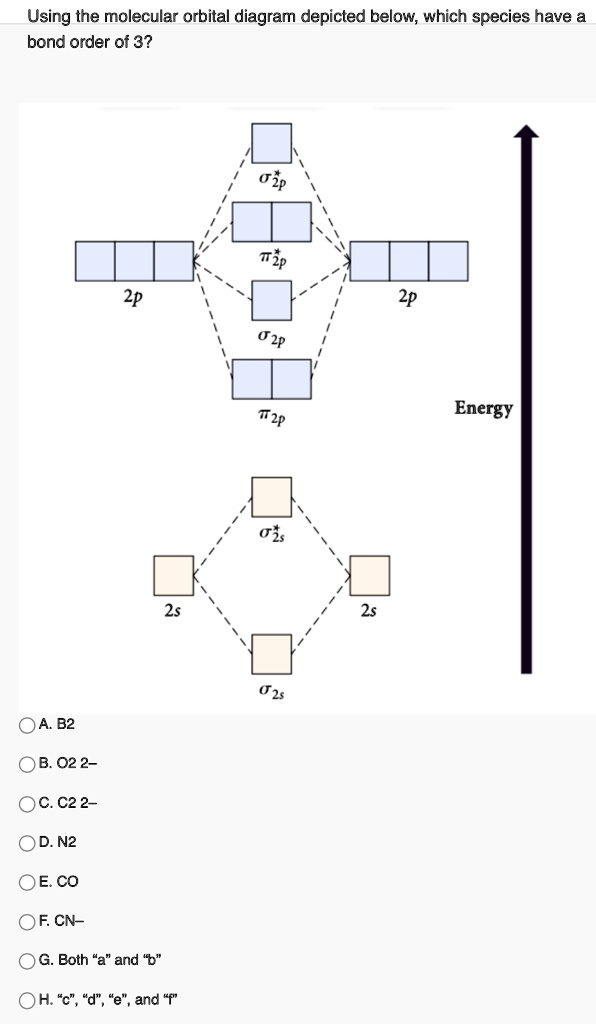
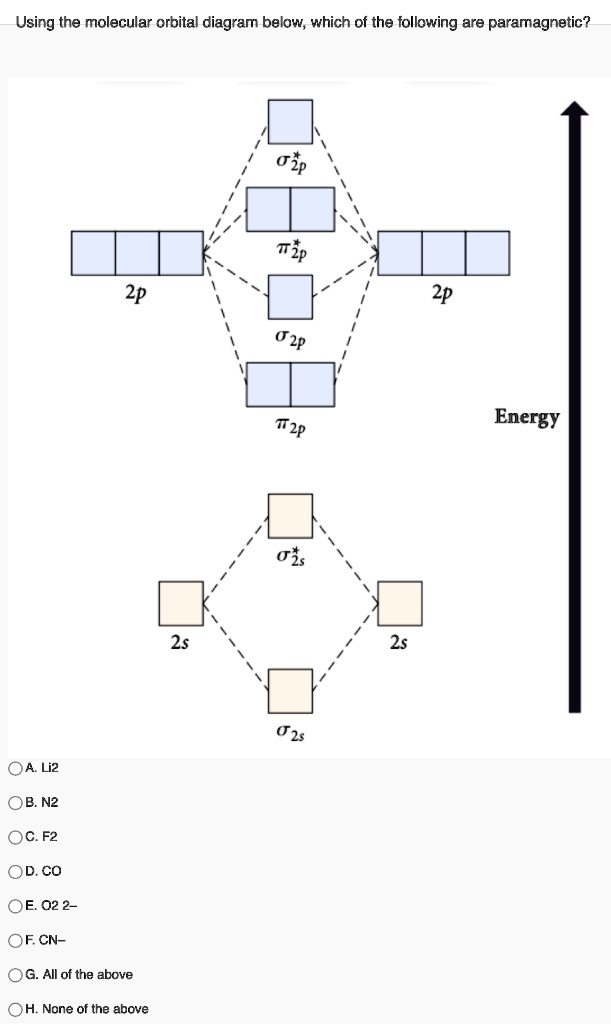
42 n2 2- molecular orbital diagram
Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond order of the molecule. Quantum chemistry molecular orbital diagram and irreducible representations dinitrogen. Molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules introduction. In the molecular orbital diagram of n2 the number of electrons in the s2p molecular orbital is.
