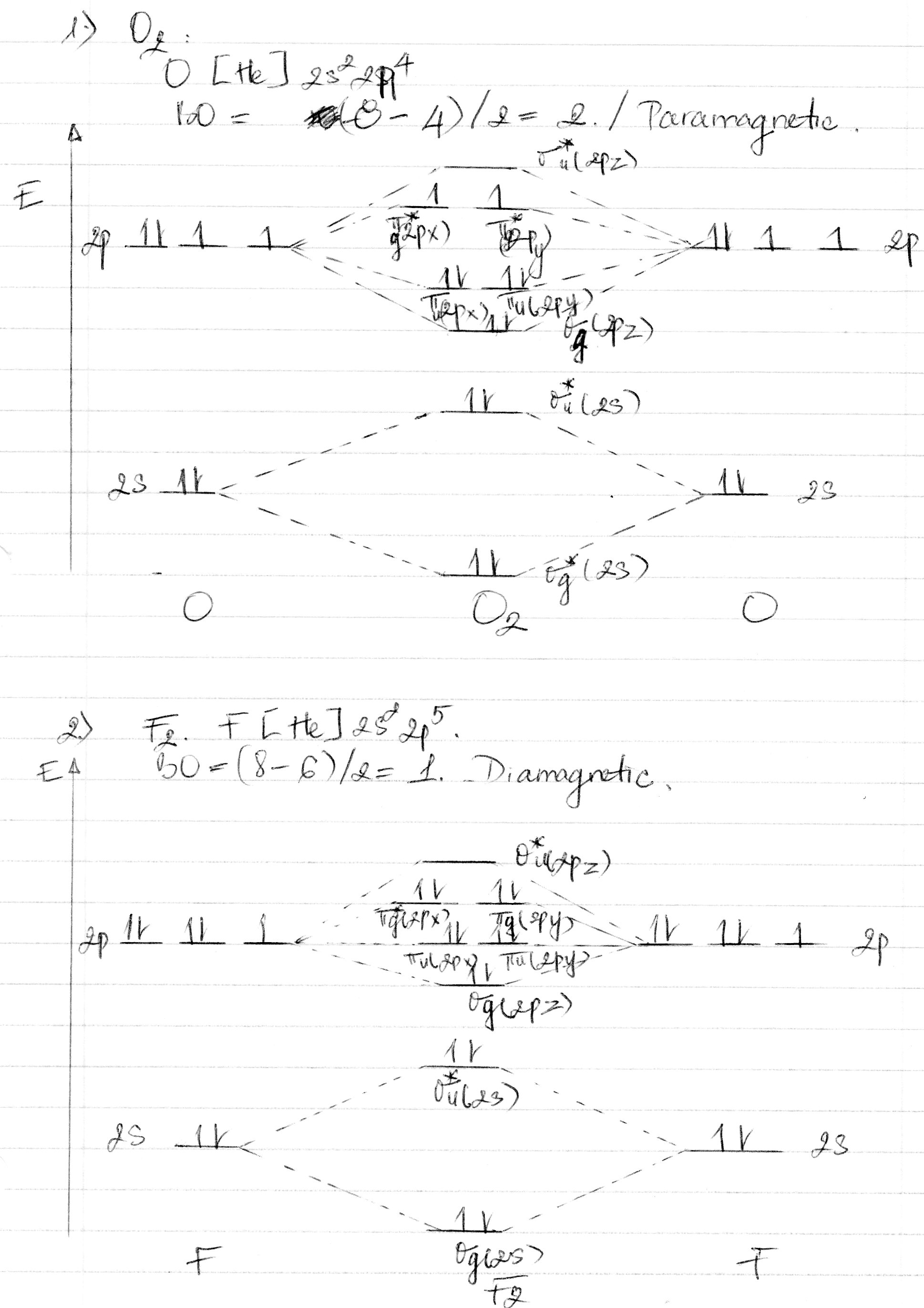
40 f2 2+ molecular orbital diagram
F2 2+ The molecular orbital diagram below may be used for the following problem(s). For oxygen and fluorine, the σ2p orbital should be lower in energy than the π2p. However, the diagram will still yield correct bond order and magnetic behavior for these molecules. 2. 21/11/2018 · The bond order is Figure The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give …
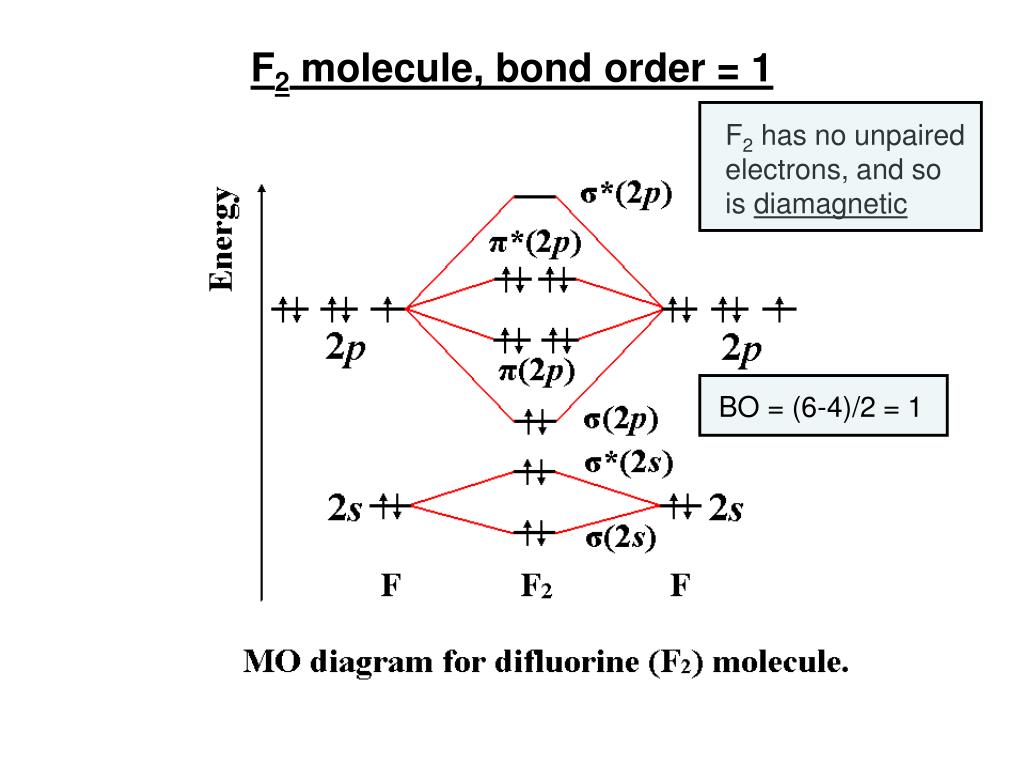
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...

F2 2+ molecular orbital diagram
A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in … Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2. A draw the molecular orbital diagram. F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Written By Unknown Friday, September 6, 2019 Add Comment A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular.
F2 2+ molecular orbital diagram. 31/12/2021 · F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals. Let us have a look at the MO diagram for … Molecular Orbital Theory ODU April 10th, 2019 - molecular orbital energy level diagram for the NO molecule We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2 The bond order is 2 5 Figure 9 42 The molecular orbital energy level diagram for both the NO and CN ions Figure 9 43 A partial molecular orbital energy level diagram for the HF orbital diagram for the … 4 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Use the molecular orbital energy level diagram to show that N2 would be expected to have a triple bond, F2 , a single bond and Ne2 , no bond.
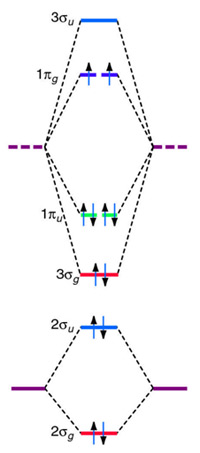
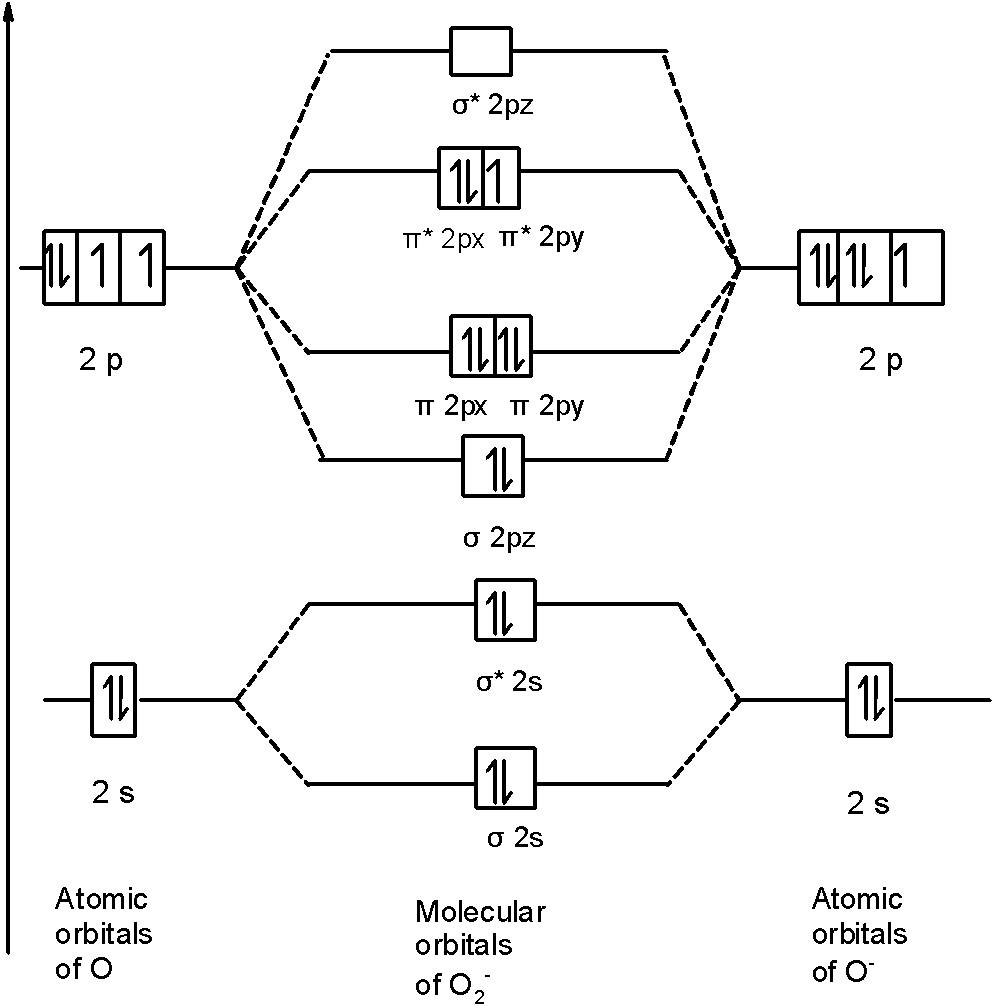
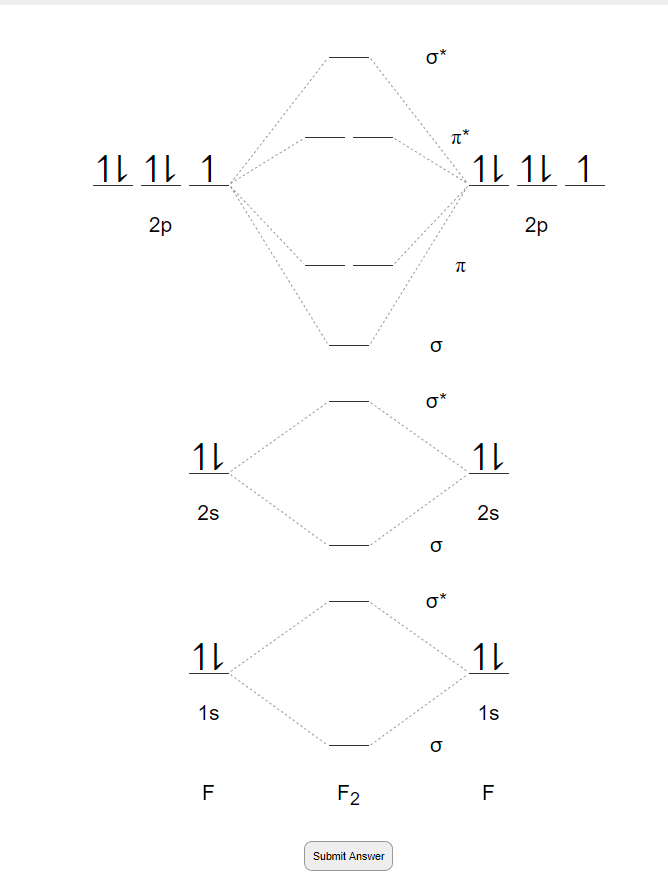
of B2. Figure 9.39: The molecular orbital energy-level diagrams, bond orders, bond energies, and bond lengths for the diatomic molecules B 2 through F2.Note that for O2 and F2 the σ2p orbital is lower in energy than the π2p orbitals. 3.O2 has 12 valence electrons. Its MO configuration is: O2 = KK(σ2s)2(σ2s*)2(σ2p)2(π2p)2(π2p)2(π2p*)(π2p*) diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO 2 in Figure 5.25. The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. * F2+ has a stronger bond than F2 *The olecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2. Sigma Bonds vs. Pi Bonds. Sigma bond allows free rotation about the bond axis. Pi bonds restrict rotation about the bond axis . The valence molecular orbital diagram for Be2+ is shown, which of the following statements correctly interpret the diagram? *Be2+ is more likley to exist than Be2-be2+ has a … The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is. To find the bond order, add the 15 electrons in the molecular orbitals (the blue-colored energy levels in the diagram) one at a time until you have used them up. They completely fill all the orbitals except the highest-energy antibonding sigma 2p orbital. Thus, there will be 8 bonding …
Mar 12, 2017 — If we have 2 N atoms then we have 14 electrons. What you do next is draw a picture like the one from google. You simply fill up the bonding orbitals first and ...6 answers · 60 votes: Here is the solution, %3E * For O2 molecule, %3E * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.What is an (F2-) bond order? - Quora5 answersFeb 9, 2016Why is the molecular orbital diagram for O₂ ...2 answersAug 1, 2019More results from www.quora.com
Question: Draw a molecular orbital diagram for F2^2- . Calculate the bond order and magnetic behavior. This problem has been solved! See the answer ...
1 answerThe F₂ molecule is obtained by the linear combination of two F atomic orbitals. When two electrons are supplemented to the antibonding orbitals of the ...
01/01/2022 · The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be: The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of ethane, we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule.
Answer (1 of 5): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To …
For example, an ns/ns overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this: and an np/np overlap for O2 and F2 gives: So, the full MO diagram is: Thus, the valence electron configuration is: (σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π* 2px)2(π* 2py)2. Answer link.
5 2 10 10 C C 2 2 20 20 C C FIG. 2. The 2σg (left panel) and 2σu (right panel) molecular orbital s of C2 The third (in terms of increasing energy) orbital of σg symmetry is shown below. This is also a linear combination of the 2s and 2pz orbital s. There is a substantial buildup of The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added.
01/11/2021 · When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals. Here, N a =10, N b =8 now put it into the …
We next look at some specific examples of MO diagrams and bond orders. Bonding in Diatomic Molecules. A dihydrogen molecule (H2) forms from two hydrogen atoms.
Molecular orbital diagram of b2. The next two would fill the 1 sigma e antibonding orbital. I can draw be2 but not this. B 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. The electronic configuration of b atom z 5 is. It is diamagnetic due to the absence of any unpaired electron.
Hey there! We have to draw a molecular orbital diagram for the F 2-ion, determine bond order and decide whether the molecule is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.. For this, we need to do the following steps: Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule.
From Molecular Orbital Diagram, which is most stable? ... C. O2 2+ D. F2 E. F2 2+ C. O2 2+ Choose the compound below that should have the highest melting point according to the ionic bonding model. A. CaS B. NaCl C. RbI D. MgO E. AlN. E. AlN. From Molecular Orbital Diagram, which is most stable? A. C2 2-B. B2
The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
After reading the theory part draw the MO diagrams for the ... H2, B2, C2, N2, O2, Ne2, F2 ... 2. Number of electrons in antibonding orbitals.13 pages
N2 molecule is consists of 2 N-atoms, the total number of electrons in N2 molecule is 14. In N2molecule's energy level diagram can be drawn as:⬆️⬆️⬆️. On the similar basis, try to draw the molecular orbital diagram of F2 molecule yourself. The atomic number of F is 9 and its electronic configuration is 1s2 2s22px22py22pz1.
Molecular orbital diagram for c2. This video shows the mo diagrams of the c2 n2 o2 and f2 molecules. Molecular orbitals are formed combining similar atomic orbitals. Just because some chemical species shows integral value of bond order doesnt mean that it should exist. Molecular orbital diagram for the molecule oxygen o2.
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2
17/10/2018 · Molecular orbital diagram of H 2 (Hydrogen molecule). Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole …
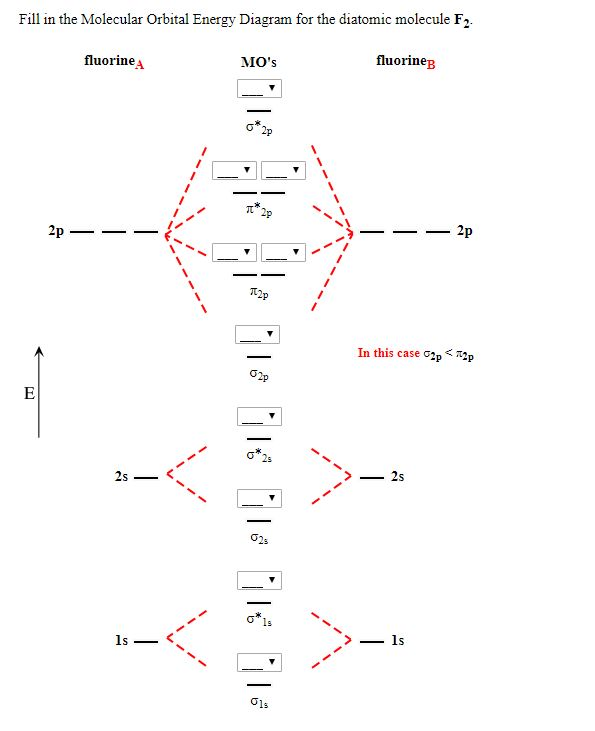
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Jestion 11 (20 pts.) . Complete the molecular orbital diagram for F2. Do not include the inner shell electrons. (5 pts.) b. Count the number of valence electrons in F2, (2 pts.) c.
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
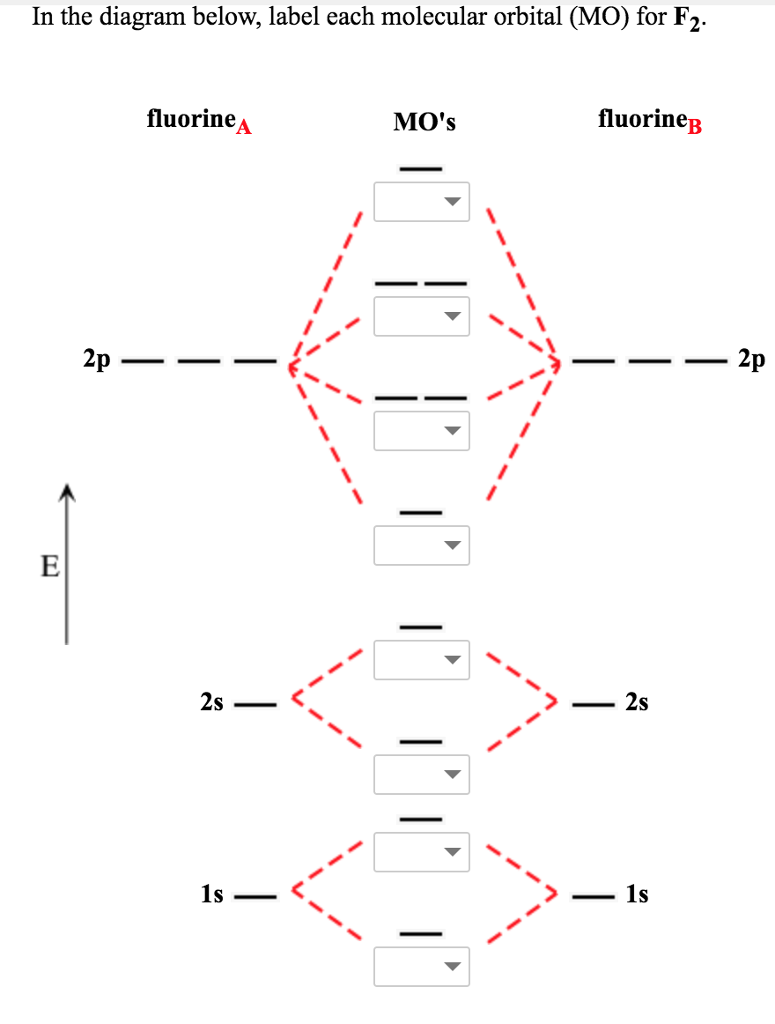
The molecular orbital diagrams for molecules and ions are drawn from the order of increasing energies shown in the molecular orbital configuration. Always remember that the number of molecular orbitals formed must be equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were combined in the molecule.
Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Question: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding.The ...
F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Written By Unknown Friday, September 6, 2019 Add Comment A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular.
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of. C would this ion exist. To further demonstrate the consistency of the lewis structures with mo. For the ion f2. A draw the molecular orbital diagram.
A) The total number of molecular orbitals formed doesn't always equal the number of atomic orbitals in the set. B) A bond order of 0 represents a stable chemical bond. C) When two atomic orbitals come together to form two molecular orbitals, one molecular orbital will be lower in energy than the two separate atomic orbitals and one molecular orbital will be higher in …






















0 Response to "40 f2 2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment