38 adiabatic expansion pv diagram
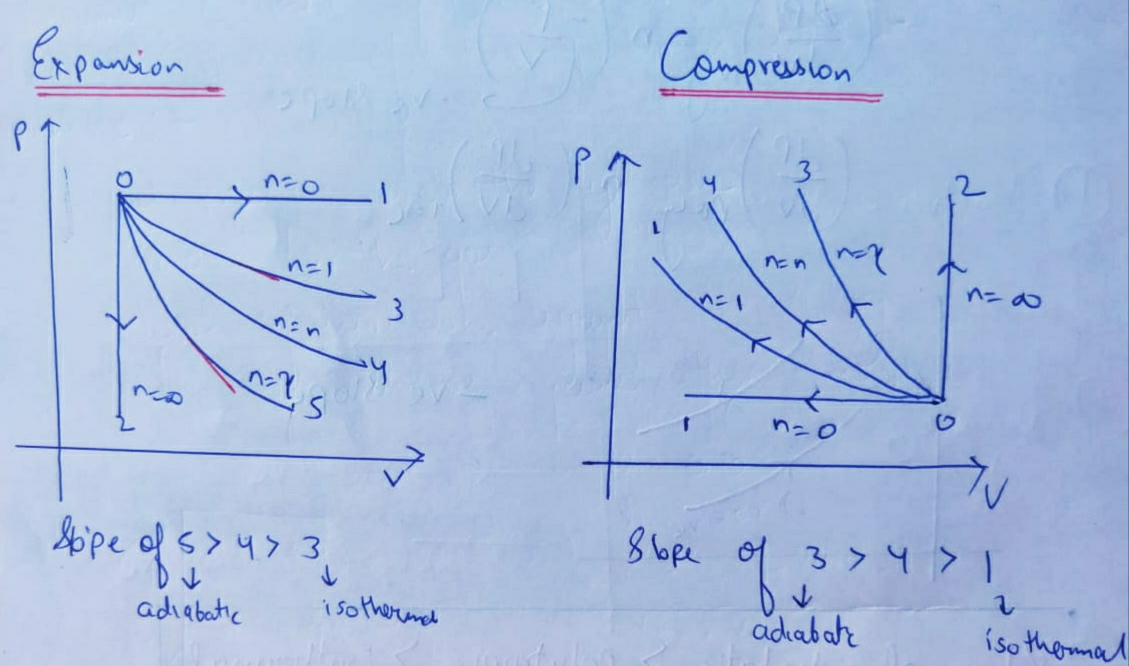
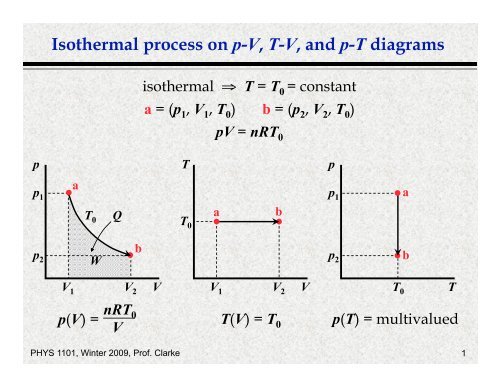
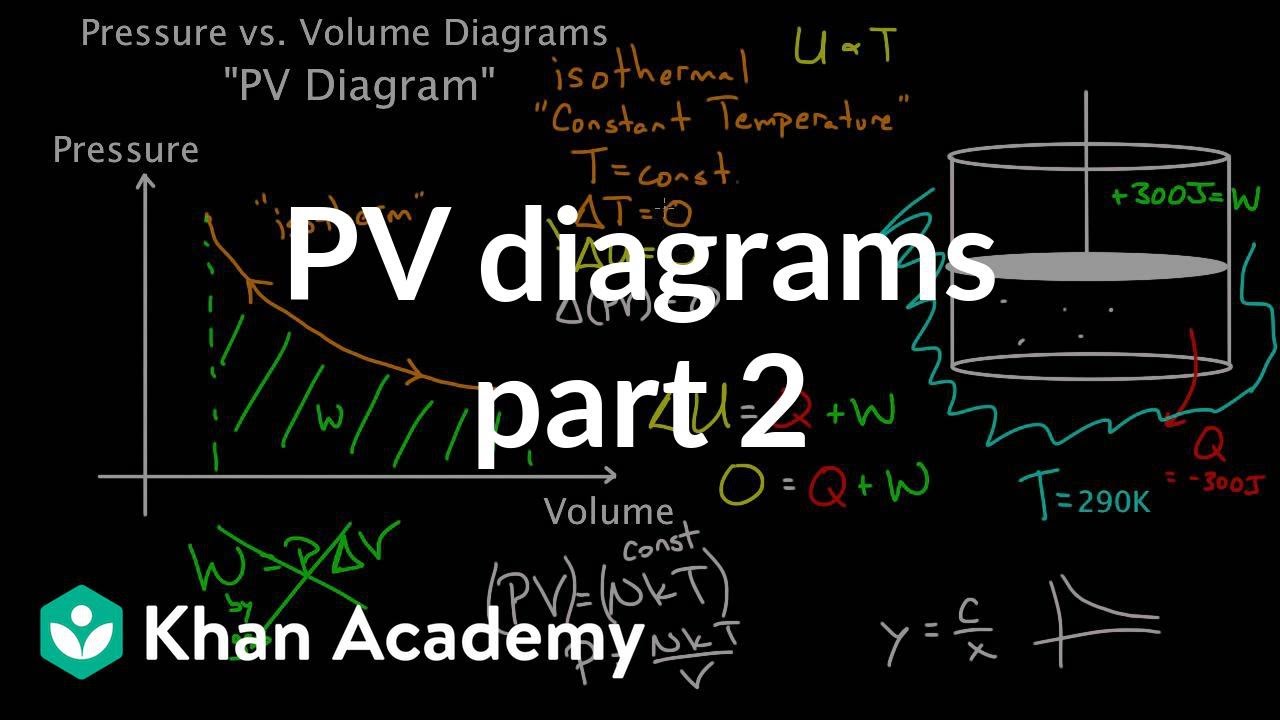
Adiabatic Process Thermodynamics | Work done Adiabaticaly | Adiabatic Expansion & Contraction | PV Diagram in Hindi / UrduAn adiabatic process is a thermodyn... So on a PV diagram, an isothermal process is gonna look something like this, it's gonna curve like 1/x and it can be an isothermal expansion if volume increases or an isothermal compression if volume decreases. So the actual shape of the line drawn on a PV diagram for an isothermal process is sometimes called an isotherm and they look like that.
Adiabatic Expansion - Adiabatic Compression. See also: What is an Ideal Gas In an ideal gas, molecules have no volume and do not interact.According to the ideal gas law, pressure varies linearly with temperature and quantity, and inversely with volume.. pV = nRT. where: p is the absolute pressure of the gas; n is the amount of substance; T is the absolute temperature
Adiabatic expansion pv diagram
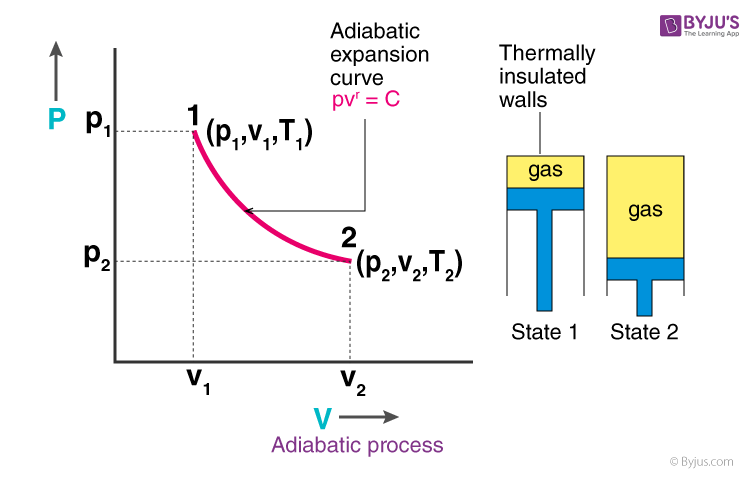
