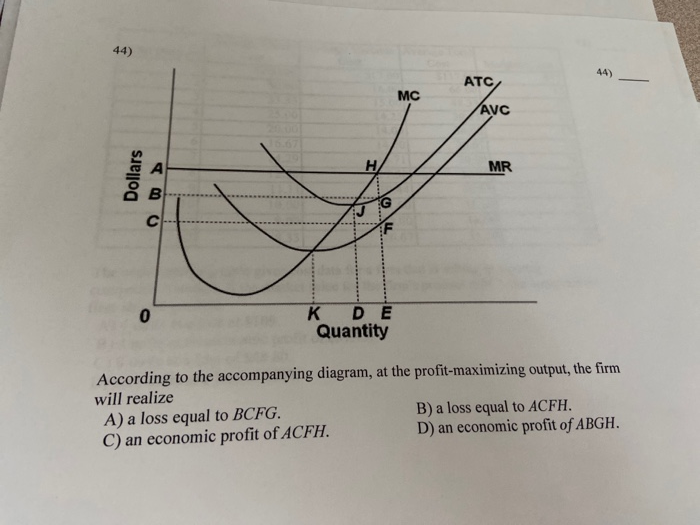
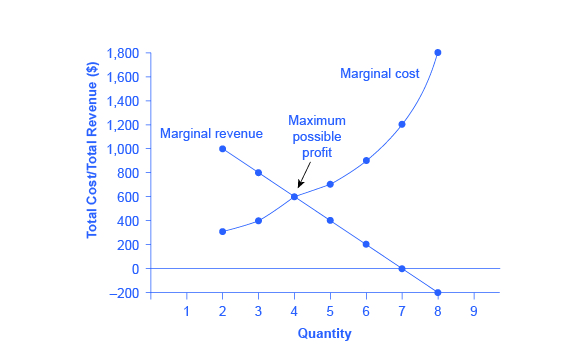
38 according to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize
Diagram of Profit Maximisation. To understand this principle look at the above diagram. If the firm produces less than Output of 5, MR is greater than MC. Therefore, for this extra output, the firm is gaining more revenue than it is paying in costs, and total profit will increase. long as bL<aK. If bL>aK then an increase in labor by one unit doesn't change output at all—in other words an increase in labor by one unit increases output by a constant amount (zero). Thus, in a sense, there is constant returns to labor. c. Imagine that a = 10, b = 10, w = 5, r = 10, and P = 20. Can you find the profit maximizing level of
14. Assume the XYZ Corporation is producing 20 units of output. It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $10 per unit. Its total fixed costs are $100 and its average variable cost is $3 at 20 units of output. This corporation: A. Should close down in the short run. B. Is maximizing its profits.
According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize
According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize A) a loss equal to ACFH. B) a loss equal to BCFG. C) an economic profit of ACFH. D) an economic profit of ABGH. The firm's short-run supply curve is According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. In the short run a purely competitive seller will. This preview shows page 57 - 63 out of 154 pages. 154) In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if A) it cannot produce at an economic profit. B) price is less than average variable cost at all outputs. C) price is less than average fixed cost at all outputs.
