37 gram positive cell wall diagram
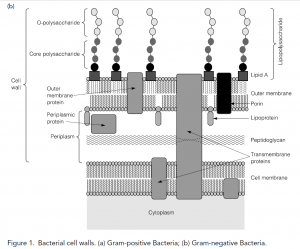
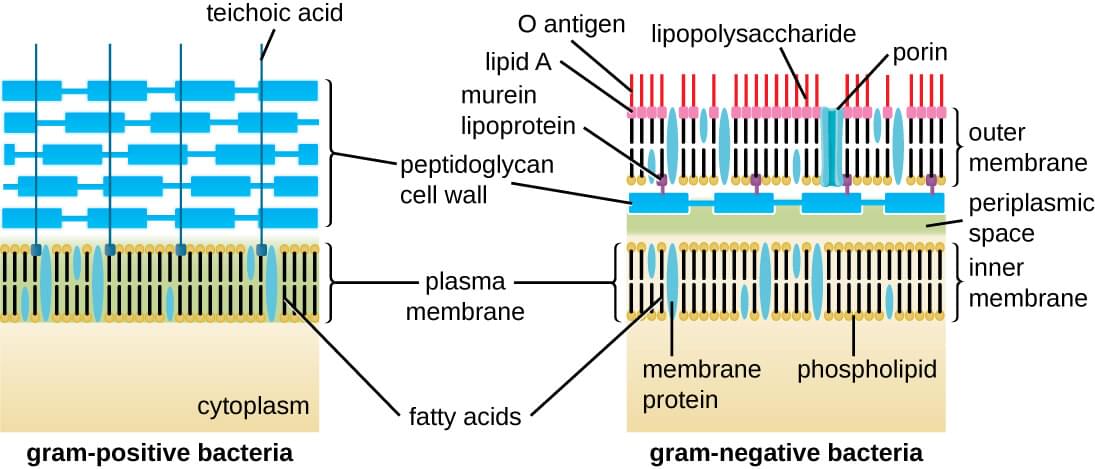
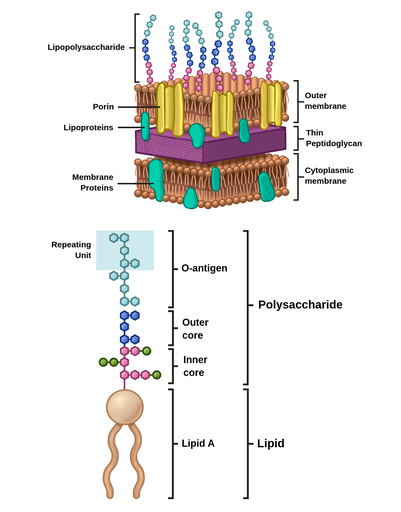
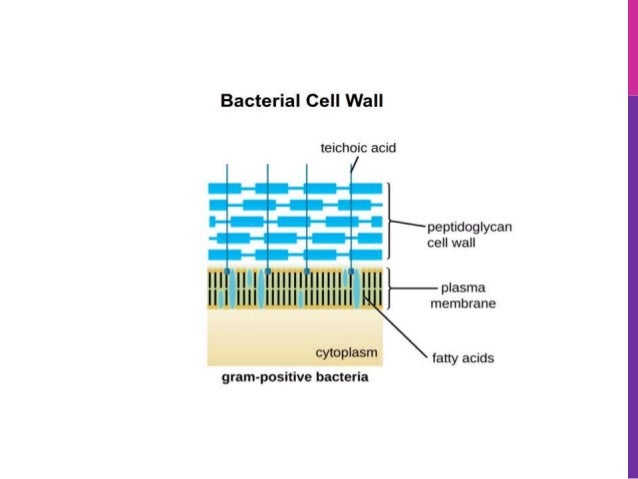
Gram-positive Cell Wall. Gram-negative Cell Wall. Outer Membrane. Cytoplasmic Membrane. Membrane Proteins. Porin. RETURN to CELL ENVELOPE . RETURN to CELL DIAGRAM ... Compare and contrast the cell walls of typical Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. 3. Relate bacterial cell wall structure to the Gram-staining reaction. 37 . 38 Bacterial Cell Wall • Peptidoglycan (murein) -rigid structure that lies just outside the cell plasma membrane
Gram staining Procedure. Retains the crystal violet dye and appear purple in colour. Does not retain the crystal violet dye and appear pink in colour. These differences between the Cell Wall of Gram-positive and Gram-negative Bacteria are classified based on their structure, composition of the cell and by the procedure of Gram staining technique.
Gram positive cell wall diagram
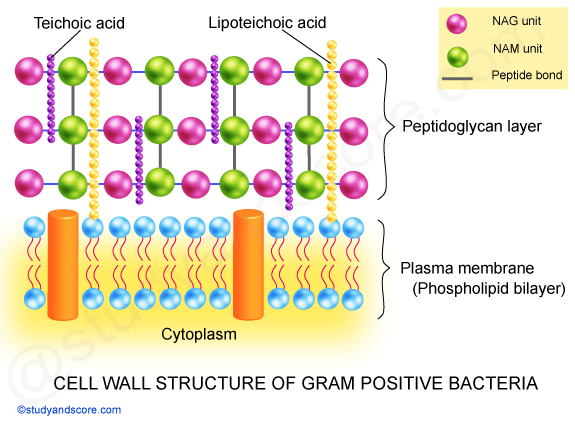
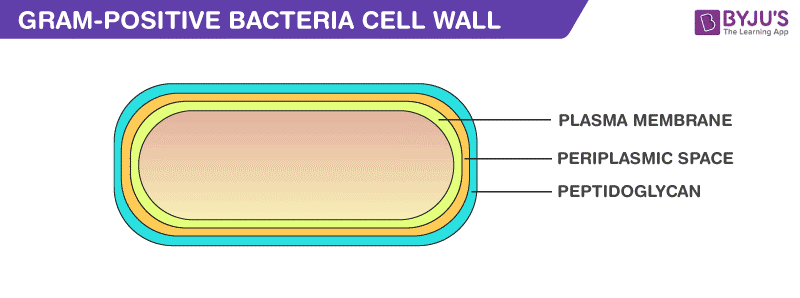
Gram-positive cell wall. The Gram-positive cell wall is thick (15-80 nm) and more homogenous than that of the thin (2 nm) Gram-negative cell wall. The Gram-positive cell wall contains large amount of peptidoglycan present in several layers that constitutes about 40-80% of dry weight of the cell wall. The gram-Positive Cell wall of Bacteria Bacterial cell wall that is gram-positive contains peptidoglycan and teichoic acids with some species having additional carbohydrates and proteins. The murein component is what gives shape to the gram-positive bacterial cell wall; it also helps the bacteria cells to resist osmotic pressure. Gram positive bacteria are a group of organisms that fall under the phylum Firmicutes (however, a few species have a Gram negative cell wall structure). As compared to Gram negative bacteria, this group of bacteria is characterized by their ability to retain the primary stain (Crystal violet) during Gram staining (giving a positive result).
Gram positive cell wall diagram. In electron micrographs, the Gram-positive cell wall appears as a broad, dense wall 20-80 nm thick and consisting of numerous interconnecting layers of peptidoglycan (see Figs. 1A and 1B). Chemically, 60 to 90% of the Gram-positive cell wall is peptidoglycan. In Gram-positive bacteria it is thought that the peptidoglycan is laid down in cables ... A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane.It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in animals but are present in most other eukaryotes including algae, fungi and plants and in most prokaryotes (except ... Briefly describe how antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, and vancomycin affect bacteria and relate this to their cell wall synthesis. State what color Gram-positive bacteria stain after Gram staining. State what color Gram-negative bacteria stain after Gram staining. State what color acid-fast bacteria stain after acid-fast staining. 4 Bacteria: Cell Walls . It is important to note that not all bacteria have a cell wall.Having said that though, it is also important to note that most bacteria (about 90%) have a cell wall and they typically have one of two types: a gram positive cell wall or a gram negative cell wall.. The two different cell wall types can be identified in the lab by a differential stain known as the Gram stain.
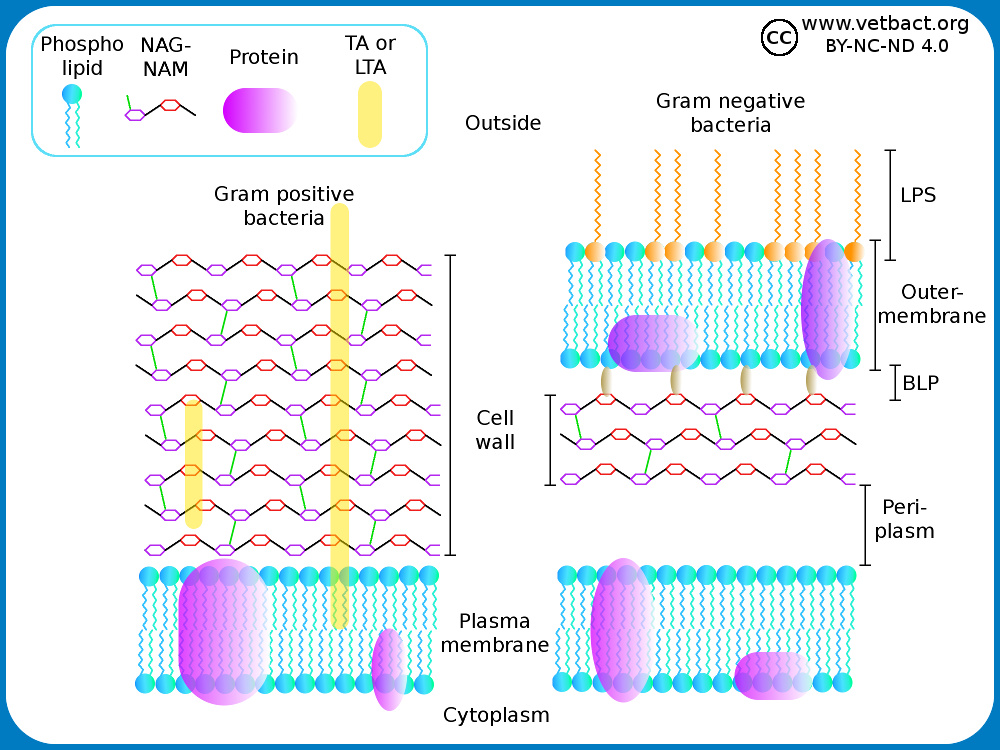
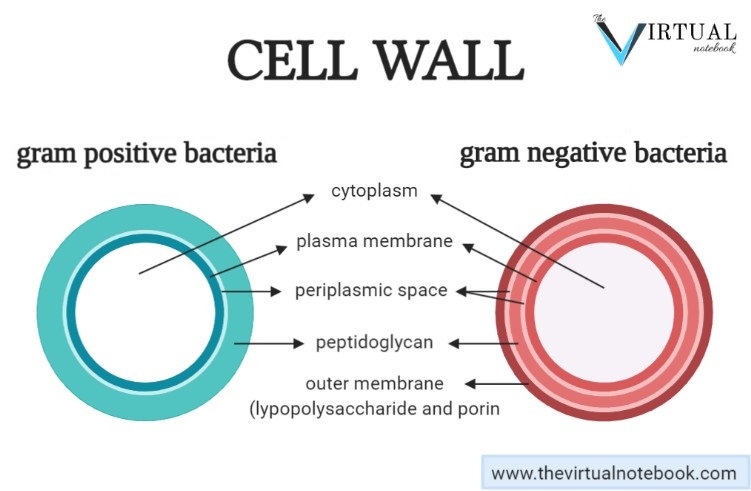
21.08.2019 · The diagram below illustrates the differences in the structure of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The two key features that lead to the differing visualization properties of Gram positive and Gram negative species are the thickness of the peptidoglycan layer and presence or absence of the outer lipid membrane. This is because the wall structure affects the cell’s ability to retain ... Gram-positive cell wall. Gram-positive cell wall is thick measuring about 15-80 nm and more homogenous compared to gram-negative cell wall. This cell wall consists of large amount of peptidoglycan arranged in several layers. Peptidoglycan in gram-positive cell wall constitutes about 40-80% of the dry weight. Gram Stain Mechanism: Gram Positive Cell Wall: Gram-positive bacteria have a thick mesh-like cell wall which is made up of peptidoglycan (50-90% of cell wall), which stains purple. Peptidoglycan is mainly a polysaccharide composed of two subunits called N-acetyl glucosamine and N-acetyl muramic acid. The cell wall of bacteria is located at the inner side of the capsule. Gram positive and gram negative. The cytoplasm is enclosed by three layers the outermost slime or capsule the middle cell wall and inner cell membrane. It gives shape to the cell. It give shaperigidity and support to the cell.
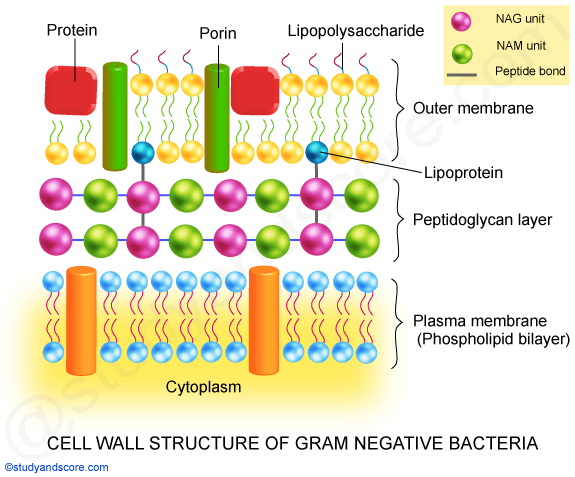
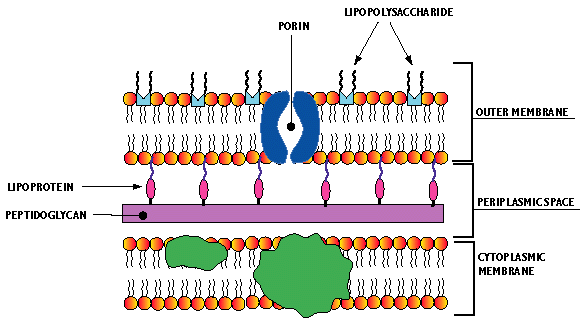
Most of the gram positive cell wall contain considerable amount of teichoic acid and teichuronic acid. In addition, they may contain polysaccharide molecules. The gram negative cell wall contains three components that lie outside the peptidoglycan layer: 1. Lipoprotein. 2. Outer membrane and . 3. Lipopolysaccharide. The results from images shown in e-i support a common process of synthesis and maturation of the cell wall on the spherical parts of Gram-positive bacteria in both spherical and rod-shaped species. Mycoplasma are bacteria that have no cell wall and therefore have no definite shape. Outer Membrane: This lipid bilayer is found in Gram negative bacteria and is the location of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in these bacteria. Gram positive bacteria lack this layer. LPS can be toxic to a host and can stimulate the host's immune system. You have isolated a motile, gram-positive cell with no visible nucleus. You can safely assume that the cell A) has 9 pairs + 2 flagella. B) has a mitochondrion. C) has a cell wall. D) lives in an extreme environment. E) has cilia.
You have isolated a motile, gram-positive cell with no visible nucleus. You can safely assume that the cell. has a cell wall. Fimbriae and pili differ in that pili … In Figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall is a gram-negative cell wall (smaller) gram-negative. In Figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall is a toxic cell wall (smaller) gram ...
Gram-Positive Cell Wall. The composition of gram-positive bacteria cell wall includes: Peptidoglycan. It is permeable, cross-linked organic polymer and rigid structure which plays an important role in providing shape and strength to the cell wall. It makes up about 90% of the cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane and protects the cell from ...
The analysis of the mycolic acid as the major characteristic of MbT cell-wall component has been used [19] to distinguish between MbT and strains of Gram-positive (S. aureus) and Gram-negative (K ...
In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycan makes up as much as 90% of the thick cell wall enclosing the plasma membrane. Gram Staining! During Gram staining, these thick, multiple layers (20-80 nm) of peptidoglycan retain the dark purple primary stain crystal violet, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink.

Protein Secretion And Surface Display In Gram Positive Bacteria Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society B Biological Sciences
The Gram-Positive Cell Wall. As mentioned in the previous section on peptidoglycan, Gram-positive bacteria are those that retain the initial dye crystal violet during the Gram stain procedure and appear purple when observed through the microscope. As we will learn in lab, this is a result of the structure and function of the Gram-positive cell wall.
This quick video describes in detail the cell wall structure of gram positive bacteria.Check out http://eacharya.tumblr.com for more!
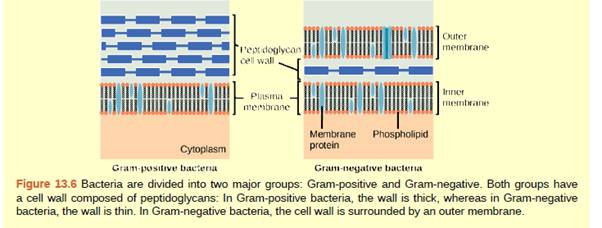
Figure 13 6 Which Of The Following Statements Is True A Gram Positive Bacteria Have A Single Cell Wall Formed From Peptidoglycan B Gram Positive Bacteria Have An Outer Membrane C The Cell Wall Of
Each of the following statements concerning the gram-positive cell wall is true EXCEPT. ... In Figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall is a gram-negative cell wall? B. In Figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall possesses lipid A/endotoxin responsible for symptoms associated with infection. B.
28.04.2017 · Cell Wall Definition. A cell wall is an outer layer surrounding certain cells that is outside of the cell membrane.All cells have cell membranes, but generally only plants, fungi, algae, most bacteria, and archaea have cells with cell walls.The cell wall provides strength and structural support to the cell, and can control to some extent what types and concentrations of molecules enter and ...
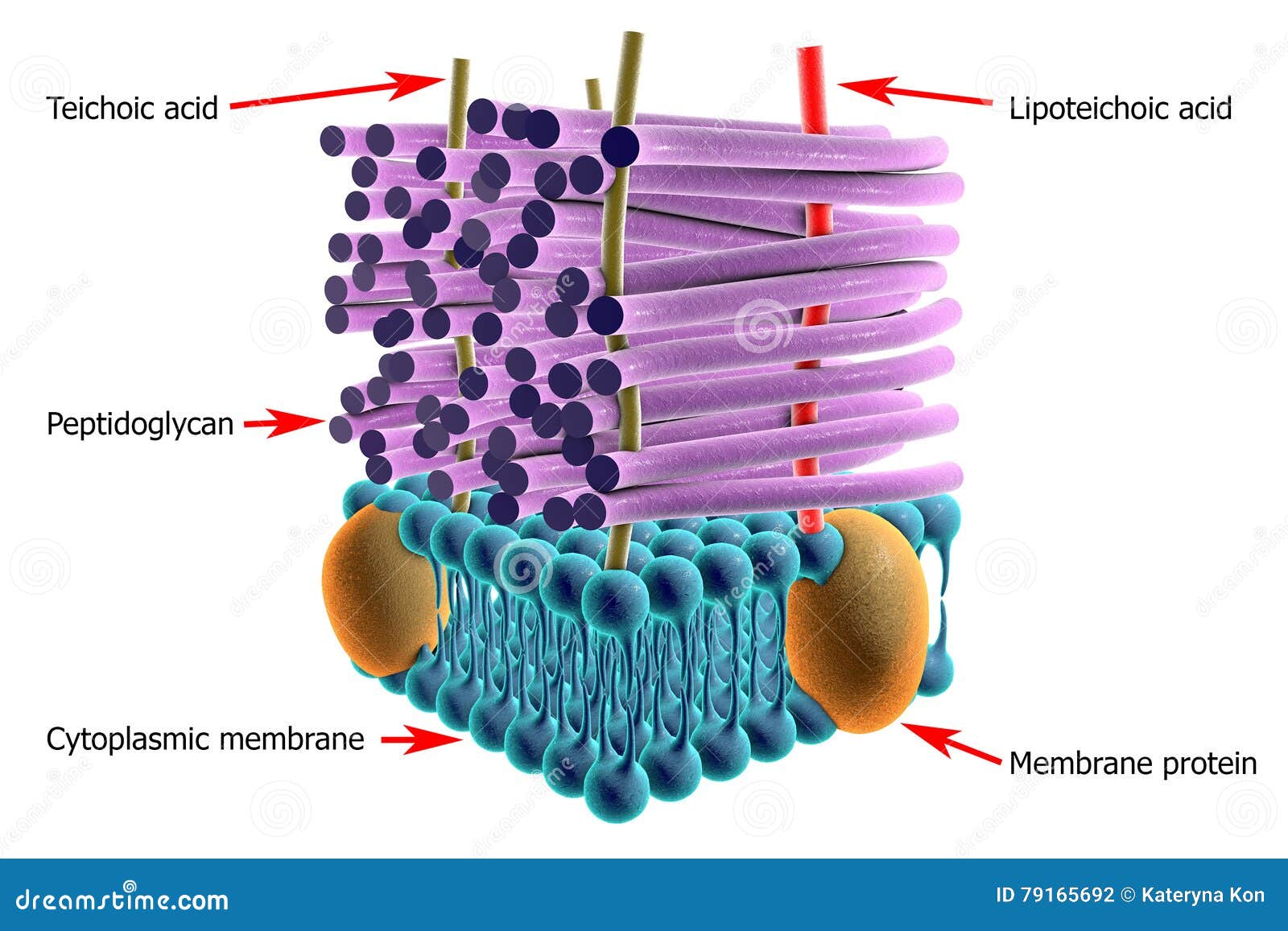
Structure Of Gram Positive Bacteria Cell Wall Stock Illustration Illustration Of Microbial Muramic 79165692
14.10.2021 · Bacteria are microscopic single-celled organisms that can be helpful, such as those that live in our guts, or harmful, such as flesh-eating bacteria.
In the cell diagram within the The Biology Lab Primer: ... Gram-positive bacteria have a single cell membrane, with a thick cell wall composed of peptidoglycan. This thick cell wall appears dark purple following a gram stain due to the high abundance of peptidoglycan In contrast, gram negative bacteria have a thin cell wall (also made of peptidoglycan) sandwiched between two cell membranes ...
15.04.2021 · For the gram-positive cell wall, it has a thickness of about 20-80nm thickness made up of a thick peptidoglycan layer outside its cell membrane, unlike the thin layer of gram-negative bacteria (10-15nm) which has a very thin layer of the peptidoglycan of 2-7nm but has a thicker lipid layer making it quite complex than the Gram-positive cell wall.
Important Chemical Components of Surface Structures. Cell Wall Peptidoglycans: Both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria possess cell wall peptidoglycans, which confer the characteristic cell shape and provide the cell with mechanical protection. Peptidoglycans are unique to prokaryotic organisms and consist of a glycan backbone of muramic acid and glucosamine (both N-acetylated), and ...
Grams positive bacteria are a category of bacteria. Their cell wall is known as gram positive cell wall. This is because it has a thick peptidoglycan layer. It is multilayered and possesses teichoic acids. In grams staining, gram positive cell wall stains in purple colour due to the retention of crystal violet stain.
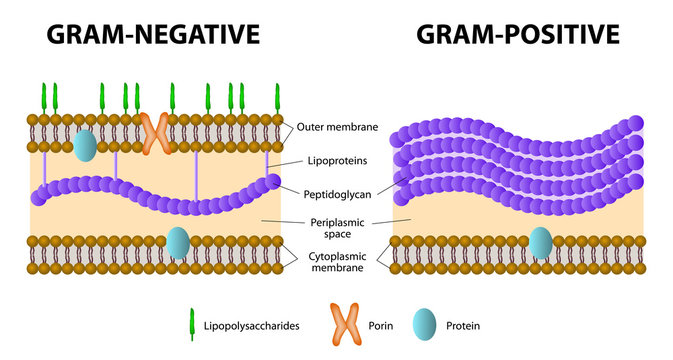
In the Gram-positive Bacteria (those that retain the purple crystal violet dye when subjected to the Gram-staining procedure), the cell wall consists of several layers of peptidoglycan. Running perpendicular to the peptidoglycan sheets is a group of molecules called teichoic acids which are unique to the Gram-positive cell wall (Figure 14).
Techoic acids consist of. 2 classes of techoic acids. Many layers of peptidoglycan, forming a thick, rigid structure. In addition to peptidoglycan, techoic acids and phosphate. Consists primarily of an alcohol. lipotechoic acid & peptidoglycan. Cell wall of gram-positive bacteria.
2) Each of the following statements concerning the gram-positive cell wall is true EXCEPT. A) it maintains the shape of the cell. B) it is sensitive to lysozyme. C) it protects the cell in a hypertonic environment. D) it contains teichoic acids. E) it is sensitive to penicillin.
Gram-negative cell walls have a dynamic feature that is not seen in their gram-positive counterparts … outer membrane vesicles are constantly being discharged from the surface of the cell during bacterial growth. As the vesicles are being extruded from the surface, they entrap some of the underlying periplasm so that they are actually small particles of gram-negative cell wall. They possess ...
Gram positive bacteria are a group of organisms that fall under the phylum Firmicutes (however, a few species have a Gram negative cell wall structure). As compared to Gram negative bacteria, this group of bacteria is characterized by their ability to retain the primary stain (Crystal violet) during Gram staining (giving a positive result).
The gram-Positive Cell wall of Bacteria Bacterial cell wall that is gram-positive contains peptidoglycan and teichoic acids with some species having additional carbohydrates and proteins. The murein component is what gives shape to the gram-positive bacterial cell wall; it also helps the bacteria cells to resist osmotic pressure.
Gram-positive cell wall. The Gram-positive cell wall is thick (15-80 nm) and more homogenous than that of the thin (2 nm) Gram-negative cell wall. The Gram-positive cell wall contains large amount of peptidoglycan present in several layers that constitutes about 40-80% of dry weight of the cell wall.
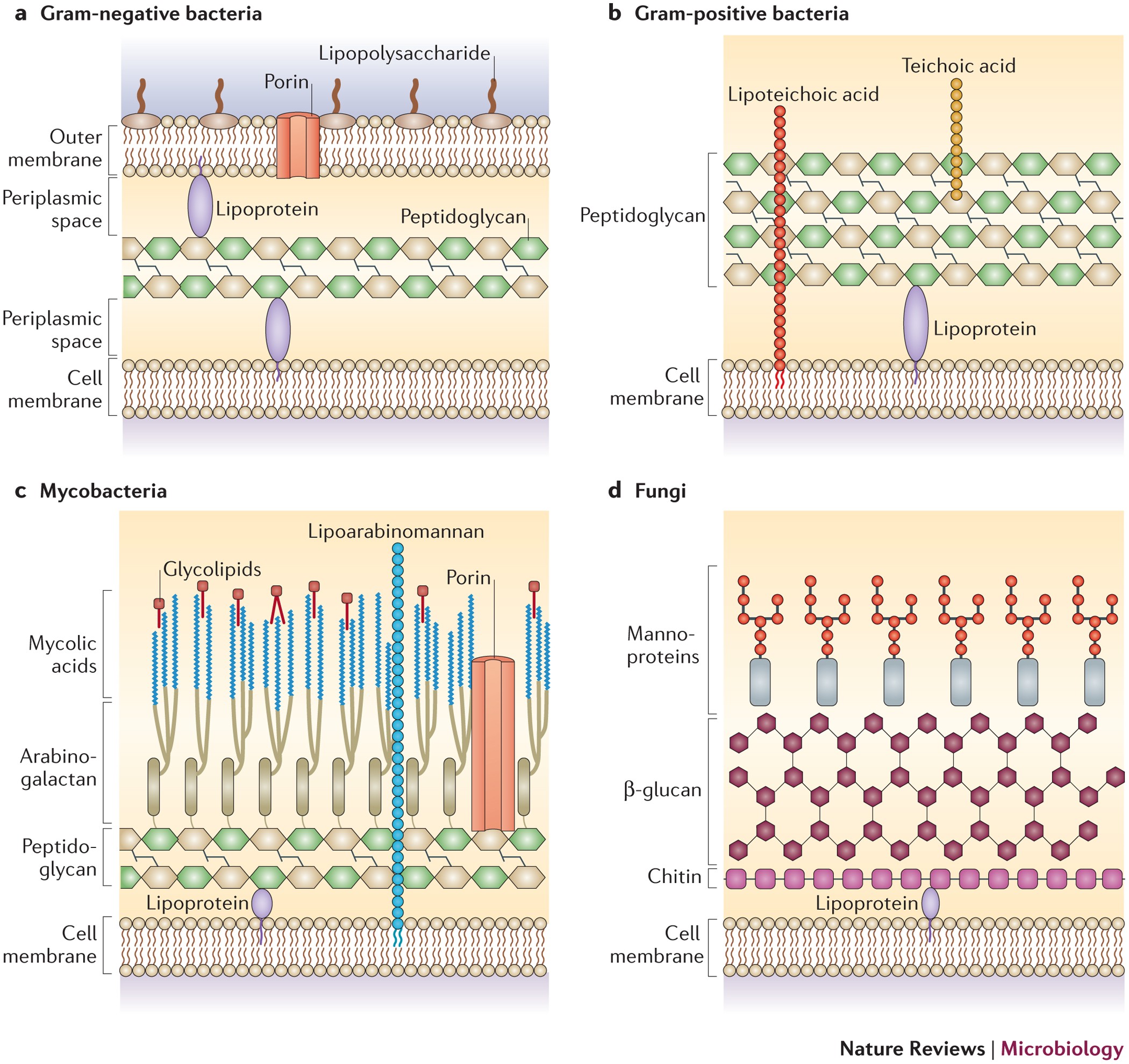
Through The Wall Extracellular Vesicles In Gram Positive Bacteria Mycobacteria And Fungi Nature Reviews Microbiology
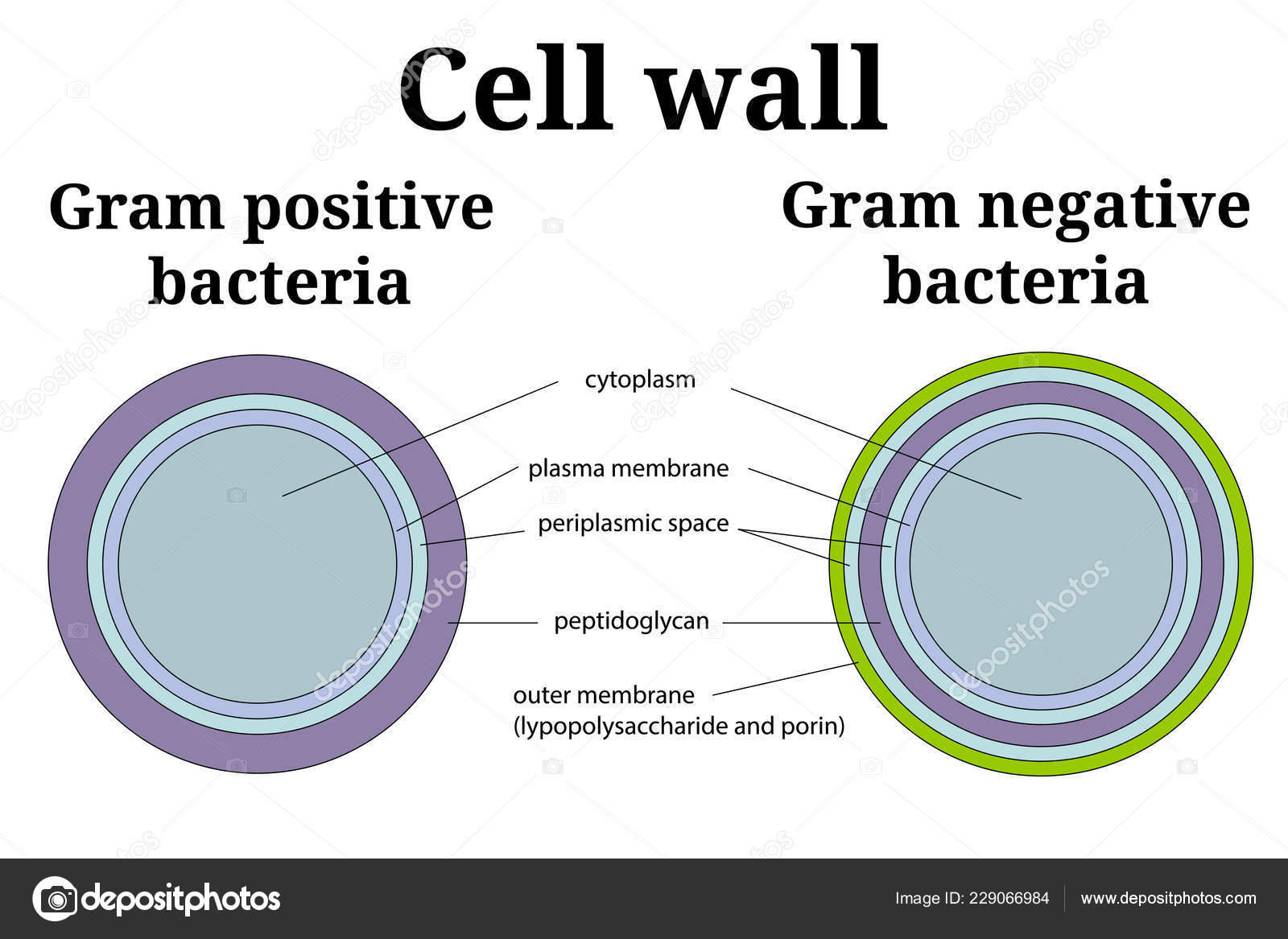
Bacteria Cell Wall Illustration Gram Positive And Gram Negative Cell Wall Differents Stock Vector Image By C Airen Creation 229066984

0614 A Comparison Of The Cell Walls Gram Positive And Gram Negative Medical Images For Powerpoint Presentation Powerpoint Templates Ppt Slide Templates Presentation Slides Design Idea













0 Response to "37 gram positive cell wall diagram"
Post a Comment