The molecular orbital diagram for even a simple octahedral complex looks complicated (Figure 5), but most of the Differences in orbital orientation create two types of molecular orbitals (σ and π) from atomic orbitals with quantum numbers n = 2; l = 1. The π molecular orbitals are doubly degenerate...
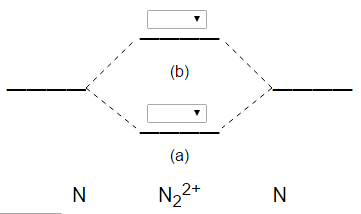
N2 2- molecular orbital diagram
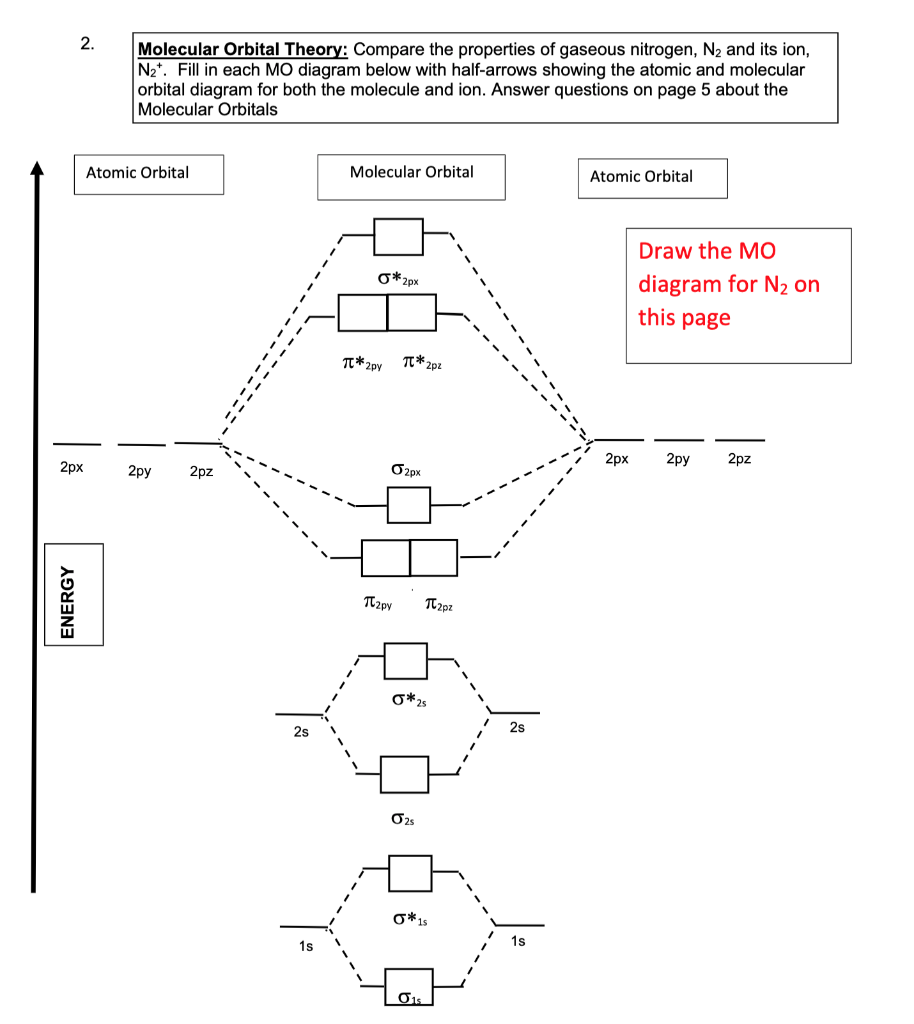
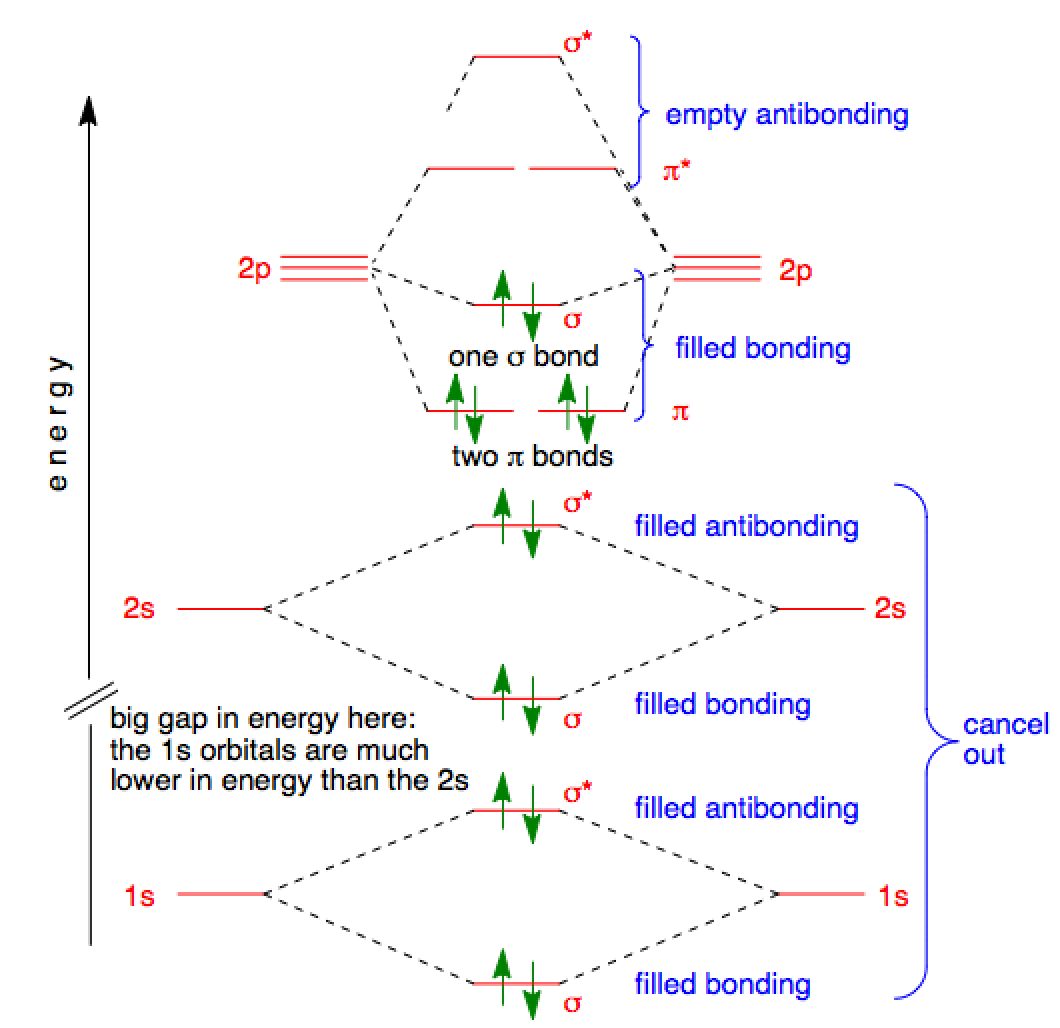
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Experimental thermodynamic data show that the N2 molecule is stable, is diamagnetic, and has a very high bond energy, 946 kJ/mol. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the... From the molecular orbital diagram of N2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Compare the atomic and molecular orbital diagrams to identify the member of each of the following pairs that has the highest first ionization energy (the most tightly bound electron) in the...
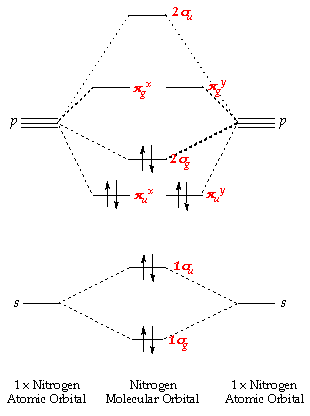
N2 2- molecular orbital diagram. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms. Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of N2 using its diagram. one atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a N2 molecule will have 14 electrons. next 2 in 2pz sigma bond( assuming that z axis is the internuclear axis ) orbital. and next 4 in 2p pi x and 2 2p pi y orbitals. Diatomic Species by Molecular Orbital Theory. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which homonuclear diatomic species - H2, N2, O2, etc. - will exist Note that by convention we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are... Figure 10. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N2 and O2...
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Molecular self-assembly has emerged as a new tool for the construction of supramolecular functional materials applied in various fields. Here we design 2,2′-bibenzimidazole derivative (BC6) containing multiple self-assembly force sites and excellent coordinational luminous ability.Systematical spectral and rheological experiment results show that BC6 could self … 02.11.2015 ... If we build the MO diagram for N2 , it looks like this: http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/ http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/. First though, notice that the p ... The second-lowest-energy molecular orbital in butadiene will have 1 node. The trick is knowing where to put it. Now that we have all the pieces, all we need to do to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the butadienyl system is to arrange the orbitals in order of increasing energy.
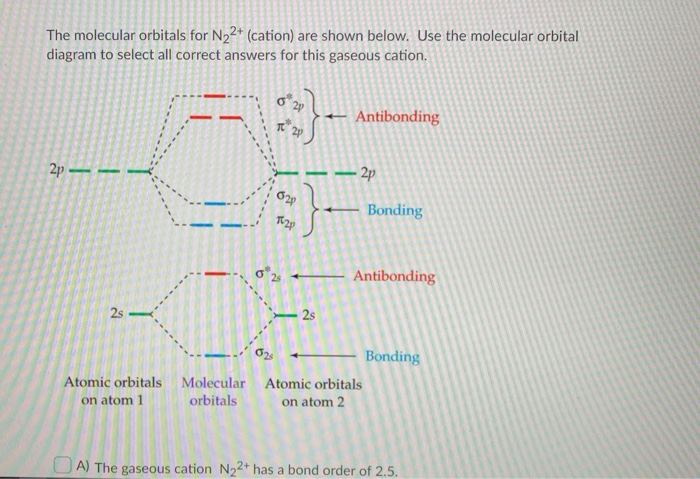
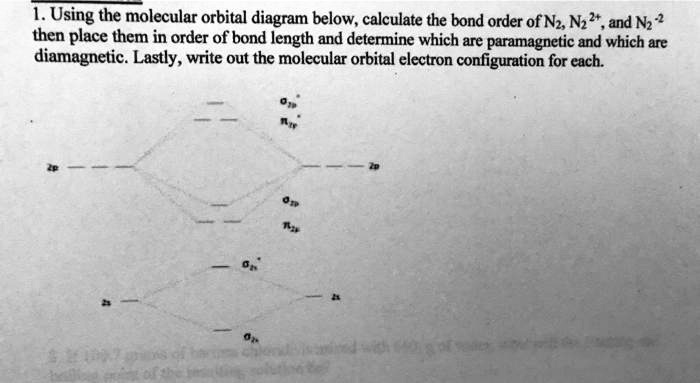
Answer : According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be, As there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen. The bond order of is, 3. The molecular orbital diagram of are shown below. Sp mixing - https://youtu.be/p3ME8DYAih4Follow me on instagram-https://www.instagram.com/trickychemistrysuman/?hl=enFollow me on facebook ... N2. 2- (16 e-): σ2. 1sσ*2. 1sσ2. 2sσ*2. 2sπ2. 2pπ2. 2pσ2. 2pπ*1. 2pπ*1. 2p. (b). Bond orders are: N2. + = 2.5 ; N2. 2+ = 2.0 ; N2 = 3.0 ; N2. - = 2.5 ; N2. Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ Draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 , N2^ + N2 ^ - . Write their electronic configuration, find the ...
I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For NX2 ...
We have spend more that 2 years to prepare these Class 11 chemistry handwritten notes. After analyzing our notes in deep, we have uploaded our notes on the website. We have covered all topics of class 11 syllabus. We have created notes as per NCERT Syllabus and guidelines. But we have added much extra topics in our notes to cover whole syllabus of class 11 chemistry for …
Natural charge on each N is -1.0 as would be expected (natural electron configuration was found to be 1sX2.00 2sX1.65 2pX4.17 3sX0.06 3pX0.05 3dX0.07 4dX0.01).
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of C2 molecule : Number of electrons in C2 molecule = 12.
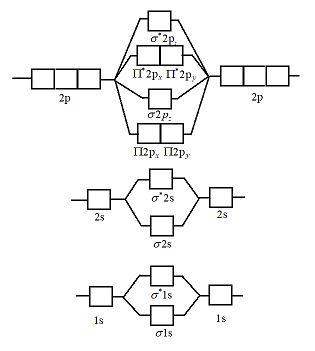
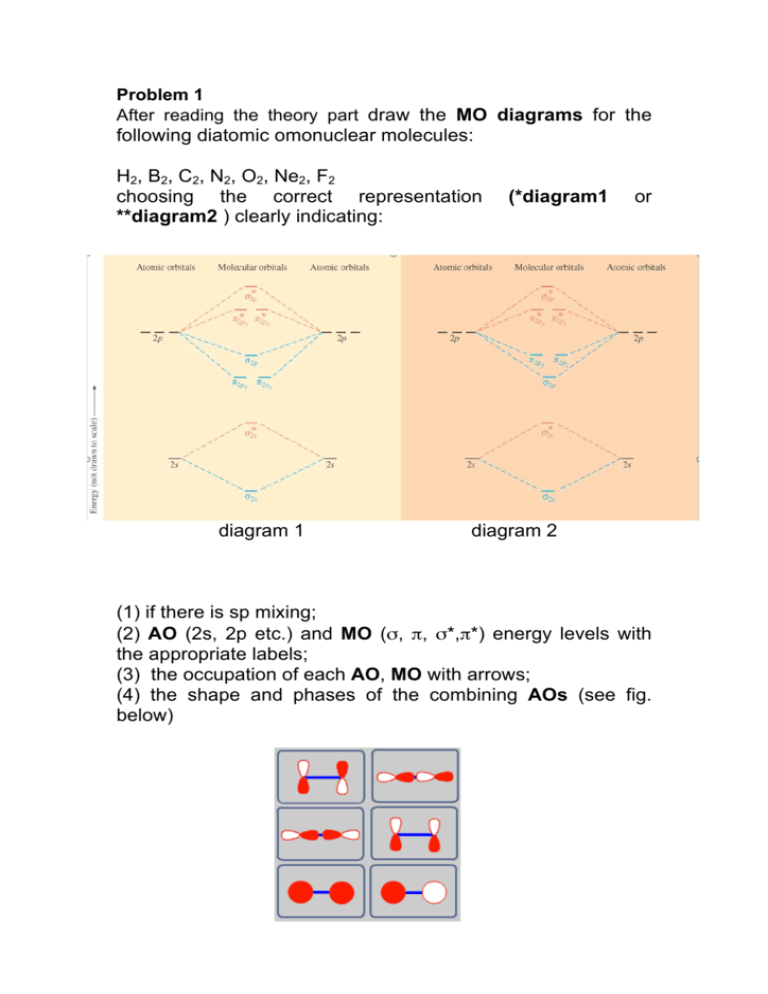
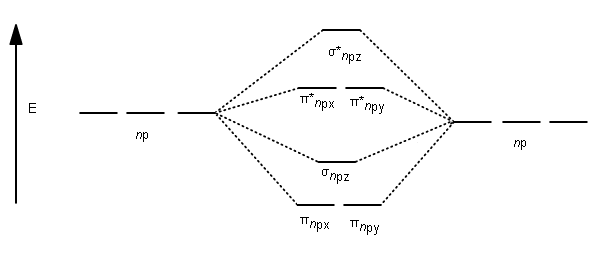
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
13.03.2019 ... write the molecular orbital diagram of n2 and calculate their bond order ... The total number of electrons present in the N2 molecule is 14.
