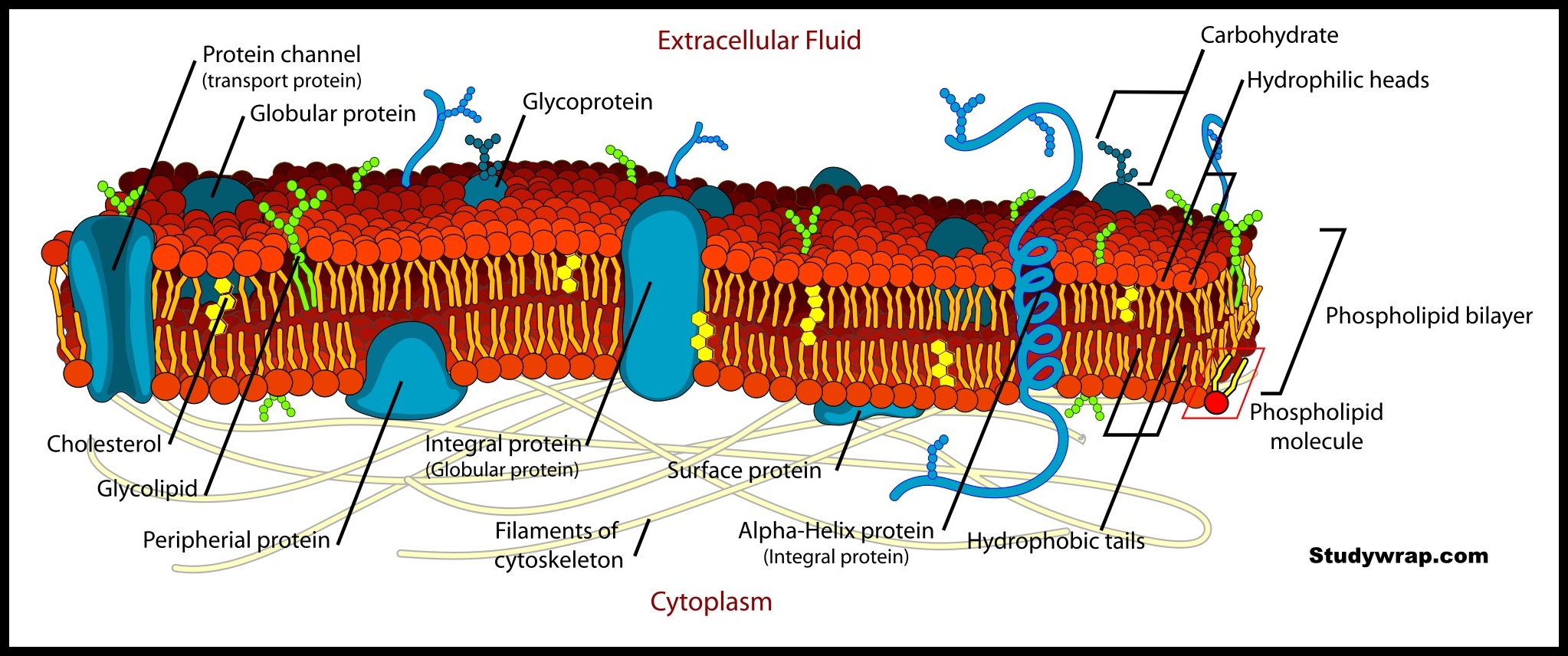
37 diagram the plasma membrane and label the component
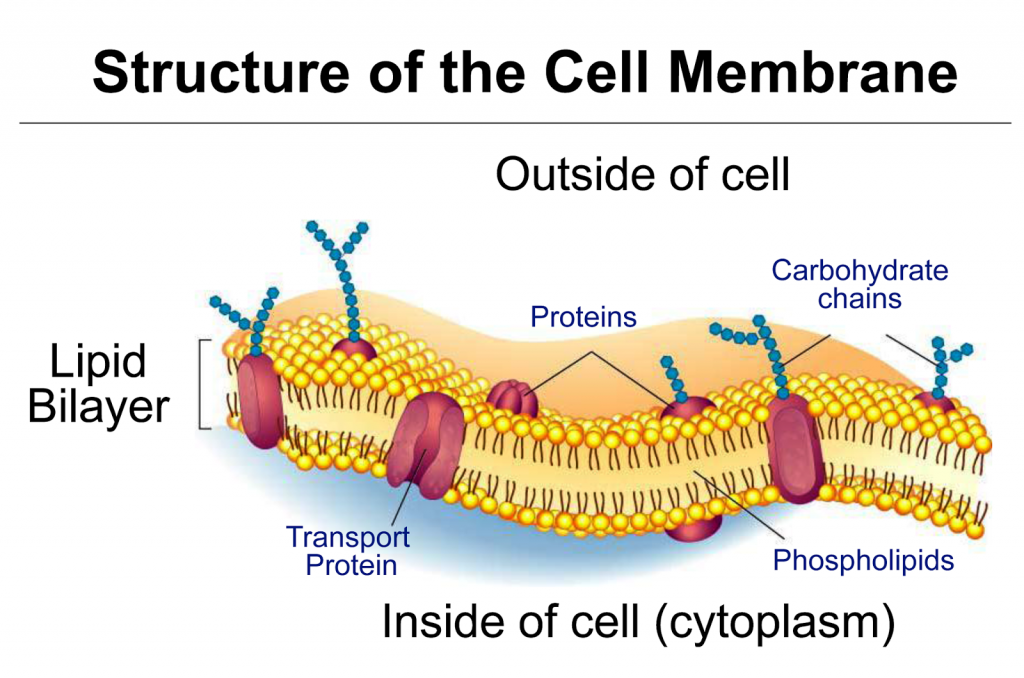
A plasma membrane's principal components are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a molecule consisting of glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate-linked head group. Image modified from OpenStax Biology. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.
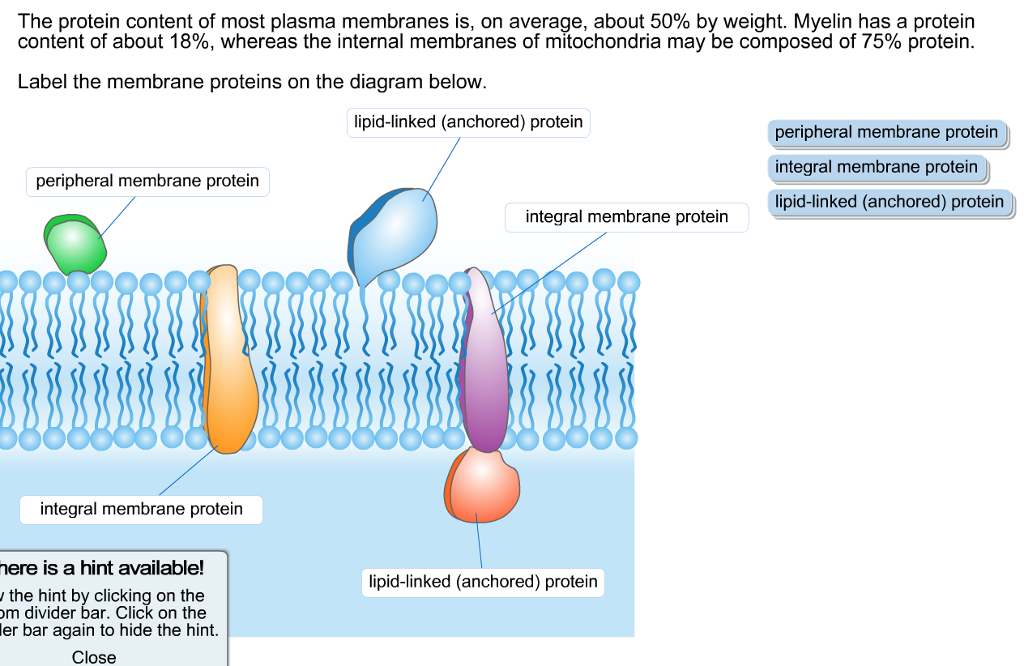
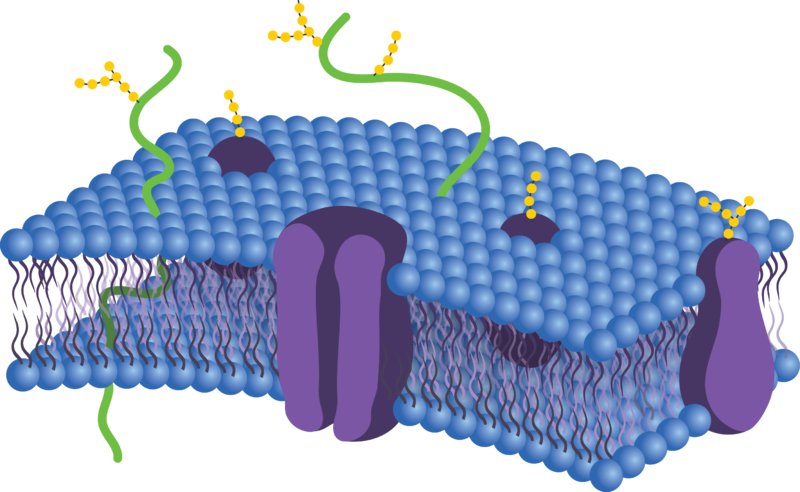
Major Components of the Cell Membrane: Membrane Proteins • Membrane proteins are embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer • More than 50 types of proteins have been found in the plasma membrane. Membrane proteins determine most of the membrane specific functions • Transport proteins, enzymes and receptor proteins (membrane ...
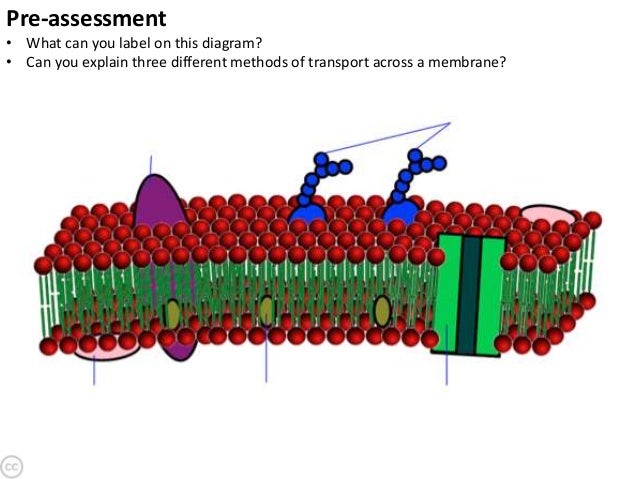
Diagram the plasma membrane and label the component
Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell's contents from outside environment 2) Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3) Communicate with other cells The Plasma Membrane: Structure and Functions Figure 3.1 is a diagram of a portion of a plasma membrane. Select four differ- ent colors and color the coding circles and the corresponding structures in the diagram. Then respond to the questions that follow, referring to Figure 3.1 and inserting your answers in the answer blanks. Phospholipid ... Like nearly all membrane proteins, CFTR is translated on ribosomes at the ER and then moves through the secretory pathway to the plasma membrane, where it carries out its transport role. The single amino acid deletion of F508 causes the protein to misfold, and instead of moving out to the plasma membrane, it is held in the ER by the protein ...
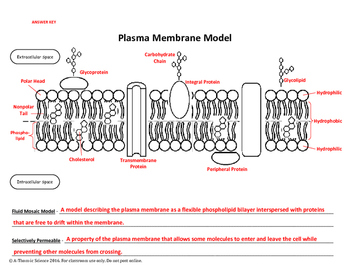
Diagram the plasma membrane and label the component. Phospholipids. The main fabric of the membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules, and the polar ends of these molecules (which look like a collection of balls in an artist's rendition of the model) (Figure 2) are in contact with aqueous fluid both inside and outside the cell.Thus, both surfaces of the plasma membrane are hydrophilic ("water loving"). • Consists of the plasma membrane and all coverings external to it • Plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer -major membrane lipids include phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and cholesterol, all of which contribute to strength of membrane -microdomains participate in variety of cellular processes 9 8. The right answer is It allows passage of particles into and out of the cell. Membrane proteins are one of the three major classes of proteins besides fibrous proteins and globular proteins. The functions of membrane proteins can be. *Signaling: Receptors coupled to G proteins. The Plasma Membrane. ... Structure of the Plasma Membrane. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer (2 layers of phospholipids back-to-back) The Phospholipid Bilayer. ... Components of the Membrane. Cholesterol: stabilize the membrane by keeping fatty acid tails from sticking to each other.