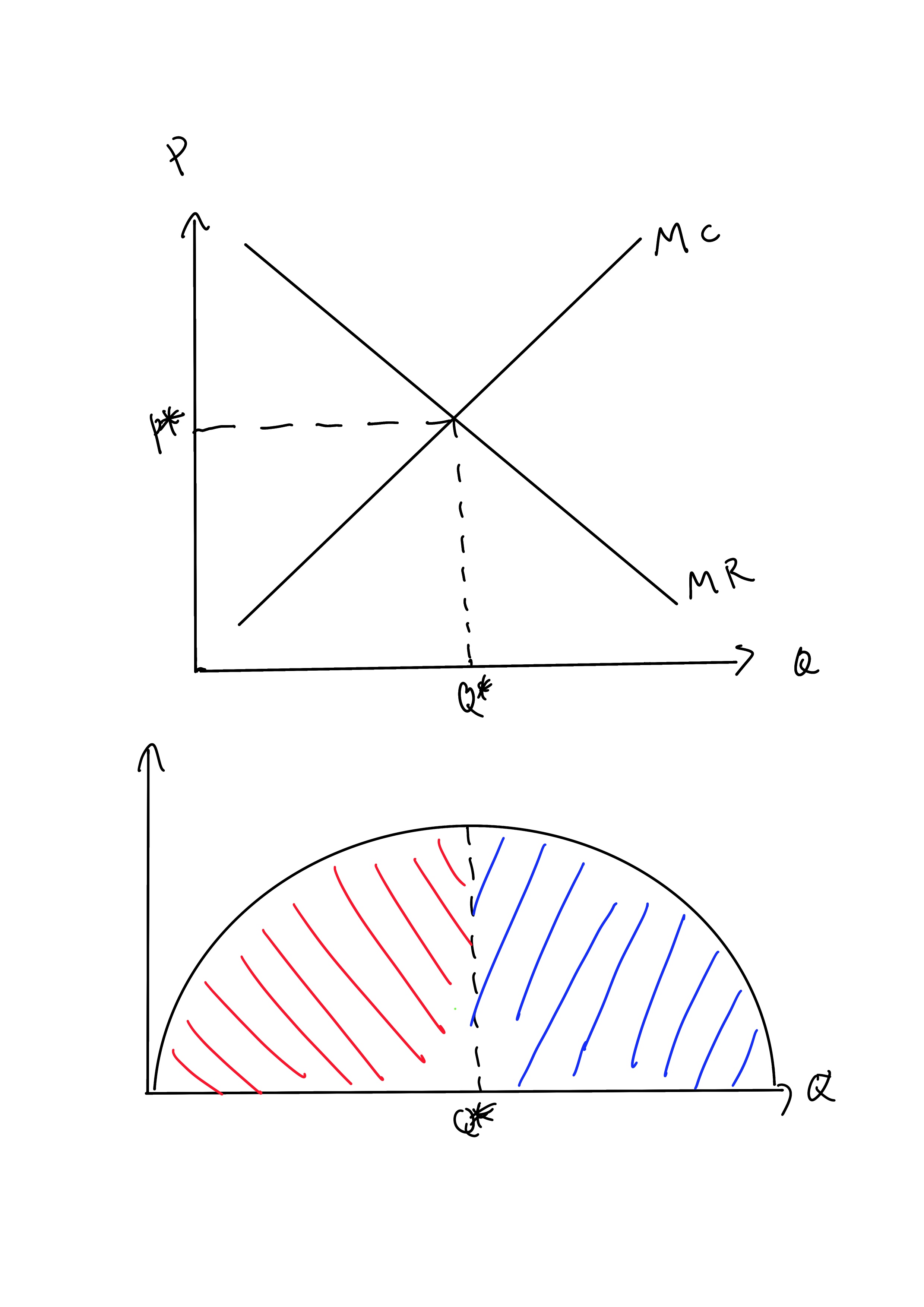
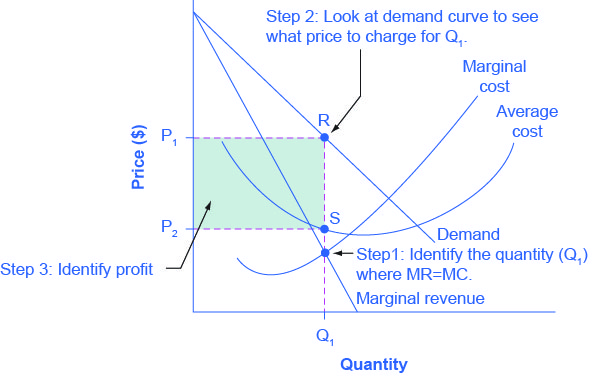
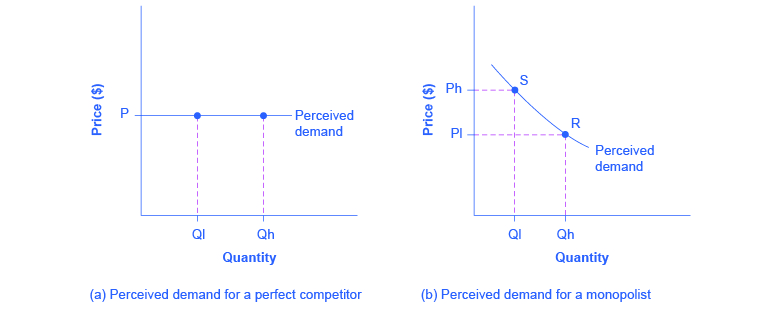
According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize. It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $400 per unit. Its Total Fixed Cost is $6000, Average Total Cost is $450, Marginal Cost is $400 at 100 units of output. ... According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit maximizing output, total variable cost is equal to ... At P2 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will ... How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Decides Price. In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. The rule for a profit-maximizing perfectly competitive firm is to produce the level of output where Price= MR = MC, so the raspberry farmer will produce a quantity of 90, which is labeled as e in Figure 4 (a). Remember that the area of a rectangle is equal to its base multiplied by its height. Find the profit-maximizing quantity and price of a perfect-price-discriminating monopolist. Find the profit-maximizing quantity and price of an imperfect-price-discriminating monopolist. Question: Each of the following firms possesses market power. Explain its source. a. Merck, the producer of the patented cholesterol-lowering drug Zetia b.
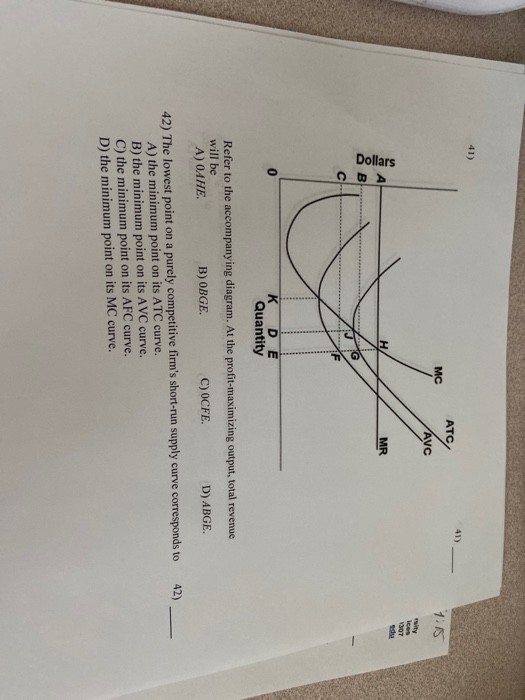
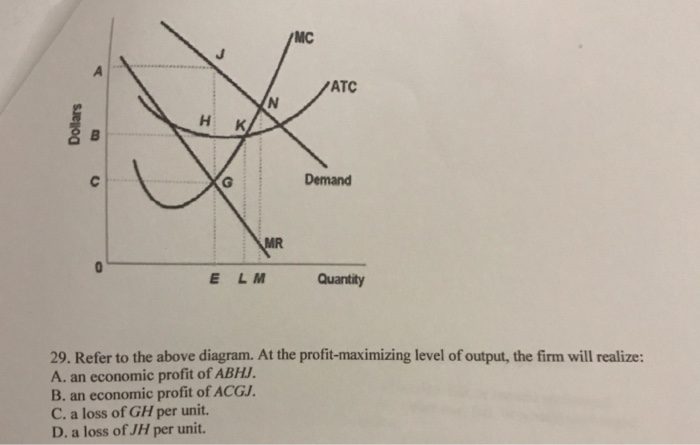
To maximize profit or minimize losses this firm will produce: 1. K units at price C. 2. D units at price J. 3. E units at price A. 4. E units at price B. 4. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total revenue will be: 1. 0AHE. 2. 0BGE. 3. 0CFE. 4. ABGE. 5. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing output, total ... Given the data in the accompanying table, at what output is total profit highest in the short run? Output. Total cost. 20. $ 70. 25. 75. 30. 85. 35. 100. 40. 125. 45. 155. 50. 190. A. 20. B. 30. C. 40. D. 50. 3. ... Which of the output levels is the profit-maximizing output level for this firm? A. Q1. B. Q2. C. Q3. D. Q4. 11. ... According to ... Ο an economic profit of ACFH. Ο an economic profit of ABGH ; Question: ATC MC AVC Dollars K DE Quantity According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize Multiple Choice τους και τιμές μας μπορεί Ο a loss equal to BCFG. Ο a loss equal to ACFH. Ο an economic profit of ACFH. according to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize a) a loss equal to BCFG b) a loss equal to ACFH c) an economic profit of ACFH d) an economic profit of ABGH
View Homework Help - ECONHW11SolS25.pdf from ECOS 2001 at The University of Sydney. 74. Award: 1.00 point According to the accompanying diagram, at the prot-maximizing output, the rm will realize a C) total revenue multiplied by total product (output). D) marginal revenue multiplied by marginal product. Answer: D 2. In the table above, if the wage rate is $8.00 per hour, the profit-maximizing number of workers is A) 1. B) 2. C) 4. D) 5. Answer: C 3. A firm in a competitive labor market will hire labor until the marginal revenue product of 42. Refer to the above diagram. At output C average fixed cost is GF. True False 43. Refer to the above diagram. At any price below R the firm will shut down in the short run. True False 44. Refer to the above diagram. If demand fell to the level of FNJ, there would be no output at which the firm could realize an economic profit. True False 45. amount of output produced. In addition, energy is a variable cost because produci ng more output almost always requires using more energy. b. When fixed costs increase, so will average total costs The average total cost curve will shift upward. In panel (a) of the accompanying diagram, this is illustrated by
120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
1, (Marginal revenue of firm 2) Step 2: Compute the profit maximizing outputs for both firms. To start with observe that equations 2) and 3) imply that MC 1 =MC 2 = 20. Start with firm 1. Profit maximization for both firms entails selecting an output at which the marginal revenue equates the marginal cost. Hence for firm 1, MR 1 = MC 1 implies by
Macroeconomics Quiz 106.pdf - 74 Award 1.00 point According to the accompanying diagram at the pro\ufb01t-maximizing output the \ufb01rm will realize a loss Award: 100 point According to the accompanying diagram,...
costs, c =10 , find the Cournot equilibrium output and profit per firm. Suppose firm 1 takes firm 2's output choice q2 as given. Then firm 1's problem is to maximize its profit by choosing its output level q1. If firm 1 produces q1 units and firm 2 produces q2 units then total quantity supplied is q1 + q2. Define Q ≡ q1 + q2. The market
According to the accompanying diagram, to maximize profit or minimize losses, this firm will produce ... At its profit-maximizing output, this firm's total profit will be. $82. ... The profit-maximizing monopolist will realize a. profit of $16. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be
At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit. answer choices . is zero. is $400. is $200. ... in the accompanying diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for. answer choices ... maximize profit, but resources will be underallocated to the product.
The firm will earn an economic profit of 0 $, because the firm ATC is tangent to Price at profit maximizing level Profit = Price — ATC * Output = 40 — 40 * 2.5 = 0 d. if the firm produces at a point that results in allocative efficiency, the price will be 25$, at this price Demand or AR = MC e. when firm produces at point that result in ...
Profit per unit of output=Total profit/Q =P-ATC Look at the graph above, firm should choose to produce output Q to maximize profit since Q is the output level at which point P=MC. The shaded area is total profit for this profit-maximizing firm. The vertical distance between point A and B = (P-ATC), which is profit per unit of output.
According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce
Multiple Choice Quiz. The market for automobiles is an example of. a. monopolistic competition. b. duopoly. c. differentiated oligopoly. d. pure oligopoly. If an industry is comprised of four firms and their market shares are 40%, 30%, 20%, and 10%, then the Herfindahl index for the industry is. a. 100. b. 200.
In the short run a purely competitive seller will. This preview shows page 57 - 63 out of 154 pages. 154) In the short run, a purely competitive seller will shut down if A) it cannot produce at an economic profit. B) price is less than average variable cost at all outputs. C) price is less than average fixed cost at all outputs.
The firm's short-run supply curve is According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market.
According to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize A) a loss equal to ACFH. B) a loss equal to BCFG. C) an economic profit of ACFH. D) an economic profit of ABGH.





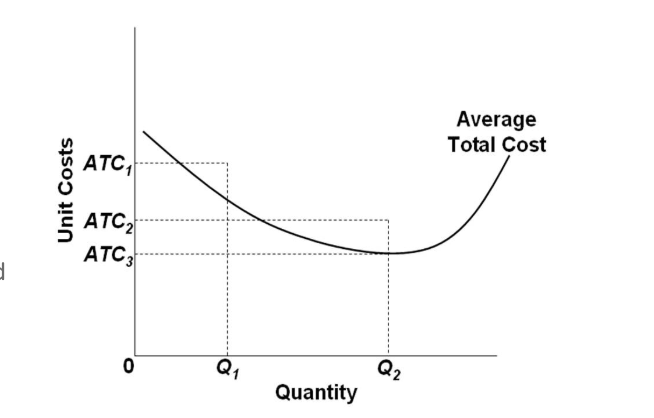
/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)










0 Response to "38 according to the accompanying diagram, at the profit-maximizing output, the firm will realize"
Post a Comment