37 newton's third law diagram
Newton's Third Law is intimately related to two huge principles in physics: Conservation of Momentum and Motion of the Center of Mass. Part I. Newton's Third Law. Atomic Springs When you push against a wall, you feel a force in the opposite direction. Newton's Third Law states that When body A exerts a force F on body B, then body B exerts a force -F on body A In other words, for every force which acts between two bodies, there is an opposite and equal force. Viewgraphs Viewgraph 1 Viewgraph 2 Viewgraph 3 Viewgraph 4 Viewgraph 5 Viewgraph 6 Viewgraph 7 Viewgraph 8 Viewgraph 9
Equilibrium from Newton's first or second law is about the resultant force at a single object. $\dagger$ (Sorry that the finger doesn't actually touch the matchbox in the diagram. To get a better feel for Newton's third law, consider yourself in a deep swimming pool where your feet are off the bottom.
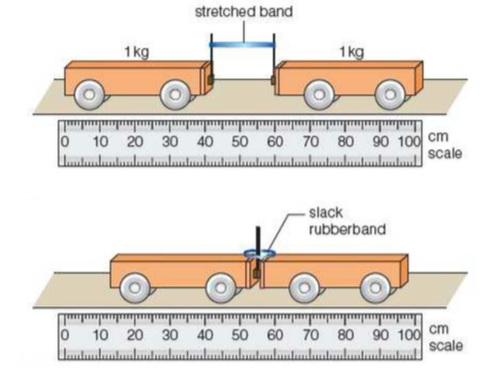
Newton's third law diagram
Newton's Third Law is confusing like that. Let's look at a force diagram again, err, free-body diagram. The chair in the above diagram pushes upwards with 588 N on a giant Tickle-me Elmo. What force does he exert on the chair?Since Newton's Third Law tells us the forces have to be equal... ⇒ Newton's third law pairs always have these properties: They act on two separate bodies. They are of the same type, for example two electrostatic forces or two ⇒ Alan is beginning to win - Alan, Ben and the rope are accelerating to the left at 2ms-2. ⇒ By drawing a free body diagram for Alan (mass 80kg)... Newton's third law tells us that for every action, there's an equal reaction going the opposite way. It's been reassuring us for 400 years, explaining why we Mathematicians draw bifurcation diagrams (the simplest look like pitchforks) to analyze how the states of a system respond to changes in their...
Newton's third law diagram. Isaac Newton's Second Law of Motion describes what happens when an external force acts upon a massive body at rest or in uniform linear motion. What happens to the body from which that external force is being applied? That situation is described by Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's third law explains the forces that enable people to walk. One force is from the foot that pushes the ground backwards. William disagrees with Eugene and says the diagram is an example of Newton's first law of motion. By referring to the free-body force diagram, state and explain who is... But, what does Newton's famous third law really mean, though? When I push on this desk with my finger right now, I'm applying a force to it. To find out, first let's draw a free body diagram for the lift, making UP the positive direction. The force of gravity on the lift is pulling it down, and it's equal to the... Some Examples of Newton's Third Law of Motion. Newton's First Law of Motion: According to this law, if no net force acts on a body, then the velocity of the body cannot change; that is, the body cannot accelerate.
Newton's Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object also exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. These two forces are referred to as a force pair. Force diagrams - Newton's 3rd Law | ExamSolutions. Смотреть позже. Поделиться. Introduction to Newton's third law of motion; part of an educational web site on astronomy, mechanics, and space. When a gun is fired, the force of the gas produced by burning gunpowder hurls out the bullet. By Newton's law, the gun itself recoils backwards. Newton's third law has practical uses in analyzing the origin of forces and understanding which forces are external to a system. Other examples of Newton's third law are easy to find. As a professor paces in front of a whiteboard, she exerts a force backward on the floor.
As stated by Newton: "To every action there is always opposed an equal reaction: Or the mutual attractions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary parts." Force pairs: Which force is stronger? Website (Physics Classroom): Newton's 3rd law. Drawing an interaction diagram provides a way to generate a representation of all the interacting objects in a process, connected as interacting pairs. Each interaction results in a force acting on each of the pairs of objects. Newton's third law provides a way to switch views between each member of a pair of linked objects. Suppose you've carefully worked out a force on one such object in an interacting pair. In classical mechanics, Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. The Third Law of Motion indicates that when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object These forces act on different objects and so they do not cancel each other. Thus, Newton's Third Law of Motion describes the relationship between the forces of interaction between two objects.
Newton's law of gravity states that the gravitational force between two bodies of masses is given by. From Newton's 2nd law, , which means if there is an acceleration there must be a force causing it, and for circular motion this force is known as the centripetal force.
Newton's third law establishes that the object you push applies an equal and opposite (BLANK) force against you. Momentum. A measure of how hard it is to stop a ...
Newton's third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Here in the present article, only the third law of motion is properly This law is stated as: "When one body exerts a force on another, the first body feels a force equivalent in the opposite direction of the force exerted."
State Newton's third law of motion. Identify the action and reaction forces in different situations. Newton's Third Law of Motion. Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first body experiences a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that it exerts.
Students are introduced to Newton's third law of motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. They practice identifying action-reaction force pairs for a variety of real-world examples, and draw and explain simplified free-body diagram vectors (arrows) of force...
Newton's Three Laws of Motion 3. To every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction. 2. The force exerted on a body equals the resulting change in the body's momentum divided by the time elapsed in the process. 1. Law of Inertia: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion...
Newton's first law is also known as the 'Law of Inertia.' Inertia is the inherent ability of a body because of which it has a tendency to maintain its original state and opposes any change in its state. Mathematically, the inertia of a body is directly proportional to its mass; therefore...
Newton's third law of motion posits that for every force applied, there is always an equal and opposite reaction. Or, if one body exerts a force on another, the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. It is not possible to exert a force on a body without a reaction...
Newton's third law: All forces in the universe occur in equal but oppositely directed pairs. There are no isolated forces; for every external force that acts on an object there is a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction which acts back on the object which exerted that external force.
Common Examples of Newton's third law of motion are: Pulling the cart by horse, Firing a bullet from a gun, Throwing a shell from a cannon, Rocket etc. Newton's 3rd law of motion states that action and reaction are always equal but opposite in direction.
Newton's Laws - Lesson 4 - Newton's Third Law of Motion. A gunpowder explosion creates hot gases that expand outward allowing the rifle to push forward on the bullet. Consistent with Newton's third law of motion, the bullet pushes backwards upon the rifle.
According to Newton's third law of motion, whenever two objects interact, they exert equal and opposite forces on each other. This is often worded as 'every action has an equal and opposite reaction'. However, it is important to remember that the two forces
Newton's three laws of motion describe movement for all things on Earth, and helped to define humankind's understanding of Newton's Second Law of Motion. The Second Law in Action. Free body diagrams are the means by which you can track the different forces acting on an object and...
Newton's third law tells us that for every action, there's an equal reaction going the opposite way. It's been reassuring us for 400 years, explaining why we Mathematicians draw bifurcation diagrams (the simplest look like pitchforks) to analyze how the states of a system respond to changes in their...
⇒ Newton's third law pairs always have these properties: They act on two separate bodies. They are of the same type, for example two electrostatic forces or two ⇒ Alan is beginning to win - Alan, Ben and the rope are accelerating to the left at 2ms-2. ⇒ By drawing a free body diagram for Alan (mass 80kg)...
Newton's Third Law is confusing like that. Let's look at a force diagram again, err, free-body diagram. The chair in the above diagram pushes upwards with 588 N on a giant Tickle-me Elmo. What force does he exert on the chair?Since Newton's Third Law tells us the forces have to be equal...
0 Response to "37 newton's third law diagram"
Post a Comment