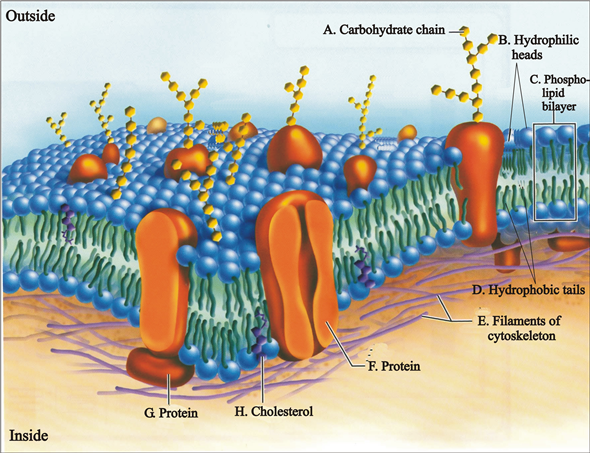
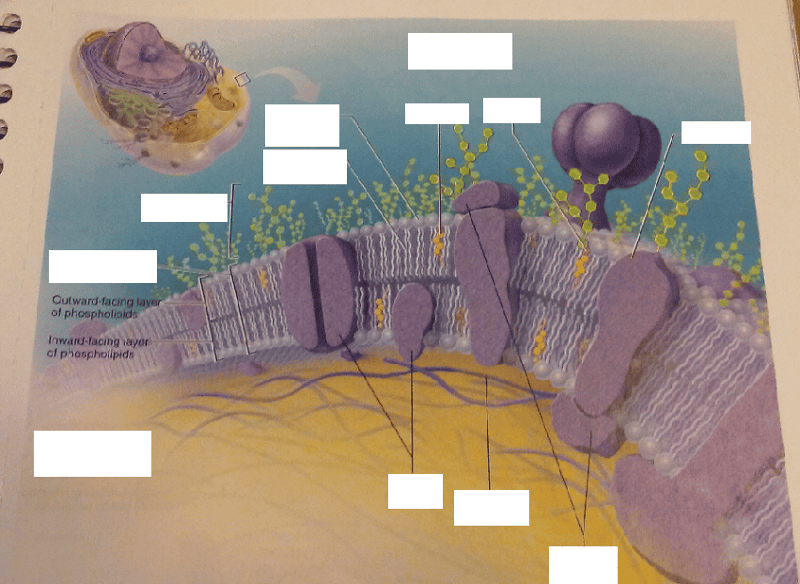
Label the components of the plasma membrane shown in the diagram below with the appropriate letter. Microfilaments of cytoskeleton Peripheral Proteins Integral Protein Phospholipid Bilayer Glycoprotein Cholesterol. Glycolipid Carbohydrate Fibers of the extracellular matrix D. The plasma membrane not only defines the borders of the cell, but also allows the cell to interact with its environment in a controlled way. Cells must be able to exclude, take in, and excrete various substances, all in specific amounts. The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the ... This is an online quiz called Can you Label the Plasma Membrane. There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Your Skills & Rank. Total Points. 0. Get started! Today's Rank--0. Today 's Points. One of us! Game Points. 13.
