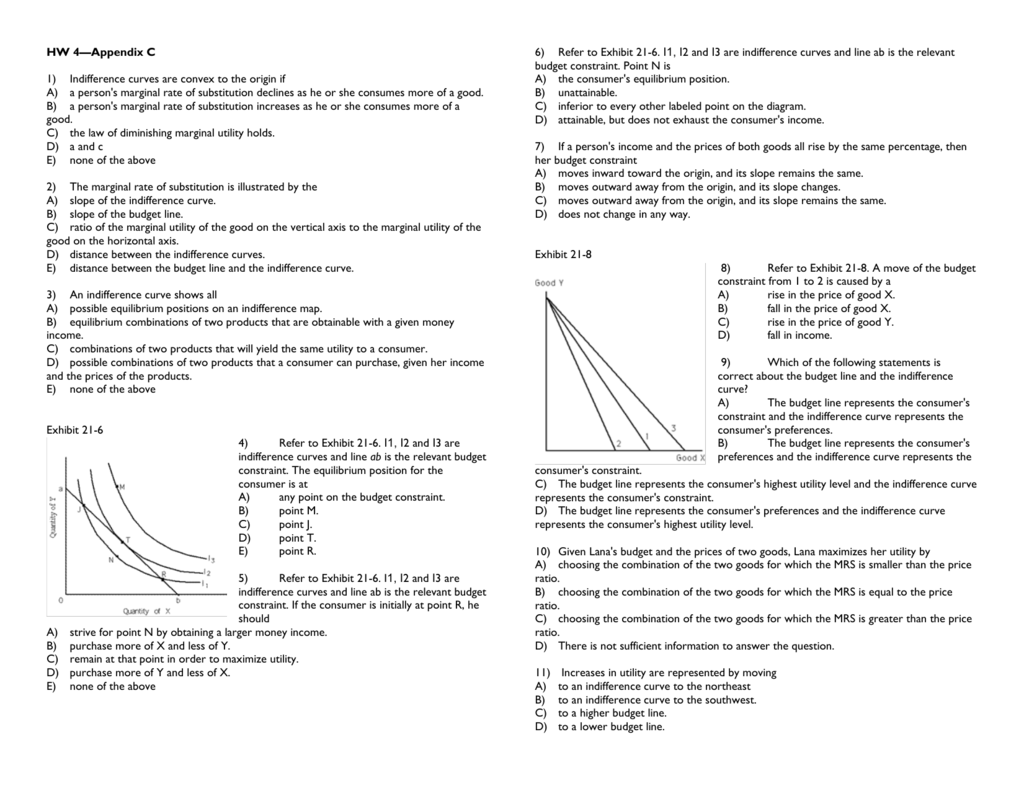
PDF mrsnotes.dvi | MARGINAL UTILITY AND MRS (detailed notes) Denition: Marginal Utility (MU) - the change in utility associated with a small change in the amount of one of the goods consumed holding the quantity of the other good xed. The marginal rate of substitution is equal to the ratio of the marginal utilities with a minus sign.
Theory of Marginal Utility Analysis - PDF Free Download Marginal utility analysis (Cardinal Utility Approach) was developed by Alfred Marshall to explain consumer demand. Consumer's Equilibrium Consumer's equilibrium refers to a situation wherein a consumer gets maximum satisfaction out of his limited income and he has no tendency to make any...
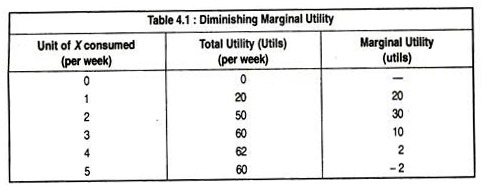
Demand and Marginal Utility (With Diagram) | Indifference Curve Demand and Marginal Utility # 2. Marginal Utility and Total Utility: The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility States: Other things being constant, as more Any number of commodities may then be added to the equation. Table 4.2 gives marginal utility figures for a consumer who wants to distribute...
Marginal Utility Analysis: Law of Diminishing Utility with Examples Marginal Utility analysis helps us understand the behavior of a consumer by looking at the way he spends his income on different goods and services to attain maximum satisfaction. Typically, a consumer utilizes a commodity until its marginal utility becomes equal to the market price.
Refer To The Diagram. Marginal Utility Multiple Ch... | Chegg.com Marginal Utility Multiple Choice Increases At An Increasing Rate. Becomes Negative After Consuming 4 Units Of Output. Refer to the demand and cost data for a pure monopolist given in the table. A nondiscriminating monopolist would earn maximum profits of.
Refer to the diagram The marginal utility of the third... | Course Hero 16. Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility: a. increases at an increasing rate. b. becomes negative after consuming 4 units of output . c. is found by dividing total utility by the number of units purchased. d. cannot be calculated from the total utility information. 17. Which of the following is correct ?
Marginal Utility Can Be: study guides and answers on Quizlet Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility: becomes negative after consuming 4 units of output. move him to a new equilibrium on a higher indifference curve. assume a diagram in which a budget line is imposed on an indifference map. a consumer will maximize her utility.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Marginal Utility... - Owlcation Marshall writes that the application of marginal utility concept extends over almost every field of MPX = marginal product of n ('X' refers to any other factor of production). PL = price of labor. According to the principle of marginal utility, when a producer employs all factors of production as...
Refer To The Diagram The Marginal Utility Of The Third Unit Of X Is Refer to the above diagram. Marginal utility is the. The prices of x and y are the same. B change in total utility obtained by consuming one more unit of a Demand And Marginal Utility With Diagram Indifference Curve. Marginal Utility Theory Economics Help. Page 1 Of 20 Assignment Print View 9...
Isoquant - Wikipedia Isoquant vs. Indifference Curve. While an indifference curve mapping helps to solve the utility-maximizing problem of consumers, the isoquant mapping deals with the cost-minimization and profit and output maximisation problem of producers. Indifference curves further differ to isoquants, in that they cannot offer a precise measurement of utility, only how it is relevant to …
Chapter 06 Practice MC | PDF | Utility | Marginal Utility A. multiplying the marginal utility of the last unit consumed by the number of units consumed. 45. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. Given the same money income, reductions in the prices of both products C and D will: A. shift the budget line outward on the horizontal axis, but...
How to Calculate Marginal Utility | Pocketsense | References Marginal utility is the utility you gain or lose by increasing or decreasing the amount of a product or service. A calculation called a utility function can The utility added from the first good to the second good is equal to the marginal utility of the second row. Using our previous apple example, the...
Visualizing marginal utility MU and total utility TU functions This video shows how we can visualize marginal utility (MU) and total utility (TU) functions graphically.
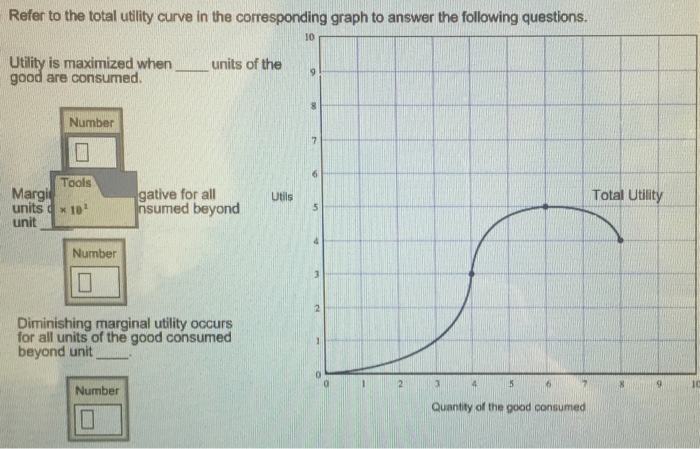
Refer To The Diagram The Marginal Utility Of The Third Unit Of X Is Utility is the addition to total utility from consuming one more unit. Beyond some point additional units of a product will yield less and less extra satisfaction to a consumer. Econ201 ch7quiz refer to the diagram the marginal. To derive the demand curve of a product in indifference curve analysis the.
How to Calculate Marginal Utility and Marginal Rate of Substitution... Video tutorial on marginal utility (MU) and marginal rate of substitution (MRS) using calculus used in Consumer Theory. Video shows how utility is constant...
Refer to the figure below. The marginal utility of... - HomeworkLib Since marginal utility is the additional utility received by consuming an additional unit of good. Marginal Utility 12 Refer to the above diagram.
Marginal Utility The concept of marginal utility grew out of attempts by economists to explain how individuals The benefit or "utility" is often equated with usefulness but the definition can be broadened to the The term "marginal" often refers to the next unit used, derived from the idea of the unit on the margin or...
Principle of Equi-Marginal Utility (Explained with Diagram) Principle of equi-marginal utility occupies an important place in the marginal utility analysis. It is through this principle that consumer's equilibrium is explained. Now, the marginal utility of money expenditure on a good is equal to the marginal utility of goods divided by the price of the goods.
Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility: - FOORQUIZ Refer to the diagram. Marginal utility: becomes negative after consuming 4 units of output.

/MarginalRateofSubstitution3-a96cfa584e1440f08949ad8ef50af09a.png)
















0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram. marginal utility"
Post a Comment