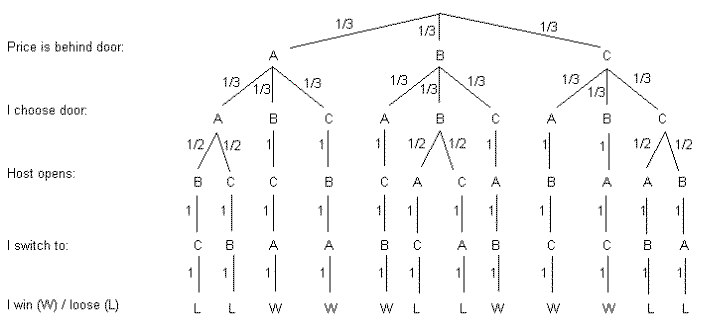
7 monty hall tree diagram
Monty Hall. Simulation Page . Solution To Monty Hall Problem. ... The probabilities can best be calculated with a tree diagram. Game Rules: 1. Pick a door. The diagram below shows the chances that you will pick the door with the car or either of the goats, Goat A or Goat B. 2. The host then reveals a goat behind one of the remaining doors. In this video I have drawn the tree diagram for Monty Hall problem. In this video I have drawn the tree diagram for Monty Hall problem.
MIT 6.042J Mathematics for Computer Science, Spring 2015View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/6-042JS15Instructor: Albert R. MeyerLicense: Creative Co...
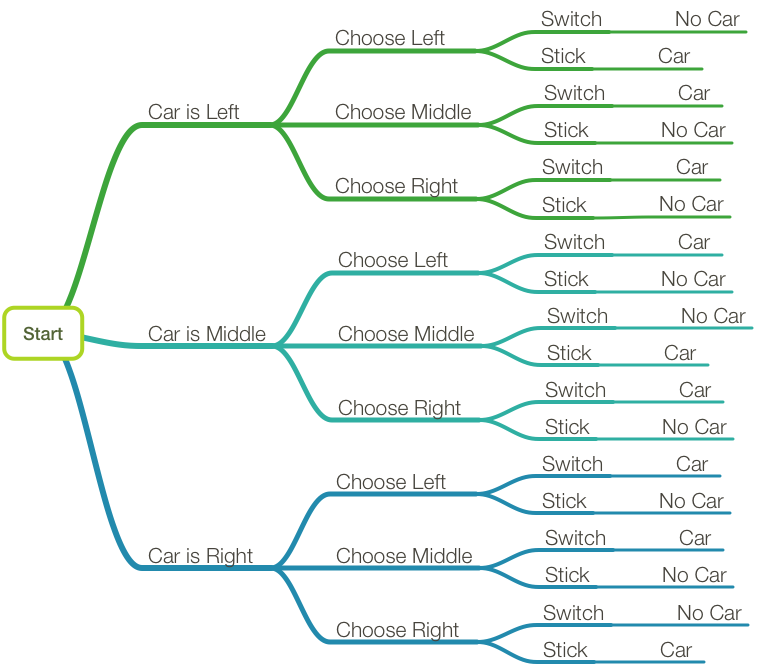
Monty hall tree diagram
6.C;C;B/ Figure 14.5 The tree diagram for the Monty Hall Problem where edge weights denote the probability of that branch being taken given that we are at the parent of that branch. For example, if the car is behind door A, then there is a 1/3 chance that the player's initial selection is door B. "mcs-ftl" — 2010/9/8 — 0:40 — page ... This is the famous Monty Hall problem. By working through Bayes Theorem, we can calculate the actual odds of winning the car if we stick with door A, or switch to door C. Bayes Theorem. Bayes Theorem describes probabilities related to an event, given another event occurs. S o, here's my stab at trying to make the solution visual by adding up the possibilities (bottom-layer or "leaf nodes") in a decision tree. Start. Monty Hall (emcee for the TV show "Let ...
Monty hall tree diagram. a tree diagram or an area model here, but you may need to draw separate diagrams for ... known as "The Monty Hall Problem," named for the game show host of Let's Make a Deal. You will have 3 tasks. Task 1: Find the experimental probability of winning when you stick with the first Using a Tree Diagram: 4.2.3: Probability Models: 4.2.4: ... 1-111 Venn Diagram A: Student eTool (Desmos) ... 6-79 Monty Hall Technology Tool (opt.) Consider the Monty Hall problem. Let’s label the door with the car behind it a and the other two doors b and c. In the game the contestant chooses a door and then Monty chooses a door, so we can label each outcome as ‘contestant followed by Monty’, e.g ab means the contestant chose a and Monty chose b. Monty Hall Problem explained with a tree diagram. Original tree diagram obtained from http://www.cut-the-knot.org/peter.shtmlAs an accompaniment to this vid...
Figure 5: Tree diagram for the Monty Hall Problem. Let C denote the event that the car is behind Door #2; the a priori probability of C is P(C) = 1/3. Let D denote the event that Monty opens Door #3; according to Figure 5 . The Monty Hall problem is a counter-intuitive statistics puzzle:. There are 3 doors, behind which are two goats and a car. You pick a door (call it door A). You're hoping for the car of course. Monty Hall, the game show host, examines the other doors (B & C) and opens one with a goat. The Monty Hall problem is based on apparent paradox that is commonly misun-derstood, even by mathematicians. In this paper we define the Monty Hall problem and use a computer simulation to shed light on it. We then provide a mathematical explanation that fits the experimental results. 1. The Monty Hall problem is a famous, seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes' theorem. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldn't. In the problem, you are on a game show, being asked to choose between three doors. Behind each door, there is either a car or a goat. You choose a door. The host, Monty Hall ...
1 Monty Hall In the September 9, 1990 issue of Parade magazine, the columnist Marilyn vos Savant ... A tree diagram is a graphical tool that can help us work through the four-step ap-proach when the number of outcomes is not too large or the problem is nicely structured. Figure 1 — Tree diagram showing the probabilities associated with the Monty Hall Problem (Diagram by the Author) When you are asked to make your first choice, there is an equal probability that the car is behind any one of the three doors. So you have a 1/3 chance of guessing it correctly. This implies that 2/3 of the times your guesses are ... The Monty Hall problem ... Conditional probability tree diagram example (Opens a modal) Tree diagrams and conditional probability Sep 13, 2021 · 2.1 Basic probability theory. In practice, causal inference is based on statistical models that range from the very simple to extremely advanced. And building such models requires some rudimentary knowledge of probability theory, so let’s begin with some definitions.
(A) Provide a general tree diagram explanation that shows the probability of winning the game if one chooses to adopt the strategy of changing doors after Monty Hall opens a non-winning door. The first three branches of your tree diagram would have probability 1/3, since there are 3 doors and any one of them could contain the winning prize.
Figure 17.1 The tree diagram for computing the probability that the local team wins two out of three games given that they won the first game. Step 1: Find the Sample Space Each internal vertex in the tree diagram has two children, one corresponding to a win for the local team (labeled W) and one corresponding to a loss (labeled L).
Monty Hall Problem: Tree Diagram. ... I am taking the liberty of forwarding the following tree-diagram, which I constructed in December 1990 and is based on the assumptions made by Marilyn vos Savant. Namely: 1. The initial placement of the auto (car) is done at random. 2. The contestant chooses a door at random.
Probability Tree Diagram of Monty Hall Problem. As we can see from the diagram, the only place where there is a random event involved is during the initial pick, the elimination process is ...
Take A Sneak Peak At The Movies Coming Out This Week (8/12) Why Your New Year’s Resolution Should Be To Go To The Movies More; Minneapolis-St. Paul Movie Theaters: A Complete Guide
4.1 Tree Diagrams A (probability) tree diagram provides a clear way to map out uncertainties for situations where there is a process that unfolds over several points in time and is surrounded by uncertainties. 4.1.1 The Monty Hall Problem Rarely has a probability problem aroused emotions as much as the Monty Hall problem.
Figure 16.1 The first level in a tree diagram for the Monty Hall Problem. The branches correspond to the door behind which the car is located. 3. The door that the host opens to reveal a goat. Every possible combination of these randomly-determined quantities is called an outcome. The set of all possible outcomes is called the sample space for ...
Simple Monty Hall: Choose one of three doors to experimentally determine the odds of winning the grand prize behind one of the doors, as in the TV program "Let's Make a Deal." Parameters: Staying or switching between the two remaining doors.
The lungs are not capable of inflating themselves, and will expand only when there is an increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity. In humans, as in the other mammals, this is achieved primarily through the contraction of the diaphragm, but also by the contraction of the intercostal muscles which pull the rib cage upwards and outwards as shown in the diagrams on the right.
S o, here's my stab at trying to make the solution visual by adding up the possibilities (bottom-layer or "leaf nodes") in a decision tree. Start. Monty Hall (emcee for the TV show "Let ...
This is the famous Monty Hall problem. By working through Bayes Theorem, we can calculate the actual odds of winning the car if we stick with door A, or switch to door C. Bayes Theorem. Bayes Theorem describes probabilities related to an event, given another event occurs.
6.C;C;B/ Figure 14.5 The tree diagram for the Monty Hall Problem where edge weights denote the probability of that branch being taken given that we are at the parent of that branch. For example, if the car is behind door A, then there is a 1/3 chance that the player's initial selection is door B. "mcs-ftl" — 2010/9/8 — 0:40 — page ...




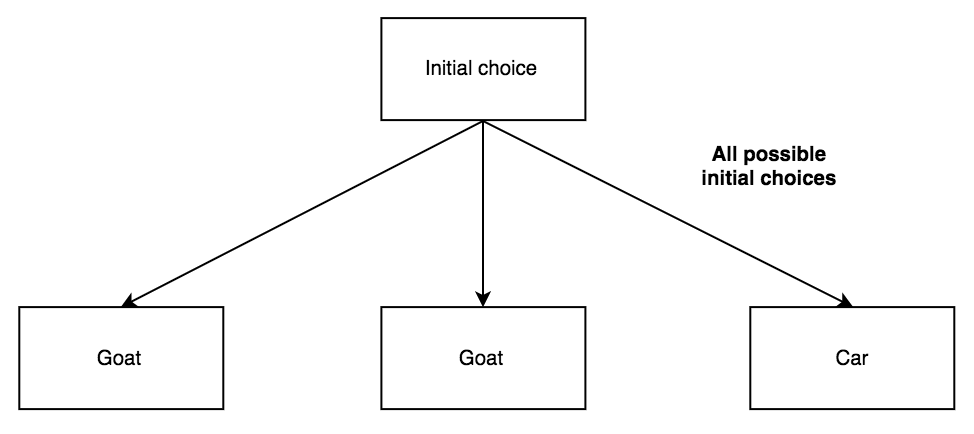






















0 Response to "7 monty hall tree diagram"
Post a Comment