1. What are the functions of the biological membrane? 2. Use a simple diagram to show the components parts of the lipid bilayer. 3. List some of lipids in the outer and inner leaflets of lipid bilayer, 4. List the different types of non-covalent interactions in the lipid bilayer. 5. How do membrane proteins interact with the membranes? 6. The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The plasma membrane is made up primarily of a bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, carbohydrates, glycolipids, and glycoproteins, and, in animal cells, cholesterol. The principal components they identified were lipids and proteins. In 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed the plasma membrane's structure. This was the first model that others in the scientific community widely accepted. It was based on the plasma membrane's "railroad track" appearance in early electron micrographs. It is selectively permeable covering of the cytoplasm that forms the innermost component of cell envelope. Bacterial plasma membrane or plasma lemma has a structure similar to that of a typical membrane. It is made of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins of various types (extrinsic, integral, trans membrane).
Structurally, there are three architectural regions: appendages (attachments to the cell surface) in the form of flagella and pili (or fimbriae); a cell envelope consisting of a capsule, cell wall and plasma membrane; and a cytoplasmic region that contains the cell chromosome (DNA) and ribosomes and various sorts of inclusions (Figure 1).
The plasma membrane provides structural support to the cell. It tethers the cytoskeleton, which is a network of protein filaments inside the cell that hold all the parts of the cell in place.This gives the cell its shape. Certain organisms such as plants and fungi have a cell wall in addition to the membrane. The cell wall is composed of molecules such as cellulose.
Chapter 5 Worksheet Name _____ Hr___ Focus question 5.1 Label the components in the following diagram of the fluid Mosaic model of membrane structure. Indicate whether regions are hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
Penetrate the hydrophobic core of the membrane. A transmembrane protein with hydrophobic regions that extend into and often completely span the hydrophobic interior of the membrane and with hydrophilic regions in contact with the aqueous solution on one or both sides of the membrane (or lining the channel in the case of a channel protein).
Plasma Membrane Functions: By definition, biological membranes are types of membranes that serve as a semi-permeable barrier within living things.Biological membranes are made up two components: phosphate groups and lipids, hence, phospholipid. But despite having these similar components, each still possesses distinct characteristics like the presence of a unique set of proteins, or different ...
Apr 14, 2021 · The plasma membrane is fluid, meaning that the components drift around freely in a lateral way. The plasma membrane is referred to as a mosaic because of the different components that make it up.
The model describes plasma membrane structure as a mosaic of components which includes proteins, cholesterol, phospholipids, and carbohydrates; it imparts a fluid character on the membrane. Thickness of the membrane is in the range 5-10nm. The proportion of constituency of plasma membrane i.e., the carbohydrates, lipids and proteins vary from cell to cell.
Chapter 7: The Plasma Membrane Structure and Function. surrounds the cell, contains the organelles, protects and separates the inside of the cell from the outside, allows and controls the passage of substances in/out of the cell. Nice work!
3.3 Bacterial Plasma Membranes 1. Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure and identify the types of lipids typically found in bacterial membranes. 2. Distinguish macroelements (macronutrients) from micronutrients (trace elements) and provide examples of each. 3. Provide examples of growth factors needed by some microorganisms. 4.
The Phospholipid Bilayer. The plasma membrane is the most thoroughly studied of all cell membranes, and it is largely through investigations of the plasma membrane that our current concepts of membrane structure have evolved. The plasma membranes of mammalian red blood cells (erythrocytes) have been particularly useful as a model for studies of membrane structure.
Like nearly all membrane proteins, CFTR is translated on ribosomes at the ER and then moves through the secretory pathway to the plasma membrane, where it carries out its transport role. The single amino acid deletion of F508 causes the protein to misfold, and instead of moving out to the plasma membrane, it is held in the ER by the protein ...
The Plasma Membrane: Structure and Functions Figure 3.1 is a diagram of a portion of a plasma membrane. Select four differ- ent colors and color the coding circles and the corresponding structures in the diagram. Then respond to the questions that follow, referring to Figure 3.1 and inserting your answers in the answer blanks. Phospholipid ...
Chapter 4: Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell's contents from outside environment 2) Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3) Communicate with other cells














![[FT_2799] Cell Membrane Diagram Labeled Insulationcell ...](https://static-cdn.imageservice.cloud/4055979/membrane-images-stock-photos-vectors-shutterstock.jpg)




0 Response to "37 diagram the plasma membrane and label the component"
Post a Comment