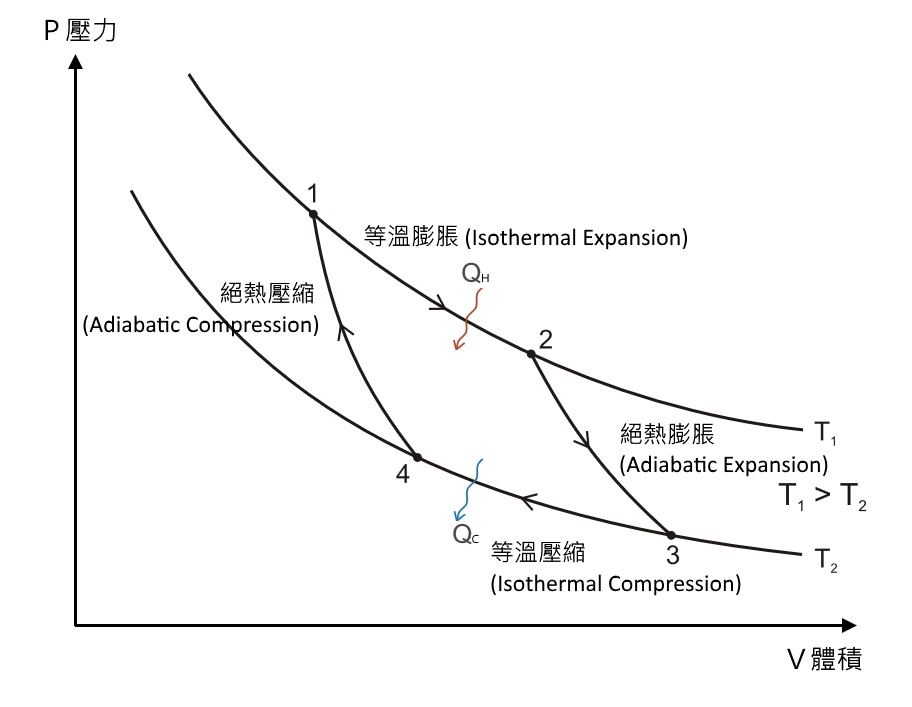
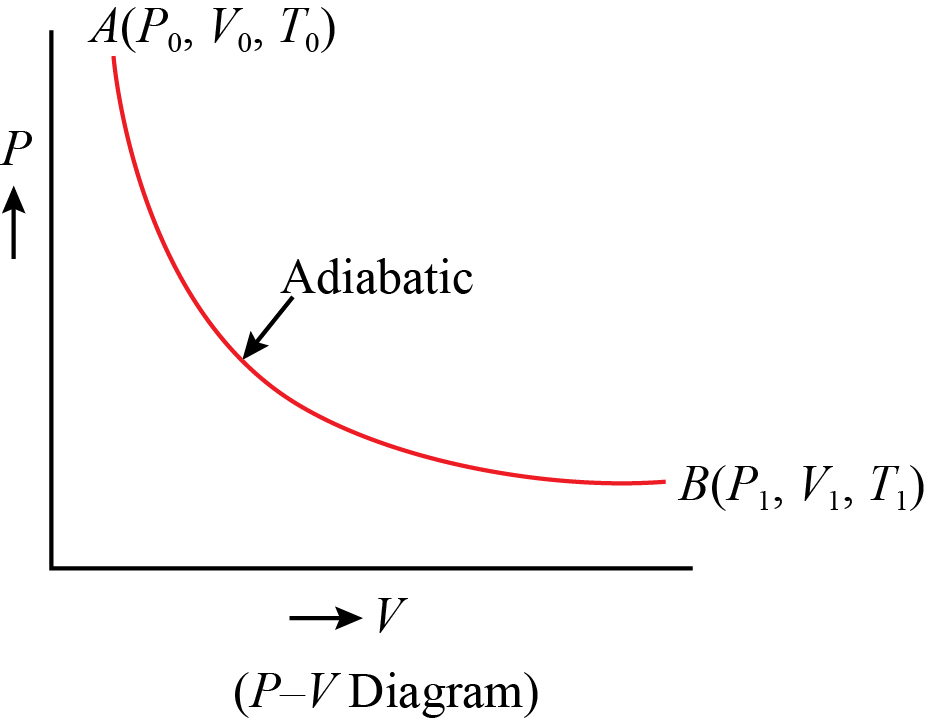
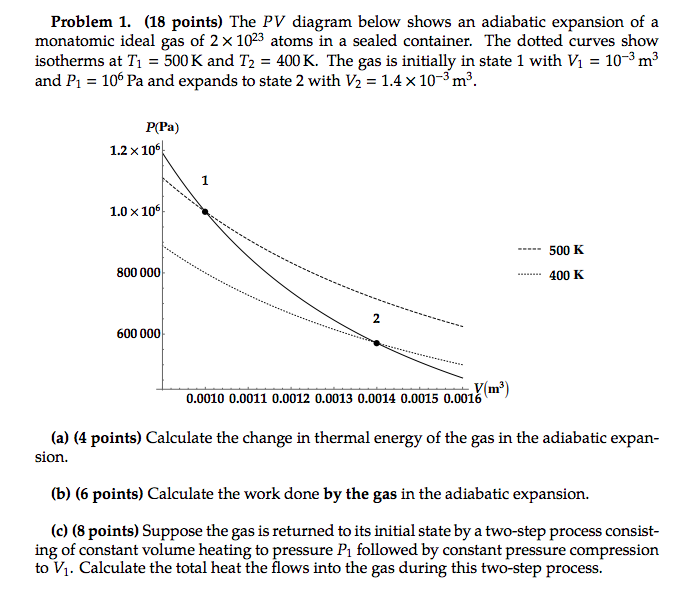
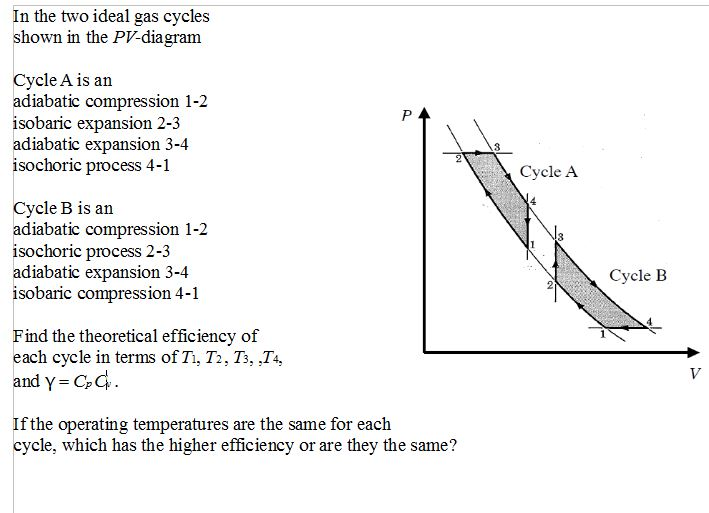
8.4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas. An adiabatic process is one in which no heat enters or leaves the system, and hence, for a reversible adiabatic process the first law takes the form dU = − PdV. But from equation 8.1.1, CV = (∂U/∂T)V. But the internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on the temperature and is ... Diesel Cycle PV and TS Diagram: Now we will study PV and TS Diagram: Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic Compression Process; Process 2-3: Constant Pressure Heat addition; Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion Process; Process 4-1: Constant volume Heat rejection A reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas is represented on the pV diagram of Figure 3.15. The slope of the curve at any point is The slope of the curve at any point is d p d V = d d V ( constant V γ ) = − γ p V . d p d V = d d V ( constant V γ ) = − γ p V .
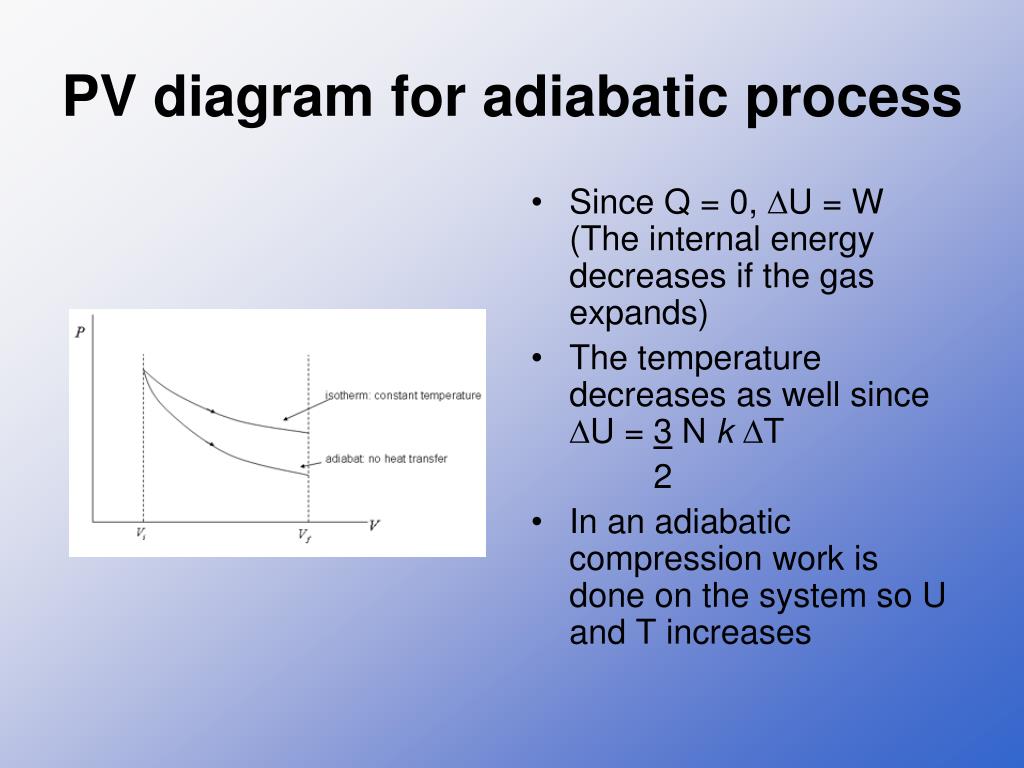
Adiabatic expansion pv diagram. Answer (1 of 2): On a PV diagram, only adiabatic and isotherm processes have asymptotic shapes. An example case for the curves for the two processes is shown here: It is not possible to just look at the shape of one curve and predict if it adiabatic or isotherm, because they look very similar. ... vPV + dP P = 0 or dV V + dP P = 0 or lnV+ lnP= const or PV = k (4) This is the standard form of the adiabatic gas law. Apparatus A piston of diameter 4.448 cm moves inside a cylinder which has pressure and temperature sensors mounted inside. Each sensor produces a small voltage which is recorded by the computer. Setup and Procedure 1. On the PV diagram below, the light blue curves are isotherms. They represent reversible isothermal expansion going left to right and reversible isothermal compression going right to left. The green line represents a reversible adiabatic expansion, left to right, and compression, right to left. PV diagrams - part 2: Isothermal, isometric, adiabatic processes. What are PV diagrams? Kinetic molecular theory of gases ... , and isobar for short. This is an isobar, this is an isobaric expansion if I go to the right, cause I know volume's increasing. And if I go to the left it would be an isobaric compression because volume would be ...
A reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas is represented on the pV diagram of . The slope of the curve at any point is The slope of the curve at any point is Quasi-static adiabatic and isothermal expansions of an ideal gas. adiabatic no heat exchange with the environment; adiabatic has a complex greek origin that means "not+through+go": α + ∆ια + βατός [a + dia + vatos] examples: "fast" processes, forcing air out through pursed lips, bicycle tire pump; PV diagram is a "steep hyperbola" Adiabats are neat. The mathematical equation for an ideal gas undergoing a reversible (i.e., no entropy generation) adiabatic process can be represented by the polytropic process equation =, where P is pressure, V is volume, and for this case n = γ, where = = +, C P being the specific heat for constant pressure, C V being the specific heat for constant volume, γ is the adiabatic index, and f is the number of ...
