39 fluorescence energy level diagram
Examples of electronic transitions include absorption (single-photon or multi-photon), relaxation (fluorescence, phosphorescence, internal conversion and ...
Fluorescence is generally studied with highly conjugated polycyclic aromatic molecules that exist at any one of several energy levels in the ground state, each associated with a specific arrangement of electronic molecular orbitals. The electronic state of a molecule determines the distribution of negative charge and the overall molecular geometry.
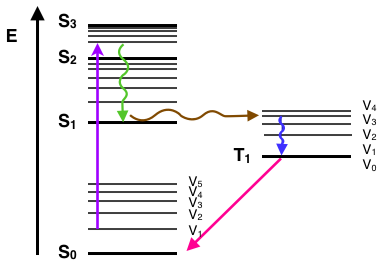
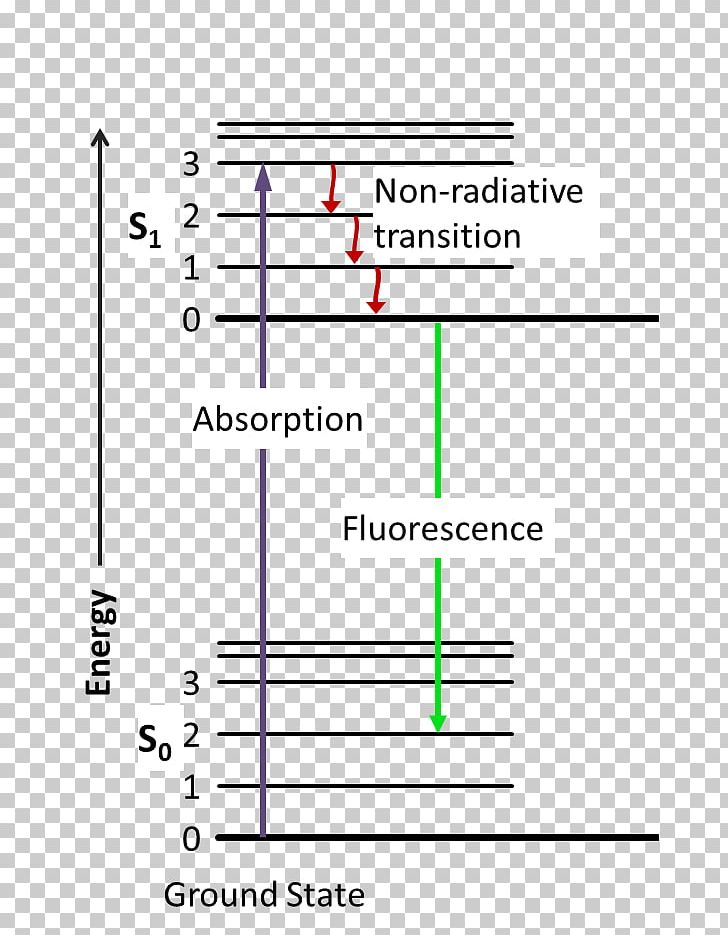
Jablonski diagram including vibrational levels for absorbance, non-radiative decay, and fluorescence. Radiative transitions involve the absorption of a photon, ...
Fluorescence energy level diagram
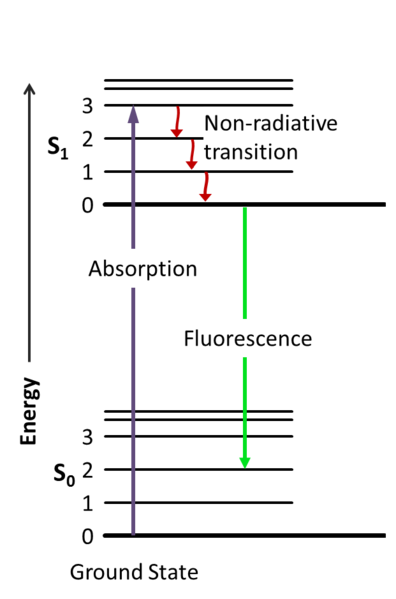
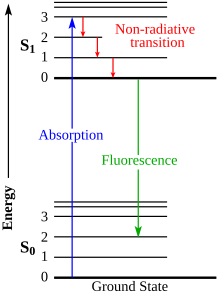
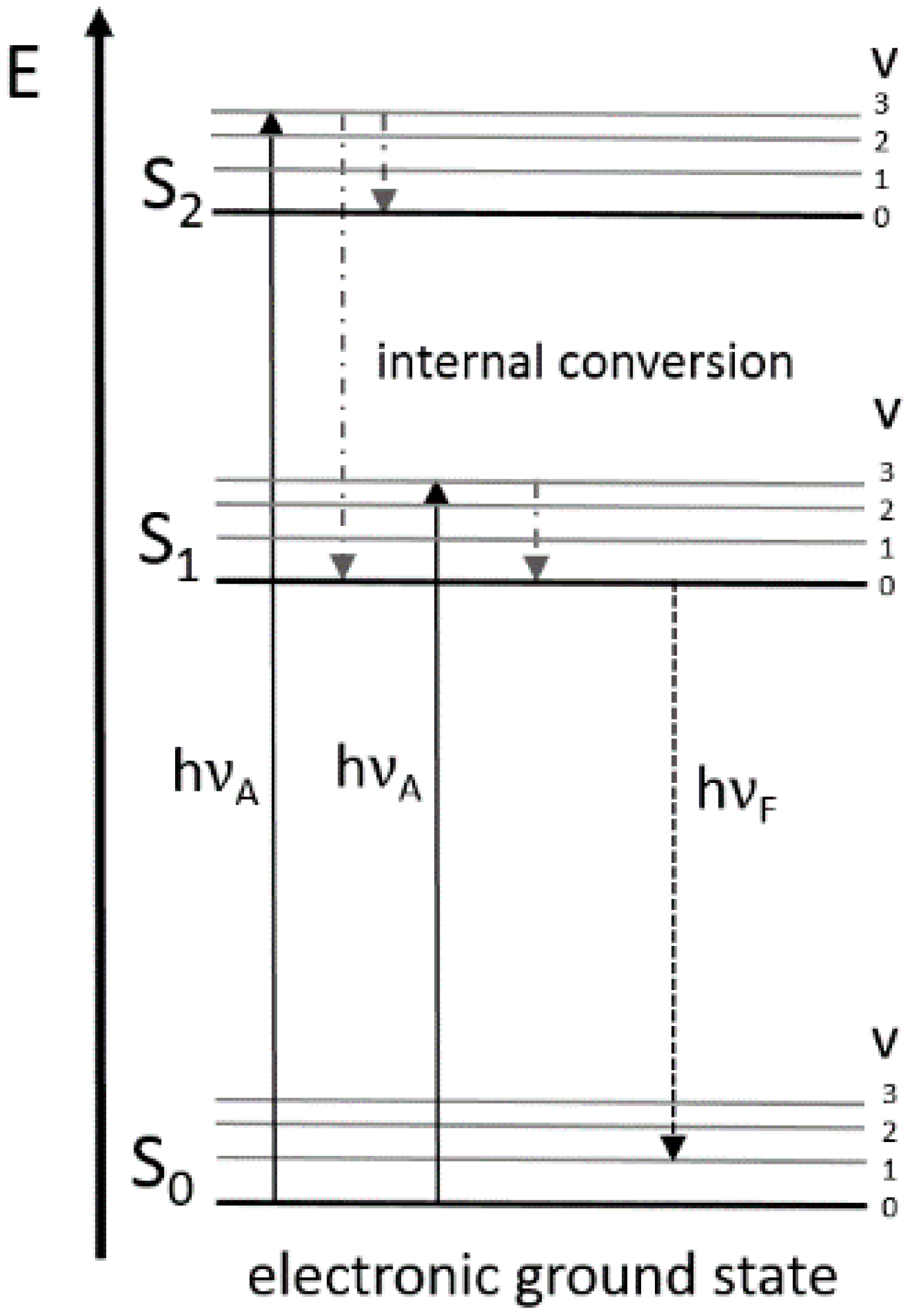
The Franck-Condon energy diagram illustrated in Figure 2 presents the vibrational energy probability distribution among the various levels in the ground (S(0)) and first excited (S(1)) states for a hypothetical molecule. Excitation transitions (red lines) from the ground to the excited state occur in such a short timeframe (femtoseconds) that ...
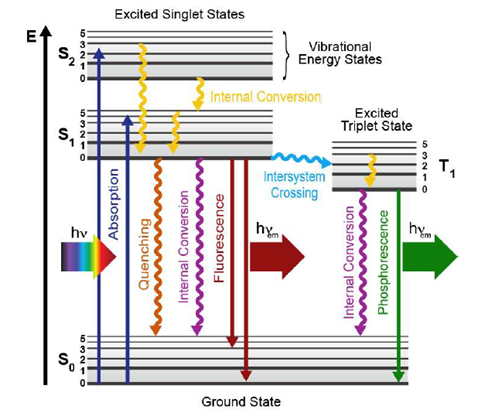
Basic Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy 1.1 Absorption and Emission of Light As fluorophores play the central role in fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging we ... quantum mechanical assembly of one-electron energy levels appropriate to the particle in the box model. In this case, one considers the potential energy of the ...
ADVERTISEMENTS: Read this article to learn about the principles of fluorescence. Fluorochromes and Light: Fluorochromes are essentially dyes, which accept light energy (e.g., from a laser) at a given wavelength and re-emit it at a longer wavelength. These two processes are called excitation and emission. The process of emission follows extremely rapidly, commonly in the […]
Fluorescence energy level diagram.
same energy. From there the molecules again lose energy until the lowest vibrational level of the first excited state is reached. From this level, the molecule can return to any of the vibrational levels of the ground state, emitting its energy in the form of fluorescence. If this process takes
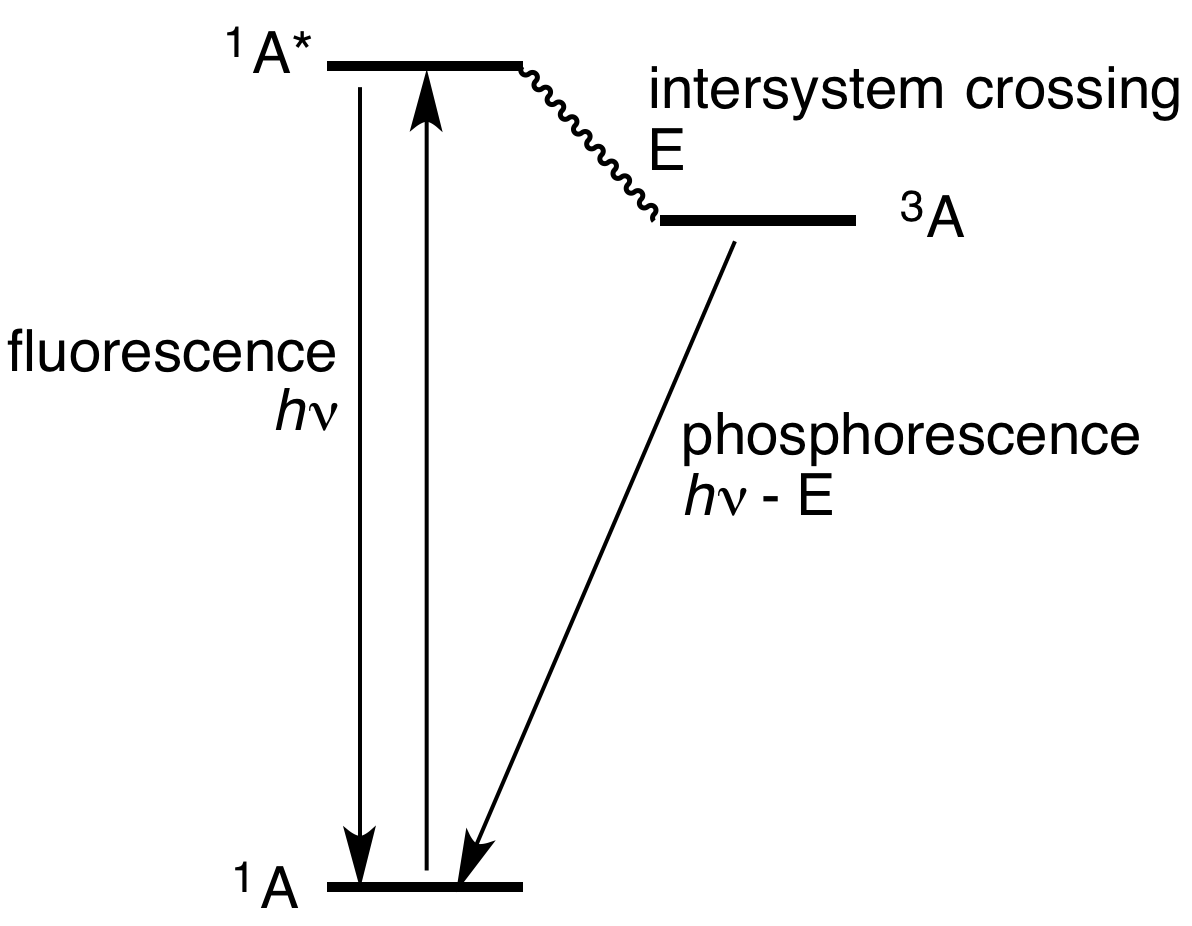
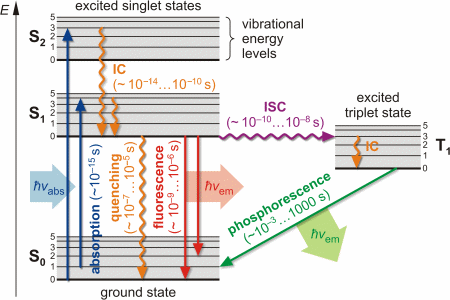
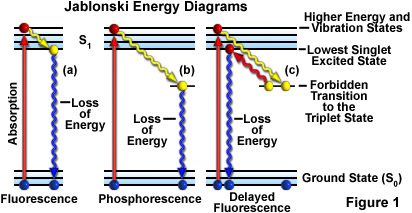
The process of the fluorescence is illustrated by the Jablonski diagram shown in Figure 1. A light quantum of energy hvA supplied by an external source is ...
Fluorescence — Another pathway for molecules to deal with energy received from photons is to emit a photon. This is termed fluorescence. It is indicated on ...Introduction · Vibrational Relaxation and... · Fluorescence · Intersystem Crossing
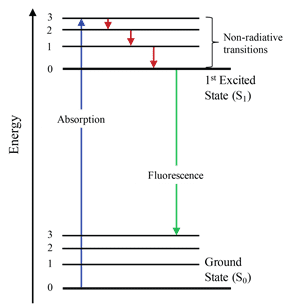
