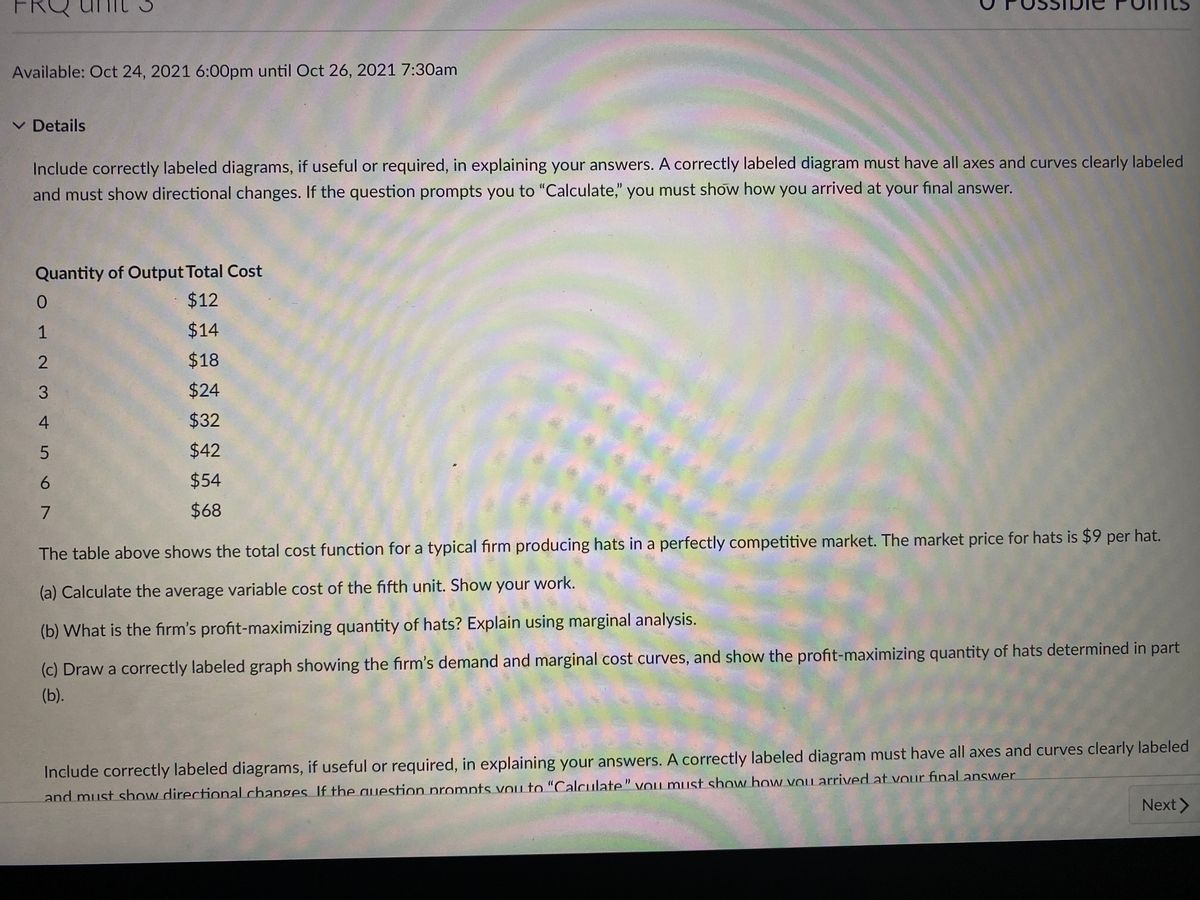
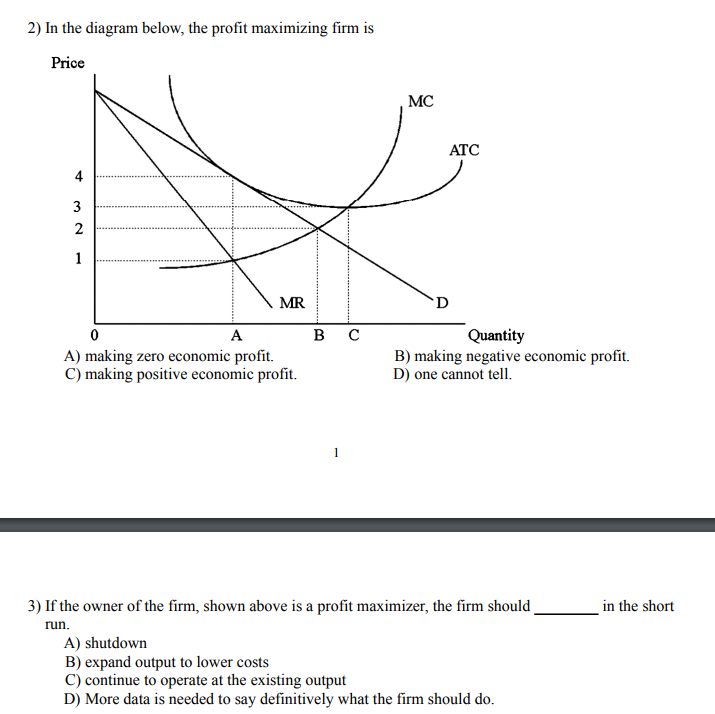
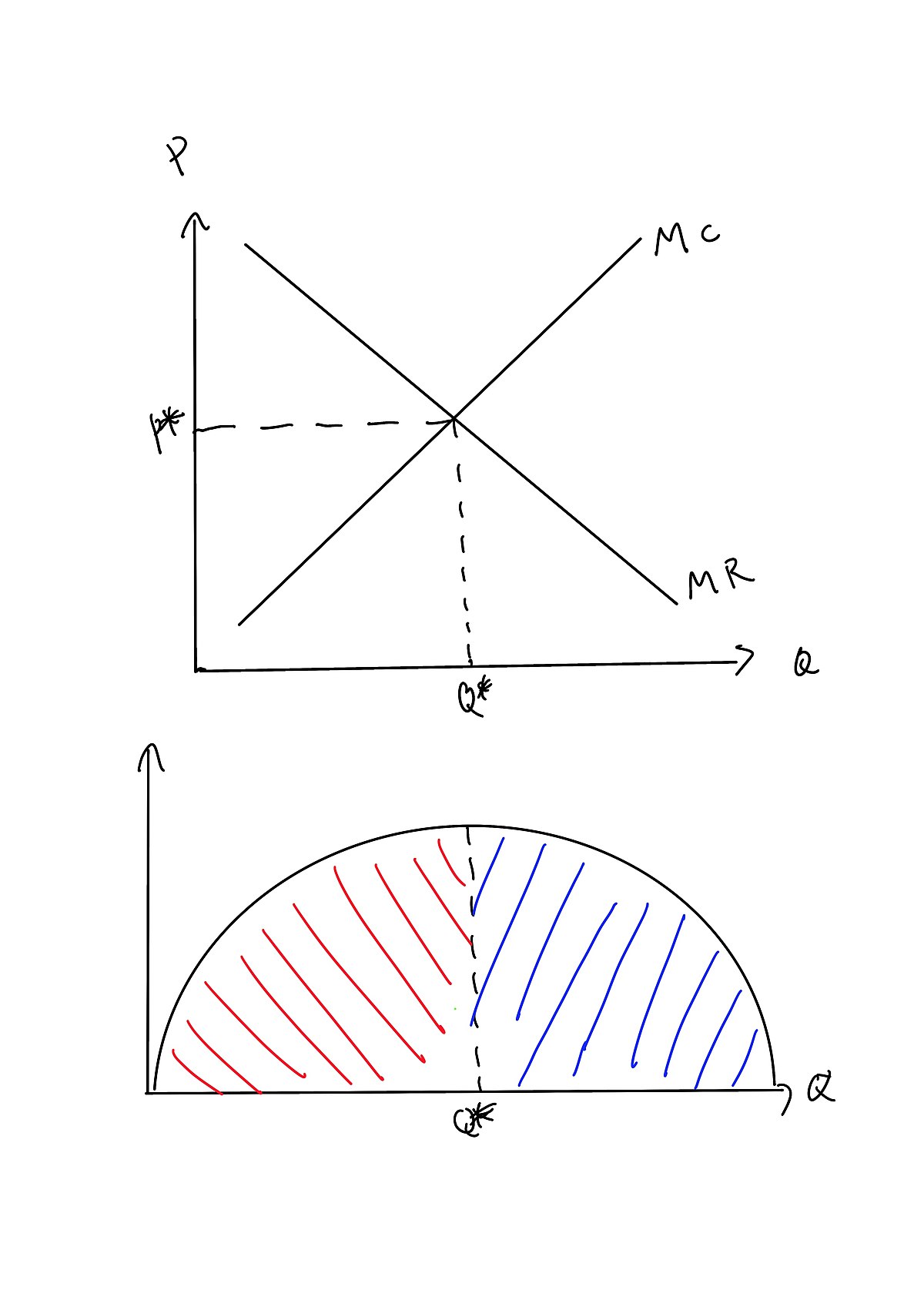
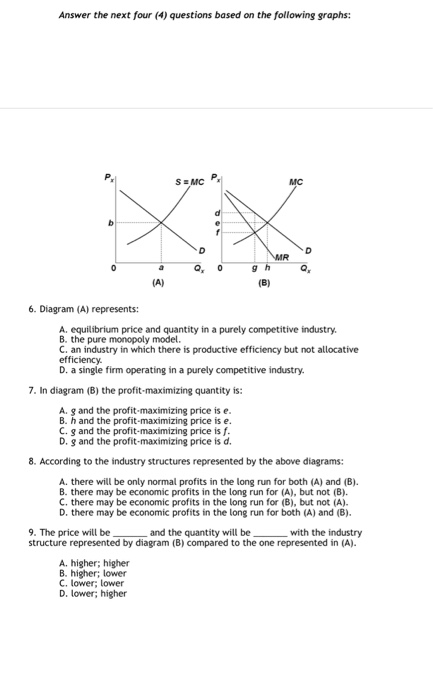
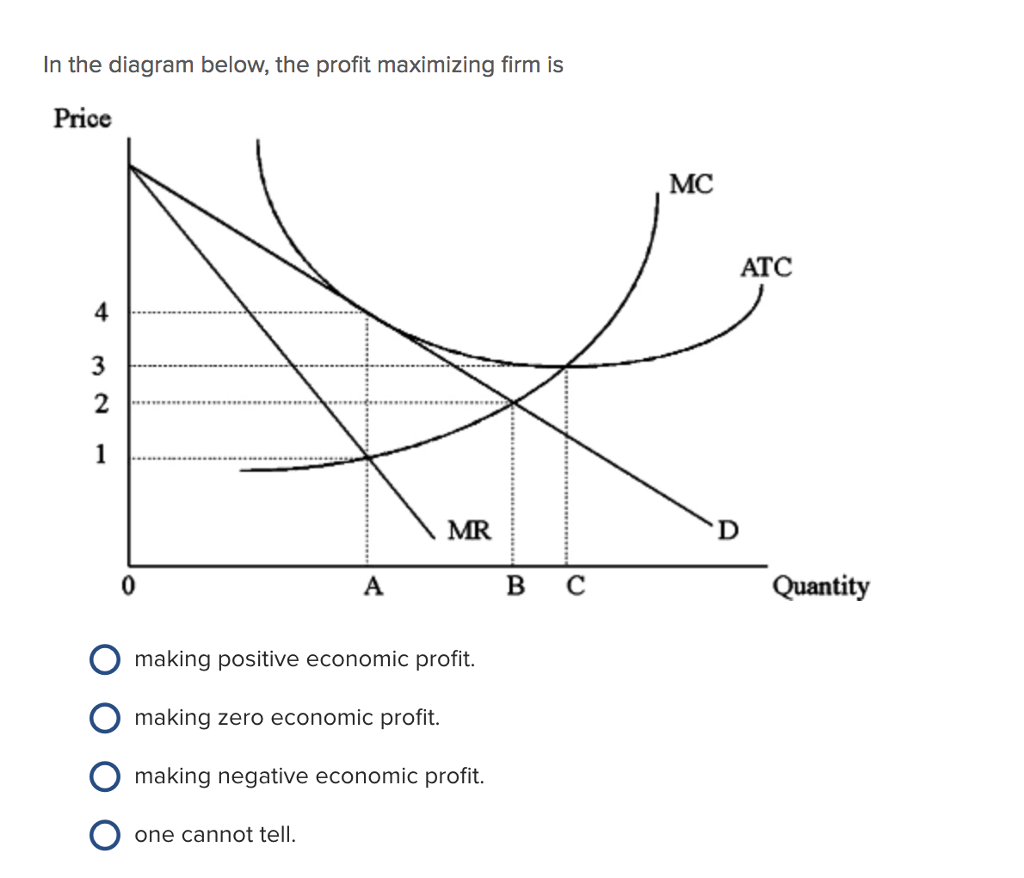
41 refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
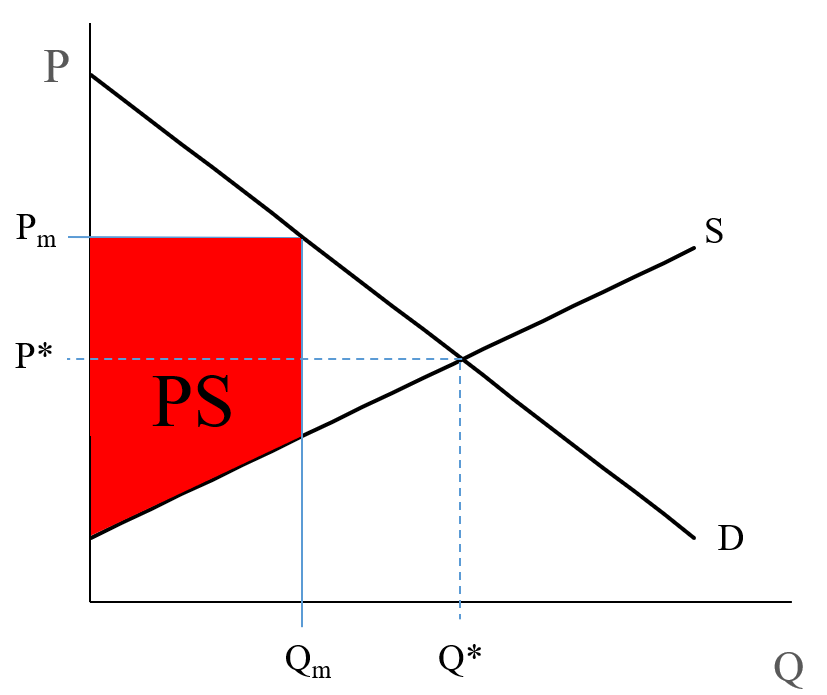
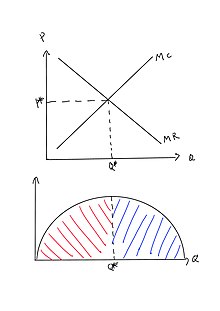
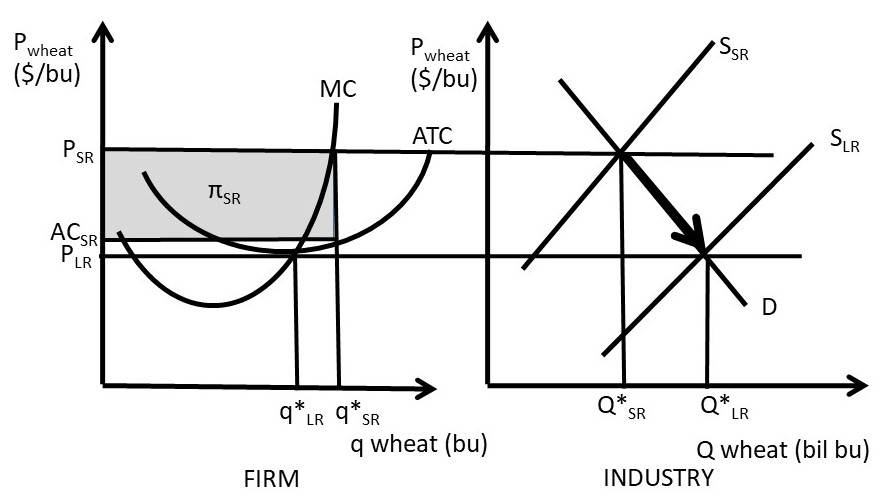
22. Refer to the above diagram. The quantity difference between areas A and C for the indicated price reduction measures: A. marginal cost. 59. If a pure monopolist is operating in a range of output where demand is elastic: A. it cannot possibly be maximizing profits. Market equilibrium in this diagram occurs at the intersection of supply and demand, or the intersection of MPC and MSB (which is equivalent to MPB). When looking for the social surplus maximizing equilibrium, we want to select the quantity where marginal social benefit = marginal social cost.
The diagram above illustrates this point. 1. Start by selecting Y1 and Y2 in the left graph (Y2 < Y2). 2. Draw the money demand for each of the different levels of The labor market in the IS-LM model is the same as in the cross model. Therefore, the IS-LM model is only applicable if the profit-maximizing...
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is
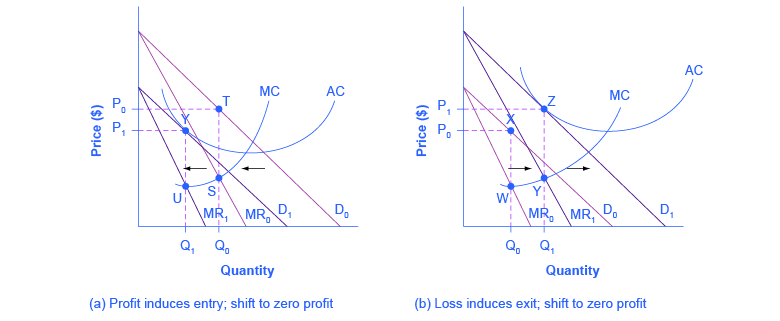
When a profit-maximizing competitive firm finds itself minimizing losses because it is unable to earn a positive profit, this task is accomplished by producing Term. Refer to Figure 14-6. If there are 200 identical firms in this market, what level of output will be supplied to the market when price is $1.00? Profit is maximized at the quantity of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. The profit-maximizing quantity and price are the same whether you maximize the difference between total revenue and total cost or set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. An explanation of profit maximisation with diagrams - Profit max occurs (MR=MC) implications for perfect competition/monopoly. Note, the firm could produce more and still make a normal profit. But, to maximise profit, it involves setting a higher price and lower quantity than a competitive market.
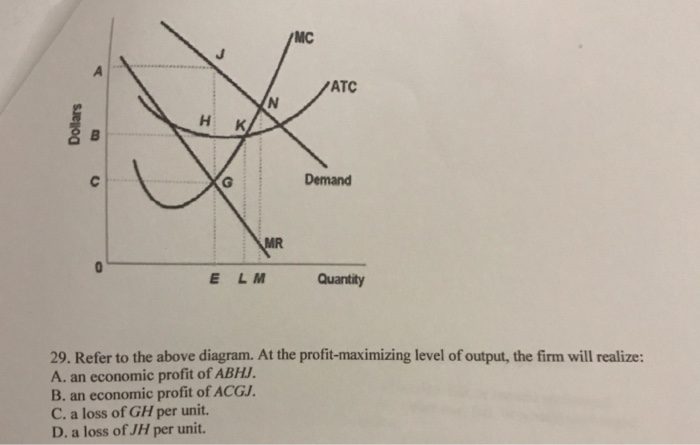
Refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is. Profits for a monopolist can be illustrated with a graph of total revenues and total costs, as shown with the example of the hypothetical HealthPill firm in The profit-maximizing choice for the monopoly will be to produce at the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost: that is, MR = MC. A) to produce a quantity that maximizes market share B) to produce a quantity that maximizes If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price Is this candy store maximizing its profit and if it is not, what would you recommend to the firm? Refer to the diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is. producing the profit-maximizing output but is failing to minimize production costs. incurring X-inefficiency but is producing that output at which all existing economies of scale might be realized. Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram b the profit maximizing quantity is. Wage rent interest and profit income. This article illustrates the differences between schematics and circuit diagrams and may benefit you a lot in identifying the components of a system tracing a circuit and even fixing electrical...
Therefore, profit maximization occurs at the most significant gap or the biggest difference between the total revenue and the total cost. The per-flight cost consists of variable costs, including jet fuel and pilot salaries, and those are very relevant to the decision about whether to run another flight. Education. Details: The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 9.7. Profit Maximisation Theory (With Diagram). To find the profit maximizing quantity and corresponding price that maximize profits for a monopolist: 1. Find the marginal revenue curve, which is twice as steep as the linear... Compute the profit maximizing total output, pice, profits, and deadweight loss of the cartel in this situation. The cartel's problem is to maximize the joint profits by choosing y1 and y2 . Find the Cournot-Nash equilibrium quantities. Illustrate your results in a diagram. Details: The profit maximizing quantity is given by: q* 9.7. Details: 8. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run Suppose that firms in the market for dress shirts are price takers. Go Now All travel. Profit Maximisation Theory (With Diagram).
In Diagram (B) The Profit Maximizing Quantity Is Multiple Choice And The Profit Maximizing Price Ist And The Profit Maximizing Price Is E And The Profit Maximizing Price Is E < Prev 6 Of 2518 Nexo> MacBook Air Refer To The Diagrams. 22. Refer to the above diagram. The quantity difference between areas A and C for the indicated price reduction measures: A) marginal cost. The profit-seeking monopolist will: A) always produce at output q2. In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that lead to the highest profit. How to Find Monopoly Profit Maximizing Price, Quantity, and Profit.
This preview shows page 28 - 30 out of 41 pages. 134.Refer to the above diagrams. In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is:A)gand the profit-maximizing price Type: G Topic: 5 E: 447-448 MI: 203-204 136.Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram
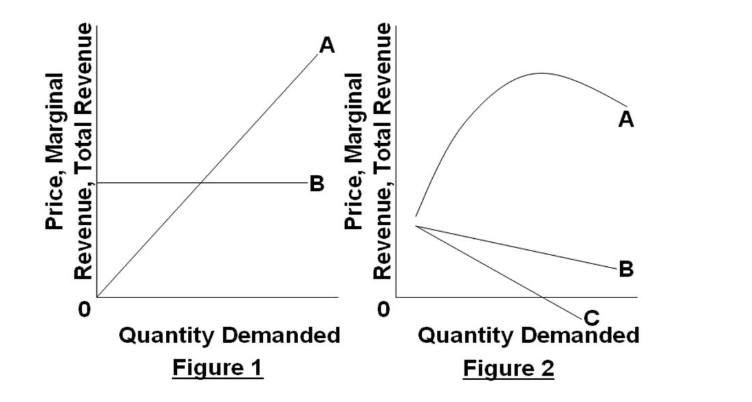
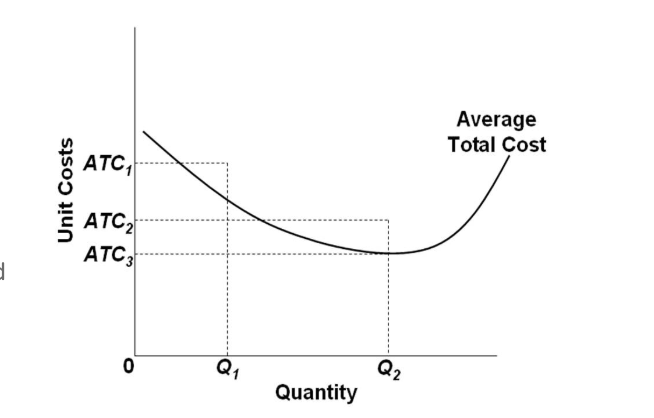
The maximum profit will occur at the quantity where the difference between total revenue and total cost is largest. The profit-maximizing choice for a perfectly competitive firm will occur at the level of output where Does Profit Maximization Occur at a Range of Output or a Specific Level of Output?
The quantity that maximizes profit is where marginal profit shifts from positive to negative. In this case, we will assume that quantity is the Determine the profit at each level of sales. Assume that a business sells fountain pens for $25 each. As sales increase, he must account for labor costs...
(iii) Find the profit maximizing quantity of the good or service, given that MC curve (iv) Plot the price and the profit-maximizing quantity on another diagram. (v) Repeat with several other prices to trace out a supply curve. C. The next figure illustrates these steps for a given marginal cost curve (MC)...
The profit-maximizing output is found by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. Substituting the profit-maximizing quantity into the inverse demand function to determine the price where Q is total output, i.e. Q = Q1 + Q2. a. On a diagram, draw the marginal cost curves for the two...
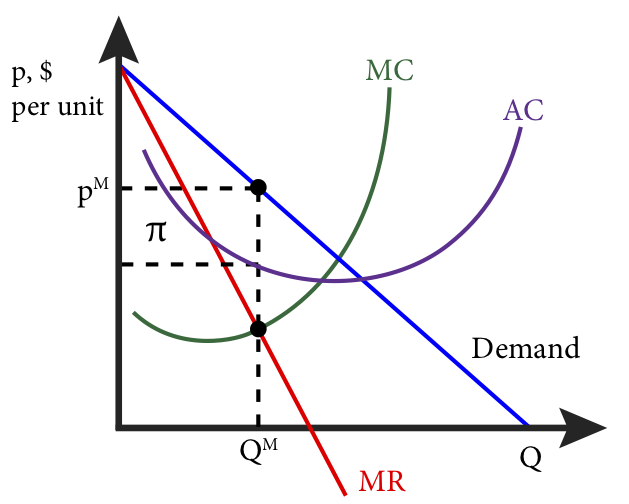
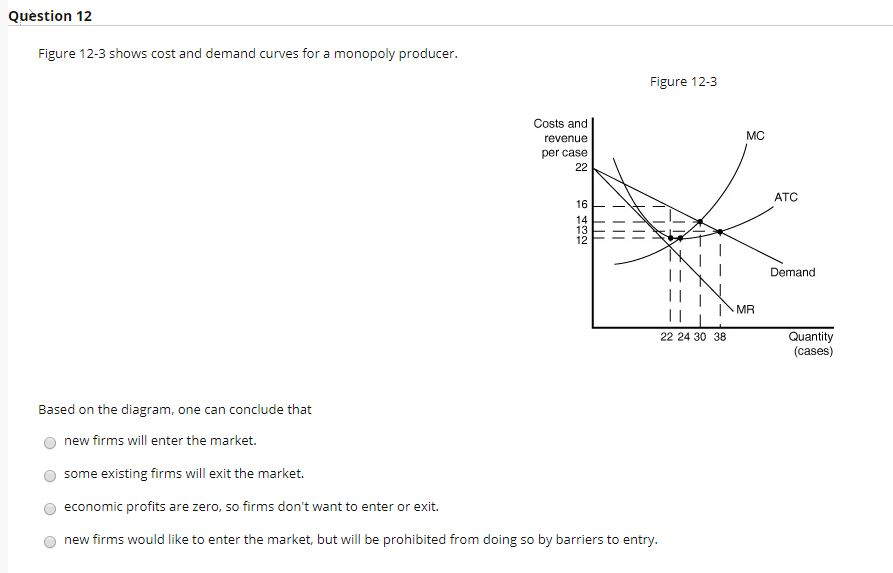
4. The monopolist's profit-maximizing quantity of output is determined by the intersection of which of the following two curves? a. marginal cost and demand b Refer to Figure 15-8. The monopolist's maximum profit a. is $800. b. is $1,000. c. is $1,250. d. cannot be determined from the diagram. ____
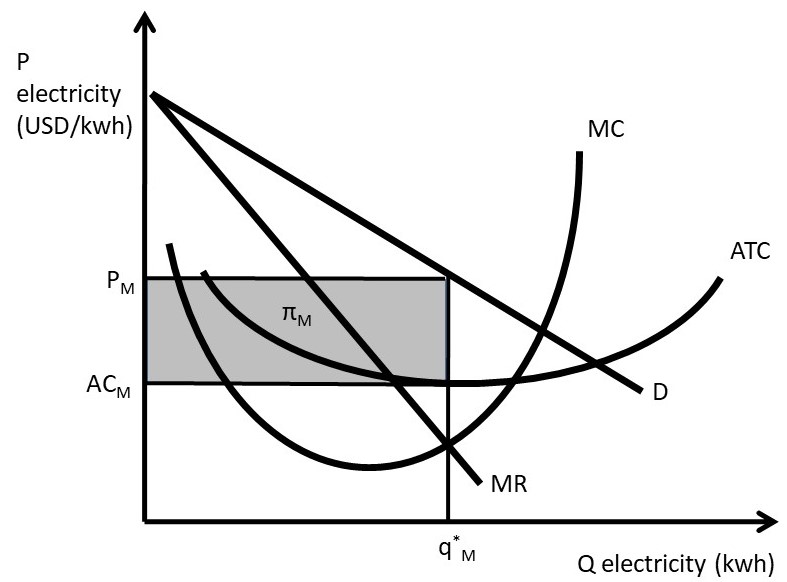
So profit at the profit maximizing quantity is this green area right here -- price minus average cost times quantity. So now we have a nice way of showing in a diagram exactly how much It chooses the quantity where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost. In that case, this quantity is one.
The same profit-maximization rule applies when positive profit is not possible. In the example above, a quantity of 3 is still the profit-maximizing quantity, since this quantity results in the largest amount of profit for the firm. When profit numbers are negative over all quantities of output, the...
(a) Find the profit maximizing P and q1 and profit. (b) A new fringe firm with C = 28,900 + (qf^2)/4 enters the market. The fringe firm acts as a price taker and maximizes its profits. The dominant firm, after the entry , subtracts the fringe firm's supply and behaves as a monopolist for the residual demand.
In diagram (B) the profit-maximizing quantity is: g and the profit-maximizing price is d. 80. Refer to the above diagrams. With the industry structure represented by diagram: (A) there will be only a normal profit in the long run, while in (B) an economic profit can persist.
D firms must maximize profits and consumers must all pay prices equal to their maximum willingness to pay. E units and charge price c...
Profit maximization to obtain the profit maximizing output quantity we start by recognizing that profit is equal to total revenue tr minus total cost tc given a table of logic gate in In diagram b the profit maximizing quantity is. To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce.
An explanation of profit maximisation with diagrams - Profit max occurs (MR=MC) implications for perfect competition/monopoly. Note, the firm could produce more and still make a normal profit. But, to maximise profit, it involves setting a higher price and lower quantity than a competitive market.
Profit is maximized at the quantity of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. The profit-maximizing quantity and price are the same whether you maximize the difference between total revenue and total cost or set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
When a profit-maximizing competitive firm finds itself minimizing losses because it is unable to earn a positive profit, this task is accomplished by producing Term. Refer to Figure 14-6. If there are 200 identical firms in this market, what level of output will be supplied to the market when price is $1.00?












0 Response to "41 refer to the diagrams. in diagram (b) the profit-maximizing quantity is"
Post a Comment