Each orbital wavefunction (φ ) is most easily described in two parts radial term - which changes as a function of distance from the nucleus angular terms - which - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital. - Electrons fill the lowest energy...
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The net contribution of the electrons to the bond strength of From the molecular orbital diagram of N2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Answer.
Figure PRS.3B-2 Reaction coordinate for (a) S N2 reaction, and (b) generalized reaction. Collision Theory when discussing the Polyani Equation. The energy barrier shown in Figure PRS.3B-2 is the shallowest barrier along the reaction coordinate. The entire energy diagram for the ABC system is shown in 3-D in Figure PRS.3B-3.
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
Below is a diagram that shows the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability. This is why the hydrogen atom has an electron configuration of 1s 1. 2) Orbitals are combined when bonds form between atoms in a molecule. There are four types of orbitals that you should be familiar with s, p, d and …
Jan 31, 2022 · N2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Each molecule has its electron configuration consisting of a sigma bond and a pi bond, known as molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital theory determines the stability order, magnetic nature, and the number of bonds in a molecule.
the pi(2p) bonding orbitals are LOWER than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.N2(2-) has a bonding order of 2, which predicts that there will be a stable double ...
In fact, based on Jupiter's composition, researchers have made the case for an initial formation outside the molecular nitrogen (N 2) snowline, which is estimated at 20–30 AU (3.0–4.5 billion km; 1.9–2.8 billion mi), and possibly even outside the argon snowline, which may be as far as 40 AU (6.0 billion km; 3.7 billion mi). Having formed at one of these extreme distances, Jupiter …
For O2, N2, NO, F2, etc, you count the number of valence electrons instead of the atomic number. The 1s electrons of O2, N2, etc. are used to fill up the sigma(1s) and sigma(1s)* molecular orbitals. Similarly, with Be2+ as well, there are 2(4) - 1 = 7 total electrons if you're filling out a complete MO...
The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N2 and O2, the order of the orbitals changes.
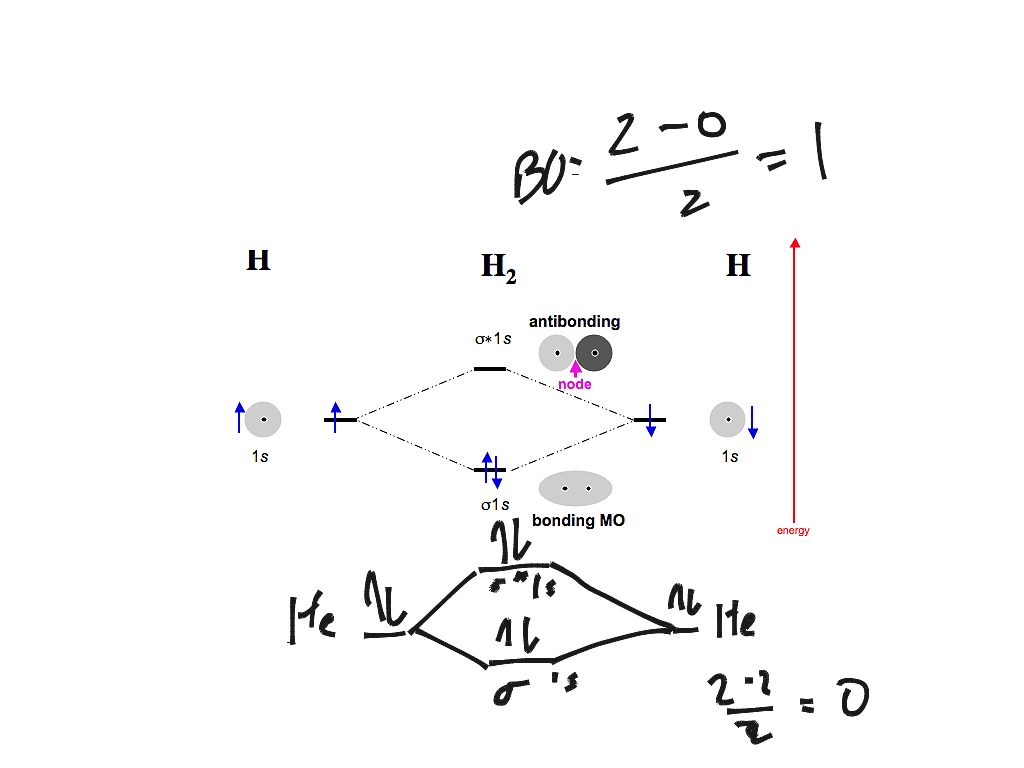
The bonding molecular orbital concentrates electrons in the region directly between the two nuclei. Placing an electron in this orbital therefore stabilizes the H2 molecule. This diagram suggests that the energy of an H2 molecule is lower than that of a pair of isolated atoms.
