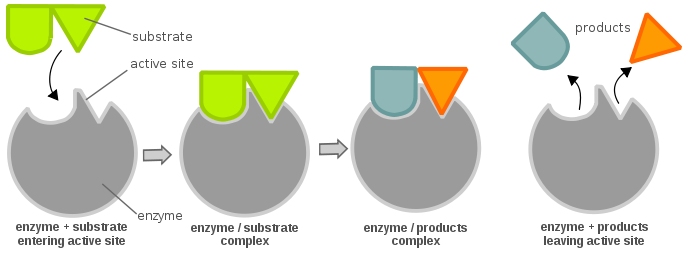
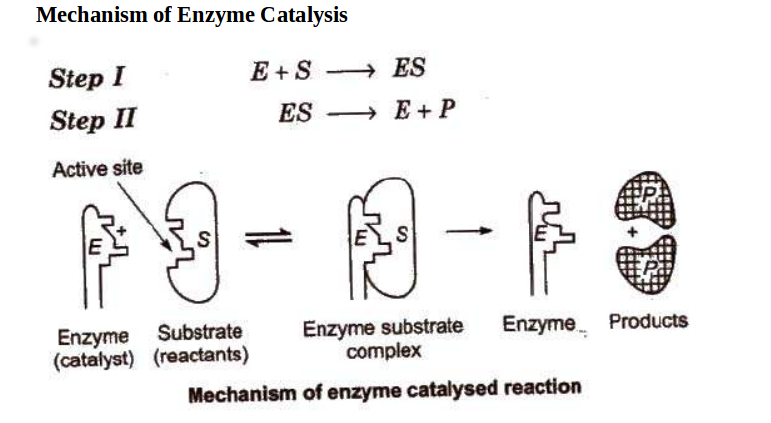
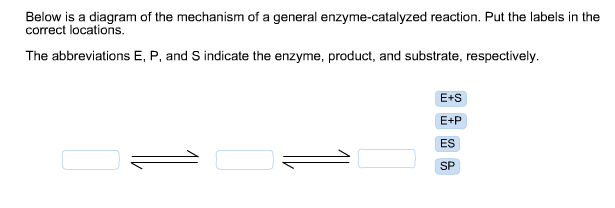
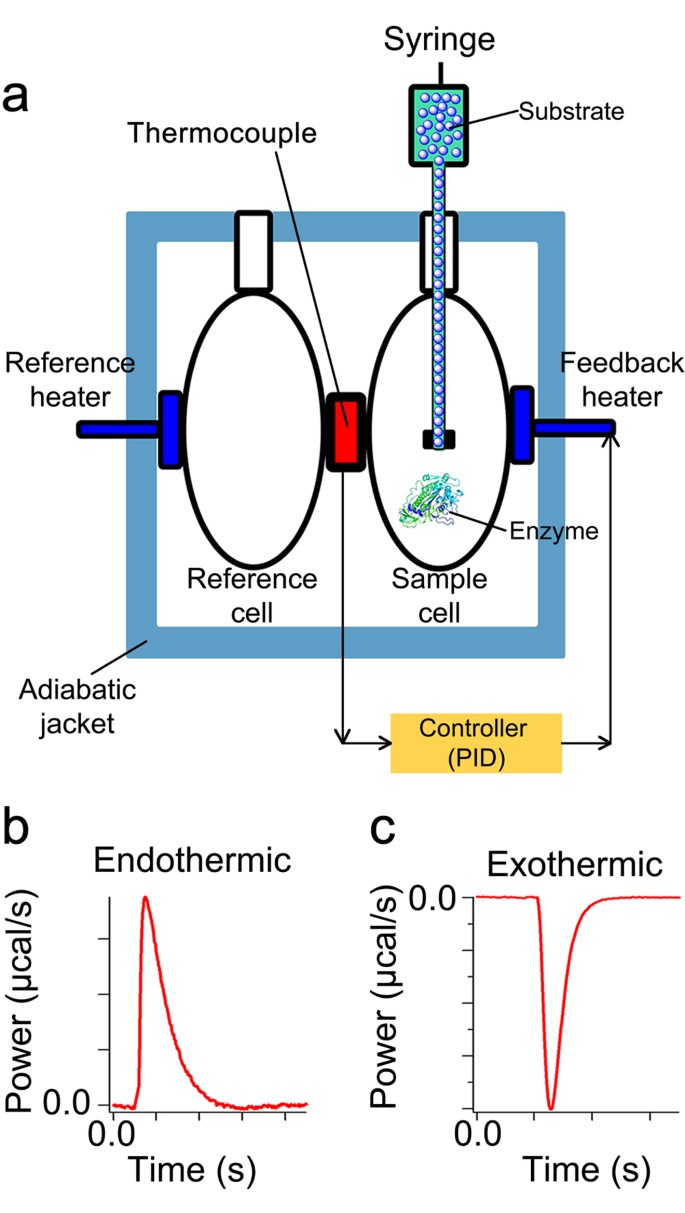
41 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts ... Most modern Biochemistry textbooks, resting on the energetic profile of enzymic reaction, try to bridge the gap between the thermodynamic and the mechanistic description of enzyme action. In this sense, the energy diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is an invaluable teaching and learning tool. Solved Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general ... Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. Question: Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations.
Enzyme Catalyzed Reaction - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Enzyme-catalyzed reaction. In a CSTR, if the reaction is controlled by enzyme catalysis and the kinetics equation follows the Michaelis-Menten equation, substituting the kinetics equation directly into Eq. (3.42) gives the residence time (11.46) τ = Vr Q0 = ( cs0 − cs) ( Km + cs) rmaxcs = ( cs0 − cs) ( Km + cs) k2cE0cs
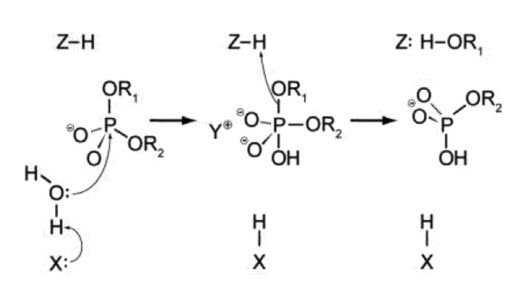
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
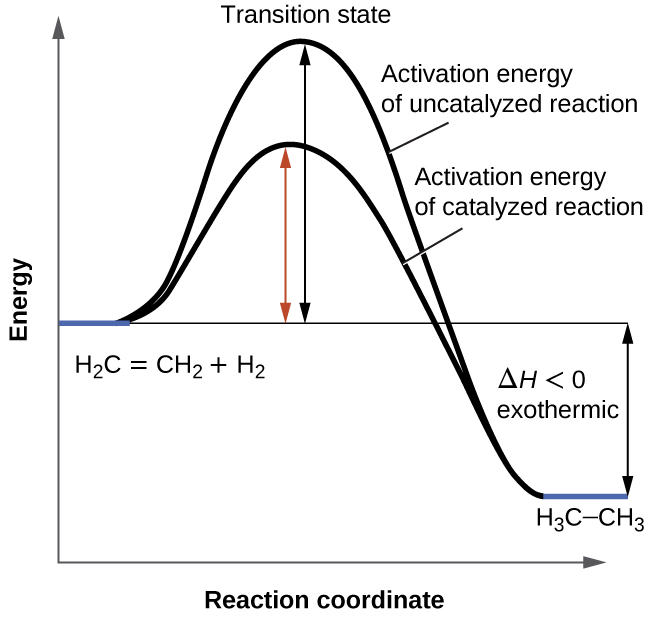
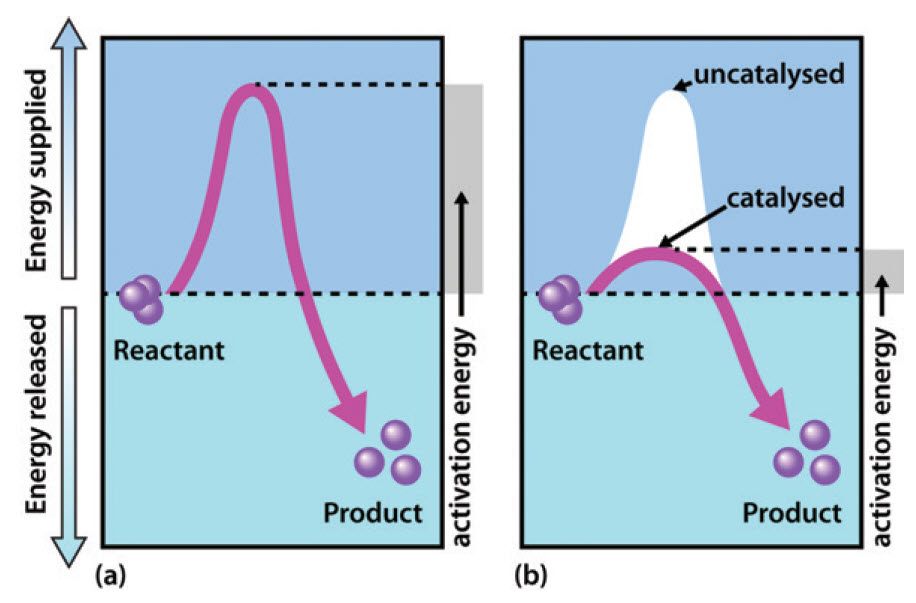
Catalysis - Chemistry Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as depicted in the reaction diagrams shown in [link]. This lower activation energy results in an increase in rate as described ... Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ... PDF our Course ID# enter NAME: For GradeScope, please write ... A. a measure of the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme B. ½ Vmax C. the first order rate constant for the enzyme catalyzed reaction D. the second order rate constant for the enzyme catalyzed reaction E. a rate constant that has the units M-1s-1 9. The most efficient substrate of an enzyme is usually considered to be the substrate with the _____.
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in ... of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in t… Show more Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively ______ Exam 2 HW Flashcards - Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme _____, but will not directly illustrate that the enzyme _____.stabilizes the transition state; orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur 2)EP (enzyme)E + (product)P This is known as the Michaelis ... mechanism for enzyme - catalyzed reaction is given by the following set of equations: (enzyme)E + ... The potential energy diagram is shown in the figure.1 answer · Top answer: (1) represents enzyme (E) and substrate (S),(2) represents enzyme - substrate intermediate 1 (ES).(3) represents enzyme product intermediate 2 ... Solved Below is a | Chegg.com This problem has been solved! Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, and S indicate the enzyme, product, andsubstrate, respectively.
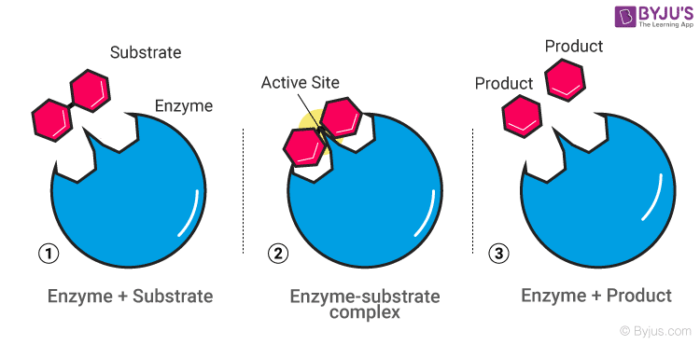
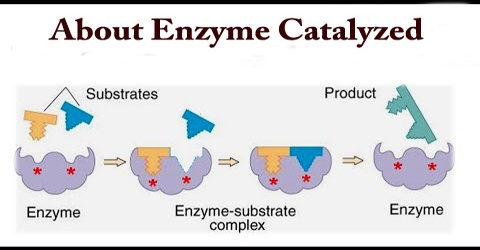
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as depicted in the reaction diagrams shown in Figure 2. This lower activation energy results in an increase in rate as ... Chapter 7 Enzyme RQ + HW Flashcards | Quizlet 1. An enzyme lowers the activation energy of a reaction, which means the transition state is not as energetically unfavorable as it would be without the presence of an enzyme. 2. An enzyme does not change the energy of the reactants or product, nor does it change the equilibrium constant of a reaction. QUIZ 2 mega quizlet Flashcards | Quizlet - An enzyme that temporarily undergoes covalent catalysis as part of its mechanism. - A type of enzyme inhibitor where KM is unaltered. - The type of reaction catalyzed by proteases. - An enzyme that is part of a pigment formation pathway and has a low-temperature optimum. - A protease enzyme with a low pH optimum. Reactions and Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysis - VEDANTU Enzyme Catalysis - An enzyme is a substance which fastens a chemical reaction. A substrate is attracted towards the active site of the enzyme which leads to the catalysis of a chemical reaction and formation of products. Read more about the Reactions and mechanism of enyme catalysis at vedantu.com.
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e - OpenStax The catalyzed reaction is the one with lesser activation energy, in this case represented by diagram b. Check Your Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step. biochemistry chapter #6 Flashcards - Quizlet 17) An enzyme stabilizes the transition state that is bound in the active site. What effect will this have on the energy diagram below? The diagram shown below is for the uncatalyzed reaction. A) Energy of point 1 is raised. B) Energy of point 2 is raised. C) Energy of point 2 is lowered. D) Energy of point 3 is lowered. E) Energy of point 4 is ... Answered: The diagram shows the mechanism of a… | bartleby Solution for The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme‑catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P and S…1 answer · Top answer: Introduction The enzyme is a biocatalyst that speeds up the reaction without taking part in the reaction by l... Enzyme Mechanism - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Enzyme-catalyzed reactions are time-dependent. ... or enzyme displacement, mechanism where one product is released prior to the binding of the second substrate. This third major type of bimolecular reaction is depicted in the following diagram where E' indicates that the enzyme exists in a chemically modified form.
Acid-base Catalysis - Creative Enzymes The lower curve (I) represents the reaction in vitro of a typical, unreactive compound: it shows only acid- and base-catalyzed reactions, and reaction is very slow at the minimum, near pH 7. For the most reactive compounds, an additional feature (curve II) is a pH-independent region, where the uncatalyzed reaction with water becomes faster than ...
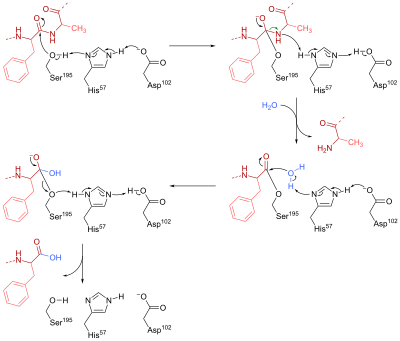
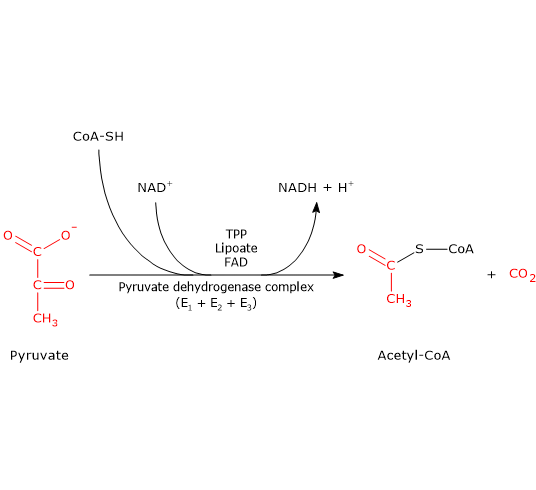
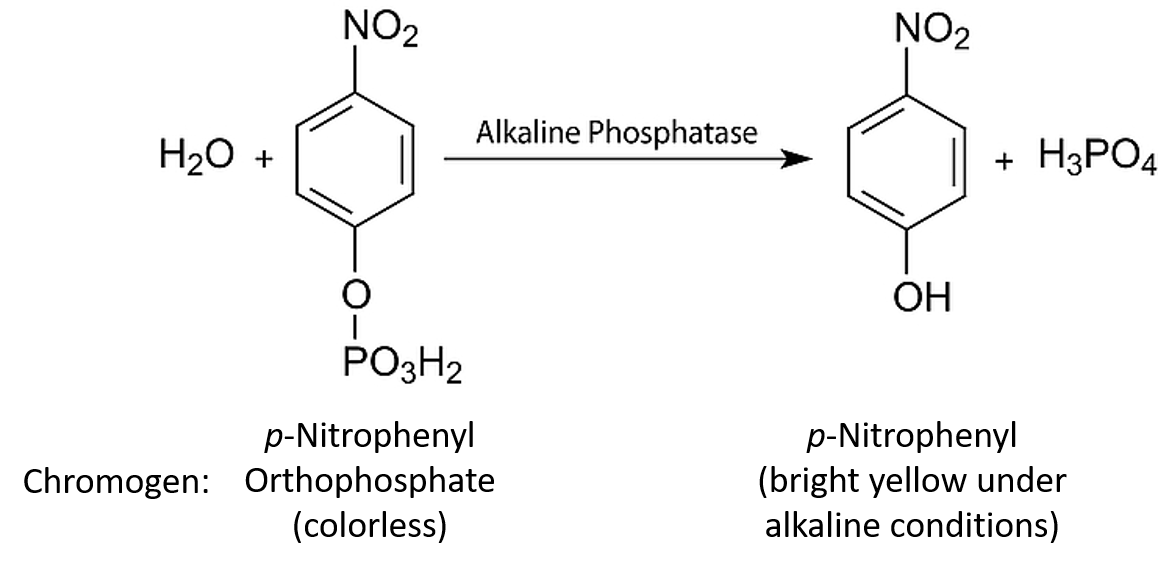
PDF Pet Enzyme - Pepsin Objectives specific reaction catalyzed by pepsin is the acid hydrolysis of the peptide bond. This reaction will break down proteins into smaller units to enable the digestive process. Pepsin demonstrates an unusual property for an enzyme; it does not actually form chemical bonds with its substrate. The unique aspect of the pepsin mechanism is the
Enzyme Catalysis | Mechanism & Characteristics Enzyme Catalyst Enzyme Catalysis: Catalysis is a phenomenon in which the rate of the reaction is altered with the help of a substance called a catalyst (the catalyst does not participate in the reaction; its concentration and composition remain unchanged). The substance used to change the rate of the reaction is called a catalyst.
PDF The Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide - Chem21Labs to the reaction below. 2 H 2 O 2 (aq) 2 H 2 O O 2 (g) A number of catalysts can be used to speed up this reac-tion, including potassium iodide, manganese (IV) oxide, and the enzyme catalase. If you conduct the catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in a closed vessel, you will be able to determine the reaction rate as a func-
ADD YOUR PAGE TITLE - College of Saint Benedict and Saint ... To understand the mechanism of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, we try to alter as many variables, one at a time, and ascertain the effects of the changes on the activity of the enzyme. Kinetic methods can be used to obtain data from which inferences about the mechanism can be made.
Mechanism of Enzyme Reaction (With Equations) ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the mechanism of enzyme reaction. In an enzyme-catalysed biochemical reaction, the enzyme molecule binds specifically and reversibly to the substrate molecule resulting in formation and breaking of chemical bonds to produce the product. Thus, there is formation of an unstable enzyme-substrate complex which immediately breaks into the […]
Chapter 7: Catalytic Mechanisms of Enzymes - Chemistry Enzymes have high substrate specificity, and can even show regiospecificity that leads to the generation of stereospecific products. Figure 7.1 Effect of an enzyme on reducint the activation energy required to start a reaction where (a) is uncatalyzed and (b) is an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Figure from Peter K. Robinson.
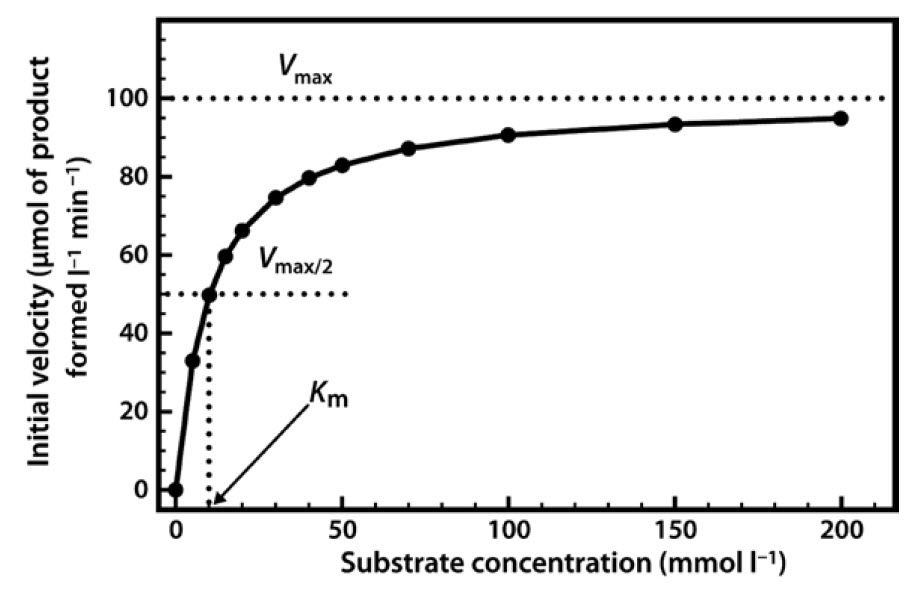
PDF Diagram Of An Enzyme Substrate Reaction Diagram Of An Enzyme Substrate Reaction enzyme diagrams diagram link, enzyme ... enzyme action with diagram, enzymes enzyme mechanism, reading enzymes biology early release, solved below is a diagram of the ... from the above we may conclude that the maximum velocity of an enzyme catalyzed reaction depends on the affinity between the enzyme and ...
Solved Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general ... Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. The abbreviations E, P, and Sindicate the enzyme, product, and substrate, respectively. ES E+P = EUS Answer Bank SP. Question: Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
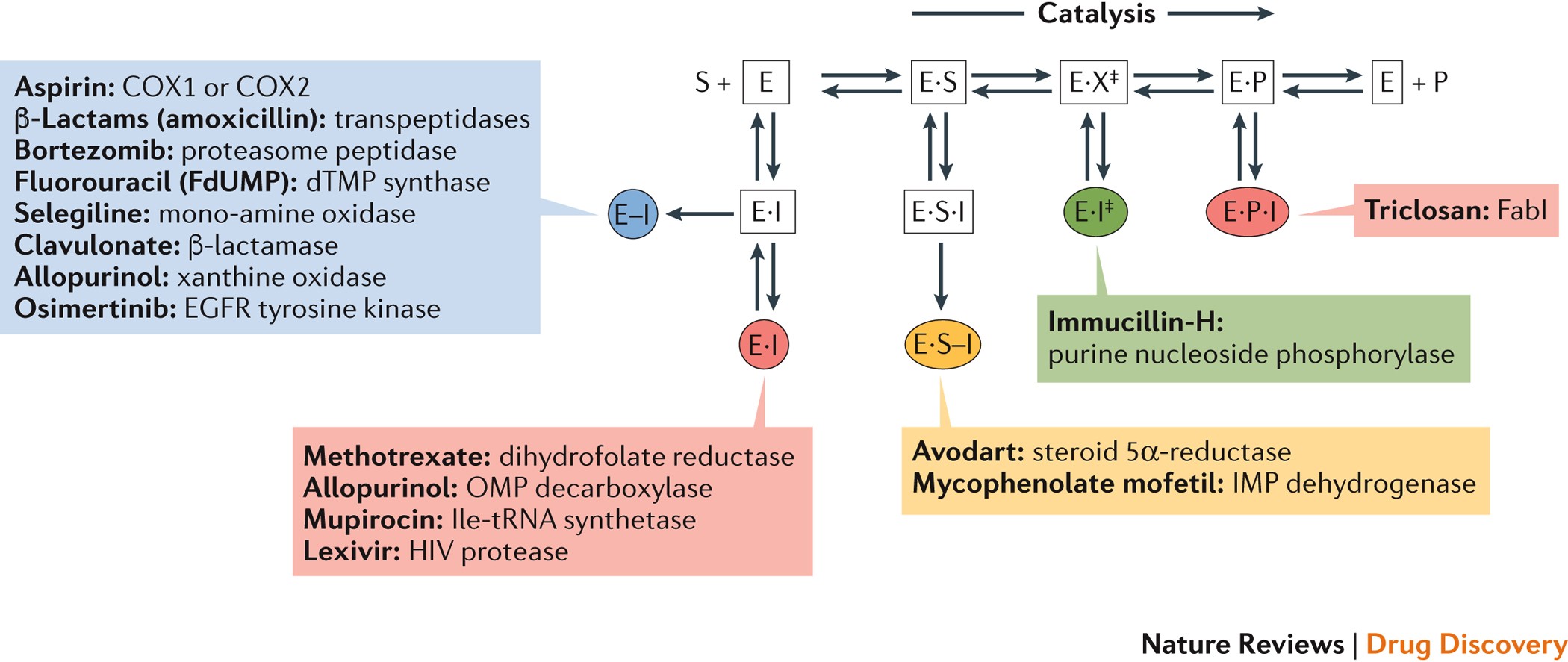
Biochemistry I Chapter 11 Problems Flashcards - Quizlet A transition state analog is a stable molecule that resembles the transition state of an enzyme catalyzed reaction, and is a potent _____ of that enzyme. *inhibitor Little can be learned about enzyme reaction mechanisms by examining the corresponding nonenzymatic reactions of model compounds.
PDF Diagram Of An Enzyme Substrate Reaction results schoolworkhelper, enzyme diagram labeled wiring diagrams, solved below is a diagram of the mechanism of chegg com, reading enzymes biology early release, analyzing graphics enzymes the biology corner, enzyme simple english wikipedia the free encyclopedia, vaughan s blog enzymes lock and key diagram, six types of
PDF our Course ID# enter NAME: For GradeScope, please write ... A. a measure of the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme B. ½ Vmax C. the first order rate constant for the enzyme catalyzed reaction D. the second order rate constant for the enzyme catalyzed reaction E. a rate constant that has the units M-1s-1 9. The most efficient substrate of an enzyme is usually considered to be the substrate with the _____.
Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ...
Catalysis - Chemistry Catalysts function by providing an alternate reaction mechanism that has a lower activation energy than would be found in the absence of the catalyst. In some cases, the catalyzed mechanism may include additional steps, as depicted in the reaction diagrams shown in [link]. This lower activation energy results in an increase in rate as described ...








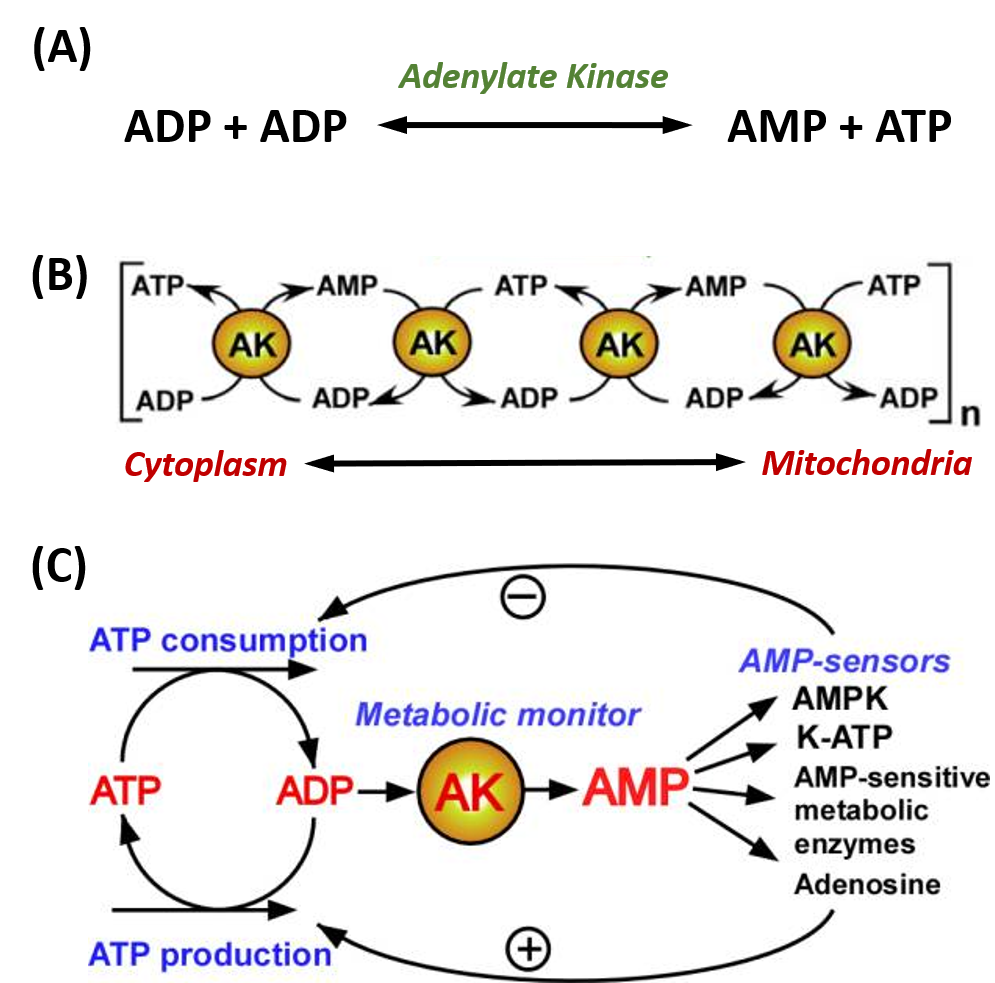
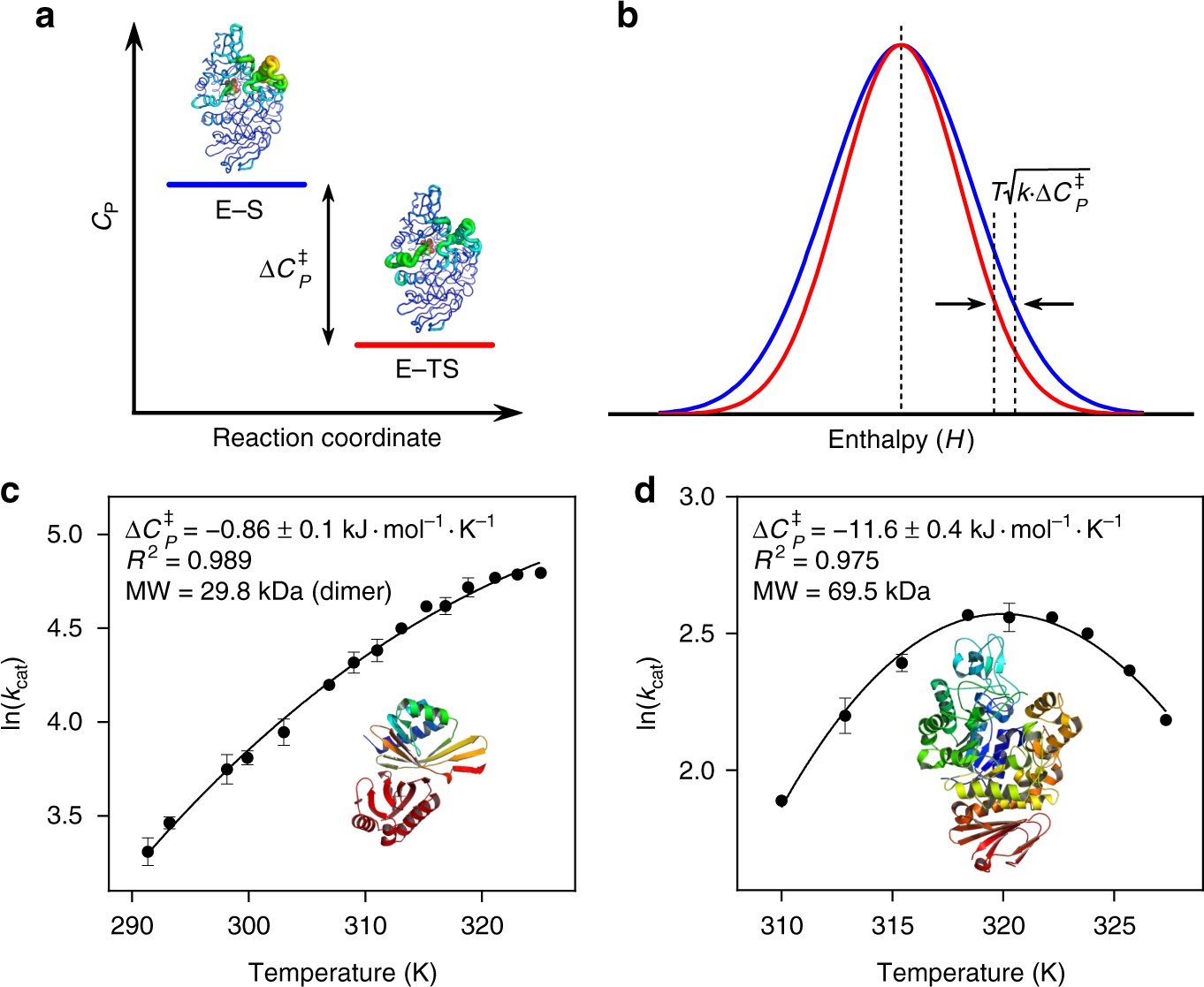

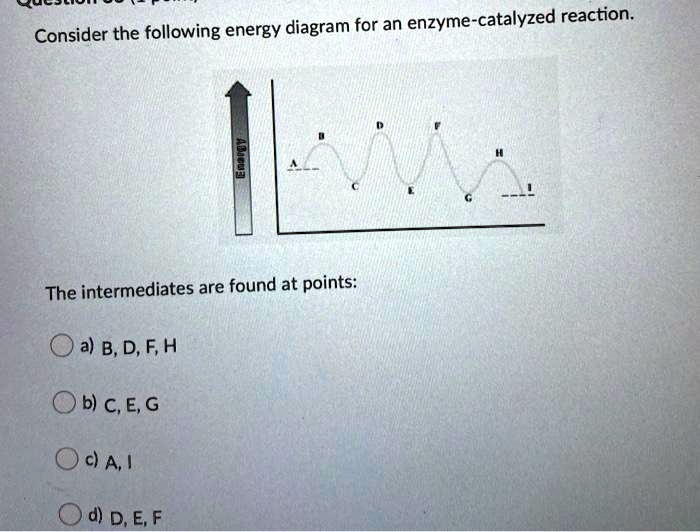
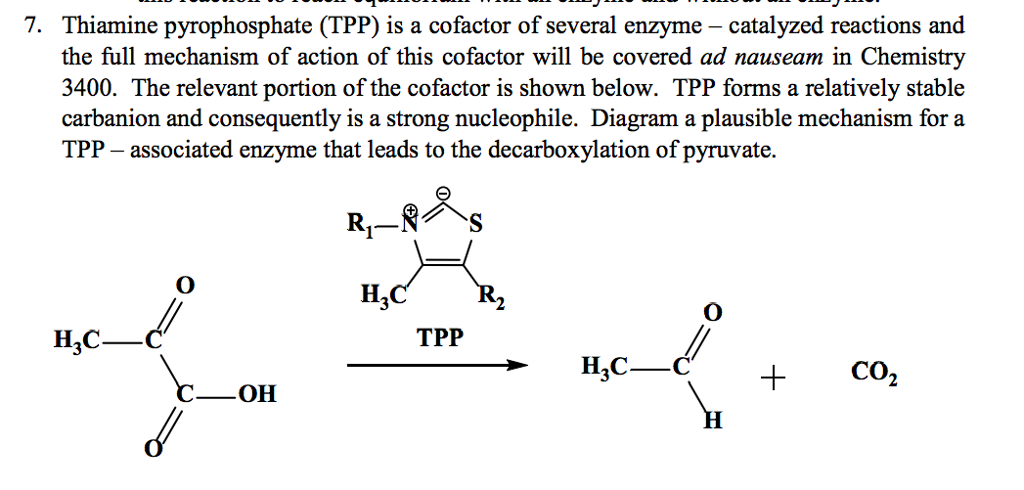






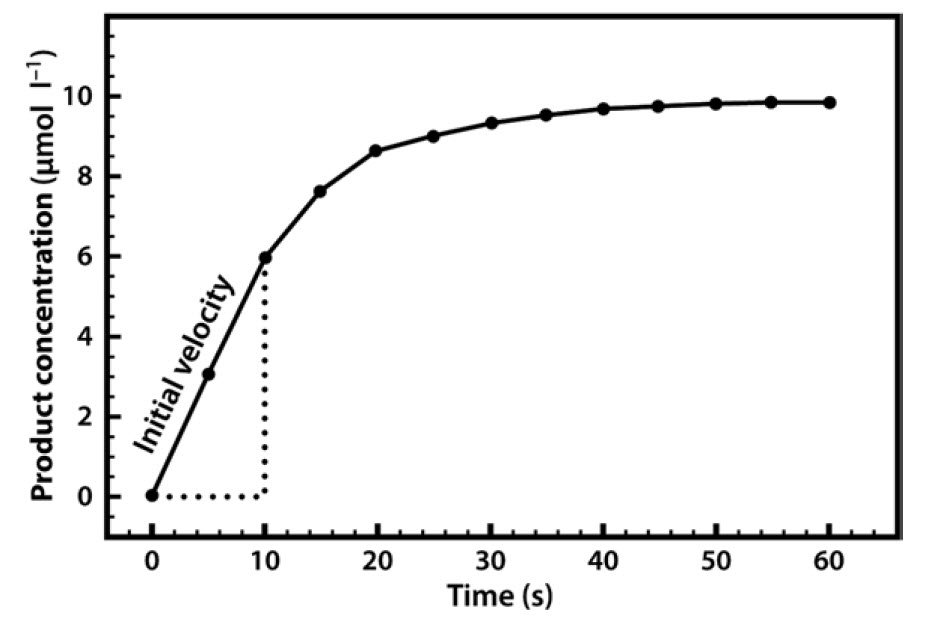

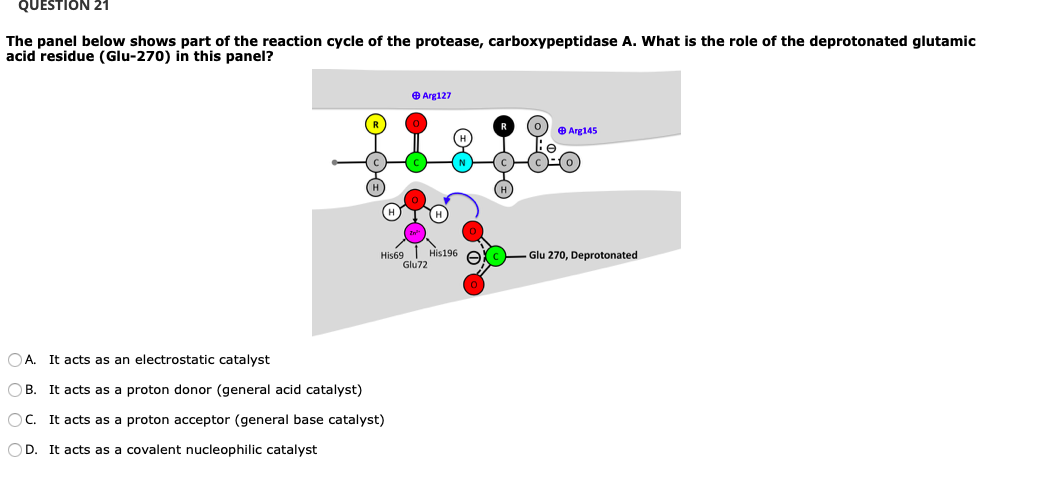
0 Response to "41 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment