41 diagram of nuclear fusion
18-09-2020 · Nuclear fusion forces diagram.svg. Diagram illustrating, in a schematic way, the technical difficulties of nuclear fusion, which much bring positively charged nuclei close enough so that the nuclear force will kick in. To demonstrate this I have drawn the ranges of the various forces as colored regions. Not to scale. Date.
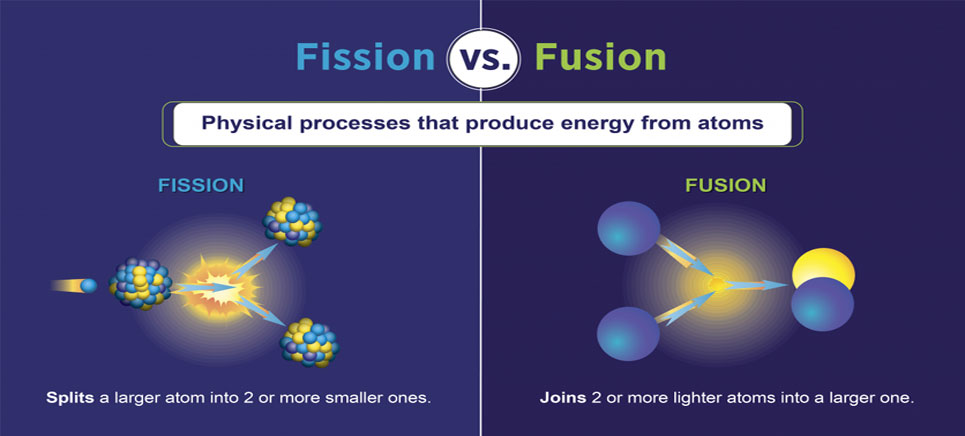
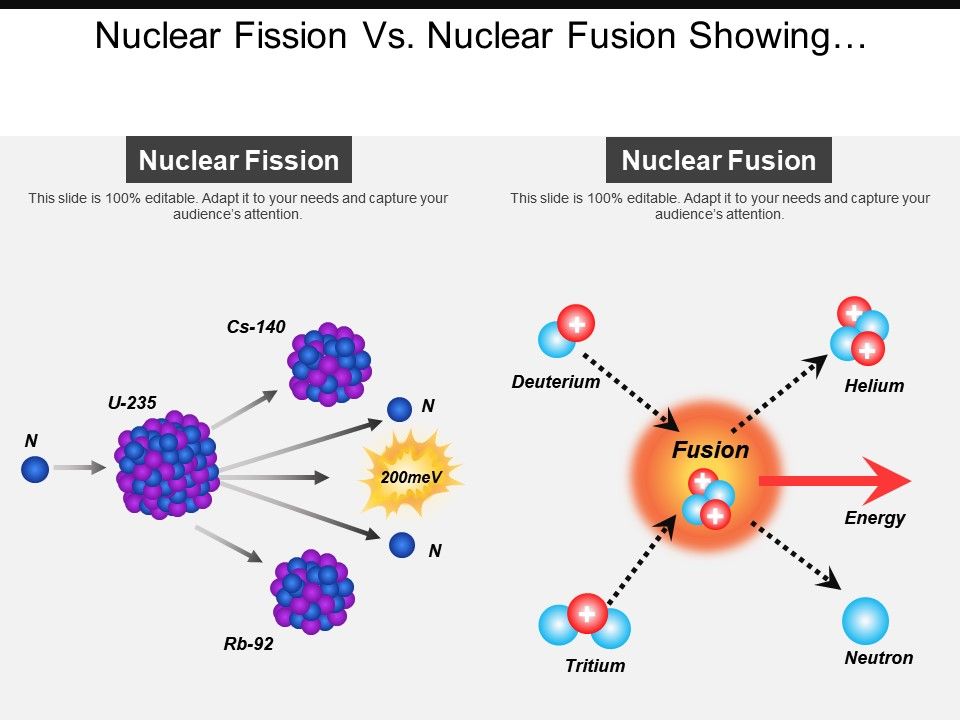
A brief history of nuclear fusion. 1890s–1920s: New-Zealand-born Sir Ernest Rutherford (1871–1937) and associates demonstrate nuclear fission ("splitting the atom") and nuclear fusion in a long series of ingenious physics experiments, which gradually reveal the structure of the atomic nucleus.
Start studying Nuclear Fusion. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Diagram of nuclear fusion
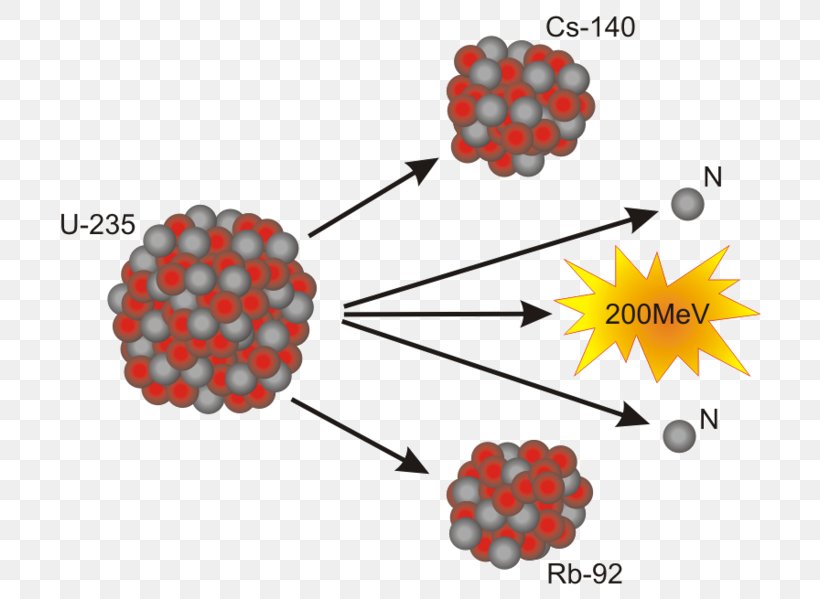
some radioactive contamination of the steam circuit and turbine, which then requires shielding of these components in addition to that surrounding the reactor. Such reactors, known as Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs), (see Fig. 1.3b) are in use in some ten countries throughout the world. Nuclear Reactor Types 4
How are nuclear fusion cross section diagrams supposed to be interpreted? I'm working on programming a particle simulation that visually shows the nuclear fusion reaction rate of deuterium