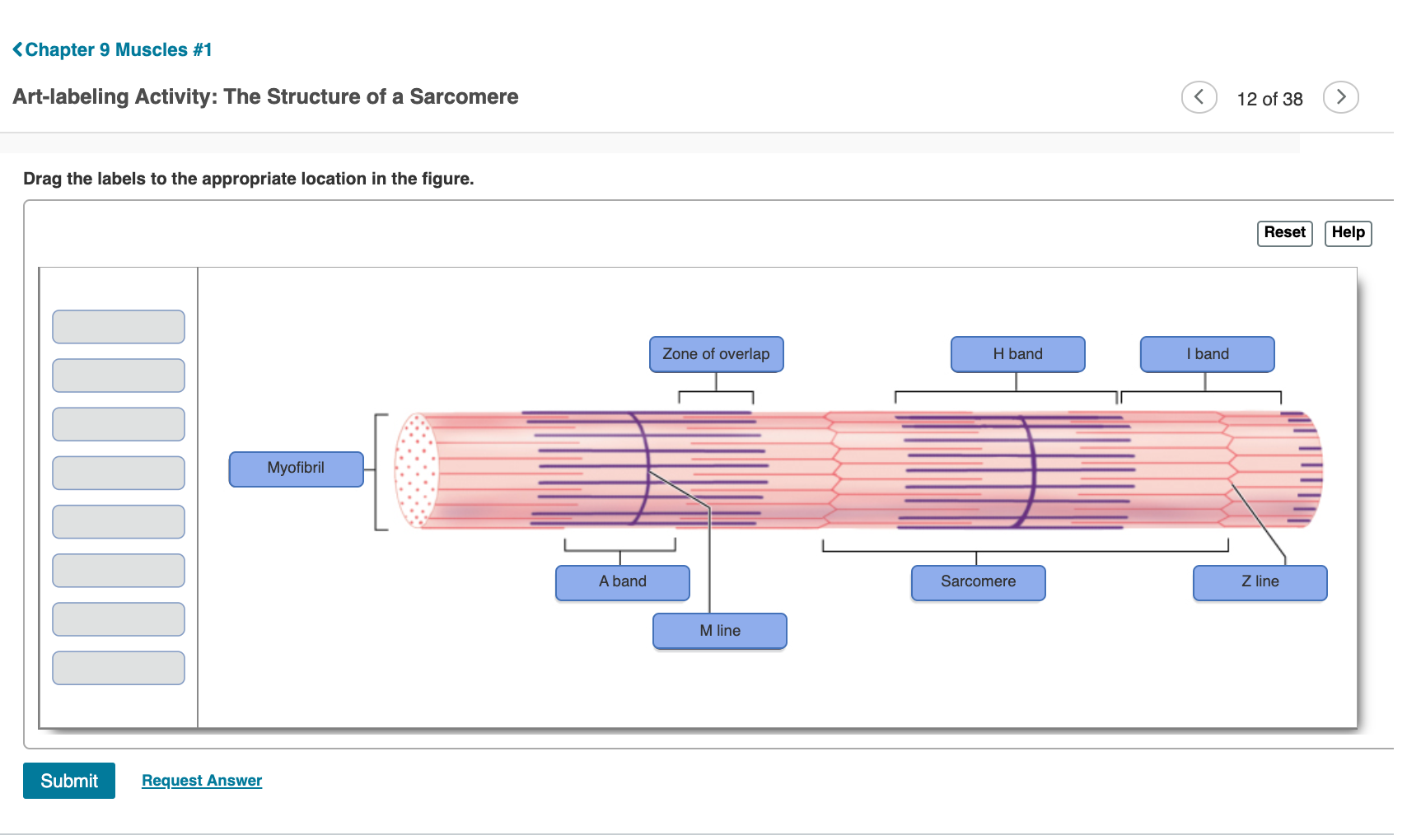
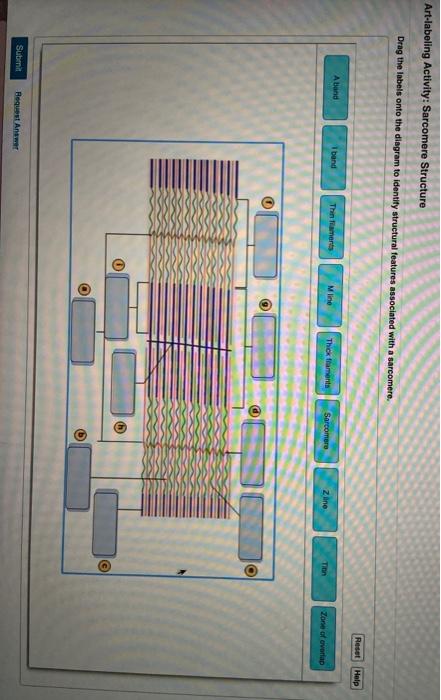
39 identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.