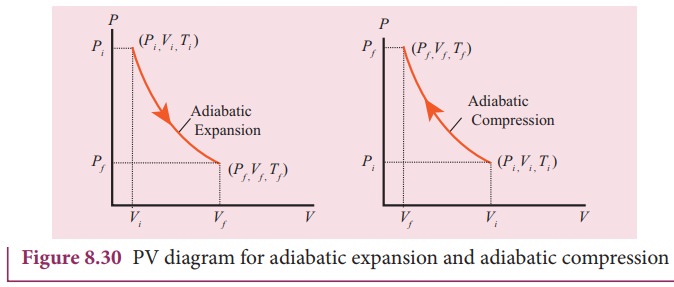
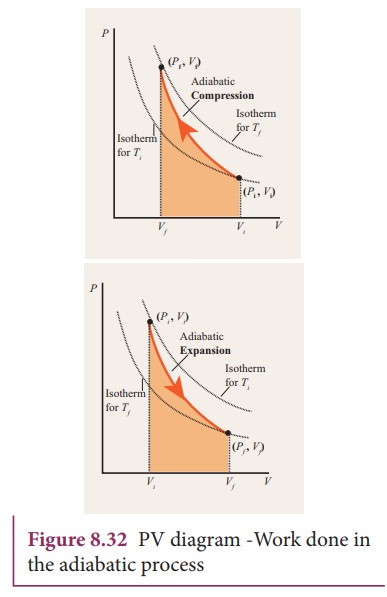
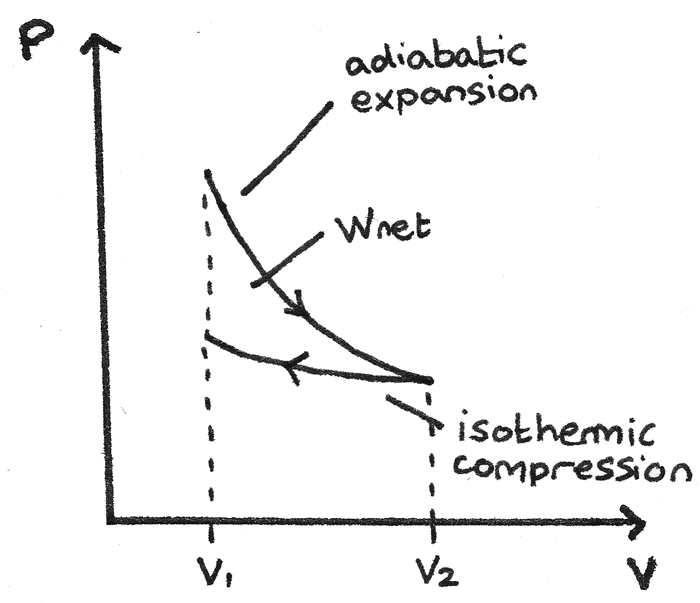
The PV diagram of an adiabatic expansion and adiabatic compression process are shown in Figure 8.30. The PV diagram for an adiabatic process is also called adiabat Note that the PV diagram for isothermal (Figure 8.25) and adiabatic (Figure 8.30) processes look similar. But actually the adiabatic curve is steeper than isothermal curve. through adiabatic expansion and ends at a temperature of 300 K, determine how much work the gas did. The PV diagram we would get for this adiabatic process is shown here. Notice how we started on the 525 K isotherm, but ended on the 300 K isotherm. The temperature did not stay constant, so this process must be adiabatic. Otto Cycle is a constant volume cycle on which petrol and gas engines work. The Otto cycle consists of 4 processes and are as follows. Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic Compression or Isentropic Compression. Process 2-3: Constant Volume heat supply. Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion or Isentropic Expansion. The compression and expansion events are modeled thermodynamically as adiabatic processes, meaning it is assumed that no heat is transferred to or from the gas during these events. An adiabatic thermodynamic process is an isentropic (constant entropy) process. The area of the P-V diagram in Figure 1 bounded by 1-2-3-4-1 is the adiabatic power.
Adiabatic is a Greek word in which 'a' means 'not', 'dia' means 'through' and 'bait' means 'hot'.So in short adiabatic is a system that does not allow heat to pass through it. Definition : It is the thermodynamic process in which there is a change in pressure, volume, and temperature of the system, but there is no ...
Processes, Adiabatic Process, PVT Relationship, PV diagram, TS diagram, Change in Internal Energy, Change in Entropy, Work done, Heat Transferred, Constant Temperature Process, PVT Relationship, PV diagram, TS diagram, Change in Internal Energy, Change in Entropy, Work
Adiabatic expansion is defined as an ideal behaviour for a closed system, in which the pressure is constant and the temperature is decreasing. What is Adiabatic Compression? Adiabatic compression of the air is defined as the compression in which no heat is added or subtracted from the air and the internal energy of the air is increased which is ...
Adiabatic Expansion - Adiabatic Compression. See also: What is an Ideal Gas. In an ideal gas, molecules have no volume and do not interact.According to the ideal gas law, pressure varies linearly with temperature and quantity and inversely with volume.. pV = nRT. where: p is the absolute pressure of the gas; n is the amount of substance; T is the absolute temperature
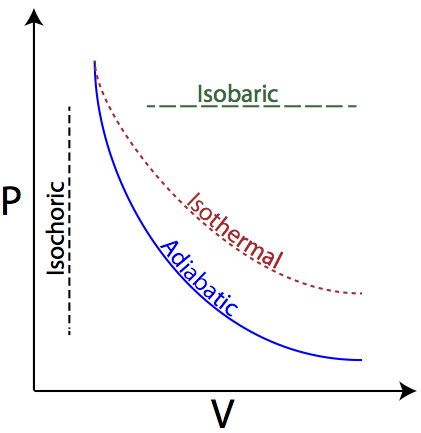
ideal gas law: pV = nRT Consider the p-V diagram below in which the system evolves from a → b → c. If T 0 ~ 240K (and thus RT 0 = 2,000 J mol-1), how many moles of gas, n, are in the system? a) 5 b) 105 c) 50 d) 1,000 e) Not enough information to tell n = = = 50 pV RT 0 100,000 2,000 isotherm isobar isochor
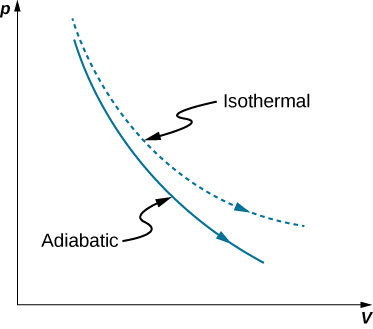
On a p-V diagram, lines of constant temperature curve from the upper left to the lower right. A process performed at constant temperature is called an isothermal process . During an adiabatic process no heat is transferred to the gas, but the temperature, pressure, and volume of the gas change as shown by the dashed line.
The most extreme form of an irreversible isothermal expansion is the adiabatic isothermal expansion of an ideal gas into vacuum. In this case no pressure-volume work is done, so in the PV diagram pressure first drops to zero, then volume increases to the final volume, and the pressure increases to the final value. The area under the curve is zero.
When an ideal gas undergoes an adiabatic expansion or compression, the adiabatic equation can be used: $$ pV^{\gamma} = \text{constant} $$ Where $\gamma$ is the adiabatic constant which depends on the molecular structure of the gas. Typical values include $\gamma = 1.67$ for a monatomic gas and $\gamma = 1.40$ for a diatomic gas.
pV γ pVγ 1 constant 2 2 1 1 1 = = T Vγ− T V γ− pV =nRT During an adiabatic expansion process, the reduction of the internal energy is used by the system to do work on the environment. During an adiabatic compression process, the environment does work on the system and increases the internal energy. Ideal gas: adiabatic process (contd)
Adiabatic Expansion (DQ = 0) Occurs if: • change is made sufficiently quickly • and/or with good thermal isolation. Governing formula: PV g = constant where g = CP/CV Because PV/T is constant (ideal gas): V g-1 T = constant (for adiabatic) P V Adiabat Isotherms. Proof of PV g =constant (for adiabatic process)
Adiabatic Process Definition Equation Reversible Adiabatic Process Example Differences Video And Faqs
1. This question does not show any research effort; it is unclear or not useful. Bookmark this question. Show activity on this post. In non isolated systems where there is no adiabatic process, P V is constant. But the graph gets steeper in adiabatic process because of the γ over the V. Why is it there in adiabatic processes and why only over ...
A reversible adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas is represented on the pV diagram of Figure 3.15. The slope of the curve at any point is The slope of the curve at any point is d p d V = d d V ( constant V γ ) = − γ p V . d p d V = d d V ( constant V γ ) = − γ p V .
Diesel Cycle PV and TS Diagram: Now we will study PV and TS Diagram: Process 1-2: Reversible Adiabatic Compression Process; Process 2-3: Constant Pressure Heat addition; Process 3-4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion Process; Process 4-1: Constant volume Heat rejection
8.4: Reversible Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas. An adiabatic process is one in which no heat enters or leaves the system, and hence, for a reversible adiabatic process the first law takes the form dU = − PdV. But from equation 8.1.1, CV = (∂U/∂T)V. But the internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on the temperature and is ...
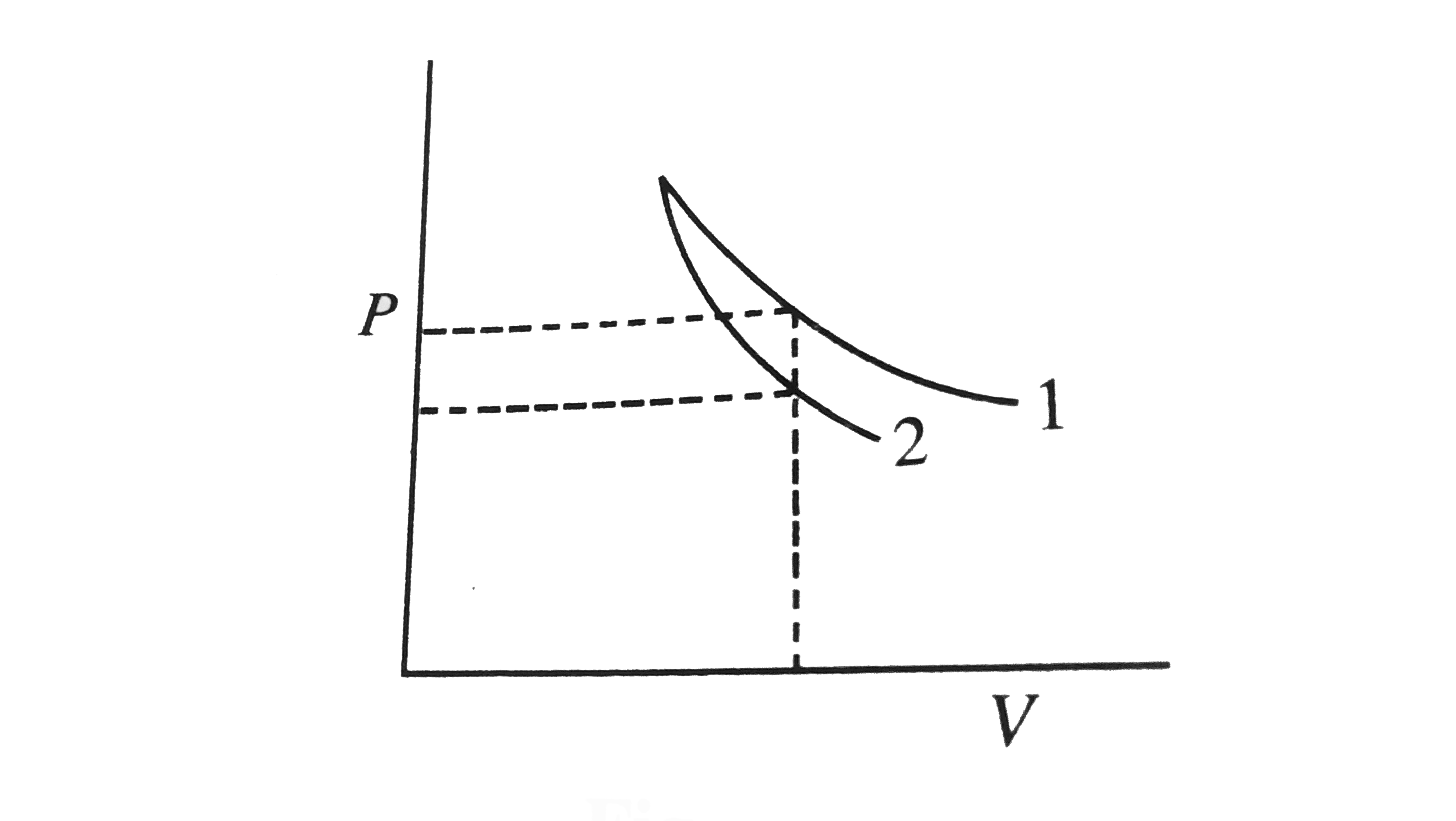
P V Plots For Two Gases During Adiabatic Processes Are Shown In The Figure Plots 1 And 2 Should Corresponds Respectively To Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Jma Htg C09 043 Q01 Png Width 80













0 Response to "38 adiabatic expansion pv diagram"
Post a Comment