at different densities and temperatures, but I'm having trouble understanding exactly how nuclear fusion cross section diagrams are supposed to be interpreted.
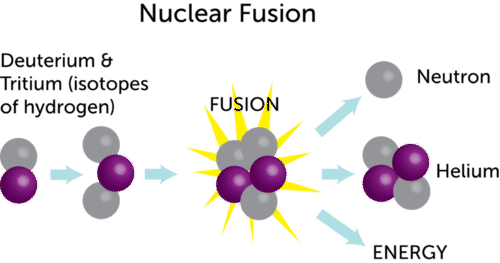
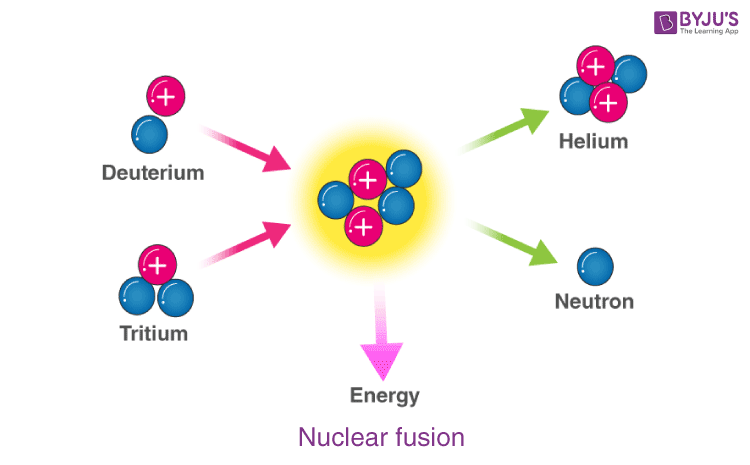
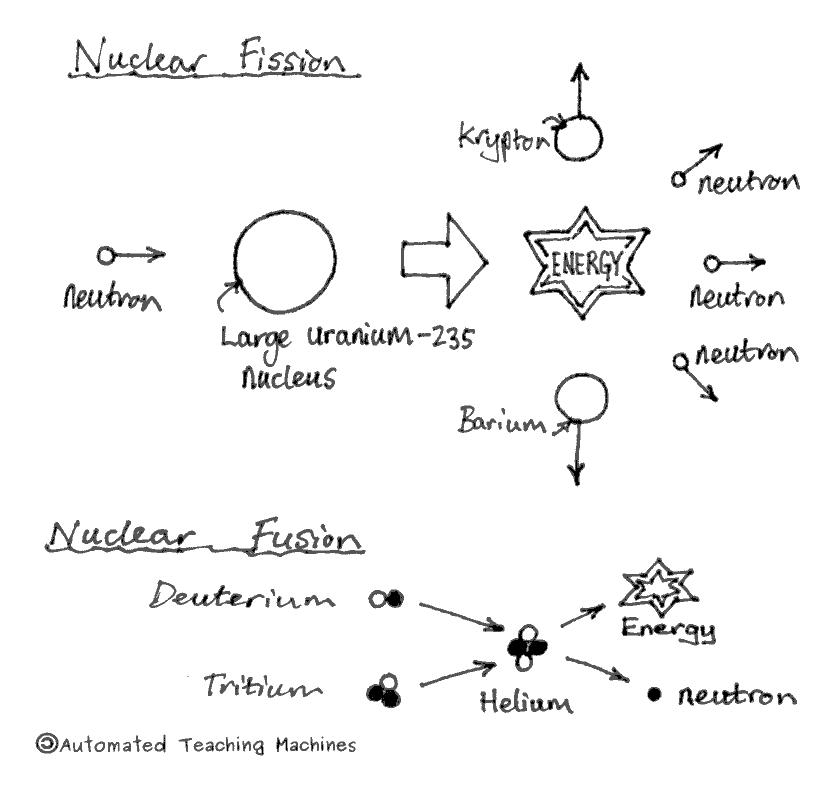
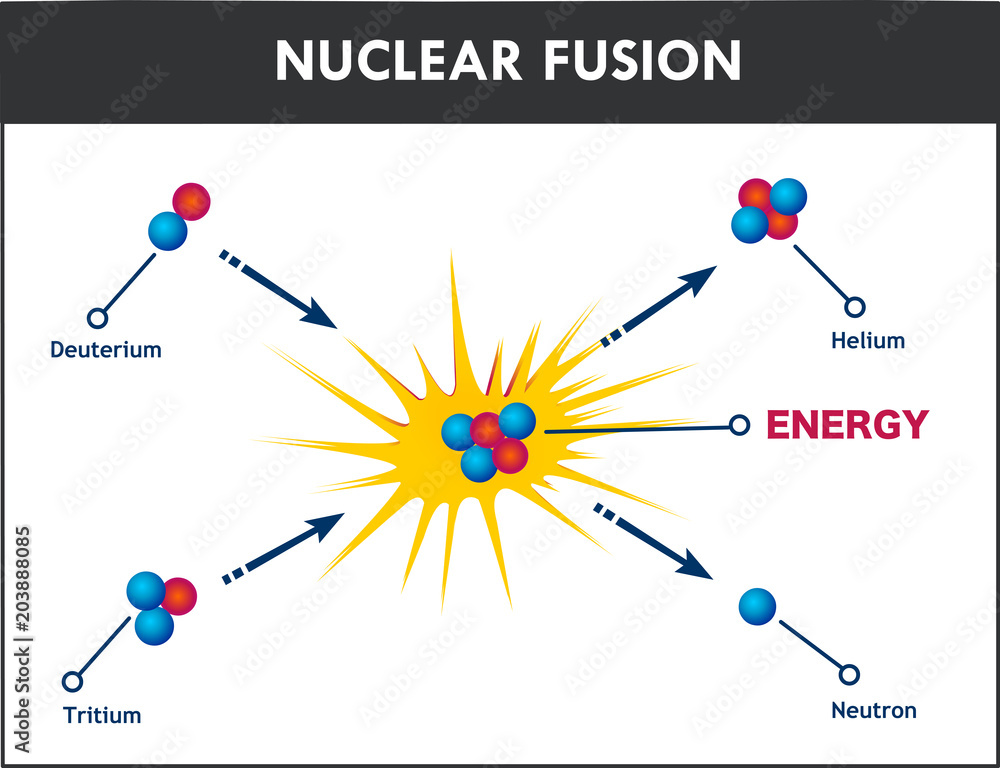
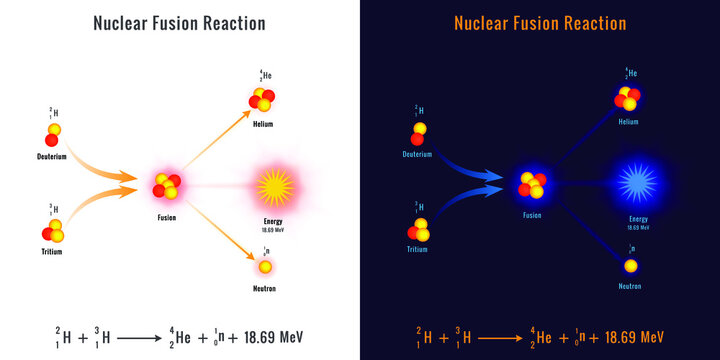
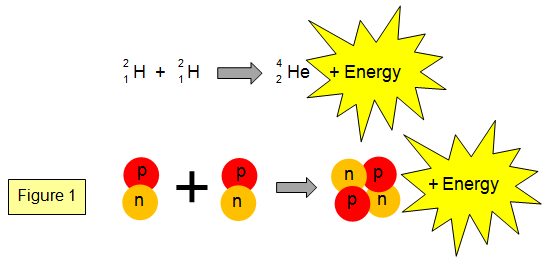
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons).The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the release or the absorption of energy.This difference in mass arises due to the difference in atomic binding energy between the nuclei before and ...
Diagram of nuclear fusion.
Fusion a type of nuclear reaction where two nuclei come together to form the nucleus of a different element. Each element has a particular number of protons in the nucleus. Isotopes of an element all have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
If we apply a lot of energy (on an atomic scale) we overcome the magnetic resistance and the two protons stick together; they have fused.In doing so they give up a little of their mass in the form of energy. In fact, the energy released is greater than the energy that was required to force the two protons together. We now have a source of energy: nuclear fusion.
26-07-2020 · Nuclear fusion is when two small, light nuclei join together to make one heavy nucleus. Fusion reactions occur in stars where two hydrogen nuclei fuse together under high temperatures and pressure ...
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together, or “fuse,” to form a single heavier nucleus. During this process, matter is not conserved because some of the mass of the fusing nuclei is converted to energy, which is released. Fusion is the process that powers active stars, releasing large quantities of energy.
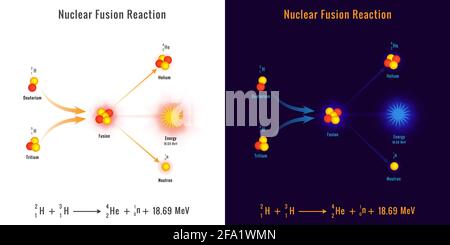
13-07-2020 · Fusion nuclear reactors are an altogether different beast from fission reactors. For starters, fusion works with much lighter elements. In the sun, we mainly see hydrogen, the lightest element, fused together to create helium, the second-lightest element. Here on Earth, fusion reactors combine deuterium and tritium as fusion fuel, two heavy ...
20-10-2016 · nuclear fusion 1. submitted by megha agarwal k11566 ee 5th sem 2. nuclear plants introduction raw materials plasma why fusion research power production fusion reactor flow diagram working of fusion reactor fusion in our world considerations safety and the environment advantages disadvantages conclusion
Fusion Reactions The concept of nuclear fusion has been described in Chapter 12. It is summarized in Figure 14-1, which is analogous to Figure 13-2 for nuclear fission. As the nuclei of two light atoms are brought closer to each other, they become increasingly destabilized, due to the electric repulsion of their positive charges.
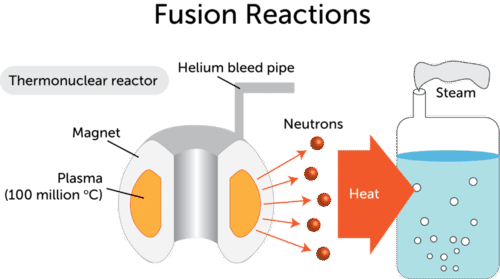
Schematic diagram of a proposed nuclear fusion power plant. The deuterium and tritium fuel burns at a very high temperature in the central reaction chamber. The energy is released as charged particles, neutrons, and radiation and it is absorbed in a lithium blanket surrounding the reaction chamber.
Magnetic Confinement: The ITER Example. The main parts of the ITER tokamak reactor are: The fusion reactor will heat a stream of deuterium and tritium fuel to form high-temperature plasma. It will squeeze the plasma so that fusion can take place. The power needed to start the fusion reaction will be about 70 megawatts, but the power yield from ...























0 Response to "41 diagram of nuclear fusion"
Post a Comment