The diagrams in Model 3 are cross sections of a sarcomere that show the filaments at various locations within a sarcomere. thick thin Fig. A 10. Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A, B, and C above. 11. In the diagram below, draw three vertical lines showing the locations within a 20. Label the diagram to the right with: fascicle, tendon, muscle fiber, endomysium, epimysium, perimysium 21. Place the following words in order from largest to smallest: fascicle, myofilament, myofibril, myofiber (muscle cell), sarcomere fascicle myofibril = bundle of myofilaments
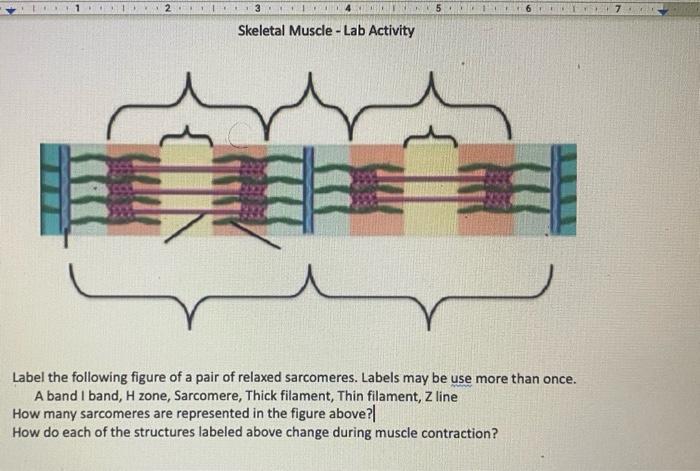
The drawing and photomicrograph below show a relaxed Sarcomere. Using the terms from the key identify each structure indi Cated by a leader line or bracket. The events that occur at a neuromuscular junction are depicted below. Identity every structure provided with a leader line. Necrosis is death of tissues in the body. Considering the.

Identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.
Jan 23, 2019 · A sarcomere is the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells which. Sarcomeres are composed of thick filaments and thin filaments. The thin filaments Look at the diagram above and realize what happens as a muscle contracts. A Fig. B Fig. C QUESTIONS: 11. Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A,B, and C above. 12. There are three sarcomeres shown in the diagram below. Sarcomere 1 Sarcomere 2 Sarcomere 3 a) In Sarcomere 1, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section indicated by Figure A in Model 3. 3) Identify the specific structure indicated by Label G. A) Muscle fascicle B) Triad C) Myofibril D) Sarcomere E) Myofilament
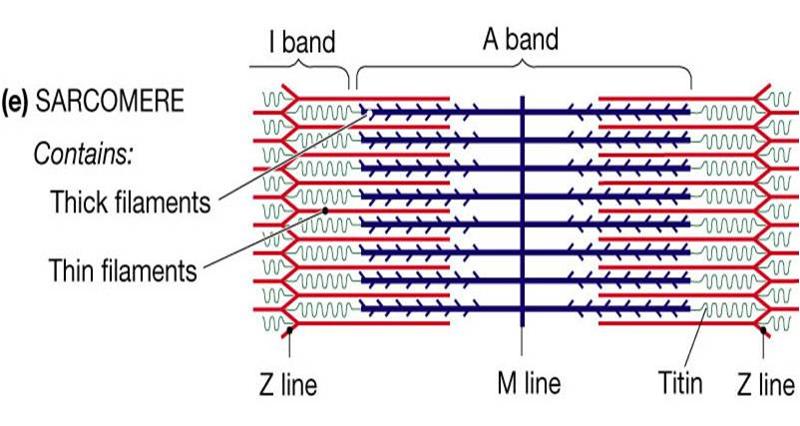
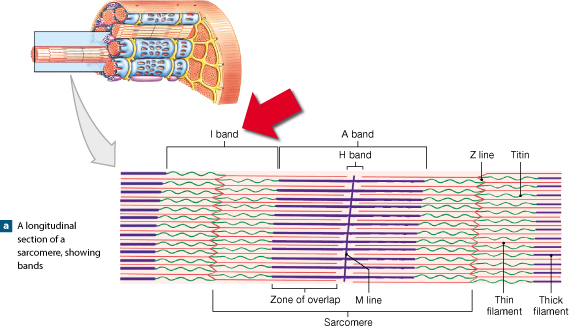
Identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above.. Sarcomere H zone Thin (actin) filament Thick (myosin) filament Z disc Z disc M line (c) Small part of one myofibril enlarged to show the myofilaments responsible for the banding pattern. Each sarcomere extends from one Z disc to the next. Recognize a sarcomere as a complete contractile unit. Relate the structure of the sarcomere to the distribution of actin and myosin within the myofibril. Describe the sliding-filament hypothesis of muscle contraction. Identify the role of calcium ions (Ca2+), the troponin-tropomyosin complex, and ATP. Recognize that The given below diagram represents the gastric glands. Label it from A to D and choose the correct option accordingly. (a) ... Identify A, B, C and D in the given diagram and choose the correct combination. (a) A-Thyroid, B-Trachea, C-Vocal cord, D-Parathyroid glands ... (b) sarcomere (c) myofibrils similar in length and diameter (d) All of the ... 11. There are three sarcomeres shown in the diagram below. Sarcomere 1 Sarcomere 2 Sarcomere 3 a) In Sarcomere 1, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section indicated by Figure A in Model 3. Draw a vertical line and label it A. b) In Sarcomere 2, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section
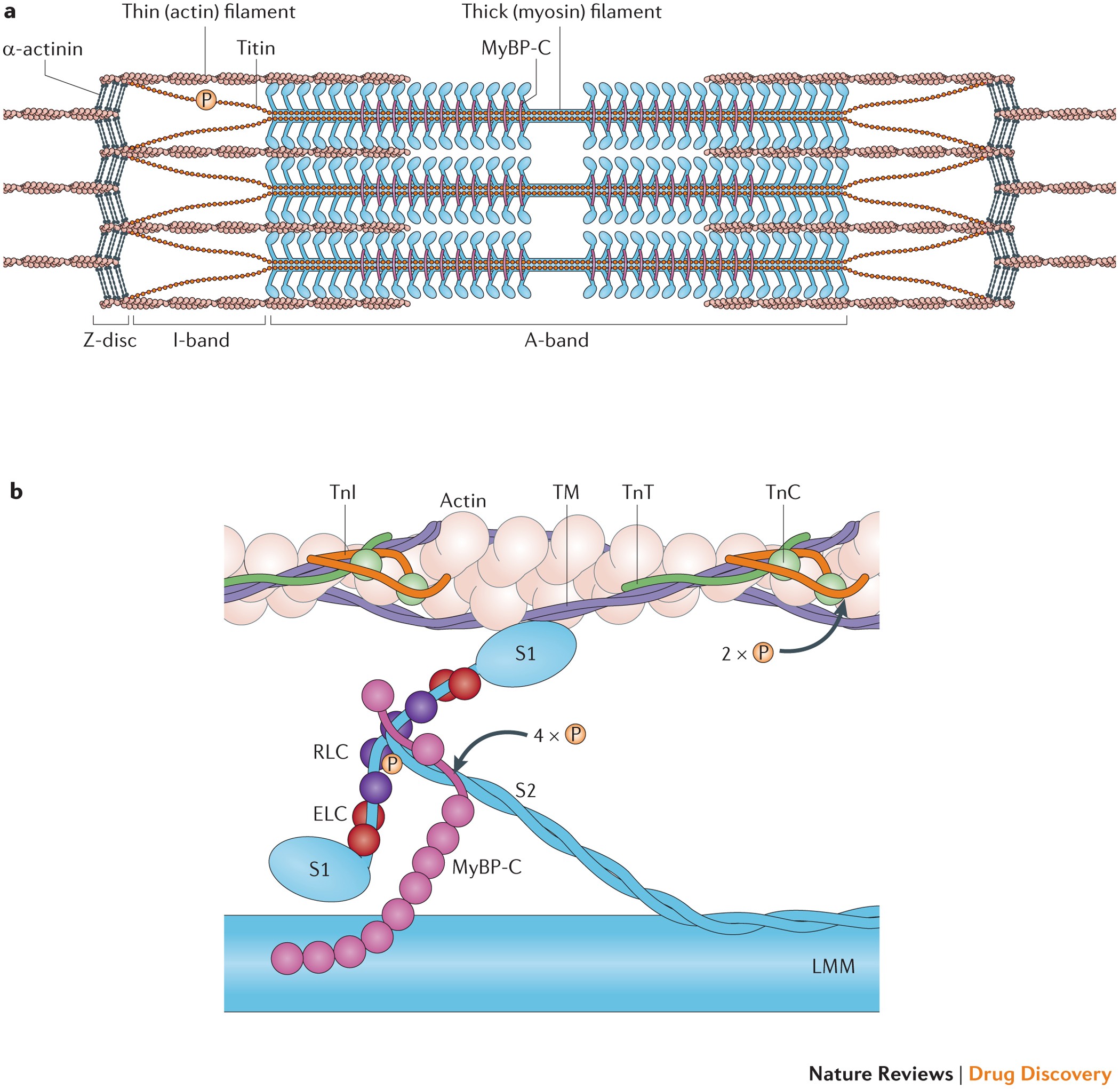
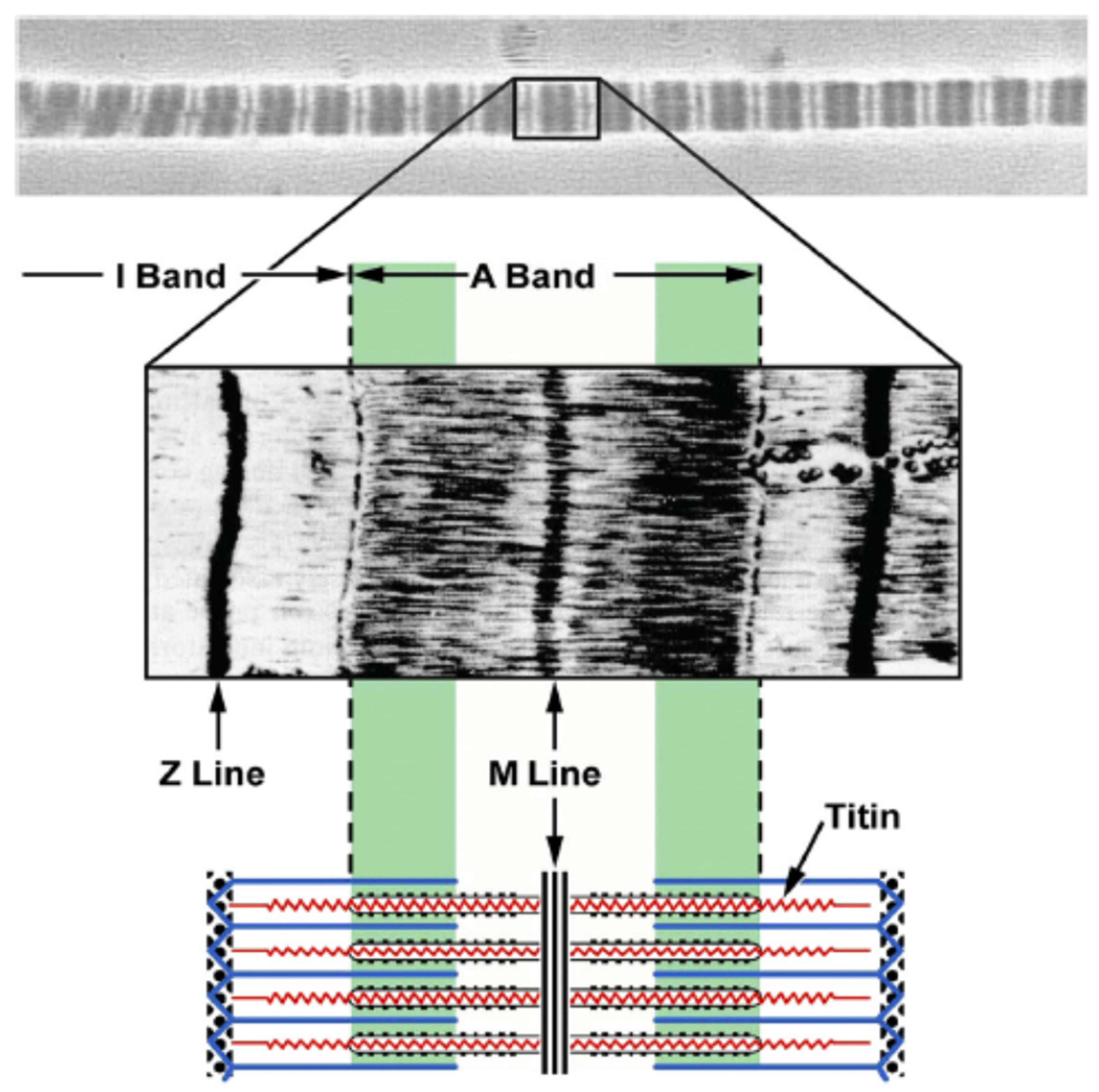
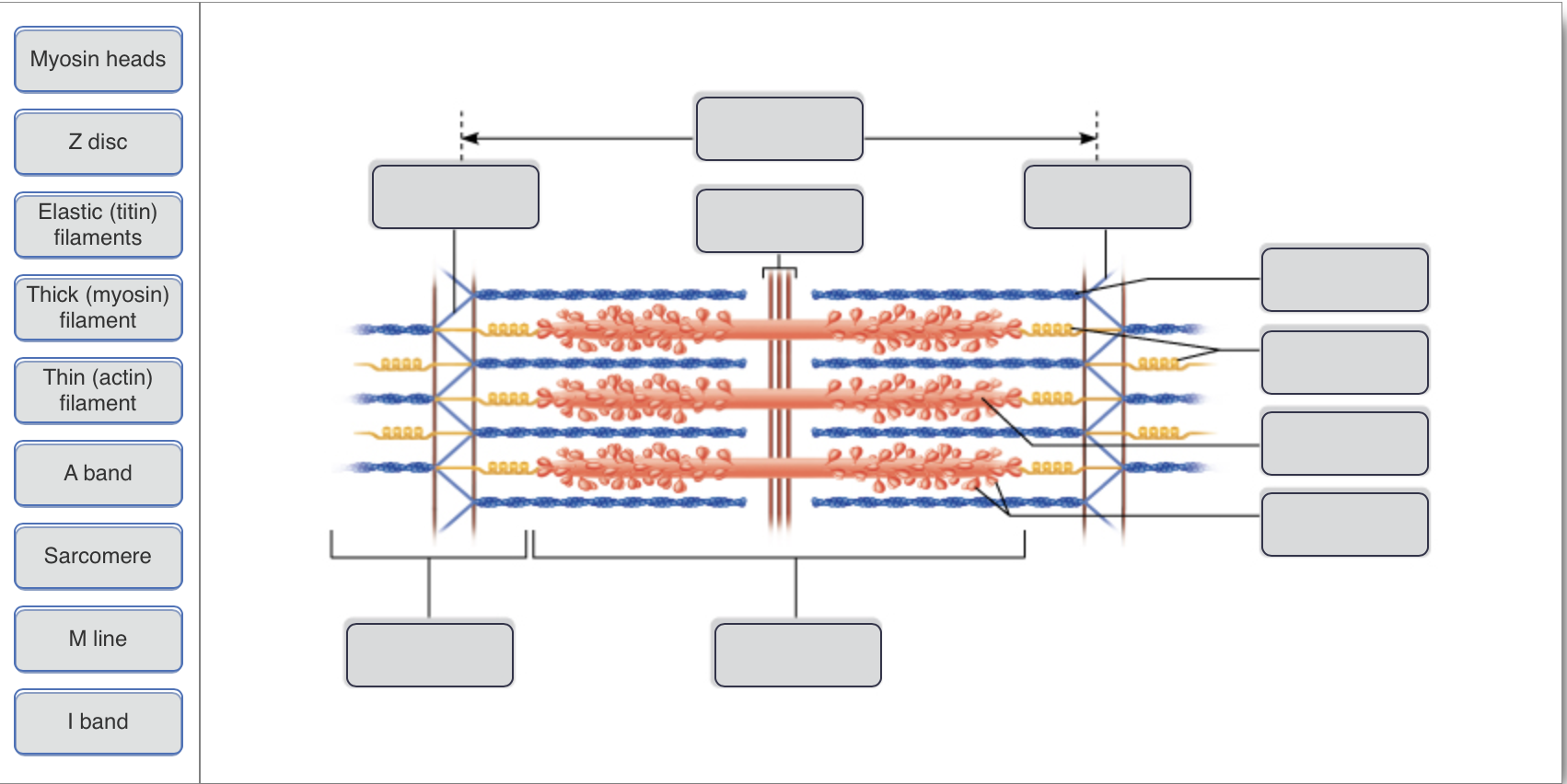
Identify the structures labeled A, B, and C in the diagram of a sarcomere above. A is a "blue" filament, attached to the Z line at the ends of a sarcomere. B is a "red" filament, crossing the M band. C is a "grey" filament attached to both B and the Z line. for the structures listed below. Use them to color the coding circles and corre- sponding structures on Figure 6—3. Then bracket and label an A band, an I band, and a sarcomere. When you have finished, draw a contracted sarcomere in the space beneath the figure and label the same structures, as well as the light and dark bands. Actin filaments A sarcomere is the functional unit of striated muscle. This means it is the most basic unit that makes up our skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type that initiates all of our voluntary movement. Herein lies the sarcomere's main purpose. Sarcomeres are able to initiate large, sweeping movement by contracting in unison. In the diagram below draw three vertical lines showing the locations within a sarcomere of the cross sections indicated by figures a b and c. A b and c above. The diagrams in model 3 are cross sections of a sarcomere that show the filaments at various locations within a sarcomere. Play this quiz called label the sarcomere and show off your skills.
Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1.) The diagram above shows the arrangement of the two protein filaments that make up a sarcomere. Name and label them on the diagram. 2.) On the diagram below label: each sarcomere, all I bands, all A bands, all H zones, all M lines and all Z lines. 3.) Explain each region of a sarcomere. locations within a sarcomere. QUESTIONS: 11. Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A, B, and C above. 12. There are three sarcomeres shown in the diagram below. Sarcomere 1 Sarcomere 2 Sarcomere 3 a) In Sarcomere 1, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section indicated by Figure A in Model 3. A, B, and C above. 2. In the diagram below, draw three vertical lines showing the locations within a sarcomere of the cross sections indicated by Figures A, B, and C. Label each of the lines. A B C thin thin thick thick A B C A Labeled Diagram of the Knee With an Insight into Its Working. To understand one of the most complex joints of our body i.e. the knee joint, you need a perfectly labeled diagram of the knee. This will help you to understand the mechanism as well as the working.
Sarcomere Definition. The sarcolemma or sarcomere is an excitable membrane cell and shares many properties with the cell membrane of the neuronal structure. The function of sarcolemma is to connect the basement membrane which wrapped all connective tissues. The sarcolemma also has an extracellular matrix containing various polysaccharides ...
The students will identify the anatomical structures of a sarcomere 2. The students will explain length relationships between relaxed and contracted sarcomeres. 3. The students will describe the overlapping of myofilaments. Model 1 - Anatomy of a Sarcomere Examine the above model, then answer the following questions: 1. Label the thick ...
11. Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A, B, and C above. 12. There are three sarcomeres shown in the diagram below. a) In Sarcomere 1, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section indicated by Figure A in Model 3. Draw a vertical line and label it A. b) In Sarcomere 2, identify the location within the sarcomere of ...
1) Muscle tissue, one of the four basic tissue groups, consists chiefly of cells that are highly specialized for. A) contraction. B) cushioning. C) conduction. D) peristalsis. E) secretion. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. A) contraction.
The diagrams in Model 3 are cross sections of a sarcomere that show the filaments at various locations within a sarcomere. 10. Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A, B, and C above. 11. In the diagram below, draw three vertical lines showing the locations within a sarcomere of the cross sections indicated by Figures A, B, and C. Label each
A sarcomere is defined as the region of a myofibril contained between two cytoskeletal structures called Z-discs (also called Z-lines), and the striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibers is due to the arrangement of the thick and thin myofilaments within each sarcomere (Figure 10.2.2).
Identify the structures labeled A, B, and C in the diagram of a sarcomere above. A = Actin filament; B = Myosin filament; C = Titin The sliding filament theory states that during muscle contraction
(ii) Explain how these structures help in the absorption of substances from the small intestine. (1) (b) (i) The scale bar on this drawing represents a length of 0.1μm.
B) B C) C D) D E) E. A) A. Identify the letter that indicates the endomysium. A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E. ... connects a muscle to underlying structures through a flat sheet or web. B) consists of a neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates. ... Which region of the sarcomere does not change in length during contraction? A) A band B) H zone C ...
Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A, B, and C above. 12. There are three sarcomeres shown in the diagram below. Sarcomere 1 Sarcomere 2 Sarcomere 3 a) In Sarcomere 1, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section indicated by Figure A in Model 3.
3) Identify the specific structure indicated by Label G. A) Muscle fascicle B) Triad C) Myofibril D) Sarcomere E) Myofilament
A Fig. B Fig. C QUESTIONS: 11. Label the thick and thin filaments in Figs. A,B, and C above. 12. There are three sarcomeres shown in the diagram below. Sarcomere 1 Sarcomere 2 Sarcomere 3 a) In Sarcomere 1, identify the location within the sarcomere of the cross section indicated by Figure A in Model 3.
Jan 23, 2019 · A sarcomere is the basic unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells which. Sarcomeres are composed of thick filaments and thin filaments. The thin filaments Look at the diagram above and realize what happens as a muscle contracts.























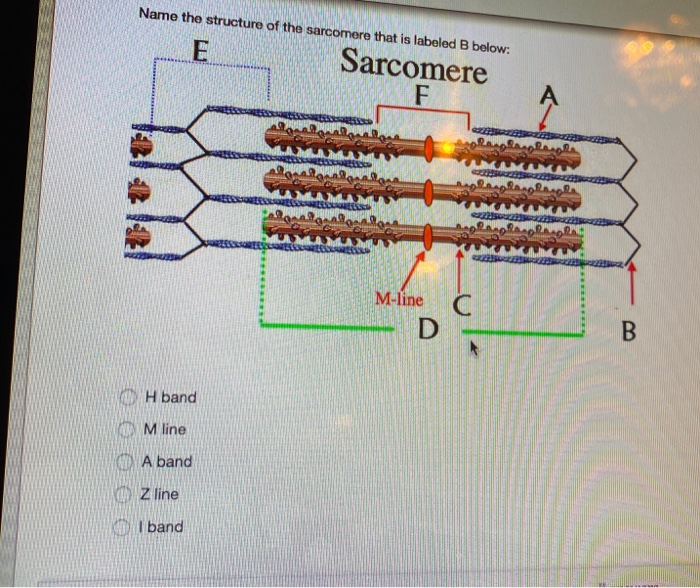
0 Response to "39 identify the structures labeled a, b, and c in the diagram of a sarcomere above."
Post a Comment