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory. Transformational properties of atomic orbitals. • When bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their • The He-I photoelectron spectrum of gaseous N2 below proves that there is the σ-π level inversion in this molecule. It also allows identify bonding...
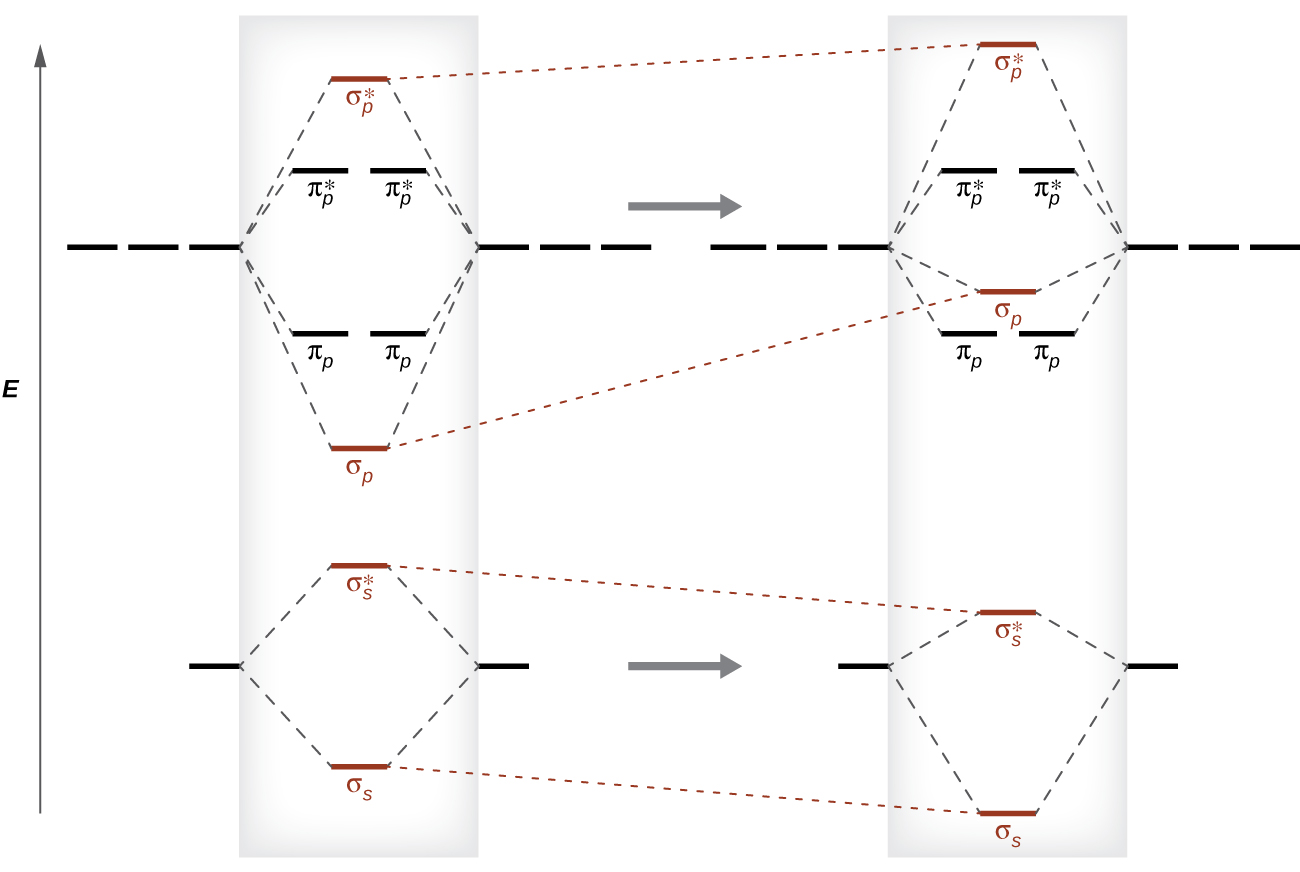
Feb 05, 2015 · Well, s-p mixing only occurs when the s and p atomic orbitals are close in energy (it's a necessary but not sufficient condition). Even though $\rm N_2^{2-}$ is isoelectronic with $\rm O_2$, the lower effective nuclear charge on nitrogen should make its s orbitals a little closer to the energies of the p orbitals than they would be in oxygen.
Chapter 2 - Molecular Orbital Theory Big-picture: Now that we understand aspects of molecular structure, we Learning goals: • Be able to construct molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear diatomic, heteronuclear diatomic, homonuclear triatomic, and heteronuclear triatomic molecules. •
N2 is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with CO and with [CN] · The formal bond order of N2 is 3, from about one σ-bond and two π-bonds ...
This second orbital is therefore called an antibonding orbital. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H2+.
molecular orbital diagram for N2. number of electrons in the sigma2p molecular orbital is. their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules. which of the following statements about nitrogen oxide, NO, is FALSE.
Molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen gas (N2)Use aufbau and Hund to fill with 10 valence electronsYou get sigma2s(2),sigma2s*(2),pi2p(4),sigma2p(2).Bond Or...
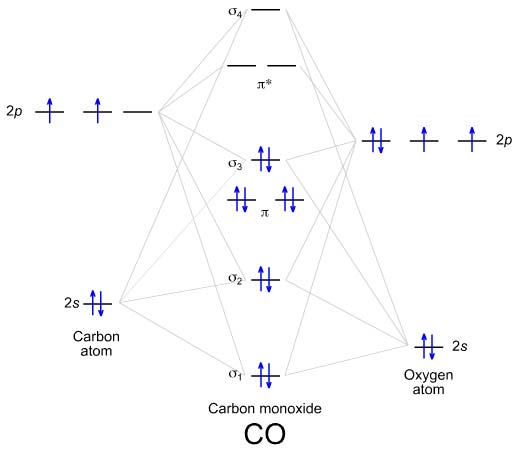
For example, homonuclear diatomic molecules of second row elements like Li2, Be2, B2 , C2, N2 , the σ 2pz MOs is higher in energy than π 2px and π 2py MOs. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if...
Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of N2 molecules. > Explain the molecular orbital structure, bond order, stability and magnetic behavior of Hydrogen molecule on the basis of molecular orbital theory.
Draw a molecular orbital diagram for [N2]2– (use only the valence orbitals of oxygen). Label all molecular and atomic orbitals, indicate which atomic orbitals contribute to each of the molecular orbitals, and determine the bond order. Do you expect that this species is diamagnetic or paramagnetic?.
Electrons of nitrogen are to be filled in this diagram. Left side represents the configuration of one atom of nitrogen molecule and the right side represents ...
From the molecular orbital diagram of N2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Compare the atomic and molecular orbital diagrams to identify the member of each of the following pairs that has the highest first ionization energy (the most tightly bound electron) in the...
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the...
Figure 9-2 Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the combination of the 1s atomic orbitals on two identical atoms (at the left) to form two MOs. Experimental thermodynamic data show that the N2 molecule is stable, is diamagnetic, and has a very high bond energy, 946 kJ/mol.
















0 Response to "42 n2 2- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment