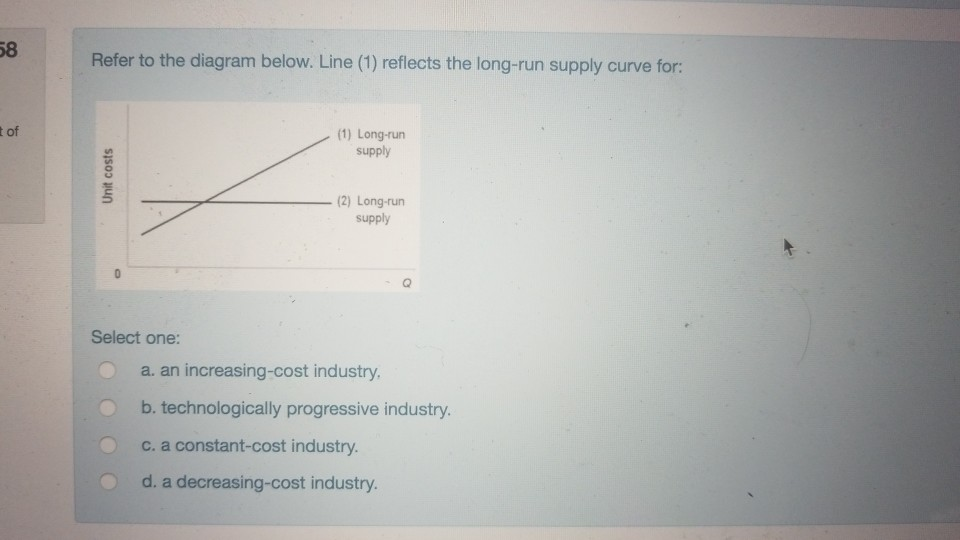
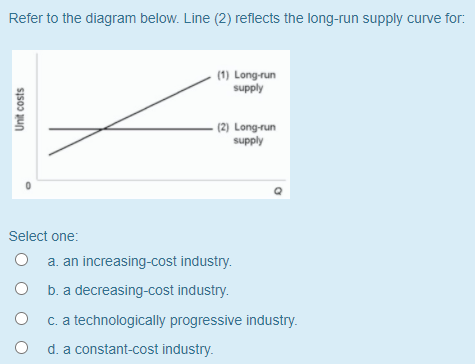
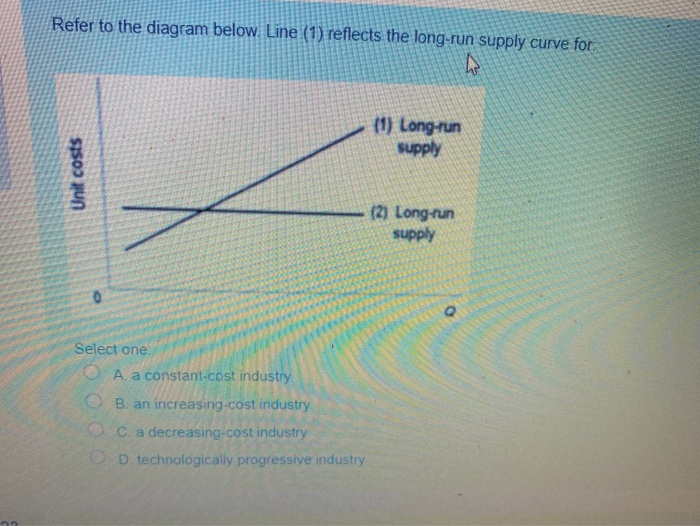
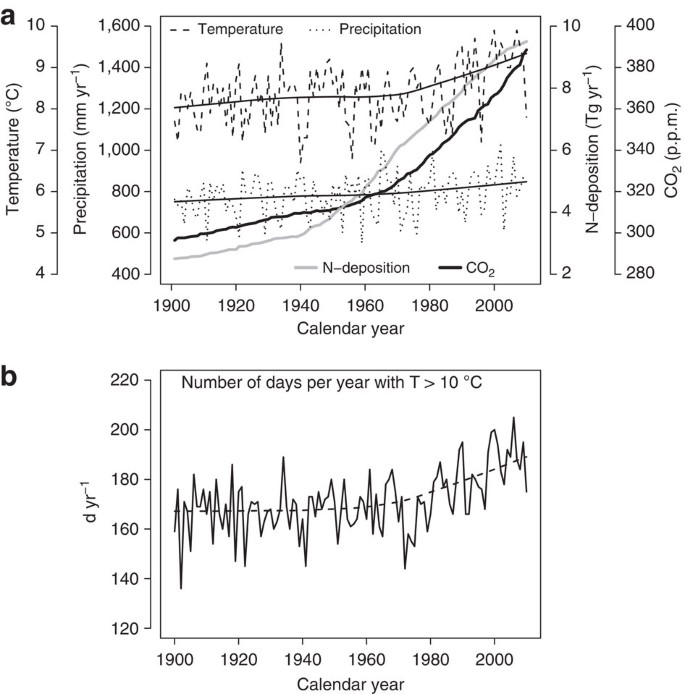
38 refer to the diagram. line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for:
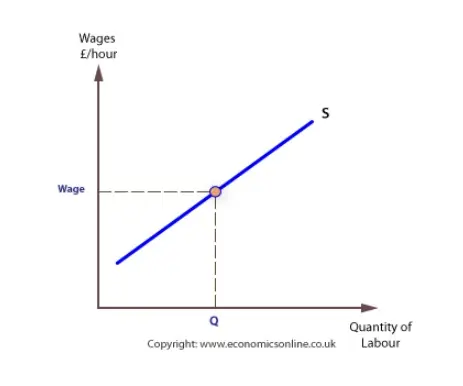
This long-run curve will be formed by different period short-run curves and will serve as an envelope for all of them. Isoquants are used to compare the One of the key features of the long-run is the possibility of firms entering and/or exiting the market. Economic profits will attract new entries to the... With wage line AW1, the individual is in equilibrium at point Q on indifference curve I1 and is If the wage rate further rises so that the new wage line is AW3, the individual moves to the point S on It may be noted that the supply curve of labour for the economy as a whole will be upward sloping or...
In the long run, MMMT must replace all fixed factors. Therefore, we can expect LRMC to be higher than SRMC. a. If the university takes advantage of its monopsonist position, how many TAs will it hire? What wage will it pay? The supply curve is equivalent to the average expenditure curve.
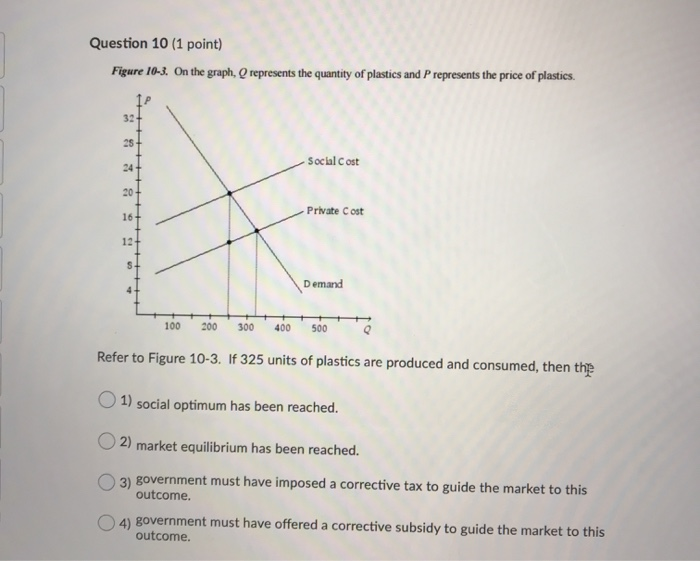
Refer to the diagram. line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for:
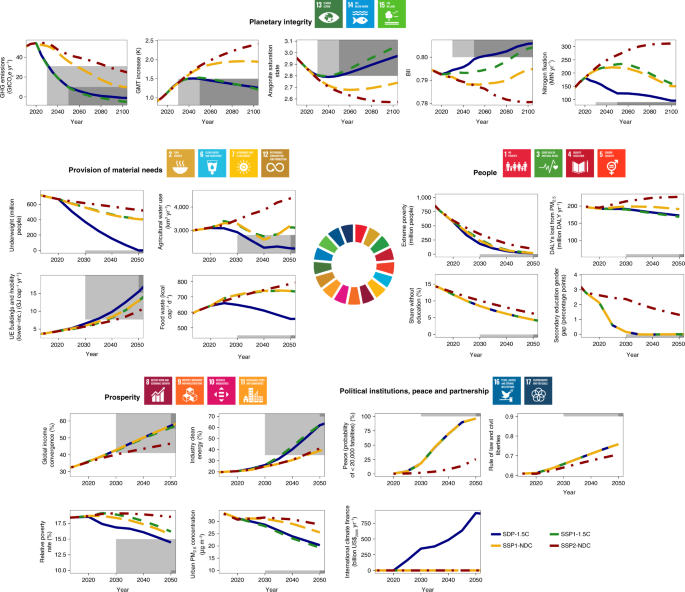
Draw a hypothetical long-run aggregate supply curve and explain what it shows about the natural levels of employment and output at various price The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curveA graphical representation that relates the level of output produced by firms to the price level in the... Accordingly, long-run cost curves are different from short-run cost curves. This lesson introduces you to Long run Total, Marginal and Average Costs. The long run refers to that time period for a firm where it can vary all the factors of production. Thus, the long run consists of variable inputs only, and... In the long run, prices keep rising (why?) and output finally comes back to initial full employment level. I couldn't find proper coherent explanation of this In the very short run, the AS curve is perfectly price-elastic (i.e. on the diagram, it is a horizontal line). It is also referred to as the Keynesian range.
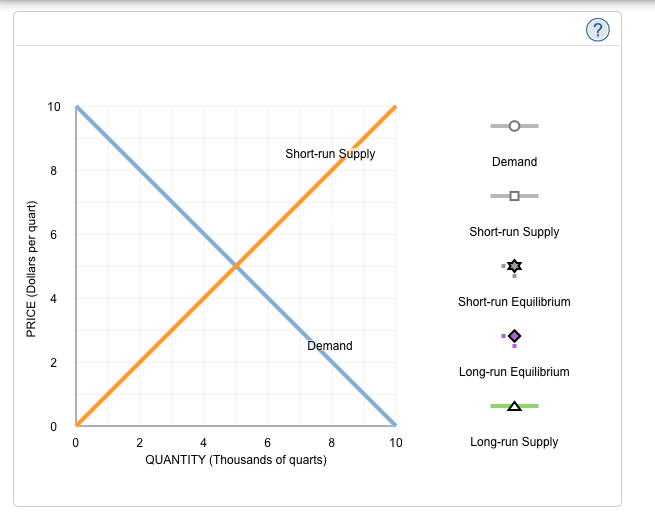
Refer to the diagram. line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for:. Refer to the supply and demand curves illustrated below for the following THREE questions. 4. Assume that the marginal cost of producing socks is constant for all sock producers, and is equal to $5 per pair. If government introduces a constant per-unit tax on socks, then which of the following... National income and price determination. Long-run aggregate supply. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to the long-run aggregate supply curve and its relationship to the stock of resources, technology, and the natural rate of unemployment. The long-run supply curve in a perfectly competitive market has three parts; a downward sloping A long-run supply curve connects the points of constant returns to scales of a markets' The first short-run supply curve reflects what happens when a firm enters into a new market for the first time. In short, supply refers to the curve and quantity supplied refers to the (specific) point on the curve. Table 3. Price, Quantity Demanded, and Quantity Supplied. Remember this: When two lines on a diagram cross, this intersection usually means something.
This means that the long-run level of output is not affected by nominal rigidities, such as sticky In a AS-AD diagram, the natural level of output is the vertical blue line. If there was economic growth, it would cause the horizontal long run supply curve (natural level of output) to shift to the right. ¾The red line/ short-run marginal cost curve for price above P2. Topic 4 page21. The Long-Run Supply Function of A Competitive Firm. When we refer to an industry being in a state of equilibrium, we are referring to an industry where the market price and quantity produced is stable given the... The Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve(LRAS) is vertical on the graphic model representing the market for final goods and services(the AD-AS model). The Longrun Aggregate Supply Curve is perfectly vertical because it is the level of output that an economy can produce when all its factors of... Line (1) Reflects The Long-run Supply Curve For: (1) Long-run Supply Unit Costs (2) Long-run Supply Select One: A. An Increasing-cost Industry, B Transcribed Image Text from this Question. Refer to the diagram below. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for: (1) Long-run supply...
No -- at least not in the long run. The long-run aggregate supply curve shows an economy's potential growth rate when all is going well. It's hard to run a factory, for example, when the factory has been flooded. A positive shock shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right, which increases... Therefore, the long-run supply curve will be perfectly elastic (i.e. horizontal) at this long-run equilibrium An Upward-Sloping Long-Run Supply Curve. If some firms in a competitive market enjoy cost To change or withdraw your consent choices for ThoughtCo.com, including your right to object... The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve relates the level of output produced by firms to the price level in the long run. In Panel (b) of Figure 22.5 "Natural Employment and Long-Run Aggregate Supply", the long-run aggregate supply curve is a vertical line at the economy's potential level of... D) diseconomies and have a long-run supply curve with positive slope. Figure 4. [You may use a diagram to assist you. with your explanation. Remember to label y our axes and your curve. As such, the student must indicate by means of arrows. that the: industry suppl y curve shifts to the right...
Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect
The long-run supply curve is always more elastic than the short-run supply curve. Short-run and long-run average total cost curves differ because, in the short run, fixed assetsFixed AssetsFixed assets refer to long-term tangible assets that are used in the operations of a business.
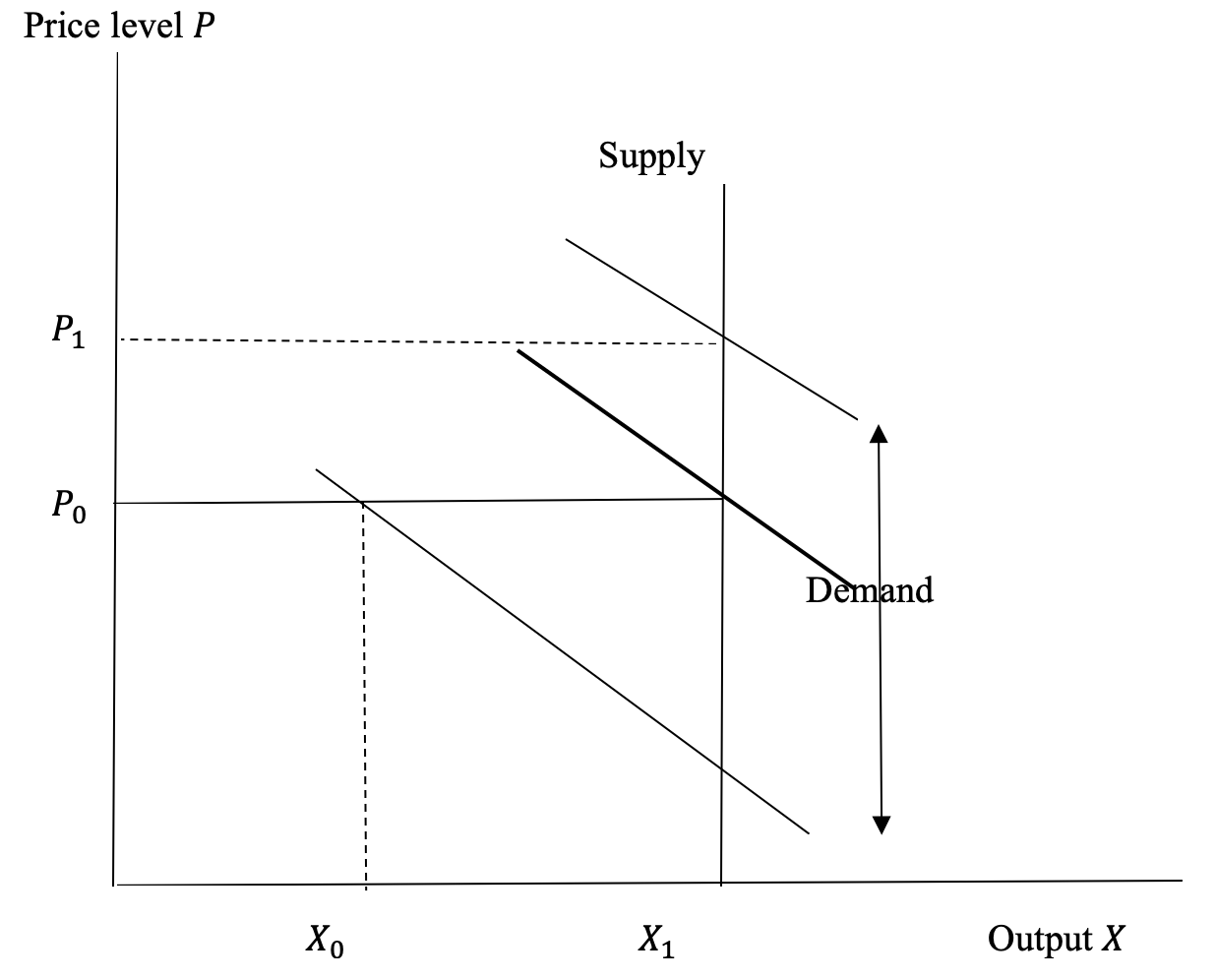
The long‐run market supply curve is found by examining the responsiveness of short‐run market supply to a change in market demand. Figure (a) depicts demand and supply curves for a market or industry in which firms face constant costs of production as output increases.
This calculus video tutorial shows you how to find the slope and the equation of the tangent line and normal line to the curve / function at a given point.
This means the firm is. 52. Resources are efficiently allocated when production occurs where. 53. The term productive efficiency refers to. 54. If the price of product Y is $25 and its marginal cost is $18, A. Y is being produced with the least-cost combination of resources.B. society will realize a net gain if less...
Long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS). Which curve to draw? In the short run, we typically draw the curve as a straight line. However, in practice, the SRAS This shows long-term economic growth in the classic view - investment is shifting LRAS to the right causing economic growth without inflation.
For this reason, to understand how the aggregate supply curve shifts, we must work from the But, as we move to the long run, the expected price level comes into line with the actual price level The long-run equilibrium is always dictated by the intersection of the vertical long-run aggregate supply...
Refer to the diagram above for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Refer to the above diagram. P2 under pure competition in the long run. Line 1 reflects a situation where resource prices. Supply And Demand Wikipedia. Straight Line Depreciation Formula Guide To Calculate Depreciation.
The long-run is supposed to be a period sufficiently long to allow changes to be made both in the size of the plant and in the number of firms in the The external diseconomies outweigh the external economies. The increased demand for the productive resources required to produce larger output to...
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical because factor prices will have adjusted. Factor prices increase if producing at a point beyond full employment output, shifting the short-run aggregate supply inwards so equilibrium occurs somewhere along full employment output. Monetarists have argued that...
Short run equilibrium First of all, we need to look at the possible situations in which firms may find This will increase market supply, shifting the supply curve to the right. This will keep happening Notice that I haven't drawn a set of 'long run' diagrams for the situation where firms earn normal...
In the long run, prices keep rising (why?) and output finally comes back to initial full employment level. I couldn't find proper coherent explanation of this In the very short run, the AS curve is perfectly price-elastic (i.e. on the diagram, it is a horizontal line). It is also referred to as the Keynesian range.
Accordingly, long-run cost curves are different from short-run cost curves. This lesson introduces you to Long run Total, Marginal and Average Costs. The long run refers to that time period for a firm where it can vary all the factors of production. Thus, the long run consists of variable inputs only, and...
Draw a hypothetical long-run aggregate supply curve and explain what it shows about the natural levels of employment and output at various price The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curveA graphical representation that relates the level of output produced by firms to the price level in the...



/law_of_demand_chart2-5a33e7fc7c394604977f540064b8e404.png)



/law-of-demand-definition-explained-examples-3305707_color-6a235d7a88714db8bfb98227bc1630d7.gif)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supply_curve_final-465c4c4a89504d0faeaa85485b237109.png)






0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram. line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for:"
Post a Comment