Figure 1-5: Fluorescence, shown in this Jablonski diagram, involves emitting a photon at a lower energy than the photon that was initially absorbed. The diagram is read from left to right – absorbance occurs first, then vibrational relaxation, then fluorescence.
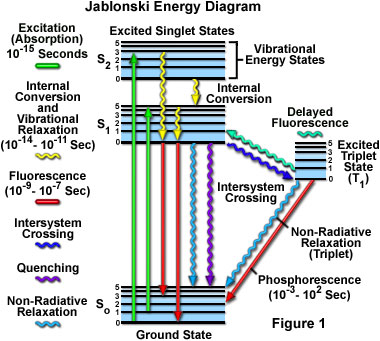
(Jablonski energy-level diagram) Energy Levels for Luminescence Transitions +quenching. S 0 S 1 T 0 transition involving emission/absorption of photon radiationless transition n +hν orescence-hν ernal ersion m crossing ernal ersion Fluorescence in the Jablonski energy-level diagram .
28 Feb 2016 — At each energy level, fluorophores can exist in a number of vibrational energy levels, which are represented by the multiple lines in each ...
A Jablonski diagram (below) is typically used to illustrate the physics of fluorescence. In the diagram electronic (energy) states are indicated by bold horizontal lines. The thin horizontal lines above them represent vibrational/rotational sublevels. Electrons are normally at the lowest energy state, indicated by S 0.
Jablonski Energy Diagram . Explore how an electron absorbs energy and transcends to a higher energy state according to a Jablonski energy-level diagram. Once an electron is in the excited state, it slowly relaxes through vibrational effects and can then drop back to the ground state by emitting a photon (fluorescence).
The energy level diagram is essentially the absorption spectrum converted to an energy scale and then tilted by 90 degrees, with the molecular energy levels shown as bands (series of parallel horizontal lines). What happens to the excess energy after a molecule absorbs light? Fluorescence results from the first, lowest energy excited state.




















0 Response to "39 fluorescence energy level diagram"
Post a Comment